Harnessing Brewery Spent Grain for Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pretreatment Methods
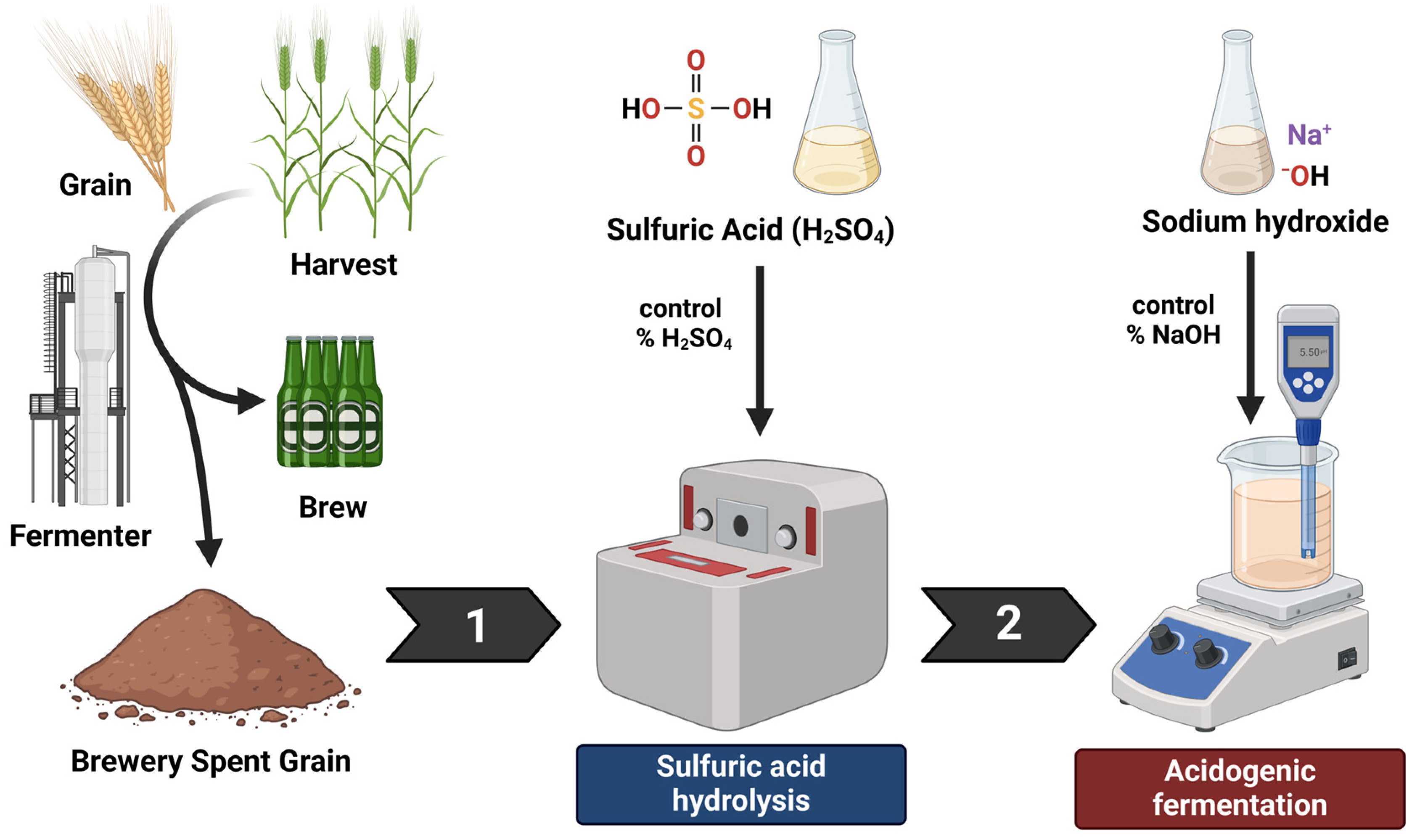
2.1. Thermally Diluted Sulfuric Acid Hydrolysis
2.2. Solid-State Enzymatic Hydrolysis (SSEH)
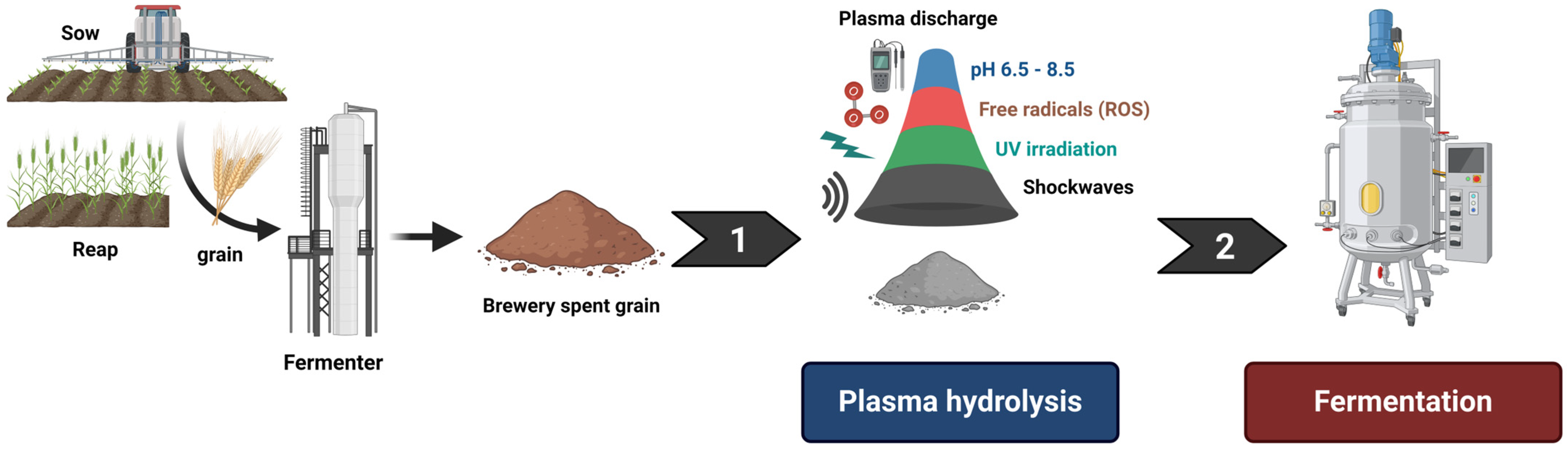
2.3. Catalysis and Non-Ionizing Radiation
3. Processing Methods
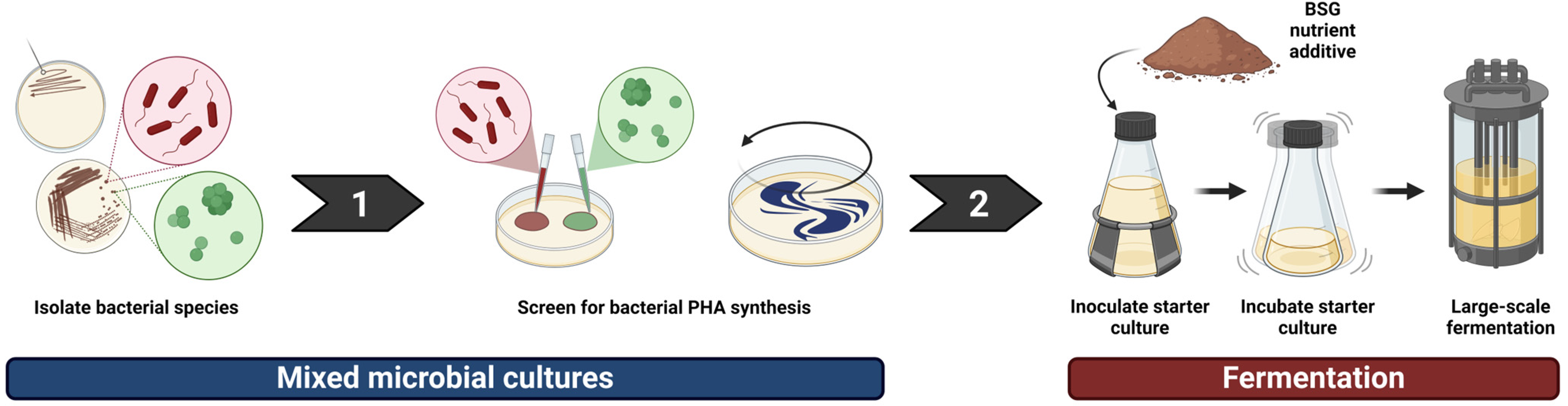
3.1. Mixed Microbial Cultures (MMCs)
3.2. Solid-State Fermentation (SSF)
4. Results
5. Discussion
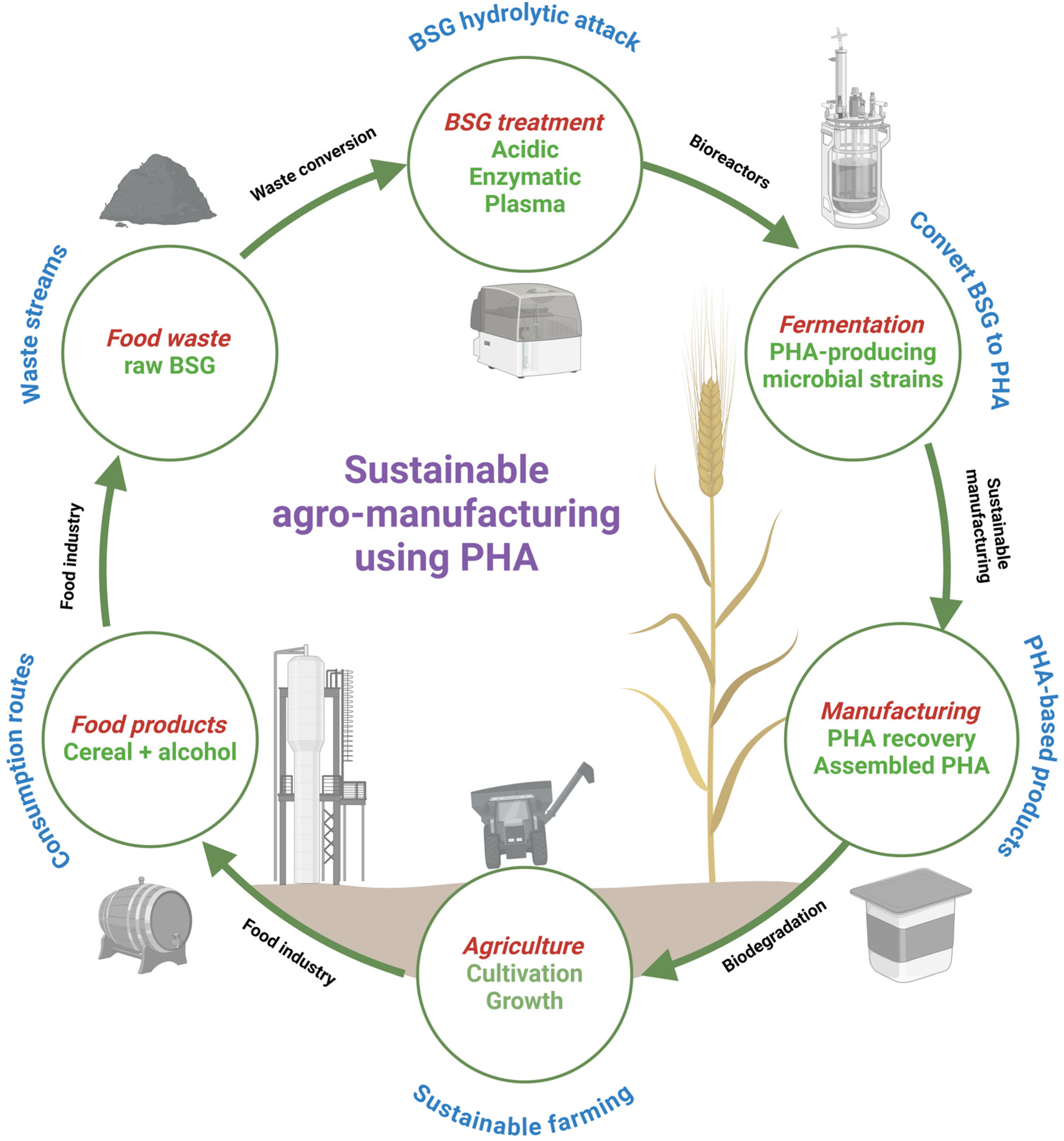
5.1. Pretreatment Processes
5.2. Temperature Effects on Microorganisms
5.3. Doehlert Design
5.4. Economic Analysis and Optimization of BSG Utilization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalheira, M.; Amorim, C.L.; Oliveira, A.C.; Guarda, E.C.; Costa, E.; Teixeira, M.R.; Castro, P.M.L.; Duque, A.F.; Reis, M.A.M. Valorization of Brewery Waste through Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production Supported by a Metabolic Specialized Microbiome. Life 2022, 12, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corchado-Lopo, C.; Martínez-Avila, O.; Marti, E.; Llimós, J.; Busquets, A.M.; Kucera, D.; Obruca, S.; Llenas, L.; Ponsá, S. Brewer’s Spent Grain as a No-Cost Substrate for Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production: Assessment of Pretreatment Strategies and Different Bacterial Strains. New Biotechnol. 2021, 62, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejin, J.; Radosavljević, M.; Mojović, L.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Djukić-Vuković, A. The Influence of Calcium-Carbonate and Yeast Extract Addition on Lactic Acid Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain Hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Budroni, M.; Zara, S.; Mannazzu, I.; Fancello, F.; Zara, G. The Role of Microorganisms on Biotransformation of Brewers’ Spent Grain. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8661–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackowski, M.; Niedźwiecki, Ł.; Jagiełło, K.; Uchańska, O.; Trusek, A. Brewer’s Spent Grains—Valuable Beer Industry by-Product. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ Spent Grain: A Review with an Emphasis on Food and Health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I. Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Valuable Feedstock for Industrial Applications: Brewer’s Spent Grain and Its Potential Applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imandi, S.B.; Karanam, S.K.; Nagumantri, R.; Srivastava, R.K.; Sarangi, P.K. Neural Networks and Genetic Algorithm as Robust Optimization Tools for Modeling the Microbial Production of Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) from Brewers’ Spent Grain. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2023, 70, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Avila, O.; Llenas, L.; Ponsá, S. Sustainable Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production via Solid-State Fermentation: Influence of the Operational Parameters and Scaling up of the Process. Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 132, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Scheel, R.A.; Nomura, C.T.; Ramarao, B.; Kumar, D. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate and Polyhydroxybutyrate-Co-MCL Copolymers from Brewer’s Spent Grains by Recombinant Escherichia coli LSBJ. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Z. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass from Low to High Solids Loading. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, T.A.; Wyman, C.E. Combined Sugar Yields for Dilute Sulfuric Acid Pretreatment of Corn Stover Followed by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of the Remaining Solids. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, O.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P.; Matsakas, L. Effect of Metals on the Regulation of Acidogenic Metabolism Enhancing Biohydrogen and Carboxylic Acids Production from Brewery Spent Grains: Microbial Dynamics and Biochemical Analysis. Eng. Life Sci. 2022, 22, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Fonseca, Y.A.; Da Silva Barreto, E.; Lomar, P.F.; Silva, S.D.Q.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Baêta, B.E.L. Biobased Production of Volatile Fatty Acids from Brewer’s Spent Grain: Optimization and Insights into the Impact of Protein Extraction on Process Performance. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 203, 109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.D.; Mishra, P.K.; Darani, K.K.; Agarwal, A.; Paul, V. Hydrothermal Treatment of Lignocellulose Waste for the Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates Copolymer with Potential Application in Food Packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Archilla, J.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.L. Two Step Process for Volatile Fatty Acid Production from Brewery Spent Grain: Hydrolysis and Direct Acidogenic Fermentation Using Anaerobic Granular Sludge. Process Biochem. 2021, 100, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Cruz-Narváez, Y.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Liceaga, A.M.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L. In Silico Bioactivity Analysis of Peptide Fractions Derived from Brewer’s Spent Grain Hydrolysates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Avila, O.; Llimós, J.; Ponsá, S. Integrated Solid-State Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Solid-State Fermentation for Producing Sustainable Polyhydroxyalkanoates from Low-Cost Agro-Industrial Residues. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 126, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Torres, L.A. Saccharification of Water Hyacinth Biomass by a Combination of Steam Explosion with Enzymatic Technologies for Bioethanol Production. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenbach, A.A.; Nokes, S.E. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Biomass at High-Solids Loadings—A Review. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 56, 526–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sanganyado, E. Biodegradability during Anaerobic Fermentation Process Impacted by Heavy Metals. In New Advances on Fermentation Processes; María Martínez-Espinosa, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-78985-313-1. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa-Torres, G.M.; Certucha-Barragán, M.T.; Almendariz-Tapia, F.J.; Monge-Amaya, O.; Acedo-Félix, E.; Pech-Canul, M.I.; Leal-Cruz, A.L.; VillaVelázquez-Mendoza, C.I. Effect of Copper and Iron on Acidogenic Biomass in an Anaerobic Packed Bed Reactor. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2014, 5, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, M.; Cui, B.; Xiao, B.; Luo, S.; Guo, D. Insight into the Ex Situ Catalytic Pyrolysis of Biomass over Char Supported Metals Catalyst: Syngas Production and Tar Decomposition. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, R.; Sarangapani, C.; Jaiswal, S.; Lu, P.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P.; Jaiswal, A.K. Improving Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Brewer Spent Grain with Nonthermal Plasma. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coats, E.R.; Loge, F.J.; Smith, W.A.; Thompson, D.N.; Wolcott, M.P. Functional Stability of a Mixed Microbial Consortium Producing PHA from Waste Carbon Sources. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 137, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Microbial Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate and Related Copolymers. In Industrial Biorefineries & White Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 575–605. ISBN 978-0-444-63453-5. [Google Scholar]
- Queirós, D.; Lemos, P.C.; Rossetti, S.; Serafim, L.S. Unveiling PHA-Storing Populations Using Molecular Methods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10433–10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.; Silva, M.; Silva, C.E.; Carvalho, G.; Reis, M.A.M. Assessment of Protein-Rich Cheese Whey Waste Stream as a Nutrients Source for Low-Cost Mixed Microbial PHA Production. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.M.L.; Lemos, P.C.; Serafim, L.S.; Oliveira, C.; Eiroa, M.; Albuquerque, M.G.E.; Ramos, A.M.; Oliveira, R.; Reis, M.A.M. Recent Advances in Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production by Mixed Aerobic Cultures: From the Substrate to the Final Product. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 885–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, G.; Presti, D.; Montiel-Jarillo, G.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E. Bioplastic Recovery from Wastewater: A New Protocol for Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) Extraction from Mixed Microbial Cultures. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, R.P.; Kumar, S.; Singh, P. Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates from Renewable Resources: A Review on Prospects, Challenges and Applications. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llimós, J.; Martínez-Avila, O.; Marti, E.; Corchado-Lopo, C.; Llenas, L.; Gea, T.; Ponsá, S. Brewer’s Spent Grain Biotransformation to Produce Lignocellulolytic Enzymes and Polyhydroxyalkanoates in a Two-Stage Valorization Scheme. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2020, 12, 3921–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, P.S. An Overview: Recycling of Solid Barley Waste Generated as a by-Product in Distillery and Brewery. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitri, S.; Salameh, S.-J.; Khelfa, A.; Leonard, E.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N.; Koubaa, M. Valorization of Brewers’ Spent Grains: Pretreatments and Fermentation, a Review. Fermentation 2022, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazanfarzadeh, Z.; Ganesan, A.R.; Mariniello, L.; Conterno, L.; Kumaravel, V. Valorization of Brewer’s Spent Grain for Sustainable Food Packaging. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, G.; Pepè Sciarria, T.; Carrara, A.; Scaglia, B.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Implementing Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production to Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste to Diversify Products and Increase Total Energy Recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, A.; Zuber, M.; Zia, K.M.; Noreen, A.; Anjum, M.N.; Tabasum, S. Microbial Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and Its Copolymers: A Review of Recent Advancements. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K. Biopolymer (PHA) Producing Microbes and Its Application. In Microbiology and Biotechnology in Human Life; JPS Scientific Publications: Tamil Nadu, India, 2019; pp. 294–327. ISBN 978-81-941936-2-3. [Google Scholar]
- Outeiriño, D.; Costa-Trigo, I.; Pinheiro De Souza Oliveira, R.; Pérez Guerra, N.; Salgado, J.M.; Domínguez, J.M. Biorefinery of Brewery Spent Grain by Solid-State Fermentation and Ionic Liquids. Foods 2022, 11, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Bunster, G.; Pavez, P. Novel Production Methods of Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Innovative Uses in Biomedicine and Industry. Molecules 2022, 27, 8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Sarsaiya, S.; Patel, A.; Juneja, A.; Singh, R.P.; Yan, B.; Awasthi, S.K.; Jain, A.; Liu, T.; Duan, Y.; et al. Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bio-Products: An Assessment of Technology, Its Importance, and Strategic Applications in Circular Bio-Economy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 127, 109876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zytner, P.; Kumar, D.; Elsayed, A.; Mohanty, A.; Ramarao, B.V.; Misra, M. A Review on Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production through the Use of Lignocellulosic Biomass. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 2120–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakati, S.R.; Vanderlaan, G.; Gacura, M.D.; Ji, X.; Chen, L.; Piovesan, D. Synthesis of Poly-Lactic Acid by Ring Open Polymerization from Beer Spent Grain for Drug Delivery. Polymers 2024, 16, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulantekin, Ö.; Alp, D. Perspective Chapter: Development of Food Packaging Films from Microorganism-Generated Polyhydroxyalkanoates. In Food Processing and Packaging Technologies—Recent Advances; Shankar Tumuluru, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-80356-995-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.Y. Characterization of Microstructure, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Delignified and Densified Poplar Wood. Materials 2021, 14, 5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, R.R.; Sivagurunathan, P.; Kim, S.-H. Effect of Severity on Dilute Acid Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and the Following Hydrogen Fermentation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21678–21684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Cheon, H.-C.; Kim, S.-H. Effects of 5-Hydromethylfurfural, Levulinic Acid and Formic Acid, Pretreatment Byproducts of Biomass, on Fermentative H2 Production from Glucose and Galactose. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 16885–16890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, N.K.; Potumarthi, R.; Baadhe, R.R.; Gupta, V.K. Chapter 1—Current Bioenergy Researches: Strengths and Future Challenges. In Bioenergy Research: Advances and Applications; Gupta, V.K., Tuohy, M.G., Kubicek, C.P., Saddler, J., Xu, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–21. ISBN 978-0-444-59561-4. [Google Scholar]
- Eronen-Rasimus, E.; Hultman, J.; Hai, T.; Pessi, I.S.; Collins, E.; Wright, S.; Laine, P.; Viitamäki, S.; Lyra, C.; Thomas, D.N.; et al. Sea-Ice Bacteria Halomonas Sp. Strain 363 and Paracoccus Sp. Strain 392 Produce Multiple Types of Poly-3-Hydroxyalkaonoic Acid (PHA) Storage Polymers at Low Temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00929-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, Y.; Tajima, K.; Nakamoto, S.; Xuerong, H.; Matsushima, T.; Ohshima, T.; Kawano, S.; Erata, T.; Dairi, T.; Munekata, M. Isolation of a Thermotolerant Bacterium Producing Medium-Chain-Length Polyhydroxyalkanoate: Thermotolerant Bacterium Producing PHA. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doehlert, D.H. Uniform Shell Designs. Appl. Stat. 1970, 19, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Show, P.L.; Lan, J.C.-W.; Loh, H.-S.; Lam, H.L.; Ling, T.C. Economic and Environmental Analysis of PHAs Production Process. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, S.; Vandi, L.-J.; Gapes, D.; Werker, A.; Oehmen, A.; Laycock, B. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Bioplastics from Organic Waste. In Biorefinery; Bastidas-Oyanedel, J.-R., Schmidt, J.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 615–638. ISBN 978-3-030-10960-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez Chavez, B.; Raghavan, V.; Tartakovsky, B. A Comparative Analysis of Biopolymer Production by Microbial and Bioelectrochemical Technologies. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 16105–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terfa, R.D.; Patel, P.N.; Kim, H.D.; Gacura, M.D.; Vanderlaan, G.; Chen, L.; Ji, X.; Piovesan, D. Harnessing Brewery Spent Grain for Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production. Macromol 2024, 4, 448-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030026
Terfa RD, Patel PN, Kim HD, Gacura MD, Vanderlaan G, Chen L, Ji X, Piovesan D. Harnessing Brewery Spent Grain for Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production. Macromol. 2024; 4(3):448-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerfa, Robe D., Priyanshi N. Patel, Hwidong D. Kim, Matthew D. Gacura, Gary Vanderlaan, Longyan Chen, Xiaoxu Ji, and Davide Piovesan. 2024. "Harnessing Brewery Spent Grain for Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production" Macromol 4, no. 3: 448-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030026
APA StyleTerfa, R. D., Patel, P. N., Kim, H. D., Gacura, M. D., Vanderlaan, G., Chen, L., Ji, X., & Piovesan, D. (2024). Harnessing Brewery Spent Grain for Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production. Macromol, 4(3), 448-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030026






