Abstract
Cadmium stress is a barrier to crop production, yield, quality, and sustainable agriculture. In the current study, we investigated the characteristics of bacterial strain Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 under cadmium (CdCl2) stress and its influence on Cd stresses in pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. It was revealed that strain OBA 2.4.1 is tolerant of up to 2 mM CdCl2, and seed treatment with the bacterium enhanced pea plant growth (length of seedlings) under 0.5 mM cadmium stress. This bacterial strain showed plant growth-promoting properties, including biofilm formation and siderophore activity. An important advantage of the studied strain OBA 2.4.1 is its ability to colonize the plant roots. Moreover, the inoculation with strain OBA 2.4.1 significantly reduced oxidative stress markers in pea seedlings under cadmium stress. These findings suggest that cadmium stress-tolerant strain OBA 2.4.1 could enhance pea plant growth by mitigating stress-caused damage, possibly providing a baseline and eco-friendly approach to address heavy metal stress for sustainable agriculture.
1. Introduction
Biotic and abiotic stresses affect plant growth, development, and crop yields. Heavy metals (HMs) adversely affect all processes occurring in plants and, in addition, are very toxic to the human body and can cause serious health problems for humans [1,2]. The rapid development of industry and manufacturing causes serious environmental pollution, especially in soil. HMs in the soil are absorbed by plant roots and accumulate in all plant tissues, seriously slowing down many physiological and molecular processes [3]. Excessive accumulation of Cd2+ in plants leads to growth retardation, a decrease in the contents of chlorophyll and carotenoids, as well as a decline in leaf area and photosynthesis rate, along with reduced plant biomass and water content and increased protease activity [4]. Cd2+ in plants can bind to proteins, causing denaturation and dysfunction, resulting in growth inhibition [5]. Cd can lead to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [1,6]. Sandalio et al. (2001) showed that Cd induces oxidative stress in Pisum sativum seedlings, promoting the accumulation of lipid peroxide and oxidized protein, and reducing catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity [7].
To mitigate the problems associated with HMs contamination, there is an urgent need for alternative environmentally friendly technologies, such as the use of plant growth-promoting microorganisms/rhizobacteria (PGPM/PGPR), for future use. This includes various taxonomic groups that have a wide range of beneficial properties for plants. Rhizospheric bacteria Pseudomonas sp. Belongs to PGPM [8,9]. These microorganisms actively colonize the plant roots, stimulate their growth, activate the immune response, and suppress the growth of soil phytopathogenic fungi and bacteria. Unlike other soil bacteria, Pseudomonas sp. Grows very quickly [8,9]. Currently, P. fluorescens, P. aureofaciens, P. chlororaphis, P. corrugate, P. putida, and others strains can be used as growth-stimulating agents, as well as protectors from the negative effects of HMs [8,9,10].
Phytoremediation by PGPR is an effective environmental measure to increase the remediation of HMs-contaminated soils. There are works showing the positive effect of Cd-Zn-tolerant PGPR Bacillus sp. Strain ZC3-2-1 in Oryza sativa. Treatment with this strain significantly increased O. sativa biomass, but the content of Cd2+ and Zn2+ per unit of rice biomass did not change significantly. This fact proves that the Bacillus sp. ZC3-2-1 can increase the efficiency of the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with Cd-Zn, promoting phytoextraction and metal immobilization [11].
Plants of the Brassicaceae family are most often recommended as phytoremediation plants, since they have a relatively high resistance to HMs and exhibit the ability to accumulate them [12,13,14]. However, their main disadvantage in phytoremediation applications is their low growth rate and low biomass yield. As an alternative, it is possible to consider plants of the Fabaceae family, which grow rapidly and gain a large biomass, but have a relatively low tolerance to HMs [15,16]. In addition, legumes form a nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with nodule bacteria and an associative symbiosis with PGPR, exerting a positive effect on plant growth and nutrition [17]. Such symbiotic interactions of legumes with beneficial bacteria increase plant adaptation to stresses, which makes it possible to use them for the bioremediation of polluted soils [9,17,18,19,20,21].
Previously, when studying the growth-promoting properties of Pseudomonas spp., four strains were selected: OBA 2.4.1, OBA 2.9, GOR 4.17, and STA 3, which were isolated from the rhizosphere of plants in the Southern Urals (Russia). The most effective strain of Pseudomonas sp. Was chosen for further research, particularly, the strain OBA 2.4.1, which increased the germination vigor of Medicago sativa L. seeds by 15% compared to the untreated control. In addition, among the studied strains of Pseudomonas sp., OBA 2.4.1 showed the greatest resistance to growth on media under Cd stress [22]. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to determine the different activity and inhibitory concentrations of Cd salts toward the growth of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1, analyzing its effect on Pisum sativum L. growth and tolerance under Cd stress.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1
The strain of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 was isolated from the rhizosphere of the Oxytropis baschkiriensis by homogenizing soil samples in a sterile LB medium (Bacto Tryptone, 1%; yeast extract, 0.55; NaCl, 0.5%; agar, 1%), with further subculture and growth at 28°C [23]. DNA from the bacteria was isolated by cell lysis in 1% Triton X100 and 1% Chelex100 suspension [24].
2.2. Molecular Genetic Identification of Bacterial Strains
To identify the isolated bacteria, the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using the universal primers fD1 5’- CCCGGGATCCAAGCTTAAGGAGGTGATCCAGCC-3’ and rD1 5’- CCGAATTCGTCGACAACAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG -3’ [25]. For amplification of the rpoD gene fragment, the primers PsEG30F5’-ATYGAAATCGCCAARCG-3’ and PsEG790R5’-CGGTTGATKTCCTTGA-3’ were used [26,27].
Nucleotide sequences were determined on an Applied Biosystems 3500 automatic sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) using the Big Dye Terminator v. 3.1. The analysis was carried out using the Lasergene software package (DNASTAR, Inc., Madison, WI, USA). Nucleotide sequences for comparative analysis were taken from the GenBank database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov accessed on 28 December 2022). Computational analysis of DNA sequence fragments was performed using the Clustal W multiple alignment method in the Megalign Lasergene program (DNASTAR, Inc. Madison, WI, USA).
To obtain a fluorescently labeled strain of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1, the pJNTurboRFP vector was used [28]. Some of the root fragments were used to visually assess the colonization of the surface of plant root hairs by bacteria using an Axio Imager M1 fluorescent microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). For this, the roots were incubated together with labeled bacteria (106 CFU/mL) for 1 day.
2.3. Biofilm Formation on Inert Surfaces
Biofilms were examined on 24-well plastic plates (polystyrene) (Corning, Inc., USA). Bacteria were grown for 24 h in Lauria–Bertani (LB) medium at 28°C and 140 rpm. The bacterial culture was diluted to 106 CFU/mL and 1 mL was transferred into the wells of the plate and incubated at 28°C and 50 rpm for 7 days. To determine the relative biofilm density, the gentian violet staining method (Agat-Med, Russia) was used [29]. The optical density of the samples was measured using an Enspire Model 2300 Multilabel Microplate Reader (Perkin Elmer, Boston, MA, USA).
2.4. Phosphate Mobilization and Siderophore Activity of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1
The determination of the ability of the Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 to mobilize inorganic phosphorus was tested on plates with Muromtsev’s medium (glucose 10 g/L, asparagine 1 g/L, K2SO4 0.2 g/L, MgSO4 0.2 g/L, corn extract 0.02 g/L, agar 20 g/L; pH 6.8) containing insoluble phosphate. As a source of phosphorus, Ca3(PO4)2 was added to the medium at a concentration of 5 g/L [30]. A daily culture of bacteria was applied as a drop on the surface of an agar medium and incubated at a temperature of 28°C.
CAS-blue agar was prepared as described by Schwyn (1986), with some modifications [31,32]. To prepare 100 mL of the medium, 6.5 g of chrome azurol S was dissolved in 5 mL of water and mixed with 1 mL of a solution containing 1 mM FeCl3 and 10 mM HCl. After that, 4 mL of a solution containing 7.3 mg of HDTMA was added to the chrome azurol solution. The resulting mixture was autoclaved and added to the sterile LB medium. The bacteria were grown on the medium for 2 days. A change in color to yellow, orange, or pink revealed the release of siderophores.
2.5. Determination of H2O2 Content
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) levels were determined according to [33]. The samples of plant material were homogenized (1:5 weight/volume) in 0.05M sodium phosphate buffer pH 6.2. The supernatant was separated by centrifugation (Eppendorf® Microcentrifuge 5415 R, Humburg, Germany, USA) at 15,000× g for 15 min. The concentration of H2O2 in the supernatant was spectrophotometrically (SmartSpecTM Plus, Bio–Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) determined using xylenol orange in the presence of Fe2+ at 560 nm. The H2O2 was expressed as µmoL g–1 FW.
2.6. Determination of the Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content
For the measurement of lipid peroxidation in leaves, the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) test, which determines MDA as an end product of lipid peroxidation [34], was used. Plant material were ground in distilled water and then homogenized in 20% trichloroacetic acid (TCA). The homogenate was centrifuged at 10,000× g for 20 min, and 0.5 mL of the supernatant was added to 1 mL 0.5% (w/v) TBA in 20% TCA. The mixture was incubated in boiling water for 30 min, and the reaction was stopped by placing the reaction tubes in an ice bath. Then, the samples were centrifuged at 10,000× g for 5 min. Absorbance was spectrophotometrically (SmartSpecTM Plus, Bio–Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) measured at 532 nm. The amount of MDA–TBA complex (red pigment) was calculated from the extinction coefficient 155 mM−1 cm −1. The MDA was expressed as nmoL g–1 FW.
2.7. Treatment of Plants with Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1
Pea seeds (Pisum sativum L., Kelvedonskoye miracle variety) were sterilized in 70% ethyl alcohol for 1 min and 10% sodium hypochlorite solution for 20 min [29]. Thereafter, the seeds were treated with Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 (107 CFU/mL) for 30 min and germinated on filter paper with sterile water (control) and various concentrations of CdCl2 (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5 mM) (stress) at 24 ± 1°C in the dark for 7 days. Seven-day-old seedlings were taken to assess their shoot length. For the analysis, 50 seedlings were used in each variant in three independent biological replicates.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All microbiological, molecular, biochemical, and physiological experiments were performed in three or more bioassays and three or four analytical tests. The arithmetic average values and confidence intervals calculated from the standard error are shown in the table and graphs (± SEM). Statistically significant differences between the mean values were evaluated using analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by the Tukey test (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the Strain OBA 2.4.1 and Its Main PGP Traits
The sequenced 16S rRNA sequence was deposited in GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank accessed on 28 December 2022) under the number OK039351 and in the rpoD gene under the number OM641958. When comparing fragments of the 16S rRNA and rpoD gene sequences with typical strains, it was found that Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 is closest in homology to Pseudomonas fluorescens. This strain is described in detail in a previous study [27].
It was revealed that the strain Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 is capable of forming biofilms on inert surfaces. In addition, siderophore activity was also observed (Figure 1).
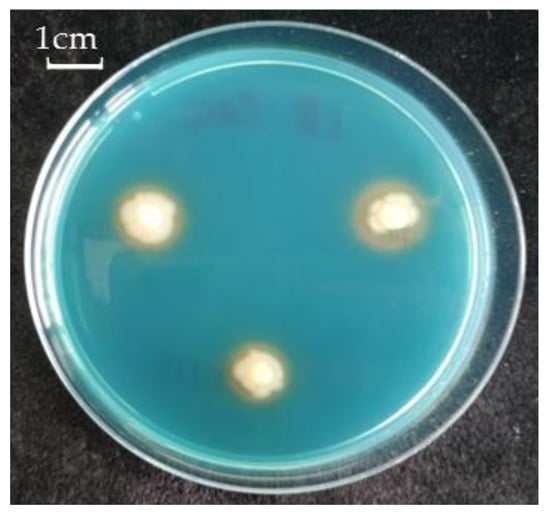
Figure 1.
Siderophore production of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1. The bar in the photograph indicates 1 cm.
3.2. Growth Analysis of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 under Cadmium Stress (0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 mM CdCl2)
The presence of Cd in the growth medium of the bacteria led to the inhibition of the growth of their colonies, especially in the presence of 1.5. and 2 mM Cd (Figure 2A). The growth analysis of the labelled bacterial colonies showed a similar result (Figure 2B).
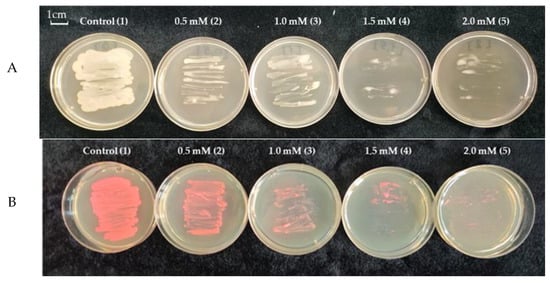
Figure 2.
A—The growth of the strain Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 (1) on LB medium, (2) with the addition of 0.5 mM Cd, (3) with the addition of 1 mM Cd, (4) with the addition of 1.5 mM Cd, (5) with the addition of 2 mM Cd; B—the growth of the strain Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 transformed with plasmid pJNTurboRFP (which gives a pink color to the bacteria) (1) on LB medium, (2) with addition of 0.5 mM Cd, (3) with addition of 1 mM Cd, (4) with addition of 1.5 mM Cd, (5) with the addition of 2 mM Cd. The bar in the photograph indicates 1 cm.
3.3. Effect of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 Strain on Pea Growth under Cd Stress
It was found that the morphometric parameters showed significant visual differences (Figure 3). Cd stress inhibits the germination and growth of pea plants (Figure 3A). The most negative effect on growth was exerted by 0.5 mM Cd. Seed pretreatment with bacterial strain OBA 2.4.1 contributed to the reduction of the inhibitory effect of Cd,. Under the action of 0.1 mM Cd, the length of these plants increased by 62%, of 0.2 mM by 20%, of 0.3 mM by 36%, of 0.4 mM by 51%, and of 0.5 mM by 118% relative to the control stressed plants (Figure 3B).

Figure 3.
Effect of Cd on the growth of pea seeds germinated on filter paper in sterile water (control) and in the presence of Cd: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 mM (A); the second variant of the seeds was treated with Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 and also grew in the presence of Cd: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 mM (B). The bar in the photograph indicates 1 cm.
It was found that treatment with Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 stimulated the growth of pea seeds; in the presence of Cd, a gradual deterioration in the growth and development of seedlings was also observed (Table 1).

Table 1.
Average length of seedlings of pea plants under different concentrations of cadmium. The presented data are the average of three repetitions (n = 50).
3.4. Effects of Strain Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 on the Content H2O2 and MDA in Pea Seedlings under Cd Stress
The results showed that Cd stress resulted in a more than twofold increase in H2O2 content (Figure 4).
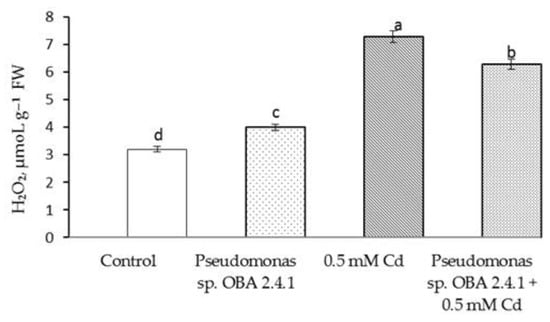
Figure 4.
Effect of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 on the content of H2O2 in 7-day-old pea seedlings under normal and Cd stress conditions. The bars indicate the mean values of three replicates ± SEM. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between the means at the level of P < 0.05 (ANOVA, LSD test).
This result is accompanied by the same level of MDA accumulation (Figure 5), but treatment with Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 significantly reduced the damage caused by stress. Thus, the content of H2O2 and MDA the outflow was higher (relative to the control) by 1.5 times and 1.6 times, respectively. At the same time, the treatment itself with Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 did not affect the state of the membrane structures under normal conditions.
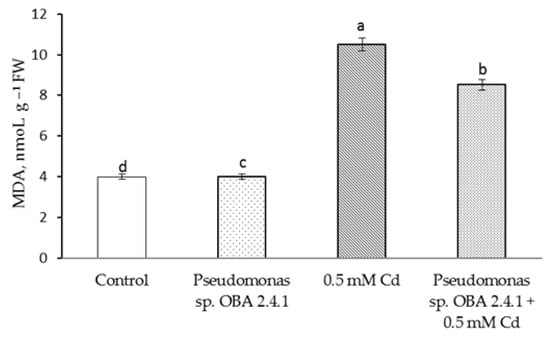
Figure 5.
Effect of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 on the content of MDA in 7-day old pea seedlings under normal and Cd stress conditions. The bars indicate the mean values of three replicates ± SEM. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between the means at the level of P < 0.05 (ANOVA, LSD test).
3.5. Bacterial Colonization of Pisum sativum L. Plant Roots
Figure 6 shows the growth of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 transformed with the pJNTurboRFP vector. The bacteria have not lost their resistance to Cd. The fluorescent label made it possible to visualize bacterial cells on the surface of the root hairs of germinated pea seedlings. Microscopy showed the formation of bacterial clusters and microcolonies of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 on the roots of peas.
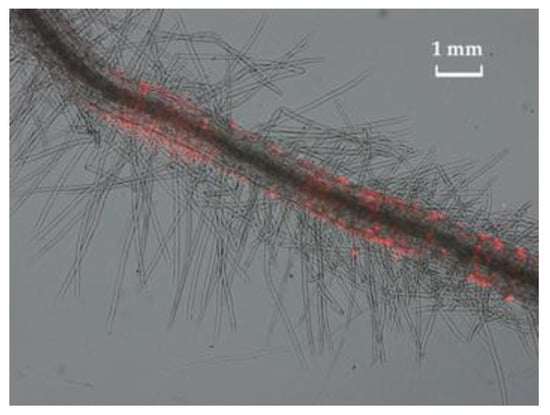
Figure 6.
Bacteria transformed with the pJNTurboRFP vector on the surface of pea plant root hairs. Microcolonies of Pseudomonas sp. 2.4.1 formed after 1 day of incubation. Visualization was made using a fluorescent microscope Axio Imager M1 (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). The bar in the photograph indicates 1 mm.
4. Discussion
For successful colonization of plant roots, the bacteria must be highly competitive. For example, the ability to form biofilms has a positive effect on the survival strategy of bacteria. There are studies showing that when P. aeruginosa bacteria formed a biofilm, they became more resistant to HMs ions (Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+) compared to single bacteria, since polymer compounds bind metal ions, preventing them from entering the biofilm [34,35]. The studied strain of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 also has the ability to form a biofilm, which characterizes it as a PGPM with good competitiveness. Another indicator of PGPM quality was the discovery of siderophore activity (Figure 1), since phosphate mobilization and siderophore activity are also traits of PGPM. Phosphate mobilization helps plants absorb phosphorus, and the secreted siderophores inhibit the growth of pathogenic fungi by reducing the amount of iron available to them in the soil. The ability to produce siderophores is another important feature of PGPM involved in plant growth stimulation [36,37]. Siderophores are low molecular weight (<1000 Da) molecules with a high specificity and affinity for a chelate or Fe3+ bond. They play an important role in stimulating plant growth, increasing resistance, and protecting against pathogens [38].
OBA 2.4.1 showed good growth on medium with cadmium stress at concentrations up to 1 mM (Figure 2A). Further, with an increase in Cd, the growth of bacteria was markedly inhibited. Similar growth was also observed in labeled bacteria (Figure 2B). This fact shows that labeled bacteria do not lose their resistance to cadmium stress.
It is well known that the antioxidant system plays a fundamental role in maintaining the redox homeostasis of plants under stress [1]. As expected, the presence of Cd in the growth medium led to the development of oxidative stress [1,39], which was accompanied by the depletion of glutathione (GSH) and ascorbate (AsA) pools, as well as the stress-induced activation of GR and APX. The over-accumulation of ROS led to the excessive synthesis of MDA and an increase in the permeability of the membrane structures. An excess of MDA, the end product of lipid peroxidation, and a depletion of GSH, which is a fundamental molecule regulating mitosis [33,39], led to the inhibition of plant growth under stress [32].
An important indicator for assessing the prospects for the use of bacteria is the assessment their influence on plant growth parameters. In this work, it was found that the strain Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 stimulated pea seed growth (Figure 3). The data obtained showed that inoculation of pea seeds with OBA 2.4.1 had a positive effect on the length of the seedlings, which may indicate an increase in plant resistance to cadmium stress at the initial stage of plant growth. Using labeled bacteria, we visually confirmed that they colonize seedling root hairs well. Due to their properties, bacteria have a beneficial effect on growth under cadmium stress.
When growing seeds under cadmium stress at low concentrations of Cd (0.1, 0.2 mM), an improvement in the growth of seedlings was observed. Further, an increase in the concentration of Cd led to the inhibition of seedlings growth. A similar effect is observed in many studies regarding cadmium stress. For example, Jalil et al. (1994) found that a low concentration of Cd2+ can promote the growth of durum wheat, but at the same time, at a relatively high concentration, wheat growth was inhibited, and Cd resistance varied in different varieties [40]. Yang et al. (2005) found that when the concentration of Cd2+ was 0-1 mg/kg, the height of the vine also increased, indicating a beneficial effect of Cd2+ on vine growth [41]. It is also worth noting that with an increase in the growth period under cadmium stress, plant growth is also inhibited; as shown in the study by Liu (2004), the height of corn seedlings under Cd2+ treatment is significantly reduced. In sorghum plants, and low concentrations of Cd2+ (≤25 mg/kg) stimulated an increase in plant height, which may be associated with their certain resistance to Cd, but high levels of Cd2+ inhibited the height growth of plants of the sorghum genus [42]. Thus, it is possible that lower concentrations of Cd2+ under growing conditions can stimulate plant growth to a certain extent, while higher concentrations suppressed their growth [43].
Many studies show that PGPM treatment has a positive effect on plants, even in the presence of HMs in the medium. For example, alfalfa Medicago sativa L. plants treated with PGPR and grown in the presence of Cu, Pb, and Zn increased shoot length by 22–77% and shoot biomass by up to 220% compared to untreated plants [44,45]. Treatment of Atriplex halimus and Arthrocnemum macrostachyum plants growing in the presence of HM showed an improvement in their morphometric parameters compared to the untreated controls. This may be due to the fact that microorganisms improve plant nutrition by dissolving phosphates, iron, and nitrogen fixation; in addition, they can stimulate plant growth by secreting auxins [46,47,48,49,50,51].
Thus, plant resistance to the toxic effect of Cd may be due to more efficient root growth due to the positive effect of substances released by microorganisms and a decrease in the concentration and accumulation of HMs in the plant root system. The predominant accumulation of Cd in the roots compared to its accumulation in the aboveground plant organs is determined by the barrier functions of the plant root system in relation to toxic HMs [52]. In our opinion, the ability of bacteria to colonize the surface of the roots makes an important contribution to reducing the toxicity of Cd in the environment.
5. Conclusions
The present study showed that seed inoculation with Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1, isolated from the rhizosphere of the Oxytropis baschkiriensis, had a growth-promoting and protective effect on pea plants under Cd stress. Treatment with OBA 2.4.1 resulted in a 2.6-fold increase in seedling length compared to the untreated plants. The bacterium exhibits PGP properties, including biofilm formation and siderophore production. Moreover, the strain OBA 2.4.1 contributed to the reduction of oxidative stress caused by Cd. The level of hydrogen peroxide and MDA is significantly lower than in untreated stressed plants. In addition, bacteria are able to colonize the roots of pea plants. This ability of bacteria also positively affects the growth and development of plants under stress. The evaluation of the current study suggests that the strain Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1, can potentially be used as a promising alternative and an environmentally friendly approach to facilitating pea growth and stress tolerance under cadmium stress. However, further field experiments are required to evaluate its full potential for mitigating heavy metals-caused stress in plants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.M. and L.K.; supervision: D.M. and L.K.; methodology: L.K., D.M., Z.V. and O.C.; software: D.M., L.K., Z.V. and O.C.; validation: D.M. and L.K.; formal analysis: D.M., L.K., Z.V. and O.C.; investigation: D.M., L.K., Z.V. and O.C.; visualization: D.M., L.K. and Z.V.; resources: L.K. and O.C.; data curation: D.M. and L.K.; writing—original draft: D.M., O.C. and L.K.; review and editing: D.M., L.K. and Z.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The publication was carried out within the framework of the state task of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation on the topic “Program for the Creation and Functioning of a Carbon Polygon in the Republic of Bashkortostan Eurasian Carbon Polygon for 2022-2023” (Publication number: FEUR-2022-0001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, T.; Li, L.; Duan, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, M. Progress in our understanding of plant responses to the stress of heavy metal cadmium. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 1836884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicas, S.I.; Laslo, V.; Timar, A.V.; Balta, C.; Herman, H.; Ciceu, A.; Gharbia, S.; Rosu, M.; Mladin, B.; Chiana, L.; et al. Nano selenium—Enriched probiotics as functional food products against cadmium liver toxicity. Materials 2021, 14, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Agrawal, M.; Agrawal, S.B. Impact of heavy metals on physiological processes of plants: With special reference to photosynthetic system. In Plant Responses to Xenobiotics; Springer: Singapore, Singapore, 2016; pp. 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.E.; Harada, E.; Wada, M.; Tsuboi, H.; Morita, Y.; Kusano, T.; Sano, H. Detoxification of cadmium in tobacco plants: Formation and active excretion of crystals containing cadmium and calcium through trichomes. Planta 2001, 213, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Khan, M.I.; Anjum, N.A.; Khan, N.A. Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants—Role of plant growth regulators. Protoplasma 2015, 252, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K.J. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandalio, L.M.; Dalurzo, H.C.; Gomez, M.; Romero-Puetas, M.C.; del Rio, L.A. Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochetkov, V.V.; Anokhina, T.O.; Siunova, T.V.; Sizova, O.I.; Boronin, A.M. Formation and prospects of organic farming in Russia. 2018. Available online: http://potatoveg.ru/en/main-topic/formation-and-prospects-of-organic-farming-in-russia-review.html (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Sharma, R.K.; Archana, G. Cadmium minimization in food crops by cadmium resistant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli, M.; Woo, S.L.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Seed treatments with microorganisms can have a siostimulant effect by Influencing germination and seedling growth of crops. Plants 2022, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wang, W.; Zheng, X.; Chen, X.; Fu, W.; Wang, G.; Ji, J.; Jin, C.; Guan, C. Improvement of the Cd and Zn phytoremediation efficiency of rice (Oryza sativa) through the inoculation of a metal-resistant PGPR strain. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, C.; Clemente, R.; Navarro-Aviñó, J.; Baixauli, C.; Ginér, A.; Serrano, R.; Walker, D.J.; Bernal, M.P. Tolerance and accumulation of heavy metals by Brassicaceae species grown in contaminated soils from mediterranean regions of Spain. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 56, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamerali, T.; Bandiera, M.; Mosca, G. Field crops for phytoremediation of metal-contaminated land. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Rehman, F.; Masoodi, A.; Ansari, A.A.; Varshney, D.; Naushin, F.; Naikoo, M.I. Roles of brassicaceae in phytoremediation of metals and metalloids. In Phytoremediation; Ansari, A., Gill, S., Gill, R., Lanza, G., Newman, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouhe, M.; Ninomiya, S.; Tohoyama, H.; Joho, M.; Murayama, T. Different characteristics of root in the cadmium-tolerance and cd-binding complex formation between mono- and dicotyledonous plants. J. Plant Res. 1994, 107, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazen, A.M.A. Assessment of heavy metal accumulation and performance of some physiological parameters in Zea Mays L. and Vicia Faba L. grown on soil amended by sewage sludge resulting from sewage water treatment in the state of Qatar. Qatar Univ. Sci. J. 1995, 5, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Belimov, A.A.; Shaposhnikov, A.I.; Azarova, T.S.; Makarova, N.M.; Safronova, V.I.; Litvinskiy, V.A.; Nosikov, V.V.; Zavalin, A.A.; Tikhonovich, I.A. Microbial consortium of PGPR, rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus makes pea mutant SGECdt Comparable with Indian mustard in cadmium tolerance and accumulation. Plants 2020, 9, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artursson, V.; Finlay, R.D.; Jansson, J.K. Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and bacteria and their potential for stimulating plant growth. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Bashan, L.E.; Hernandez, J.-P.; Bashan, Y. The potential contribution of plant growth-promoting bacteria to reduce environmental degradation—A comprehensive evaluation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 61, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sagasti, M.T.; Marino, D. PGPRs and nitrogen-fixing legumes: A perfect team for ecient Cd phytoremediation? Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ullah, A.; Heng, S.; Farooq, M.; Munis, H.; Fahad, S.; Yang, X. Phytoremediation of heavy metals assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 117, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakimova, L.R.; Chubukova, O.V.; Muryasova, A.R.; Simoroz, E.V.; Chumakova, A.K.; Vershinina, Z.R. Impact of Pseudomonas spp. on Medicago sativa L. plants under the inhibitory effect of cadmium salts. Taurida Her. Agrar. Sci. 2022, 2, 155–163. Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=49231774 (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Desoky, E.S.M.; Merwad, A.R.M.; Semida, W.M.; Ibrahim, S.A.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Rady, M.M. Heavy metals-resistant bacteria (HM-RB): Potential bioremediators of heavy metalsstressed Spinacia oleracea plant. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubukova, O.V.; Vershinina, Z.R.; Matnyazov, R.T.; Baymiev, A.K.; Baymiev, A.K. Creation of an inducible vector system based on the rhizobia nodA gene promoter. Ekol. Genet. 2021, 19, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baymiev, A.K.; Akimova, E.S.; Gumenko, R.S.; Vladimirova, A.A.; Muldashev, A.A.; Chemeris, A.V.; Baymiev, A.K. Genetic diversity and phylogeny of root nodule bacteria isolated from nodules of plants of the Lupinaster genus inhabiting the southern Urals. Russ. J. Genet. 2019, 55, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet, M.; Bennasar, A.; Lalucat, J.; García-Valdés, E. An rpoD-based PCR procedure for the identification of Pseudomonas species and for their detection in environmental samples. Mol. Cell Probes. 2009, 23, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubukova, O.V.; Khakimova, L.R.; Akimova, E.S.; Vershinina, Z.R. Phylogeny and Properties of New Pseudomonas spp. from the rhizosphere of Southern Ural leguminous plants. Microbiology 2022, 91, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baymiev, A.K.; Yamidanov, R.S.; Matniyazov, R.T.; Blagova, D.K.; Chemeris, A.V. Preparation of fluorescent labeled nodule bacteria strains of wild legumes for their detection in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vershinina, Z.R.; Chubukova, O.V.; Nikonorov, Y.M.; Khakimova, L.R.; Lavina, A.M.; Karimova, L.R.; Baymiev, A.K. Effect of rosr gene overexpression on biofilm formation by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Microbiology 2021, 90, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegorshina, A.A.; Khayrullin, R.M.; Lukyantsev, M.A.; Kuramshina, Z.M.; Smirnova, Y.V. Phosphate-mobilizing activity of the endophytic Bacillus subtilis strains and their effect on wheat roots micorrhization ratio. J. Sib. Fed. Univ. Biol. 2011, 4, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Schwynan, B.; Neilands, J.B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslennikova, D.; Nasyrova, K.; Chubukova, O.; Akimova, E.; Baymiev, A.; Blagova, D.; Ibragimov, A.; Lastochkina, O. Effects of Rhizobium leguminosarum Thy2 on the growth and tolerance to cadmium stress of wheat plants. Life 2022, 12, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindschedler, L.V.; Minibaeva, F.; Gardner, S.L.; Gerrish, C.; Davies, D.R.; Bolwell, G.P. Early Signalling events in the apoplastic oxidative burst in suspension cultured french bean cells involve cAMP and Ca2+. New Phytol. 2001, 151, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslennikova, D.; Lastochkina, O. Contribution of ascorbate and glutathione in endobacteria bacillus subtilis- mediated drought tolerance in two Triticum aestivum L. genotypes contrasting in drought sensitivity. Plants 2021, 10, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitzel, G.M.; Parsek, M.R. Heavy metal resistance of biofilm and planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishchik, V.N.; Vorob'ev, N.I.; Provorov, N.A.; Khomyakov, Y.V. Mechanisms of plant and microbial adaptation to heavy metals in plant–microbial systems. Microbiology 2016, 85, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.F.; Rasool, A.; Mansoor, S.; Saleem, S.; Baba, T.R.; Haq, S.M.; Rehman, S.A.; Adetunji, C.O.; Popesc, S.M. Potential applications of Rhizobacteria as eco-friendly biological control, plant growth promotion and soil metal bioremediation. In Sustainable Crop Production Recent Advances; Meena, V., Choudhary, M., Meena, S.K., Yadav, R.P., Eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2022; pp. 104–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.; Swapnil, P.; Divyanshu, K.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, Y.N.; Zehra, A.; Marwal, A.; Upadhyay, R.S. PGPR-mediated induction of systemic resistance and physiochemical alterations in plants against the pathogens: Current perspective. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 828–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Ayub, A.; Hussain, S.; Waraich, E.A.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Ishfaq, M.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, N.; Maqsood, M.F. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Recent progress on morpho-physiological effects and remediation strategies. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 212–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Selles, F.; Clarke, J.M. Effects of cadmium on growth and the uptake of cadmium and other elements by durum wheat. Plant Nutr. 1994, 17, 1839–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Bu, Y.S.; Guo, X.Y. Research on effects of soil exogenous cadmium and lead pollution on rape growth. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2005, 3, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.X. Effects of cadmium and zinc interaction on corn seedling physiological and biochemical characteristics. Yi Chun Coll. J. 2004, 26, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Da-Lin, L.; Kai-Qi, H.; Jing-Jing, M.; Wei-Wei, Q.; Xiu-Ping, W.; Shu-Pan, Z. Effects of cadmium on the growth and physiological characteristics of sorghum plants. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 15770–15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raklami, A.; Oufdou, K.; Tahiri, A.I.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Navarro-Torre, S.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.D.; Meddich, A.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Pajuelo, E. Safe cultivation of Medicago sativa in metal-polluted soils from semi-arid regions assisted by heat- and metallo-resistant PGPR. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkolewska, A.; Piechalak, A.; Ciszewska, L.; Antos-Krzemińska, N.; Skrzypczak, T.; Hanć, A.; Sitko, K.; Małkowski, E.; Barałkiewicz, D.; Małecka, A. Combined use of companion planting and PGPR for the assisted phytoextraction of trace metals (Zn, Pb, Cd). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 13809–13825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R. Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, D.; Thakker, J.N.; Dhandhukia, P.C. Portraying mechanics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1127500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Torre, S.; Barcia-Piedras, J.M.; Caviedes, M.A.; Pajuelo, E.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.D.; Mateos-Naranjo, E. Bioaugmentation with bacteria selected from the microbiome enhances Arthrocnemum macrostachyum metal accumulation and tolerance. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Páliz, K.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, R.; Duarte, B.; Caviedes, M.A.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Caçador, M.I.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.D.; Pajuelo, E. Investigating themechanisms underlying phytoprotection by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in Spartina densifloraunder metal stress. Plant Biol. 2018, 20, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnoua, M.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Pérez-Romero, J.A.; Barcia-Piedras, J.M.; Lotmani, B.; Redondo-Gómez, S. Combined effect of Cr-toxicity and temperature rise on physiological and biochemical responses of Atriplex halimus L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 132, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odoh, C.K.; Eze, C.N.; Apki, U.K.; Unah, V.U. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): A novel agent for sustainable food production. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2019, 14, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabayev, V.P.; Ostroumov, V.E.; Bocharnikova, E.A. Plant and soil mechanisms of plant resistance to cd toxicity under application of plant growth promoting rhizobacterium in soil contaminated with heavy metal. Biol. Bull. 2019, 46, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).