Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: Dye Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
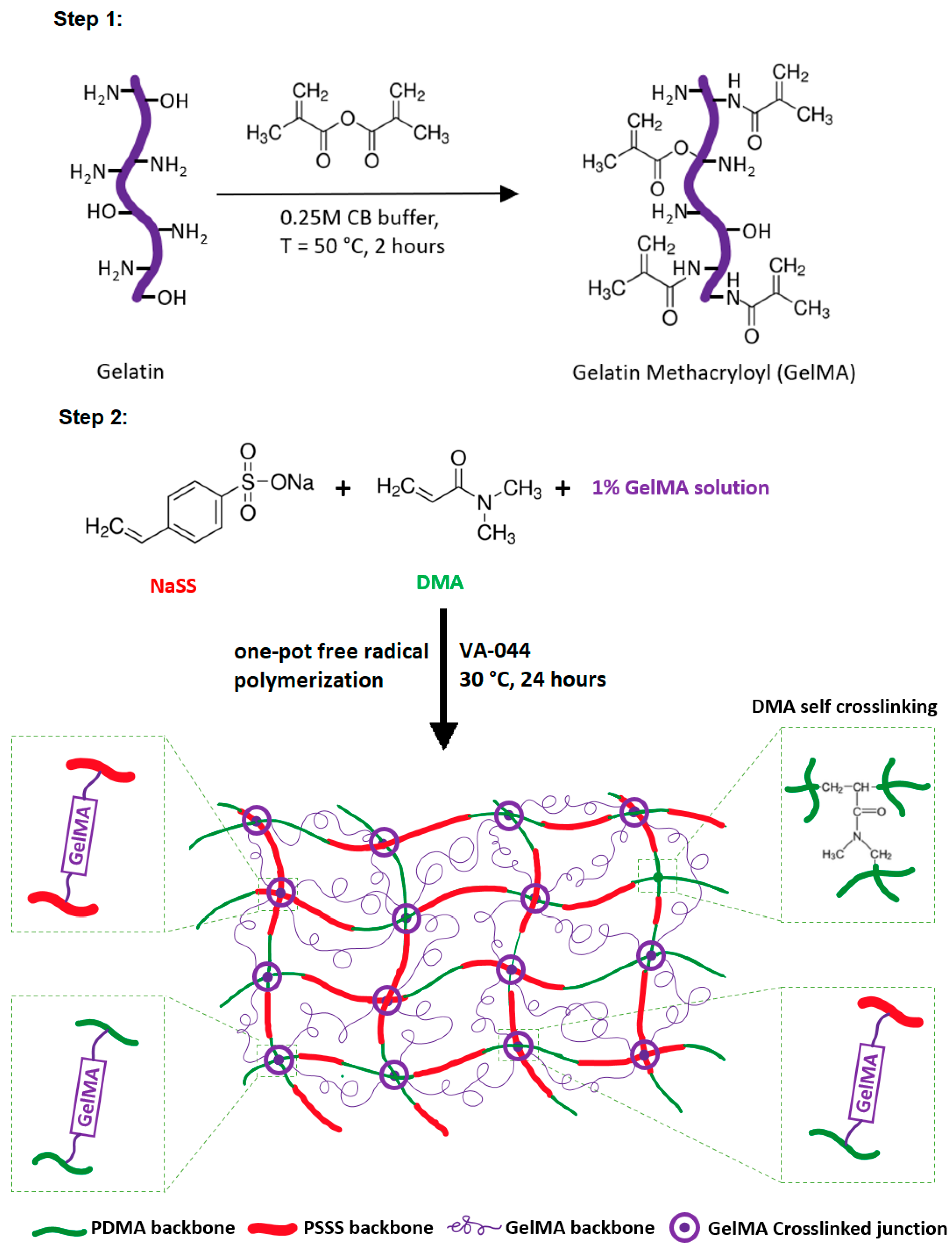
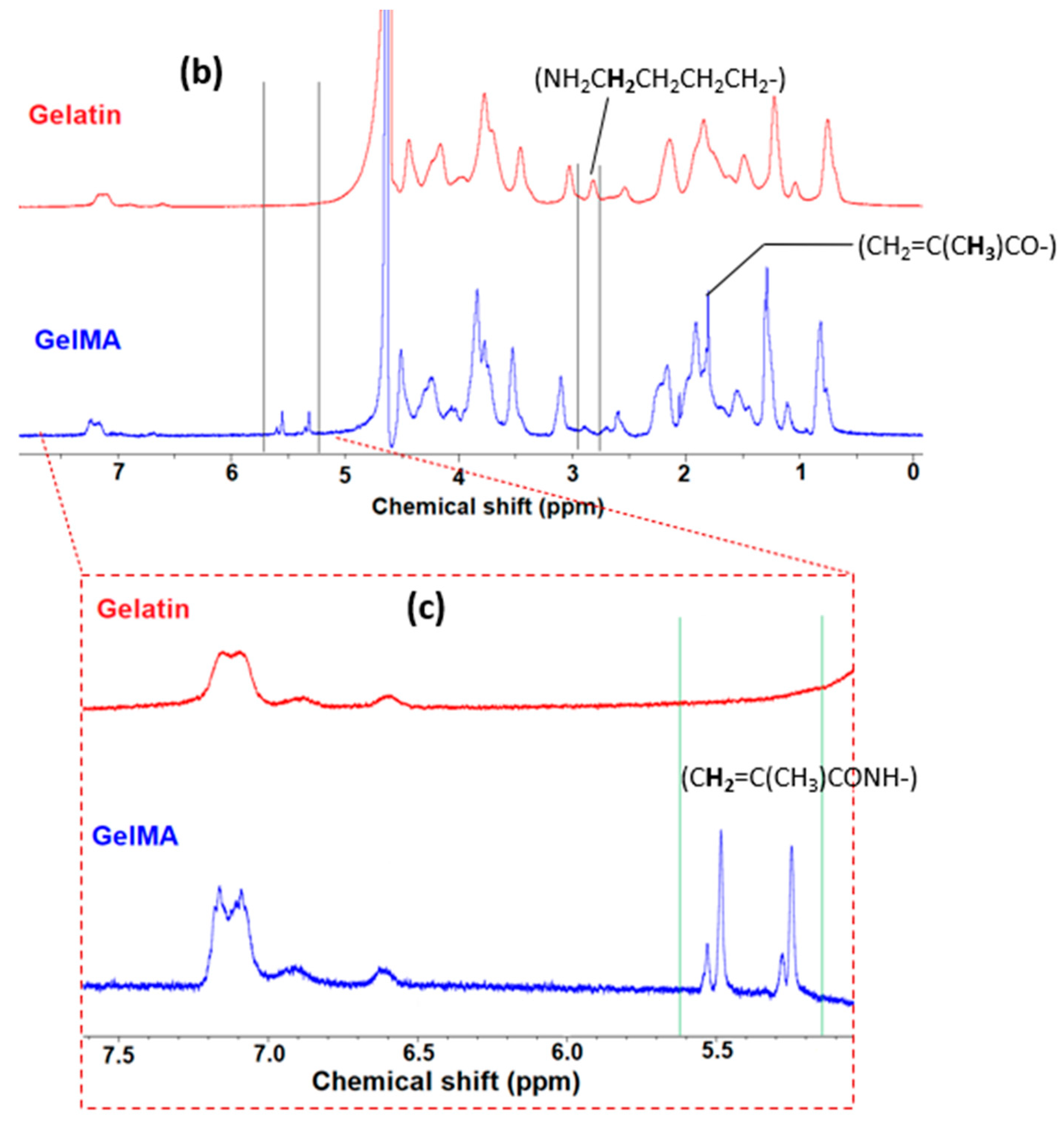
2.2. Preparation of Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA)
2.3. Preparation of Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels
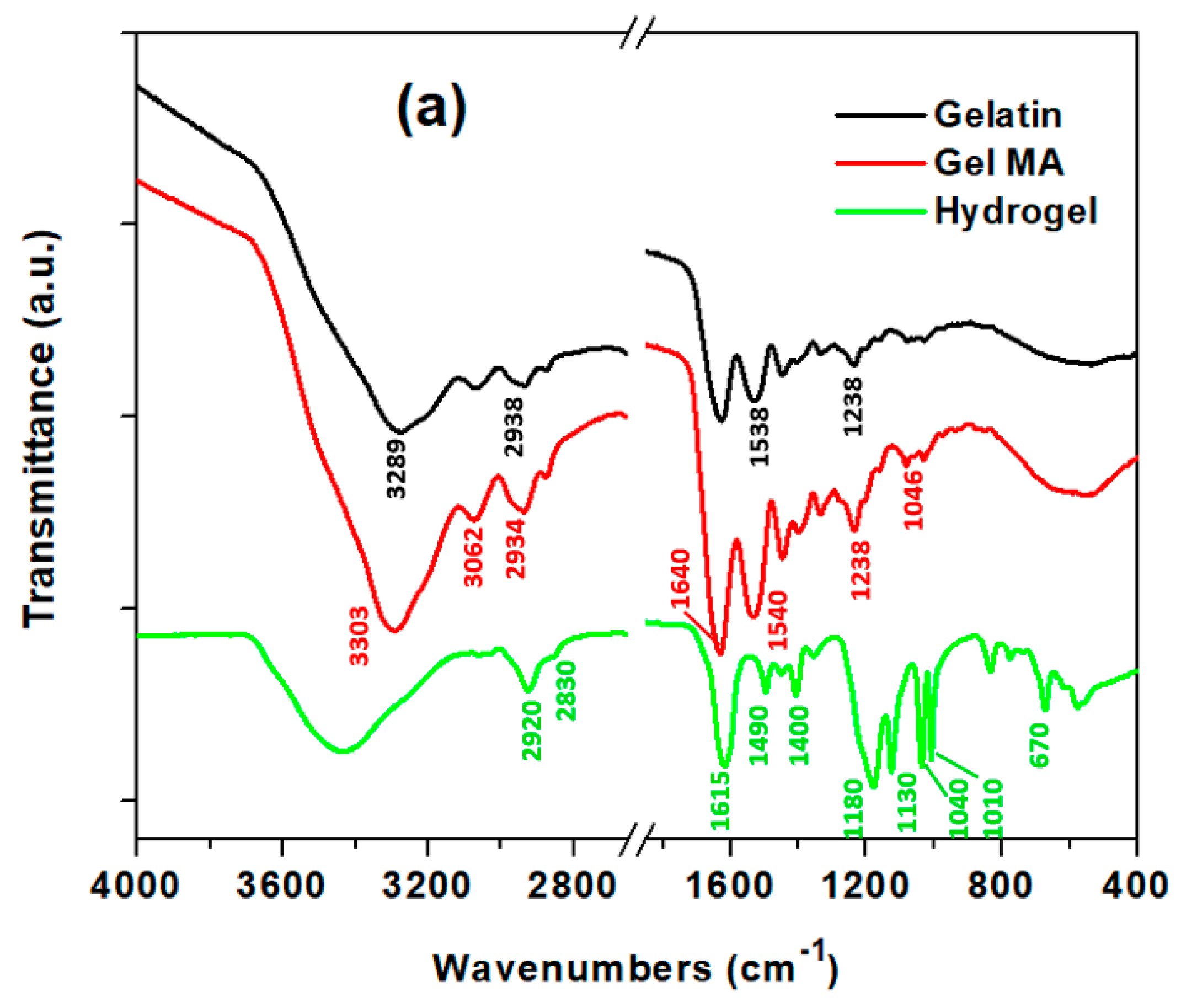
2.4. Physiochemical Characterization
2.5. Swelling Measurements
2.6. Dye Adsorption Studies
2.7. Reusability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Super-Adsorbent Hydrogel
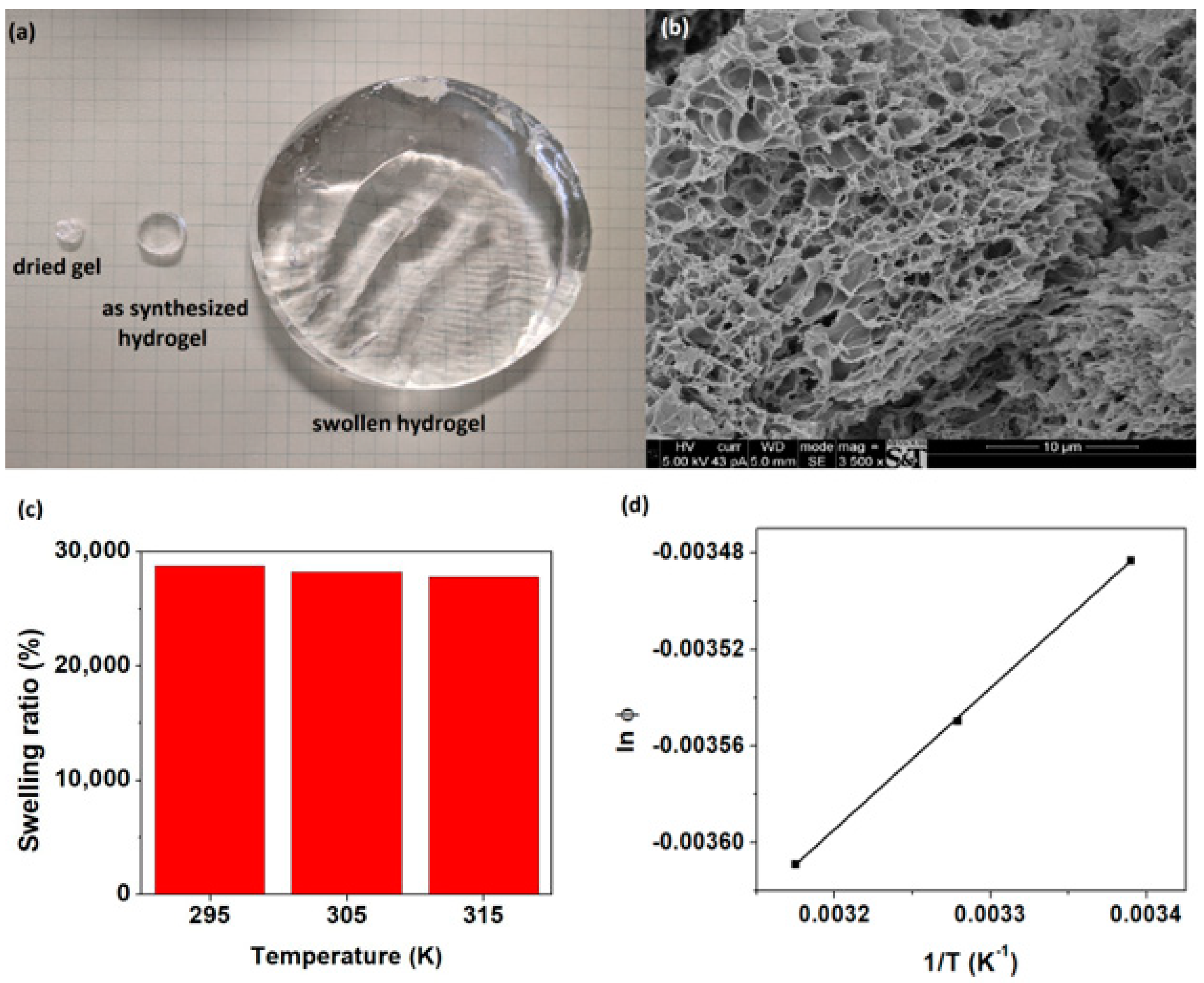
3.2. Swelling of Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels
3.3. MB Dye Adsorption Studies
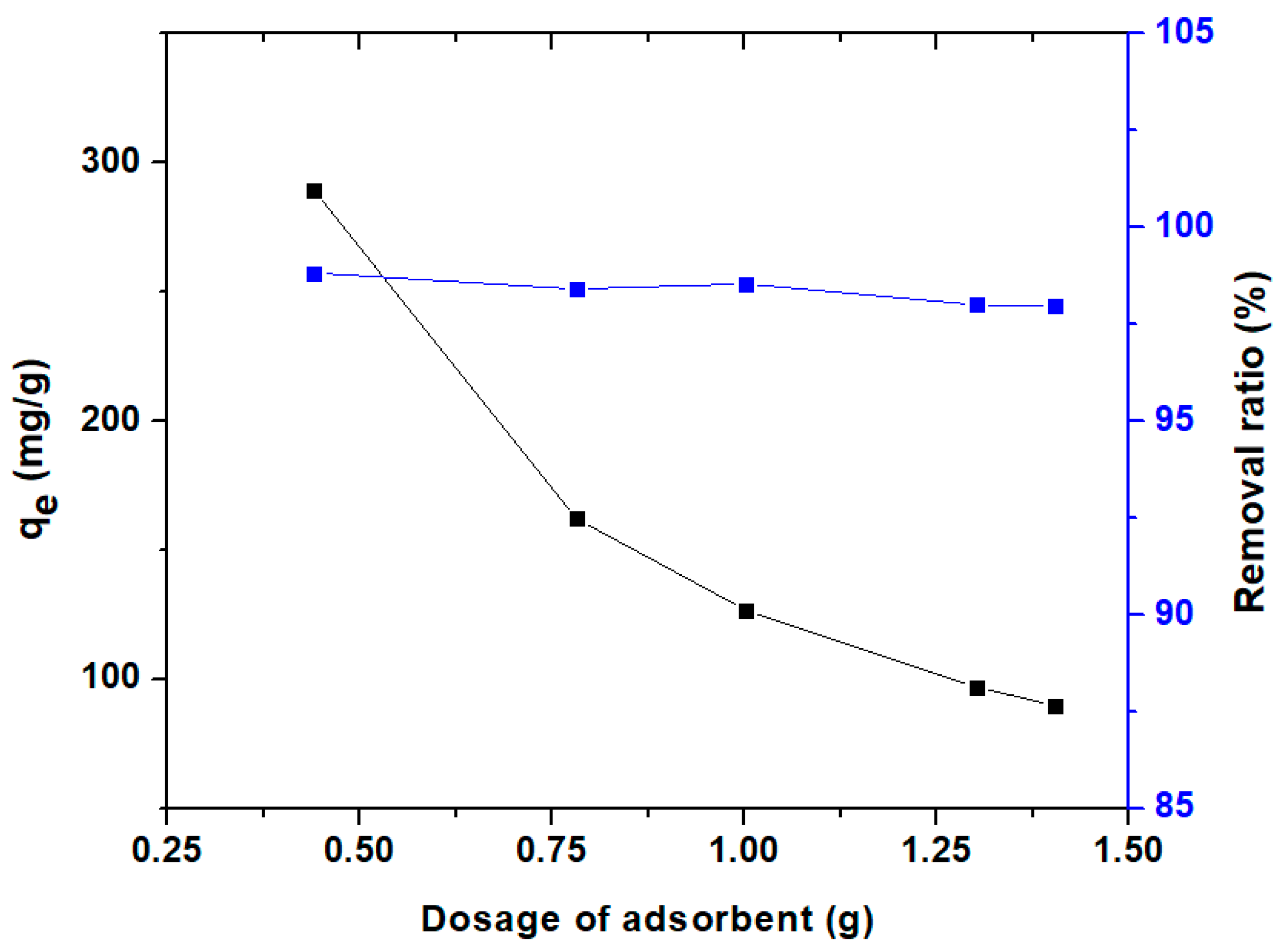
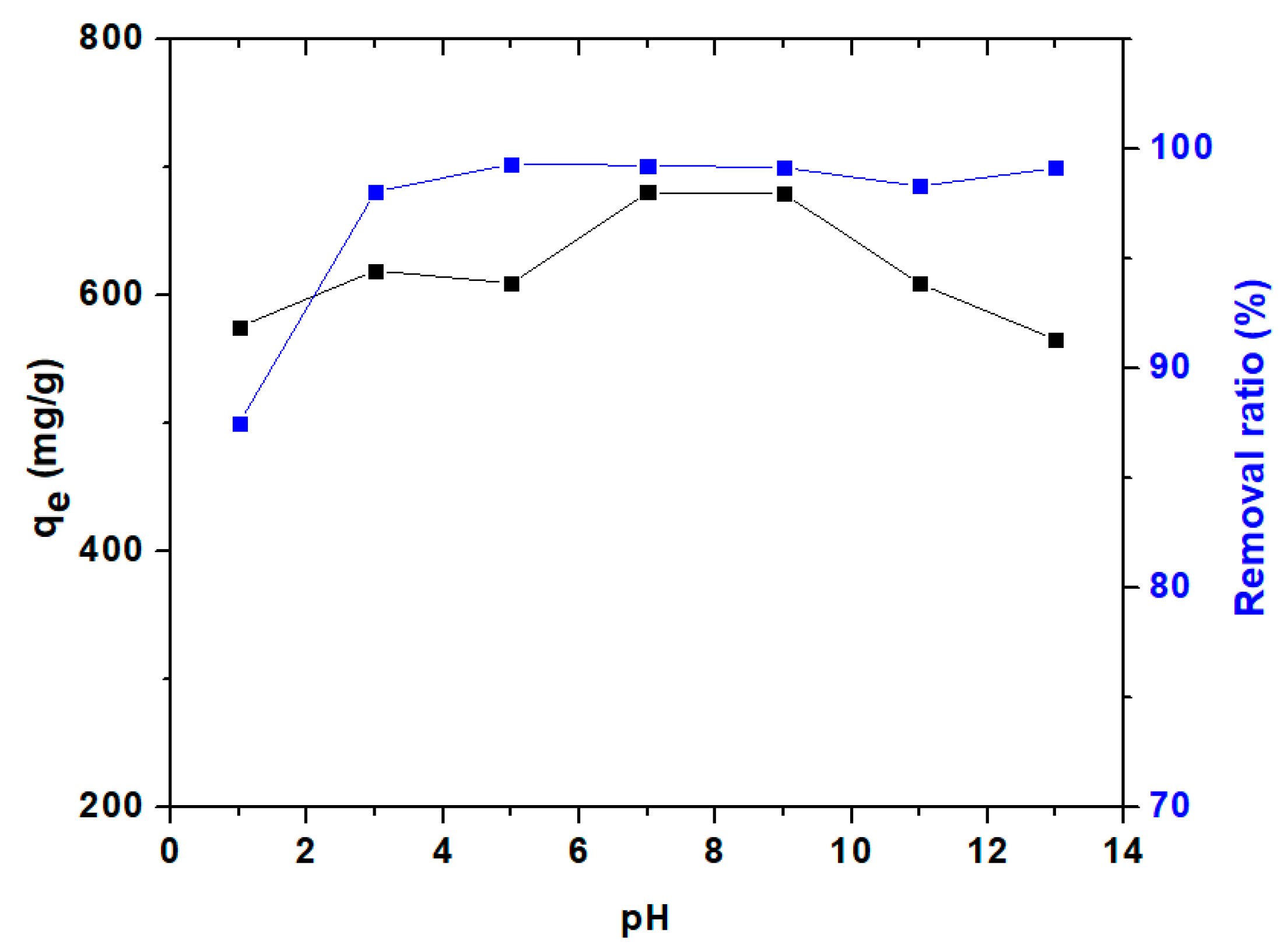
3.3.1. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage and pH
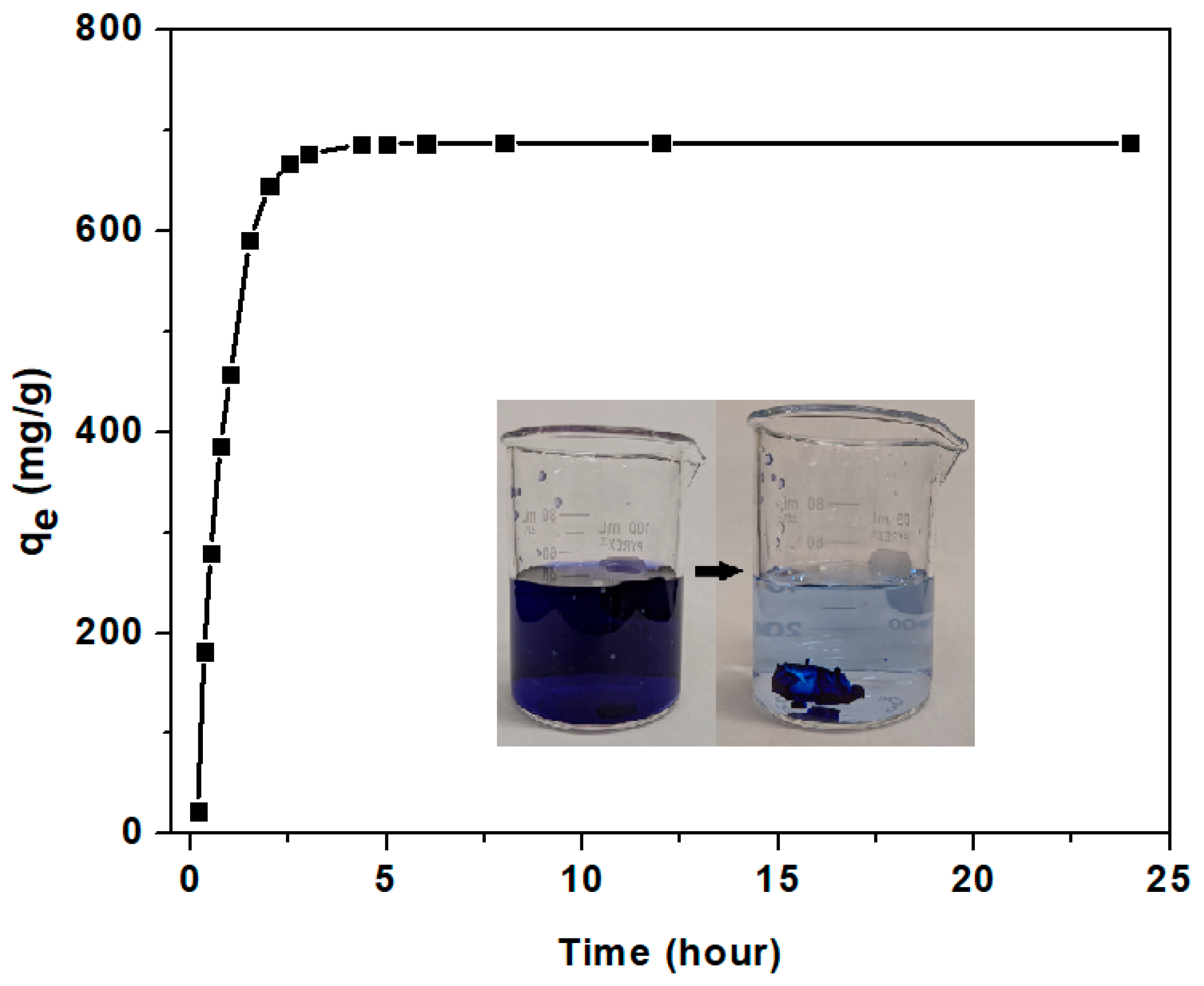
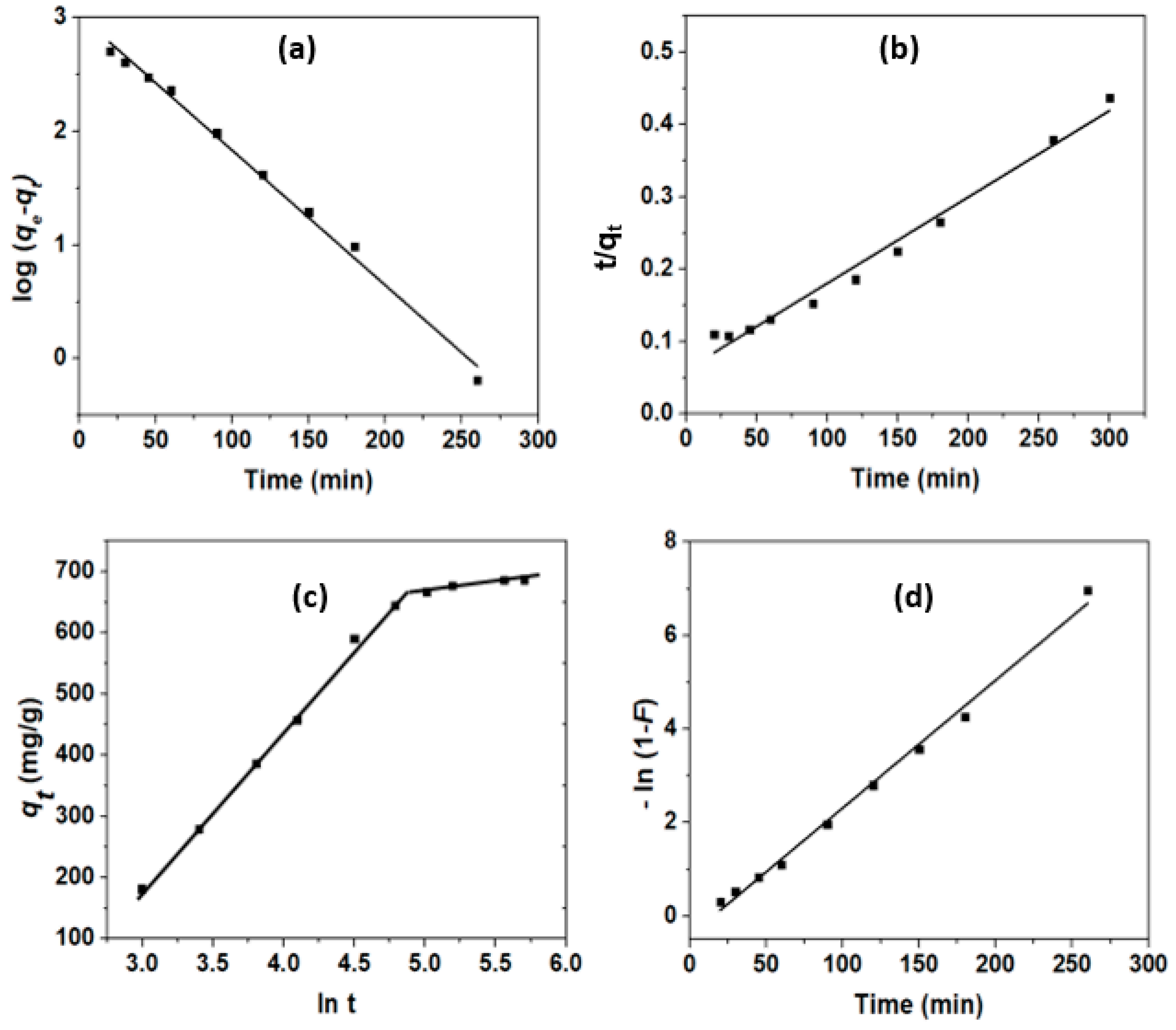
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
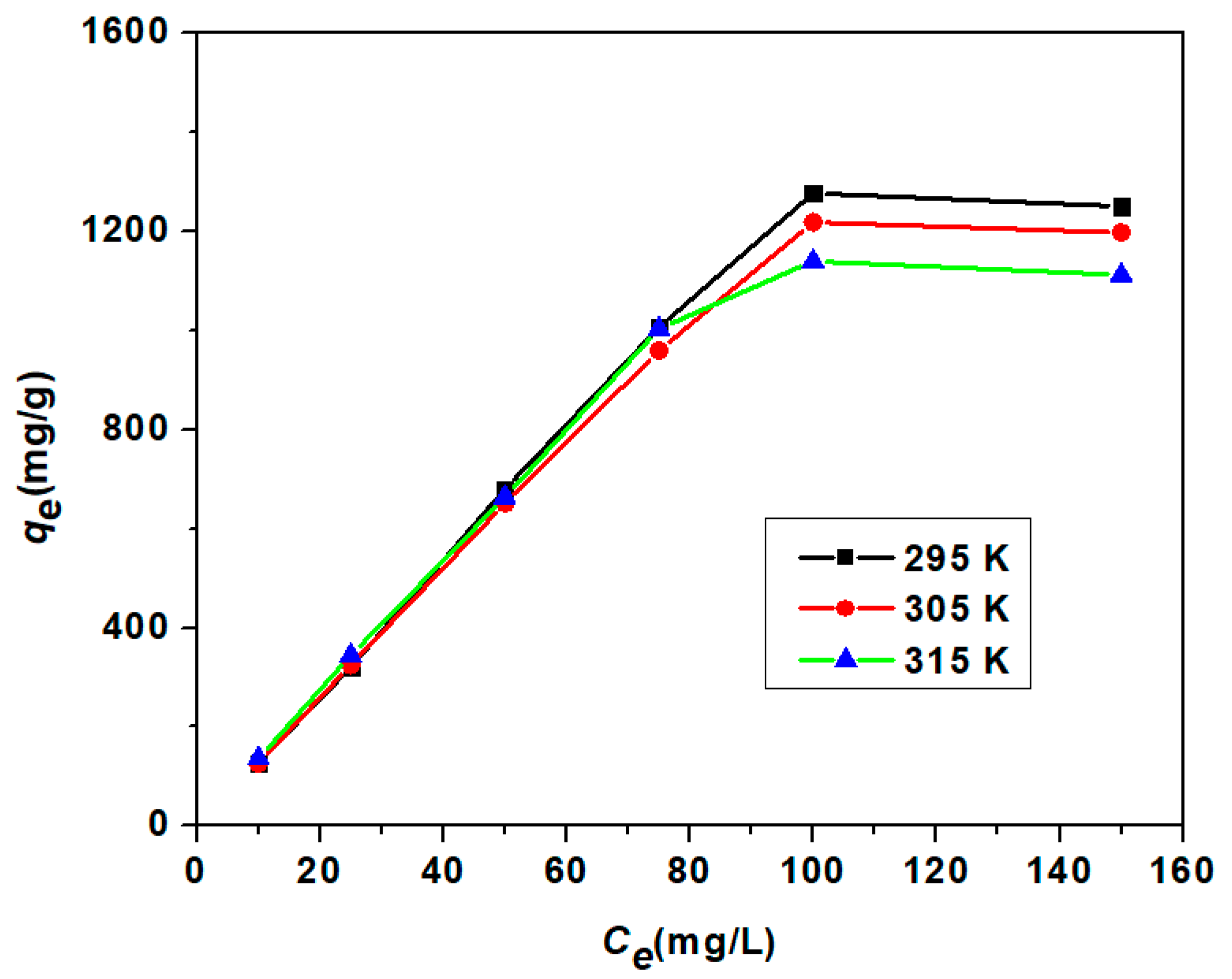
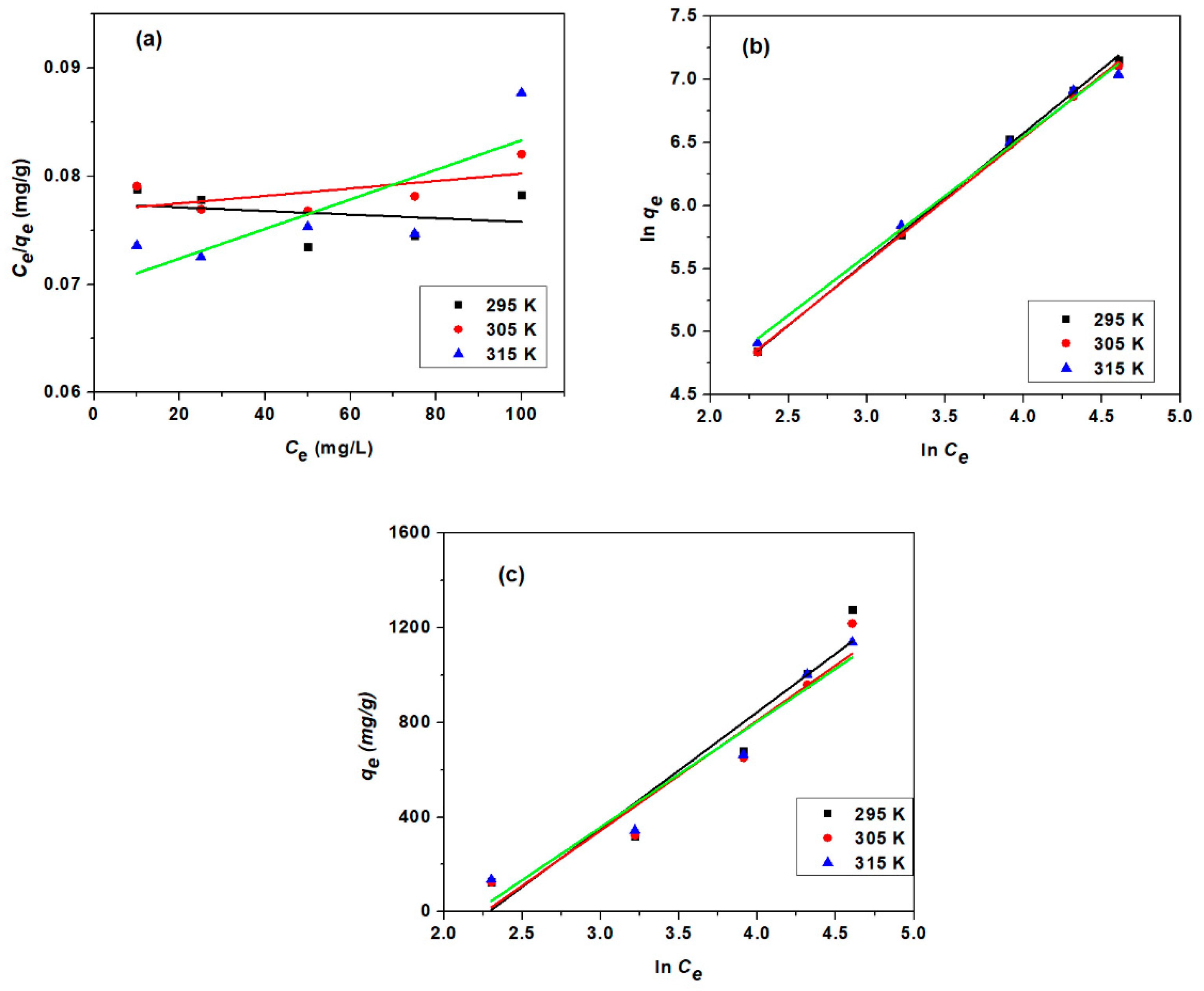
3.3.3. Adsorption Isotherm Study
3.3.4. Thermodynamics of the Adsorption Process
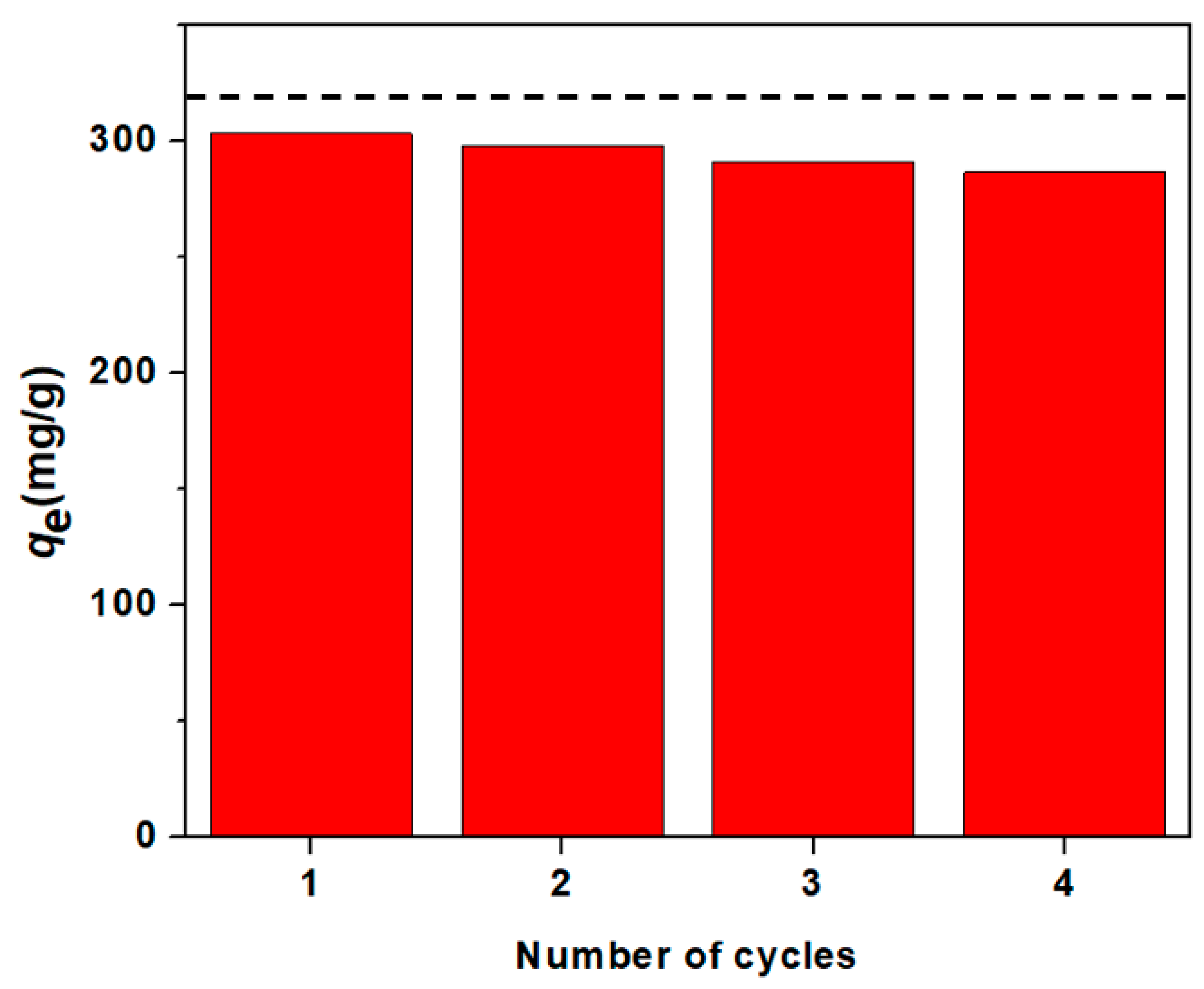
3.4. Recycalbility/Reusability of NaSS-DMA Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sokolowska-Gajda, J.; Freeman, H.S.; Reife, A. Synthetic dyes based on environmental considerations. Part 2: Iron complexes formazan dyes. Dye Pigment 1996, 30, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methneni, N.; Morales-González, J.A.; Jaziri, A.; Mansour, H.B.; Fernandez-Serrano, M. Persistent organic and inorganic pollutants in the effluents from the textile dyeing industries: Ecotoxicology appraisal via a battery of biotests. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşli, I.; Tünay, O.; Orhon, D. Wastewater control and management in a leather tanning district. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan Hanafi, M.; Sapawe, N. A review on the water problem associate with organic pollutants derived from phenol, methyl orange, and remazol brilliant blue dyes. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 31, A141–A150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohgard, M.; Ekholm, A.K. A method for the characterization of the aerosols emitted from handling of dye pigments in the paint manufacturing industry. J. Aerosol Sci. 1990, 21, S733–S736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Bhattacharya, S.N. 7—Automotive dyes and pigments. In Handbook of Textile and Industrial Dyeing; Clark, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 231–251. [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright, M. 6—Dyes for the medical industry. In Handbook of Textile and Industrial Dyeing; Clark, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 204–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hefford, R.J.W. 5—Colourants and dyes for the cosmetics industry. In Handbook of Textile and Industrial Dyeing; Clark, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 175–203. [Google Scholar]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V.; Chakma, S. Advances in the preparation of hydrogel for wastewater treatment: A concise review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Rakholiya, P.; Shindhal, T.; Shah, A.V.; Ngo, H.H. Trends in dye industry effluent treatment and recovery of value added products. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 39, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, D.; Agarwal, S.; Singh, P. Adsorptional photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue onto pectin–CuS nanocomposite under solar light. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 243, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, I.M.; Nigam, P.; Singh, D.; Marchant, R. Microbial decolorization of textile-dyecontaining effluents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 58, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhado, E.; Pandey, S.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Ramontja, J. Preparation and characterization of xanthan gum-cl-poly(acrylic acid)/o-MWCNTs hydrogel nanocomposite as highly effective re-usable adsorbent for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Villoslada, I.; González, R.; Hess, S.; Rivas, B.L.; Shibue, T.; Nishide, H. Complex Formation between Rhodamine B and Poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) Studied by 1H-NMR. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21576–21581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, J.R.; Guedes Maniero, M.; Nogueira de Araújo, R. A comparative study on the degradation of RB-19 dye in an aqueous medium by advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, J.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, P.; Song, B.; Cao, W.; Liu, H.; Huan, S. Enhanced degradation performance of organic dyes removal by bismuth vanadate-reduced graphene oxide composites under visible light radiation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 559, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalla, A.H.; Bhat, M.A.; Yaseen, Z. Hydrogels for removal of recalcitrant organic dyes: A conceptual overview. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5938–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.B.; Rodrigues, F.H.A.; Paulino, A.T.; Martins, A.F.; Fajardo, A.R. Recent advances on composite hydrogels designed for the remediation of dye-contaminated water and wastewater: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labanda, J.; Sabaté, J.; Llorens, J. Modeling of the dynamic adsorption of an anionic dye through ion-exchange membrane adsorber. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Wang, A. Adsorption of dyes onto palygorskite and its composites: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1274–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muya, F.N.; Sunday, C.E.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E. Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution through hydrogel adsorption: A critical review. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Zhou, F.; Li, L.; Cao, M.; Zuo, D.; Liu, H. Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption of chitosan-based semi-IPN hydrogel composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-S.; Liang, R.; Sun, G. Super-adsorbent hydrogel for removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17612–17624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.Q.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Ardiyanta, D.; Shimoyama, Y. CO2-Activated Adsorption: A New Approach to Dye Removal by Chitosan Hydrogel. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 14103–14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, C.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.-W. COD reduction and decolorization of textile effluent using a combined process. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 95, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, Y.H.; Aly, R.O.; Abdel-Aal, S.E. Synthesis and characterization of Na-alginate/acrylamide hydrogel and its application in dye removal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Yang, R.; Qu, L.; Li, Z. Poly(sodium styrene sulfonate) functionalized graphene as a highly efficient adsorbent for cationic dye removal with a green regeneration strategy. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 152, 109973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Rashidimoghadam, S. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Vitamin C-multi walled carbon nanotubes composites and their applications for removal of methylene blue: Advanced comparison between linear and nonlinear forms of adsorption isotherms and kinetics models. Polymer 2019, 160, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Behranvand, V.; Mallakpour, F. Adsorptive performance of alginate/carbon nanotube-carbon dot-magnesium fluorohydroxyapatite hydrogel for methylene blue-contaminated water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Ghorai, S.; Rana, D.; Roy, I.; Sarkar, G.; Saha, N.R.; Orasugh, J.T.; De, S.; Sadhukhan, S.; Chattopadhyay, D. Design of an efficient and selective adsorbent of cationic dye through activated carbon—Graphene oxide nanocomposite: Study on mechanism and synergy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 260, 124090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Hu, D.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Chang, C. Superabsorbent Cellulose–Clay Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Highly Efficient Removal of Dye in Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 7217–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Ullah, A. Chapter 14—Biopolymers in environmental applications: Industrial wastewater treatment. In Biopolymers and Their Industrial Applications; Thomas, S., Gopi, S., Amalraj, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 331–349. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadzadeh Pakdel, P.; Peighambardoust, S.J. A review on acrylic based hydrogels and their applications in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ferng, L.; Wei, Y.; Yang, C.; Ji, H.-F. Effects of acidity on the size of polyaniline-poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) composite particles and the stability of corresponding colloids in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 381, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, K.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Mirzadeh, H.; Kheirabadi, M. Solvent-, ion- and pH-specific swelling of poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid) superabsorbing gels. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 17, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriano, B.H.; Banik, S.J.; Sharma, R.; Rumore, D.; Hwang, W.; Briber, R.M.; Raghavan, S.R. Superabsorbent Hydrogels That Are Robust and Highly Stretchable. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 4445–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Dong, C.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Men, J. Preparation of sulfonate chitosan microspheres and study on its adsorption properties for methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2334–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhado, E.; Pandey, S.; Ramontja, J. Microwave assisted synthesis of xanthan gum-cl-poly (acrylic acid) based-reduced graphene oxide hydrogel composite for adsorption of methylene blue and methyl violet from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Ferracci, G.; Zheng, J.; Cho, N.-J.; Lee, B.H. Gelatin methacryloyl and its hydrogels with an exceptional degree of controllability and batch-to-batch consistency. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salunkhe, B.; Schuman, T.; Al Brahim, A.; Bai, B. Ultra-high temperature resistant preformed particle gels for enhanced oil recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekiari, V.; Sotiropoulou, M.; Bokias, G.; Lianos, P. Use of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) hydrogel to extract cationic dyes and metals from water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 312, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Vera, M.; Rivas, B.L.; Sánchez, S.; Urbano, B.F. Magnetic methacrylated gelatin-g-polyelectrolyte for methylene blue sorption. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 43799–43810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, K.; Kumar, P.; van Vuuren, S.F.; Pillay, V.; Choonara, Y.E. Three-Dimensional Printability of an ECM-Based Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Biomaterial for Potential Neuroregeneration. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21368–21383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, D.F.S.; Costa, P.C.; Almeida, I.F.; Dias-Pereira, P.; Correia-Sá, I.; Bastos, V.; Oliveira, H.; Vilela, C.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R. Swellable Gelatin Methacryloyl Microneedles for Extraction of Interstitial Skin Fluid toward Minimally Invasive Monitoring of Urea. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 2000195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirahama, H.; Lee, B.H.; Tan, L.P.; Cho, N.-J. Precise Tuning of Facile One-Pot Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.C.; Jablonsky, M.J.; Mays, J.W. NMR and FT-IR studies of sulfonated styrene-based homopolymers and copolymers. Polymer 2002, 43, 5125–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaslan, D.; Dudu, T.E.; Şahiner, N.; Aktas, N. Synthesis and preparation of responsive poly(Dimethyl acrylamide/gelatin and pomegranate extract) as a novel food packaging material. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdravković, A.; Nikolić, L.; Ilić-Stojanović, S.; Nikolić, V.; Najman, S.; Mitić, Ž.; Ćirić, A.; Petrović, S. The removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by hydrogels based on N-isopropylacrylamide and acrylic acid. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 4797–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubinstein, M.; Colby, R.H.; Dobrynin, A.V.; Joanny, J.-F. Elastic Modulus and Equilibrium Swelling of Polyelectrolyte Gels. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, T.; Dohi, S.; Tachi, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kojima, C.; Matsumoto, A. One-Shot Preparation of Polyacrylamide/Poly(sodium styrenesulfonate) Double-Network Hydrogels for Rapid Optical Tissue Clearing. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21083–21090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brannon-Peppas, L.; Peppas, N.A. Equilibrium swelling behavior of pH-sensitive hydrogels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjiri, M.T.; Marandi, G.B.; Kurdtabar, M. Poly(AA-co-VPA) hydrogel cross-linked with N-maleyl chitosan as dye adsorbent: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic investigation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, G.R.; Mosallanezhad, A. Facile and green rout to prepare magnetic and chitosan-crosslinked κ-carrageenan bionanocomposites for removal of methylene blue. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 10, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapwanit, S.; Sooksimuang, T.; Trakulsujaritchok, T. Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue dye by kappa-carrageenan/poly(glycidyl methacrylate) hydrogel beads: Preparation and characterization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6221–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Lu, T.; Zhao, W.-F.; Zhao, C.-S. Ionic-Strength Responsive Zwitterionic Copolymer Hydrogels with Tunable Swelling and Adsorption Behaviors. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safronov, A.P.; Smirnova, Y.A.; Pollack, G.H.; Blyakhman, F.A. Enthalpy of Swelling of Potassium Polyacrylate and Polymethacrylate Hydrogels. Evaluation of Excluded-Volume Interaction. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.R.; Datta, S.; Gui, M.; Coker, E.L.; Huggins, F.E.; Daunert, S.; Bachas, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Reactive nanostructured membranes for water purification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dąbrowski, A. Adsorption—From theory to practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 93, 135–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, B.; Sorial, G.A. Applicable models for multi-component adsorption of dyes: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, B.C.; Paulino, F.A.A.; Cardoso, V.A.; Pereira, A.G.B.; Fajardo, A.R.; Rodrigues, F.H.A. Cellulose nanowhiskers improve the methylene blue adsorption capacity of chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Torres, C.; González, F.; Shibue, T.; Nishide, H. Binding of Methylene Blue to Polyelectrolytes Containing Sulfonate Groups. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Jofré, M.; Miranda, V.; Chandía, P.; González, R.; Hess, S.; Rivas, B.L.; Elvira, C.; San Román, J.; Shibue, T.; et al. π-Stacking of rhodamine B onto water-soluble polymers containing aromatic groups. Polymer 2006, 47, 6496–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopičić, Z.R.; Stojanović, M.D.; Marković, S.B.; Milojković, J.V.; Mihajlović, M.L.; Kaluđerović Radoičić, T.S.; Kijevčanin, M.L.J. Effects of different mechanical treatments on structural changes of lignocellulosic waste biomass and subsequent Cu(II) removal kinetics. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4091–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonin, J.-P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajjumba, G.W.; Emik, S.; Öngen, A.; Özcan, H.K.; Aydın, S. Modelling of Adsorption Kinetic Processes—Errors, Theory and Application. In Modelling of Adsorption Kinetic Processes—Errors, Theory and Application, Advanced Sorption Process Applications; Edebali, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- León, G.; Saura, F.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Miguel, B. Activated Olive Stones as a Low-Cost and Environmentally Friendly Adsorbent for Removing Cephalosporin C from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Townsend, T.G.; Mazyck, D.; Boyer, T.H. Equilibrium and intra-particle diffusion of stabilized landfill leachate onto micro- and meso-porous activated carbon. Water Res. 2012, 46, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, G.E.; Adamson, A.W.; Myers, L.S. The Exchange Adsorption of Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Organic Zeolites. II. Kinetics1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, F.; Tassinari, F.; Libertini, E.; Lanzi, M.; Mucci, A. Π-Stacking Signature in NMR Solution Spectra of Thiophene-Based Conjugated Polymers. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5775–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Grainger, D.W. Thermo-sensitive swelling behavior in crosslinked N-isopropylacrylamide networks: Cationic, anionic, and ampholytic hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 49, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, Q.; Gao, T.; Dong, K.; Wei, G.; Yao, J. Facile Preparation of Tannic Acid–Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Beads for Methylene Blue Removal from Simulated Solution. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7523–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H. Eco-friendly polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels reinforced with graphene oxide and bentonite for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, X. Amine functionalized sodium alginate hydrogel for efficient and rapid removal of methyl blue in water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayaphan, J.; Maijan, P.; Boonsuk, P.; Chantarak, S. Synthesis of photodegradable cassava starch-based double network hydrogel with high mechanical stability for effective removal of methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Cai, K.; Chen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B. pH-responsive poly(gellan gum-co-acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel: Synthesis, and its application for organic dye removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, H.; Maity, A.; Ray, S.S. Effective removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using gum ghatti-based biodegradable hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Al-Absi, R.S. Mechanistic understanding of the adsorption and thermodynamic aspects of cationic methylene blue dye onto cellulosic olive stones biomass from wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajeh, M.; Dastafkan, K.; Bohlooli, M.; Ghaffari-Moghaddam, M. CHAPTER 10 Sample Preparation and Extraction Techniques Using Nanomaterials. In Advanced Environmental Analysis: Applications of Nanomaterials; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 221–283. [Google Scholar]
| Pseudo-First-Order Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 (mg/L) | qe (mg/g) | k1 (/min) | R2 |
| 50 | 1048.14 | 0.0273 | 0.9933 |
| Pseudo-second-order model | |||
| C0 (mg/L) | qe (mg/g) | k2 × 10−5 (/min) | R2 |
| 50 | 833.33 | 2.3598 | 0.9813 |
| Elovich model | |||
| C0 (mg/L) | α (mg/g/min) | β (g/mg) | R2 |
| 50 | 31.0951 | 0.005 | 0.9323 |
| Liquid film diffusion model | |||
| C0 (mg/L) | kfd (/min) | R2 | |
| 50 | 0.02733 | 0.9933 | |
| Adsorbent Chemical Signature | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Poly (AA-co-VPA) hydrogel cross-linked with N-maleyl chitosan | 66.89 | [54] |
| Chitosan-crosslinked κ-carrageenan bionanocomposites | 130.4 | [55] |
| Tannic Acid–Poly (vinyl alcohol)/Sodium Alginate | 147.06 | [73] |
| PVA/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel | 165.73 | [74] |
| κ-Carrageenan/poly (glycidyl methacrylate) hydrogel | 166.62 | [56] |
| Amine functionalized sodium alginate hydrogel | 400 | [75] |
| Poly (acrylic acid) (PAA), cassava starch (CS) and poly (vinyl alcohol) | 417 | [76] |
| Poly (gellan gum-co-acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel | 423.46 ± 13.60 | [77] |
| Gg-cl-P(AAm-co-MAA) hydrogel polymer | 694.44 | [78] |
| Cellulose/MMT | 782.9 | [33] |
| Xanthan gum-cl-poly (acrylic acid) based-reduced GO hydrogel | 793.65 | [40] |
| Sulfonate chitosan microspheres | 820.1 | [39] |
| Poly (sodium styrenesulfonate-co-dimethylacrylamide) crosslinked with gelatin methacryloyl | 1270 | [This work] |
| Poly (sodium styrene sulfonate) functionalized graphene (PSS-rGO) | 1300 | [29] |
| Model | Parameter | Unit | 295 K | 305 K | 315 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir Isotherm | qm | mg/g | 3861 | 3344.48 | 2439.02 |
| KL | L/mg | 0.00392 | 0.00454 | 0.00702 | |
| R2 | 0.5617 | 0.6528 | 0.7572 | ||
| Freundlich Isotherm | n | 0.9843 | 1.0095 | 1.0572 | |
| KF | L/mg | 12.317 | 13.1713 | 15.9272 | |
| R2 | 0.9988 | 0.9989 | 0.994 | ||
| Temkin Isotherm | β | J/mol | 4.9755 | 5.2674 | 5.4859 |
| KT | L/mg | 0.1016 | 0.1041 | 0.1107 | |
| R2 | 0.902 | 0.9063 | 0.9295 |
| Thermodynamic Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/mol/K) | ||
| 295 K | 305 K | 315 K | ||
| −37.2 | −38.6 | −40.4 | 0.14 | 2.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salunkhe, B.; Schuman, T.P. Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: Dye Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Properties. Macromol 2021, 1, 256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1040018
Salunkhe B, Schuman TP. Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: Dye Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Properties. Macromol. 2021; 1(4):256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1040018
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalunkhe, Buddhabhushan, and Thomas P. Schuman. 2021. "Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: Dye Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Properties" Macromol 1, no. 4: 256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1040018
APA StyleSalunkhe, B., & Schuman, T. P. (2021). Super-Adsorbent Hydrogels for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution: Dye Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Properties. Macromol, 1(4), 256-275. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1040018







