Liposomal Formulations of L-Asparaginase Conjugated with Cationic Polymers for Enhanced Internalization into Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Labeling of Formulations
2.2.1. L-ASNase Covalent Conjugation
2.2.2. Fluorescent Labeling of L-ASNase
2.2.3. Liposome Preparation
2.3. FTIR Spectroscopy of EcA Formulations
2.4. In Vitro Release Study
2.5. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
2.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.7. CLSM Image Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design Rationale: Conjugate Synthesis and Liposomal Formulation
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Formulation
3.2.1. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.2.2. Loading Degree and Activity Studies
Activities Comparison of Native L-ASNase with Conjugates
Activities Comparison of Liposomal Formulations with Non-Liposomal Preparations
Stability of Liposomal L-ASNase Formulations During Storage
3.2.3. Circular Dichroism Spectra and Secondary Structure Analysis of EcA Formulations
3.3. In Vitro L-ASNase Release Kinetics
3.4. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Liposomal Formulations of EcA and Its Conjugates
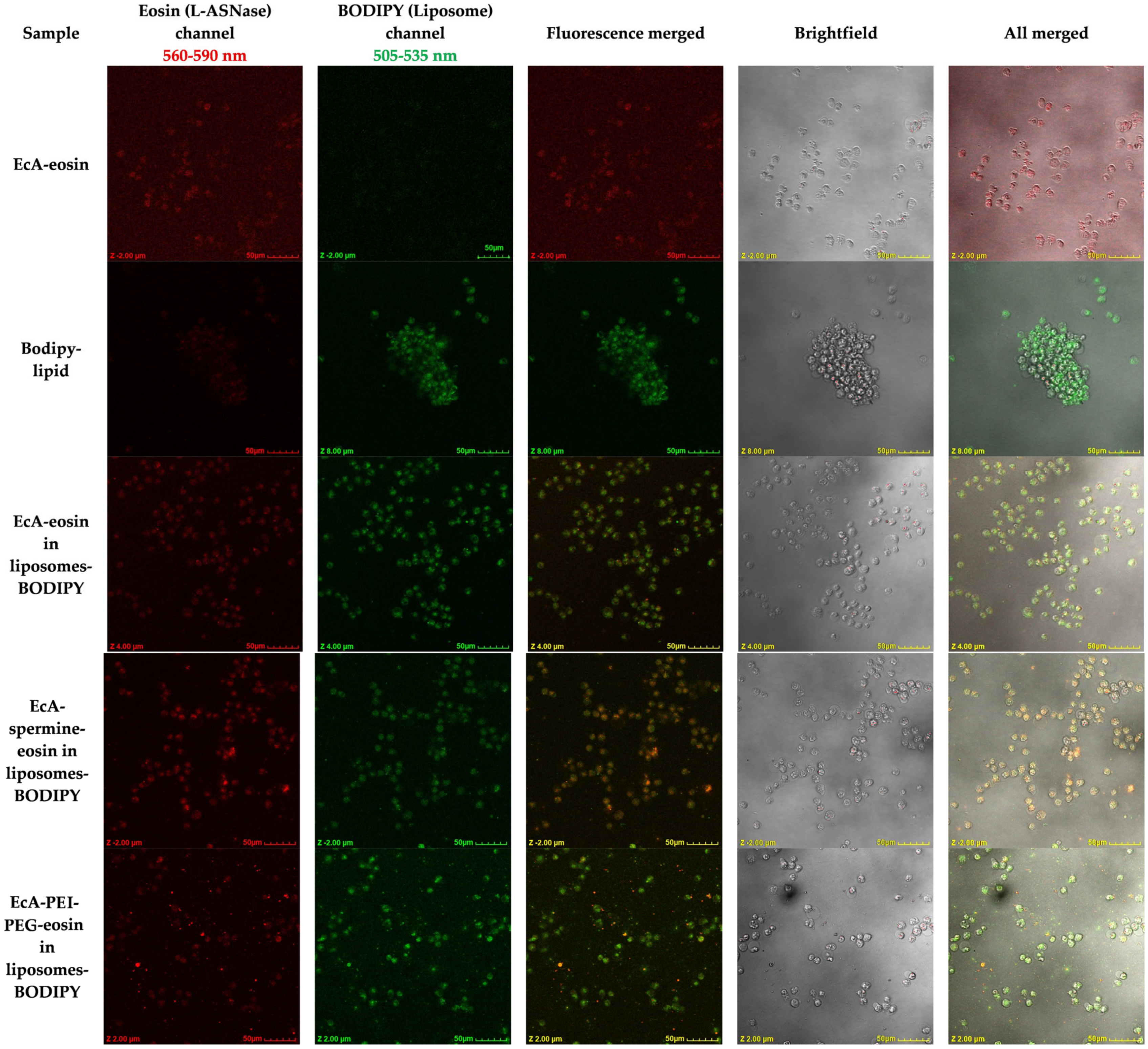
3.5. Cellular L-ASNase and Liposome Uptake and Colocalization by CLSM
3.6. Correlation Between Binding to Raji Cells and Cytotoxicity of L-ASNase Formulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| CD | Circular dichroism |
| CL | Cardiolipin |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared |
| L-ASNase | L-asparaginase |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| spm | spermine |
References
- de Moura, W.A.F.; Schultz, L.; Breyer, C.A.; de Oliveira, A.L.P.; Tairum, C.A.; Fernandes, G.C.; Toyama, M.H.; Pessoa-Jr, A.; Monteiro, G.; de Oliveira, M.A. Functional and Structural Evaluation of the Antileukaemic Enzyme L-Asparaginase II Expressed at Low Temperature by Different Escherichia coli Strains. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maese, L.; Rau, R.E. Current Use of Asparaginase in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoblastic Lymphoma. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 902117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juluri, K.R.; Siu, C.; Cassaday, R.D. Asparaginase in the Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults: Current Evidence and Place in Therapy. Blood Lymphat. Cancer Targets Ther. 2022, 12, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenicek Krleza, J.; Katusic Bojanac, A.; Jakovljevic, G. Determination of L-Asparaginase Activity and Its Therapeutic Monitoring in Children with Hematological Malignancies in a Single Croatian Center. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, C.M.; Canellos, G.P. L-Asparaginase Resistance in Human Leukemia—Asparagine Synthetase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1969, 18, 2578–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, H.; Ahn, Y.-M.; Otokawa, T.; Watanabe, B.; Hegazy, L.; Hiratake, J.; Richards, N.G.J. A Sulfoximine-Based Inhibitor of Human Asparagine Synthetase Kills L-Asparaginase-Resistant Leukemia Cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5915–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.; Taurino, G.; Bianchi, M.G.; Kilberg, M.S.; Bussolati, O. Asparagine Synthetase in Cancer: Beyond Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakhova, M.A.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Alexandrova, S.S.; Sokolov, N.N.; Kudryashova, E.V. Regulation of Catalytic Activity of Recombinant L-Asparaginase from Rhodospirillum Rubrum by Conjugation with a PEG-Chitosan Copolymer. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 2018, 73, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcenberg, J.S.; Ericsson, L.; Roberts, J. Amino Acid Sequence of the Diazooxonorleucine Binding Site of Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas 7A Glutaminase—Asparaginase Enzymes. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottobre, M.; Colitto, L.; Marcone, M.I.; Krystal, E.; Moran, L.; Wittmund, L.E.; Gimenez, V.; Makiya, M. A Pediatric Laboratory Experience: Measurement of L-Asparaginase Activity in Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. A Multicentric Study. Blood 2024, 144, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrman, M.; Cedar, H.; Schwartz, J.H. L-Asparaginase II of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashburn, L.T.; Wriston, J.C. Tumor Inhibitory Effect of L-Asparaginase from Escherichia coli. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1964, 105, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belén, L.H.; Lissabet, J.B.; de Oliveira Rangel-Yagui, C.; Effer, B.; Monteiro, G.; Pessoa, A.; Farías Avendaño, J.G. A Structural in Silico Analysis of the Immunogenicity of L-Asparaginase from Escherichia coli and Erwinia carotovora. Biologicals 2019, 59, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, V.S.; Kazanov, M.D.; Dyakov, I.N.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Aleksandrova, S.S. Comparative Immunogenicity and Structural Analysis of Epitopes of Different Bacterial L-Asparaginases. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinndorf, P.A.; Gootenberg, J.; Cohen, M.H.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Drug Approval Summary: Pegaspargase (Oncaspar®) for the First-Line Treatment of Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Oncologist 2007, 12, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.J.; Beier, R.; Da Palma, J.; Lanvers, C.; Ahlke, E.; Von Schütz, V.; Gunkel, M.; Horn, A.; Schrappe, M.; Henze, G.; et al. PEG-Asparaginase (Oncaspar) 2500 u/M2 BSA in Reinduction and Relapse Treatment in the ALL/NHL-BFM Protocols. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2002, 49, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würthwein, G.; Lanvers-Kaminsky, C.; Hempel, G.; Gastine, S.; Möricke, A.; Schrappe, M.; Karlsson, M.O.; Boos, J. Population Pharmacokinetics to Model the Time-Varying Clearance of the PEGylated Asparaginase Oncaspar® in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, A.R. Pegaspargase (Oncaspar). J. Pediatr. Oncol. Nurses 1995, 12, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghorst, S.; Hempel, G.; Poppenborg, S.; Franke, D.; König, T.; Baumgart, J. Comparative Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Characterisation of a New Pegylated Recombinant E. coli L-Asparaginase Preparation (MC0609) in Beagle Dog. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, V.P.; Mutaliyeva, B.; Sharipova, A.; Ulaganathan, V.; Lanka, S.S.; Aidarova, S.; Suigenbayeva, A.; Tleuova, A. L-Asparaginase Delivery Systems Targeted to Minimize Its Side-Effects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 316, 102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnikov, I.D.; Kudryashova, E.V. Targeted Polymeric Micelles System, Designed to Carry a Combined Cargo of L-Asparaginase and Doxorubicin, Shows Vast Improvement in Cytotoxic Efficacy. Polymers 2024, 16, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Venkatesh, D.N. Design and Evaluation of Liposomal Delivery System for L-Asparaginese. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnikov, I.D.; Ezhov, A.A.; Kudryashova, E.V. Receptor-Mediated Internalization of L-Asparaginase into Tumor Cells Is Suppressed by Polyamines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorselen, D.; Piontek, M.C.; Roos, W.H.; Wuite, G.J.L. Mechanical Characterization of Liposomes and Extracellular Vesicles: A Protocol. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Guimarães, M.; Cachumba, J.J.M.; Bueno, C.Z.; Torres-Obreque, K.M.; Lara, G.V.R.; Monteiro, G.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Pessoa, A.; Rangel-Yagui, C.d.O. Peg-Grafted Liposomes for L-Asparaginase Encapsulation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harijan, M.; Singh, M. Zwitterionic Polymers in Drug Delivery: A Review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2022, 35, e2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranja, A.G.; Pathak, V.; Lammers, T.; Shi, Y. Tumor-Targeted Nanomedicines for Cancer Theranostics. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Kawakami, S.; Yamada, M.; Yamashita, F.; Hashida, M. Enhanced Gene Transfection in Macrophages Using Mannosylated Cationic Liposome-Polyethylenimine-Plasmid DNA Complexes. J. Drug Target. 2001, 9, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.E.M.; Gaspar, M.M.; Lopes, F.; Jorge, J.S.; Perez-Soler, R. Liposomal L-Asparaginase: In Vitro Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 96, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.C.S.; Perez-Soler, R.; Morais, J.G.; Cruz, M.E.M. Liposomal Palmitoyl-L-Asparaginase: Characterization and Biological Activity. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1994, 34, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.M.; Perez-Soler, R.; Cruz, M.E.M. Biological Characterization of L-Asparginase Liposomal Formulations. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1996, 38, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girão, L.F.C.; Carvalheiro, M.C.; Ferreira-Silva, M.; da Rocha, S.L.G.; Perales, J.; Martins, M.B.F.; Ferrara, M.A.; Bon, E.P.S.; Corvo, M.L. Asp-Enzymosomes with Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Asparaginase Ii Expressed in Pichia Pastoris: Formulation Design and In Vitro Studies of a Potential Antileukemic Drug. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Flores, F.; Zárate-Romero, A.; Torres, A.G.; Huerta-Saquero, A. Encapsulation of Asparaginase as a Promising Strategy to Improve in Vivo Drug Performance. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, N.; Mathur, A.; Singh, R.P. L-Asparaginase: Insights into the Marine Sources and Nanotechnological Advancements in Improving Its Therapeutics. In Engineered Nanomaterials for Innovative Therapies and Biomedicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 67–98. [Google Scholar]
- Dobryakova, N.V.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Sokolov, N.N.; Aleksandrova, S.S.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Kudryashova, E.V. Improvement of Biocatalytic Properties and Cytotoxic Activity of L-Asparaginase from Rhodospirillum Rubrum by Conjugation with Chitosan-Based Cationic Polyelectrolytes. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnikov, I.D.; Kudryashova, E. V A Novel Approach for the Activity Assessment of L-Asparaginase Formulations When Dealing with Complex Biological Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhoverkov, K.V.; Sokolov, N.N.; Abakumova, O.Y.; Podobed, O.V.; Kudryashova, E.V. The Formation of Conjugates with PEG–Chitosan Improves the Biocatalytic Efficiency and Antitumor Activity of L-Asparaginase from Erwinia Carotovora. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 2016, 71, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobryakova, N.V.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Sokolov, N.N.; Aleksandrova, S.S.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Kudryashova, E.V. Rhodospirillum Rubrum L-Asparaginase Conjugates with Polyamines of Improved Biocatalytic Properties as a New Promising Drug for the Treatment of Leukemia. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.W.; Lam, J.K. Endosomal Escape Pathways for Non-Viral Nucleic Acid Delivery Systems. In Molecular Regulation of Endocytosis; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnikov, I.D.; Shishparyonok, A.N.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Alexandrova, S.S.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Kudryashova, E. V Structural Features Underlying the Mismatch Between Catalytic and Cytostatic Properties in L-Asparaginase from Rhodospirillum Rubrum. Catalysts 2025, 15, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, E.V.; Sukhoverkov, K.V. “Reagent-Free” l-Asparaginase Activity Assay Based on CD Spectroscopy and Conductometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



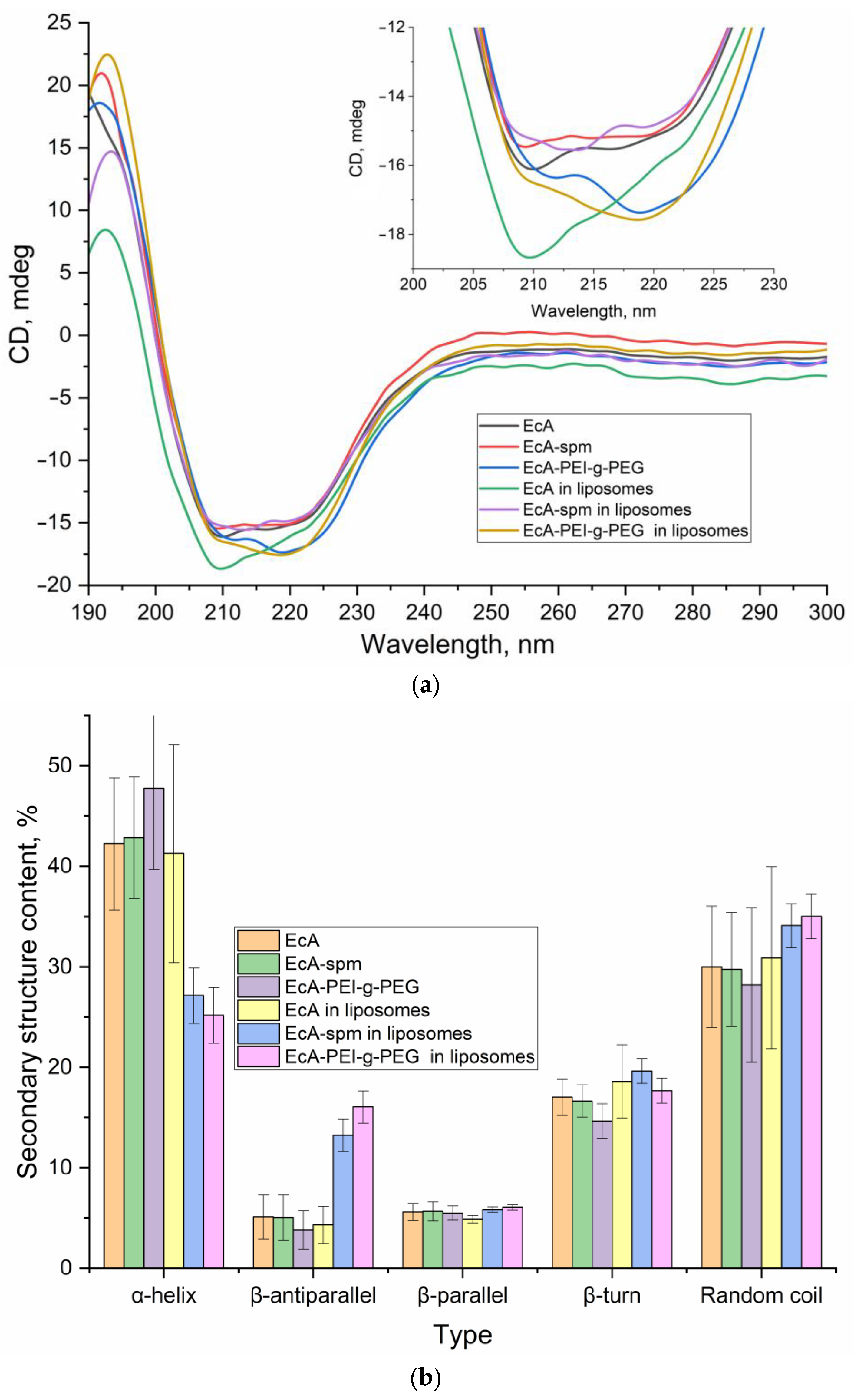





| L-ASNase Entrapment Efficiency, % | EcA | EcA-spm | EcA-PEI-g-PEG |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 100 nm liposomes | 63 ± 2 | 89 ± 1 | 82 ± 2 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 400 nm liposomes | 70 ± 5 | 97 ± 1 | 94 ± 1 |
| Final L-ASNase/lipid ratio, µg/µmol | EcA | EcA-spm | EcA-PEI-g-PEG |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 100 nm liposomes | 85 ± 3 | 120 ± 2 | 111 ± 3 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 400 nm liposomes | 95 ± 7 | 131 ± 2 | 127 ± 2 |
| L-ASNase activity, U/mg | EcA | EcA-spm | EcA-PEI-g-PEG |
| Non liposomal | 330 ± 20 | 380 ± 14 | 327 ± 15 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 100 nm liposomes | 355 ± 18 | 365 ± 13 | 306 ± 22 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 400 nm liposomes | 364 ± 23 | 370 ± 25 | 350 ± 18 |
| L-ASNase residual activity after a month of storage at +4 °C in PBS, U/mg | EcA | EcA-spm | EcA-PEI-g-PEG |
| Non liposomal | 208 (63% from initial) | 315 (83% from initial) | 245 (75% from initial) |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 100 nm liposomes | 298 (84% from initial) | 339 (93% from initial) | 278 (91% from initial) |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 400 nm liposomes | 280 (77% from initial) | 333 (90% from initial) | 284 (81% from initial) |
| L-ASNase residual activity after a week of storage at +37 °C in bovine blood serum, U/mg | EcA | EcA-spm | EcA-PEI-g-PEG |
| Non liposomal | 20 ± 5 | 140 ± 10 | 170 ± 10 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 100 nm liposomes | 150 ± 15 | 230 ± 15 | 210 ± 20 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 400 nm liposomes | 140 ± 10 | 205 ± 20 | 190 ± 15 |
| Parameter | EcA | EcA in Liposomes | EcA-spm in Liposomes | EcA-PEI-g-PEG in Liposomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T50%, min | 24 ± 2 | 45 ± 5 | 56 ± 7 | 70 ± 5 |
| T80%, min | 52 ± 5 | 240 ± 20 | 330 ± 35 | 420 ± 50 |
| IC50, U/mL | EcA | EcA-spm | EcA-PEI-PEG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non liposomal | 35 ± 5 | 8 ± 1 | 7 ± 1 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 100 nm liposomes | 20 ± 5 | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 4.7 ± 0.5 |
| In PC/Cl 80/20 400 nm liposomes | 9 ± 2 | 11 ± 1 | 13 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zlotnikov, I.D.; Ezhov, A.A.; Borisov, A.V.; Lukyanov, A.V.; Babkov, D.A.; Kudryashova, E.V. Liposomal Formulations of L-Asparaginase Conjugated with Cationic Polymers for Enhanced Internalization into Cancer Cells. Macromol 2025, 5, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040054
Zlotnikov ID, Ezhov AA, Borisov AV, Lukyanov AV, Babkov DA, Kudryashova EV. Liposomal Formulations of L-Asparaginase Conjugated with Cationic Polymers for Enhanced Internalization into Cancer Cells. Macromol. 2025; 5(4):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZlotnikov, Igor D., Alexander A. Ezhov, Alexander V. Borisov, Andrey V. Lukyanov, Denis A. Babkov, and Elena V. Kudryashova. 2025. "Liposomal Formulations of L-Asparaginase Conjugated with Cationic Polymers for Enhanced Internalization into Cancer Cells" Macromol 5, no. 4: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040054
APA StyleZlotnikov, I. D., Ezhov, A. A., Borisov, A. V., Lukyanov, A. V., Babkov, D. A., & Kudryashova, E. V. (2025). Liposomal Formulations of L-Asparaginase Conjugated with Cationic Polymers for Enhanced Internalization into Cancer Cells. Macromol, 5(4), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040054









