The Role of Microarray in Modern Sequencing: Statistical Approach Matters in a Comparison Between Microarray and RNA-Seq
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Profile of the Study Participants
2.2. RNA Isolation, Hybridization and Sequencing
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Downstream Analysis
3. Results
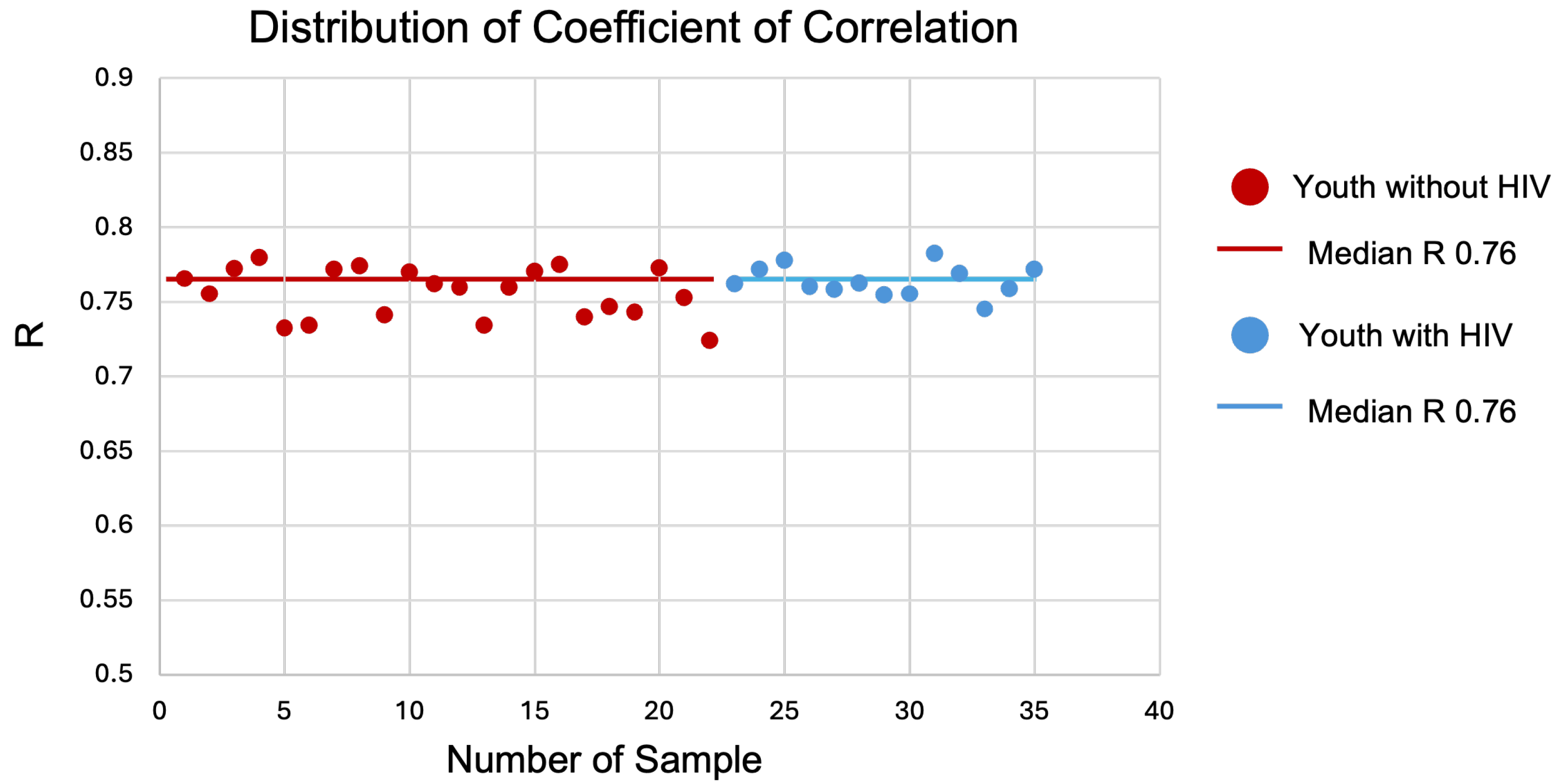
3.1. High Correlation of Gene Expression and Concordance of DEGs
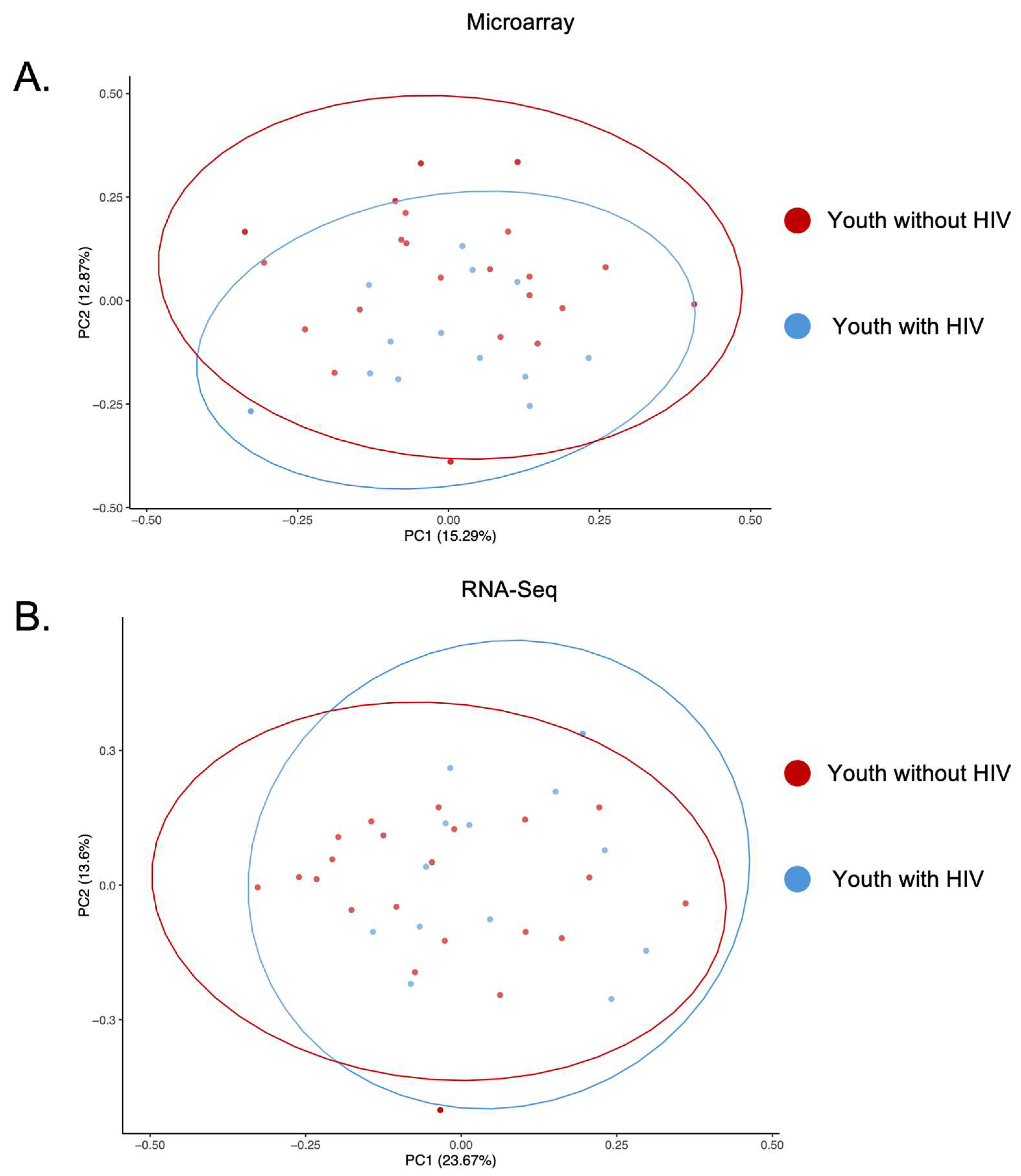
3.2. PCA of Microarray and RNA-Seq
3.3. RNA-Seq Demonstrates a Greater Dynamic Range of Fold Change
3.4. High Concordance of Canonical Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| AIDS | Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene(s) |
| GEO | Gene expression omnibus |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| PBCs | Peripheral blood cells |
| ATN | Adolescent Medicine Trial Network |
| YWOH | Youth without HIV |
| YWH | Youth with HIV |
| ART | Antiretroviral therapy |
| RMA | Robust multi-array averaging |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| TPM | Transcripts per million |
| VST | Variance-stabilizing transformation |
| NB | Negative binomial |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| KS | Kolmogorov–Smirnov |
| AD | Anderson–Darling |
| ML | Machine learning |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
References
- Baechler, E.C.; Batliwalla, F.M.; Reed, A.M.; Peterson, E.J.; Gaffney, P.M.; Moser, K.L.; Gregersen, P.K.; Behrens, T.W. Gene expression profiling in human autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 210, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper-Knock, J.; Kirby, J.; Ferraiuolo, L.; Heath, P.R.; Rattray, M.; Shaw, P.J. Gene expression profiling in human neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, C.; Piccart, M.J. Taking gene-expression profiling to the clinic: When will molecular signatures become relevant to patient care? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for gene expression and epigenomics data sets: 23-year update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, D138–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.S.; Van Vleet, T.R.; Ciurlionis, R.; Buck, W.R.; Mittelstadt, S.W.; Blomme, E.A.; Liguori, M.J. Comparison of RNA-Seq and microarray gene expression platforms for the toxicogenomic evaluation of liver from short-term rat toxicity studies. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kloet, F.M.; Buurmans, J.; Jonker, M.J.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Increased comparability between RNA-Seq and microarray data by utilization of gene sets. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gong, B.; Bushel, P.R.; Thierry-Mieg, J.; Thierry-Mieg, D.; Xu, J.; Fang, H.; Hong, H.; Shen, J.; Su, Z. The concordance between RNA-seq and microarray data depends on chemical treatment and transcript abundance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Fung-Leung, W.-P.; Bittner, A.; Ngo, K.; Liu, X. Comparison of RNA-Seq and microarray in transcriptome profiling of activated T cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e78644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwemer, L.M.; Hui, L.; Wick, H.C.; Bianchi, D.W. RNA-Seq and expression microarray highlight different aspects of the fetal amniotic fluid transcriptome. Prenat. Diagn. 2014, 34, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Williams, J.; Antoniou, E.; McCombie, W.R.; Wu, S.; Zhu, W.; Davidson, N.O.; Denoya, P.; Li, E. Parallel comparison of Illumina RNA-Seq and Affymetrix microarray platforms on transcriptomic profiles generated from 5-aza-deoxy-cytidine treated HT-29 colon cancer cells and simulated datasets. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, Y.; Hertwig, F.; Thierry-Mieg, J.; Zhang, W.; Thierry-Mieg, D.; Wang, J.; Furlanello, C.; Devanarayan, V.; Cheng, J.; et al. Comparison of RNA-seq and microarray-based models for clinical endpoint prediction. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim-Chang, J.J.; Donovan, K.; Loop, M.S.; Hong, S.; Fischer, B.; Venturi, G.; Garvie, P.A.; Kohn, J.; Rendina, H.J.; Woods, S.P.; et al. Higher soluble CD14 levels are associated with lower visuospatial memory performance in youth with HIV. Aids 2019, 33, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, S.L.; Bethel, J.; Garvie, P.A.; Patton, D.E.; Thornton, S.; Kapogiannis, B.G.; Ren, W.; Major-Wilson, H.; Puga, A.; Woods, S.P. Neurocognitive functioning in antiretroviral therapy-naïve youth with behaviorally acquired human immunodeficiency virus. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 53, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Dinasarapu, A.R.; Borkar, S.A.; Chang, K.F.; De Paris, K.; Kim-Chang, J.J.; Sleasman, J.W.; Goodenow, M.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of recreational marijuana in virally suppressed youth with HIV-1 are reversed by use of tobacco products in combination with marijuana. Retrovirology 2022, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkar, S.A.; Yin, L.; Venturi, G.M.; Shen, J.; Chang, K.F.; Fischer, B.M.; Nepal, U.; Raplee, I.D.; Sleasman, J.W.; Goodenow, M.M. Youth Who Control HIV on Antiretroviral Therapy Display Unique Plasma Biomarkers and Cellular Transcriptome Profiles Including DNA Repair and RNA Processing. Cells 2025, 14, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, L.; Cope, L.; Bolstad, B.M.; Irizarry, R.A. affy—Analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FASTQC. FastQC. 2015. Available online: https://qubeshub.org/resources/fastqc (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimaran, S.; Selby, H.M.; Okrah, K.; Ruberman, C.; Leek, J.T.; Quackenbush, J.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Bravo, H.C.; Johnson, W.E. BatchQC: Interactive software for evaluating sample and batch effects in genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3836–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.; Venables, B.; Bates, D.M.; Hornik, K.; Gebhardt, A.; Firth, D.; Ripley, M.B. Package ‘mass’. Cran R 2013, 538, 822. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A Language for Data Analysis and Graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Statistics. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Core Team. R: A Language and Enviroment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Horikoshi, M.; Li, W. ggfortify: Unified interface to visualize statistical results of popular R packages. R J. 2016, 8, 474–485. [Google Scholar]
- Maechler, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Struyf, A.; Hubert, M.; Hornik, K. Cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and Extensions. R Package Version 2.1.8.1. 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cluster (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2013, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Song, P.X. Nonparametric tests for differential gene expression and interaction effects in multi-factorial microarray experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, R.K.; Murthy, K.N.; Kumar, M. Nonparametric statistical test approaches in genetics data. Int. J. Comput. Biol. 2016, 5, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackstadt, A.J.; Hess, A.M. Filtering for increased power for microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Kerns, R.T.; Peddada, S.D.; Bushel, P.R. Principal component analysis-based filtering improves detection for Affymetrix gene expression arrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczyk, M.; Jaksik, R.; Polanski, A.; Polanska, J. Adaptive filtering of microarray gene expression data based on Gaussian mixture decomposition. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailman, M.D.; Feolo, M.; Jin, Y.; Kimura, M.; Tryka, K.; Bagoutdinov, R.; Hao, L.; Kiang, A.; Paschall, J.; Phan, L.; et al. The Ncbi Dbgap Database of Genotypes and Phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Microarray 1 | RNA-Seq 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Expressed Genes | |||
| Unique | 2251 | 8656 | |
| Shared | (86%) | 13,577 | (61%) |
| Total | 15,828 | 22,323 | |
| DEGs (FDR = 0.05) | |||
| Unique | 204 | 2172 | |
| Shared | (52%) | 223 | (9%) |
| Total | 427 | 2395 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raplee, I.D.; Borkar, S.A.; Yin, L.; Venturi, G.M.; Shen, J.; Chang, K.-F.; Nepal, U.; Sleasman, J.W.; Goodenow, M.M. The Role of Microarray in Modern Sequencing: Statistical Approach Matters in a Comparison Between Microarray and RNA-Seq. BioTech 2025, 14, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030055
Raplee ID, Borkar SA, Yin L, Venturi GM, Shen J, Chang K-F, Nepal U, Sleasman JW, Goodenow MM. The Role of Microarray in Modern Sequencing: Statistical Approach Matters in a Comparison Between Microarray and RNA-Seq. BioTech. 2025; 14(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaplee, Isaac D., Samiksha A. Borkar, Li Yin, Guglielmo M. Venturi, Jerry Shen, Kai-Fen Chang, Upasana Nepal, John W. Sleasman, and Maureen M. Goodenow. 2025. "The Role of Microarray in Modern Sequencing: Statistical Approach Matters in a Comparison Between Microarray and RNA-Seq" BioTech 14, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030055
APA StyleRaplee, I. D., Borkar, S. A., Yin, L., Venturi, G. M., Shen, J., Chang, K.-F., Nepal, U., Sleasman, J. W., & Goodenow, M. M. (2025). The Role of Microarray in Modern Sequencing: Statistical Approach Matters in a Comparison Between Microarray and RNA-Seq. BioTech, 14(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030055






