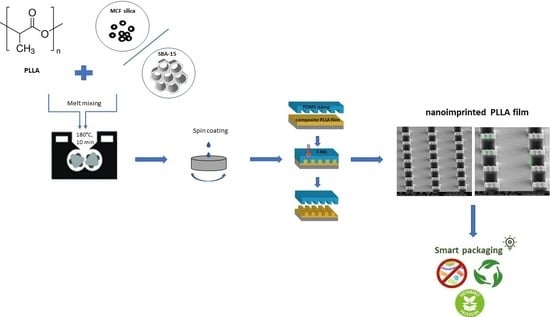
Bottom-Up Development of Nanoimprinted PLLA Composite Films with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for Smart Packaging Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MCF and SBA-15 Silica
2.3. Nanocomposite Preparation
2.4. Preparation of Films by Spin-Coating
2.5. Patterning of PLLA Nanocomposite Films by NIL
2.6. Nanoparticle Characterization Methods
2.6.1. Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.6.2. N2 Porosimetry
2.6.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.7. Characterization of the Prepared Films
2.7.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7.4. Nanoindentation
2.7.5. Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
3.1.1. FT-IR
3.1.2. Porosity
3.1.3. TGA Analysis
3.2. Characterization of the Imprinted Nanocomposite Films
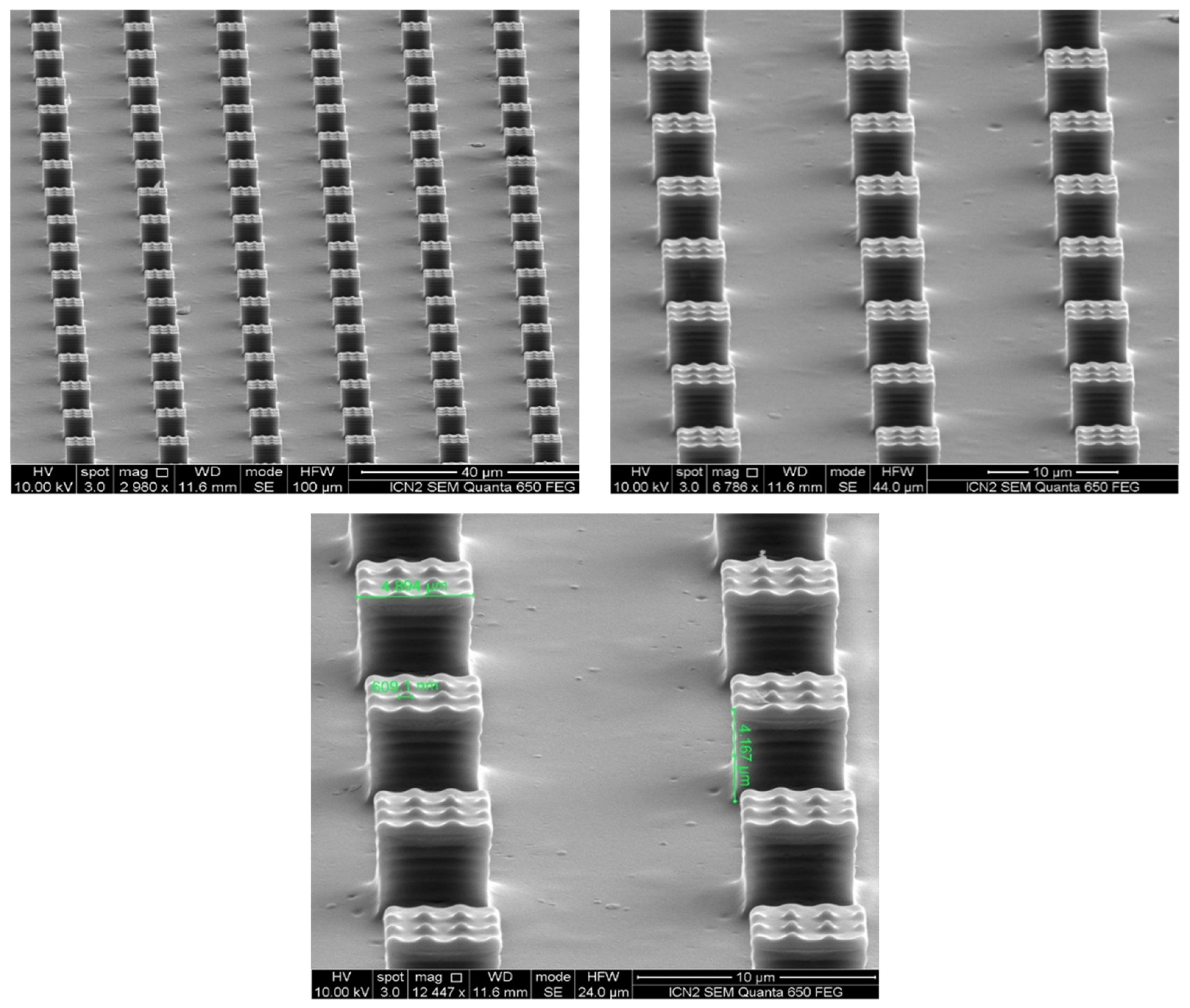
3.2.1. Morphological Study of Micro- and Nanosized Topographies
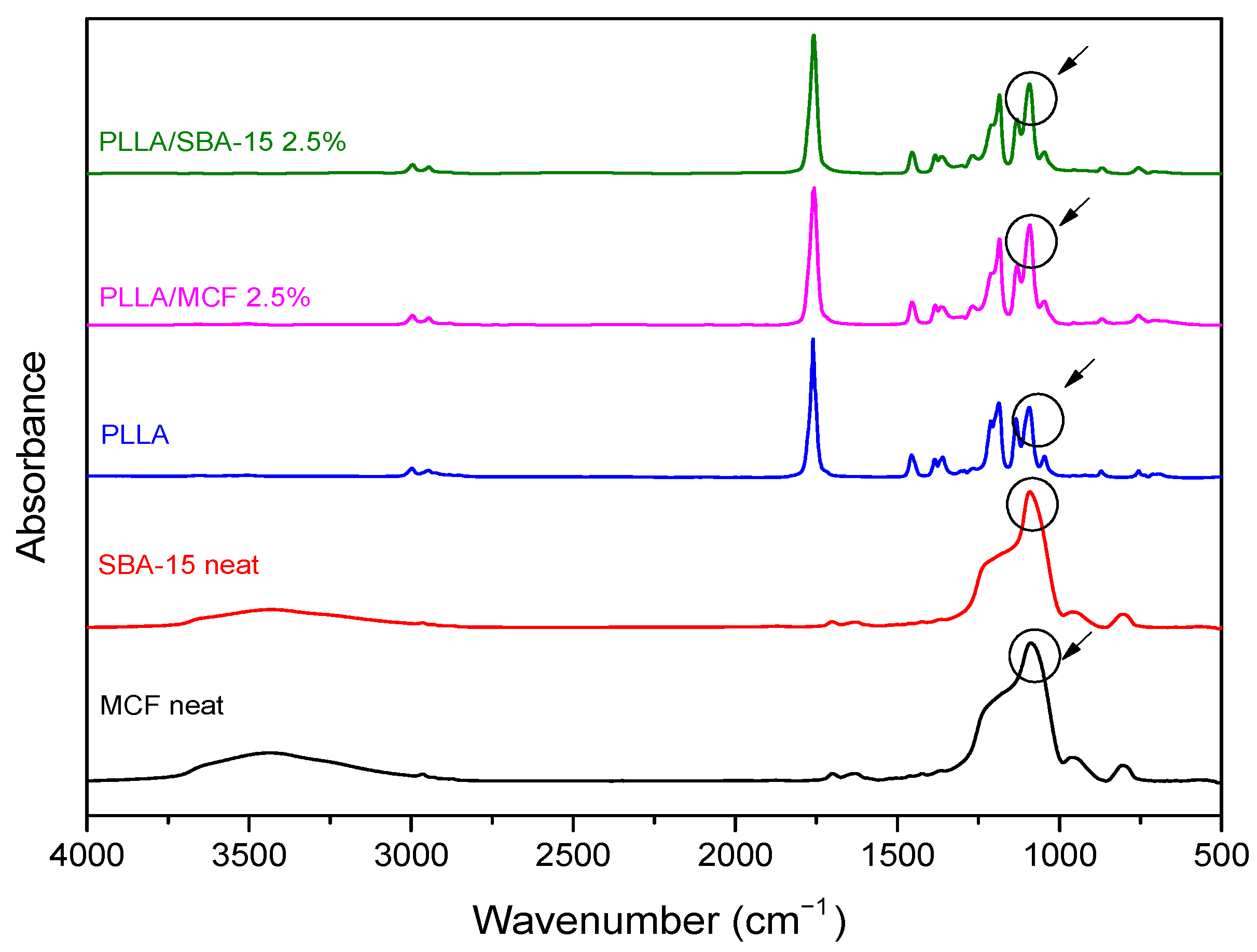
3.2.2. Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
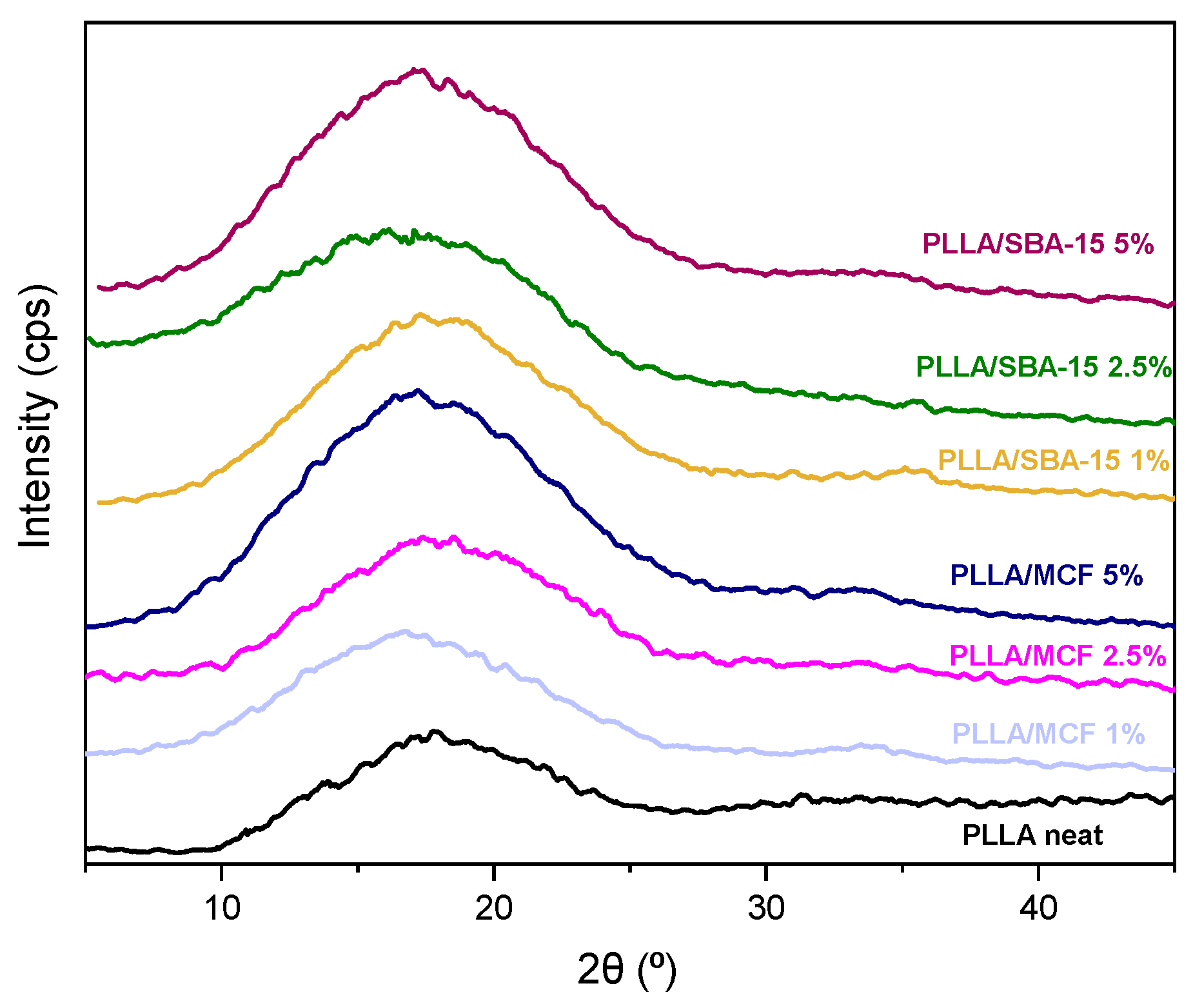
3.2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
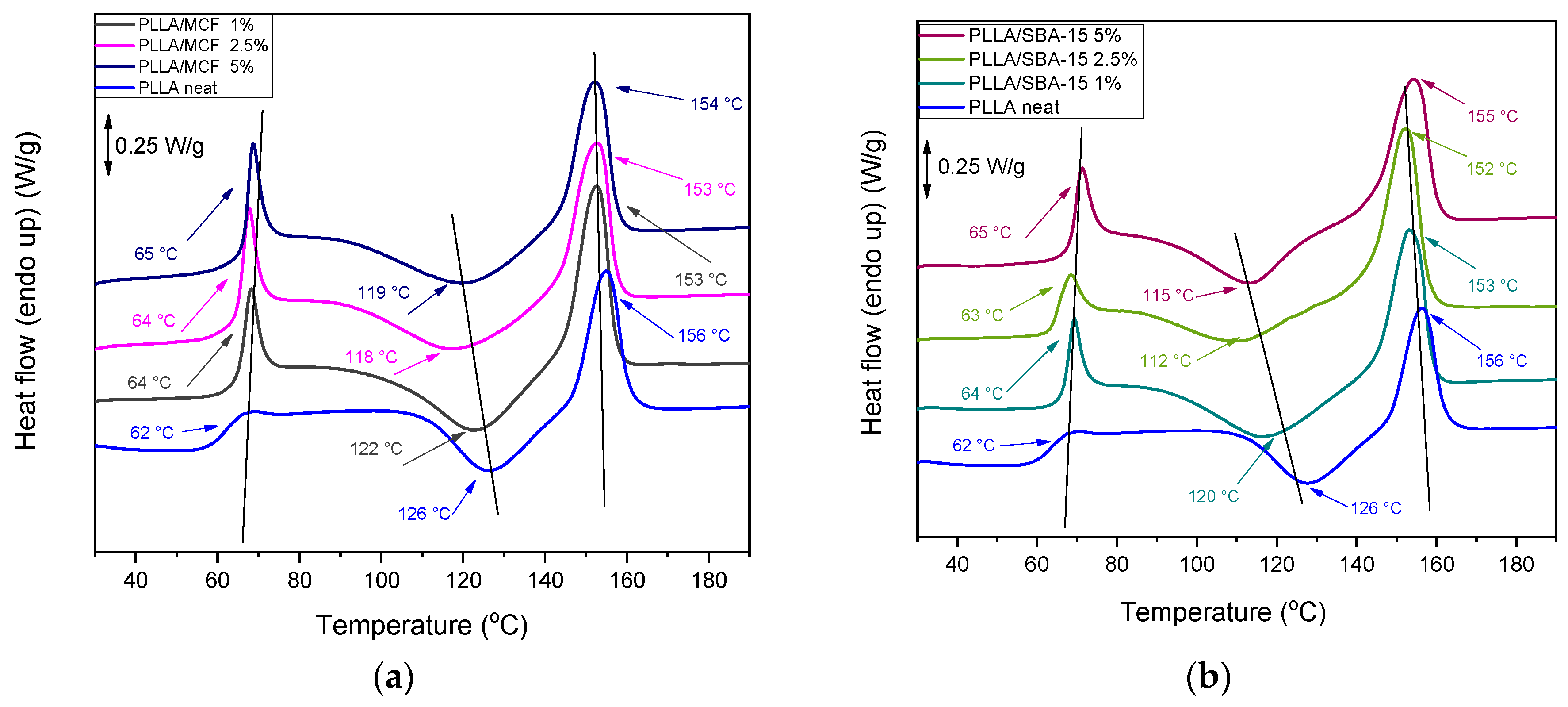
3.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
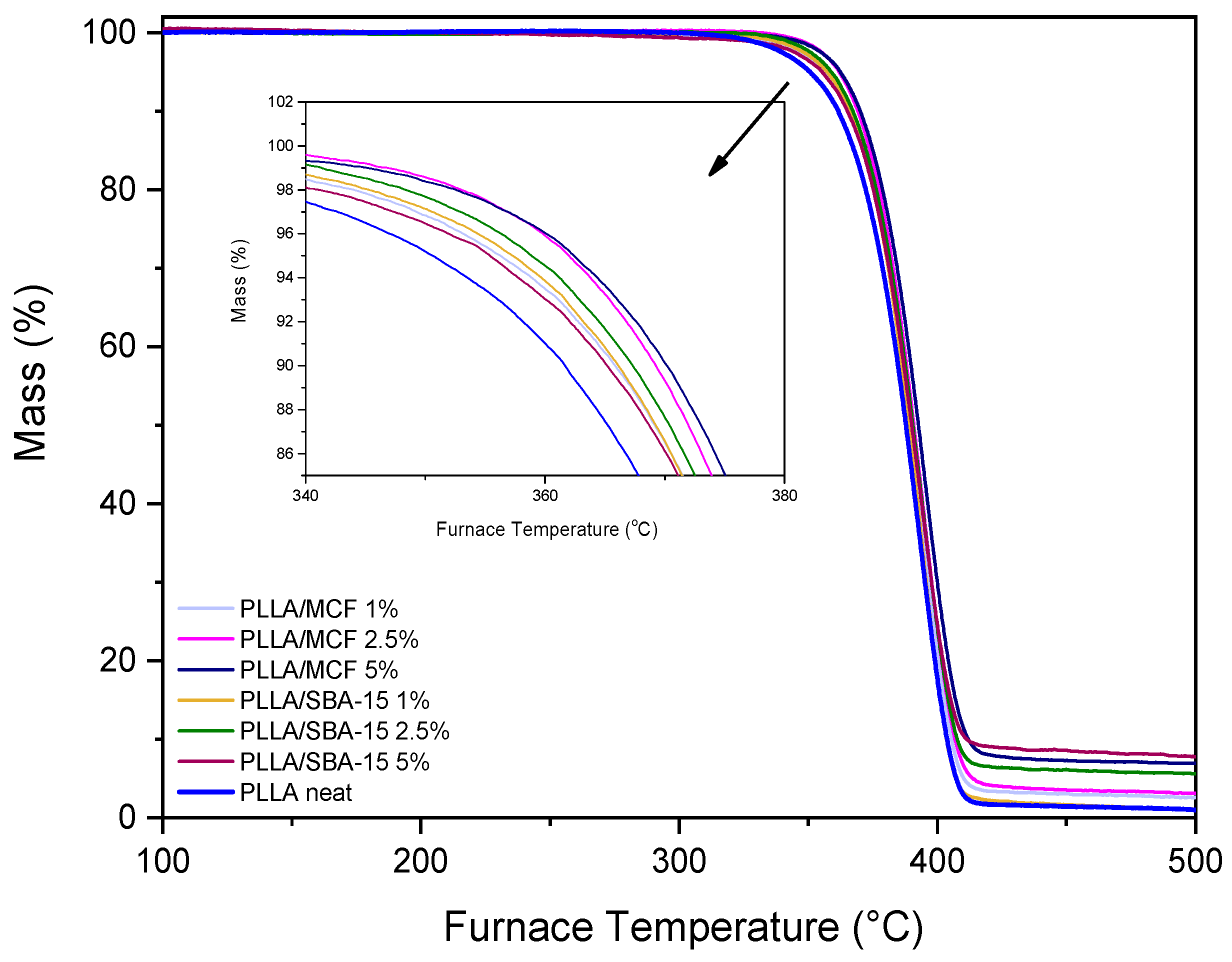
3.2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.2.6. Nanoindentation Tests
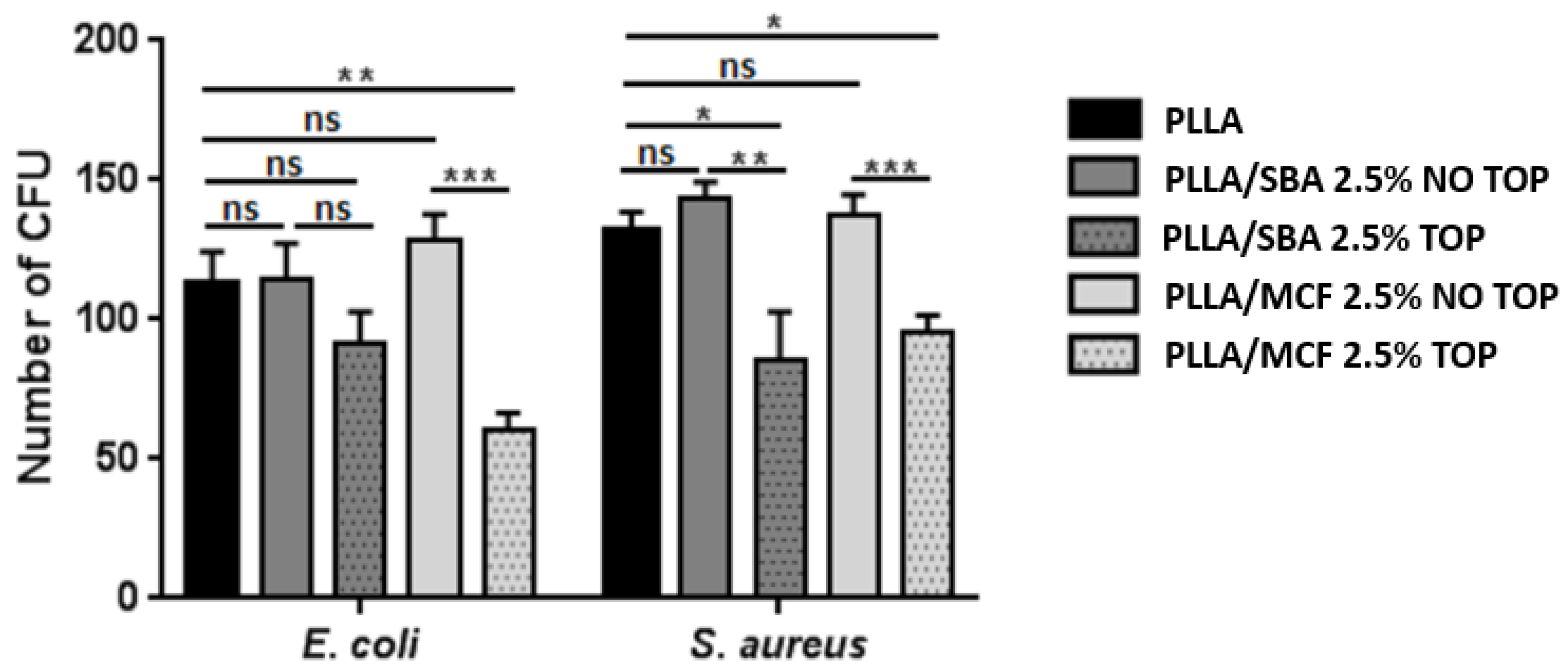
3.2.7. Antibacterial Activity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamshidian, M.; Tehrany, E.A.; Imran, M.; Jacquot, M.; Desobry, S. Poly-Lactic Acid: Production, applications, nanocomposites, and release studies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 552–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rubio, A.; Gavara, R.; Lagaron, J.M. Bioactive packaging: Turning foods into healthier foods through biomaterials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Biodegradable and Compostable Shopping Bags under Investigation by FTIR Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Lin, H.; Zou, L.; Brody, A.L.; Li, Z.; Qazi, I.M.; Pavase, T.R.; Lv, L. A comprehensive review on the application of active packaging technologies to muscle foods. Food Control 2017, 82, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Zuccari, G. Nanotechnology application in food packaging: A plethora of opportunities versus pending risks assessment and public concerns. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Bikiaris, D.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Diamanti, E.; Gournis, D.; Klonos, P.; Giannoulidis, E.; Pissis, P. Evaluation of the formed interface in biodegradable poly(l-lactic acid)/graphene oxide nanocomposites and the effect of nanofillers on mechanical and thermal properties. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 597, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, P.; O’Brien, M. Polylactides “NatureWorks® PLA”. Biopolym. Online 2002, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.P.; Kumar, V. New emerging trends in synthetic biodegradable polymers—Polylactide: A critique. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4053–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.L.S. An Overview of the Synthesis and Synthetic Mechanism of Poly(Lactic acid). Mod. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasprilla, A.J.R.; Martinez, G.A.R.; Lunelli, B.H.; Jardini, A.L.; Filho, R.M. Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices—A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, M.; Schwarch, G.; Coudane, J. Present and Future of PLA Polymers. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 1995, 32, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataman-Önal, Y.; Munier, S.; Ganée, A.; Terrat, C.; Durand, P.Y.; Battail, N.; Martinon, F.; Le Grand, R.; Charles, M.H.; Delair, T.; et al. Surfactant-free anionic PLA nanoparticles coated with HIV-1 p24 protein induced enhanced cellular and humoral immune responses in various animal models. J. Control. Release 2006, 112, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.L.; Fan, G. Effects of the glycerophosphate-polylactic copolymer formation on electrospun fibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 443, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, R.E.; Kolstad, J.J.; Borzelleca, J.F.; Dixler, D.S.; Filer, L.J.; Ladu, B.N.; Pariza, M.W. Safety assessment of polylactide (PLA) for use as a food-contact polymer. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1995, 33, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafaka, P.I.; Barmbalexis, P.; Bikiaris, D.N. Novel electrospun nanofibrous matrices prepared from poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate) blends for controlled release formulations of an anti-rheumatoid agent. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 88, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberg, S.; Zhu, X.X. Polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 282, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Pendleton, P. Mesoporous silica SBA-15 for natural antimicrobial delivery. Powder Technol. 2012, 223, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjadian, F.; Roointan, A.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Hosseini, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, pharmaceutical applications, biodistribution, and biosafety assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 684–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Che, E.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanaki, S.; Siafaka, P.I.; Zachariadou, D.; Nerantzaki, M.; Giliopoulos, D.J.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Kostoglou, M.; Nikolakaki, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. PLGA/SBA-15 mesoporous silica composite microparticles loaded with paclitaxel for local chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; Del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhou, H.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, H.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. Synergistic antimicrobial activities of tea tree oil loaded on mesoporous silica encapsulated by polyethyleneimine. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Teng, J.; Hu, L.; Lan, X.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, M. Pepper fragrant essential oil (PFEO) and functionalized MCM-41 nanoparticles: Formation, characterization, and bactericidal activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5168–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanaki, S.; Tseklima, M.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Nerantzaki, M.; Giliopoulos, D.J.; Triantafyllidis, K.; Kostoglou, M.; Bikiaris, D.N. Use of mesoporous cellular foam (MCF) in preparation of polymeric microspheres for long acting injectable release formulations of paliperidone antipsychotic drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Martino, L.; Coppola, R.; De Feo, V. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, K.P.; Nisha, S.A.; Sakthivel, R.; Pandian, S.K. Eugenol (an essential oil of clove) acts as an antibacterial agent against Salmonella typhi by disrupting the cellular membrane. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Arfa, A.; Combes, S.; Preziosi-Belloy, L.; Gontard, N.; Chalier, P. Antimicrobial activity of carvacrol related to its chemical structure. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.S.; Karuppayil, S.M. A status review on the medicinal properties of essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan Tas, B.; Sehit, E.; Erdinc Tas, C.; Unal, S.; Cebeci, F.C.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Unal, H. Carvacrol loaded halloysite coatings for antimicrobial food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 20, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Rodriguez, B.; Figueroa-Lopez, K.J.; Bernardos, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Cabedo, L.; Torres-Giner, S.; Lagaron, J.M. Electrospun Antimicrobial Films of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Containing Eugenol Essential Oil Encapsulated in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, H.; Bian, Y.-Y.; Ali, B.; Jamil, A.; Majeed, U.; Khan, Q.F.; Iqbal, K.J.; Shoemaker, C.F.; Fang, Z. Essential oil encapsulations: Uses, procedures, and trends. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58449–58463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerantzaki, M.; Kehagias, N.; Francone, A.; Fernández, A.; Sotomayor Torres, C.M.; Papi, R.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Bikiaris, D.N. Design of a Multifunctional Nanoengineered PLLA Surface by Maximizing the Synergies between Biochemical and Surface Design Bactericidal Effects. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, A.; Francone, A.; Thamdrup, L.H.; Johansson, A.; Bilenberg, B.; Nielsen, T.; Guttmann, M.; Sotomayor Torres, C.M.; Kehagias, N. Design of Hierarchical Surfaces for Tuning Wetting Characteristics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7701–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.J.; Correlo, V.M.; Reis, R.L. Micro/nano replication and 3D assembling techniques for scaffold fabrication. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Palani, A.; Gilliopoulos, D.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Bikiaris, D.N. Mechanical properties and crystallization of high-density polyethylene composites with mesostructured cellular silica foam. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 113, 1651–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic triblock and star diblock copolymer and oligomeric sufactant syntheses of highly ordered, hydrothermally stable, mesoporous silica structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoulia, S.A.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Lemonidou, A.A. Preparation and characterization of vanadia catalysts supported on non-porous, microporous and mesoporous silicates for oxidative dehydrogenation of propane (ODP). Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 110, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, L.; Klonos, P.A.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Psochia, E.; Sanusi, O.M.; Hocine, N.A.; Benelfellah, A.; Giliopoulos, D.; Triantafyllidis, K.; Kyritsis, A.; et al. Comparative study of crystallization, semicrystalline morphology, and molecular mobility in nanocomposites based on polylactide and various inclusions at low filler loadings. Polymer (Guildf.) 2021, 217, 123457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Tang, Y.; Rothstein, J.P.; Watkins, J.J.; Carter, K.R. Large-area, continuous roll-to-roll nanoimprinting with PFPE composite molds. Nanotechnology 2013, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khang, D.Y.; Lee, H.H. Sub-100 nm Patterning with an Amorphous Fluoropolymer Mold. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2445–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.E.; Manna, D.; Mettetal, M.R.; May, R.M.; Dannemiller, E.M.; Chung, K.K.; Brennan, A.B.; Reddy, S.T. Surface micropattern limits bacterial contamination. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouquerol, J.F.; Rouquerol, K.S.W.; Sing, P.L.; Aix, G.M. Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids Principles, Methodology and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; ISBN 9780080970356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Inclusion of telmisartan in mesocellular foam nanoparticles: Drug loading and release property. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macina, D.; Piwowarska, Z.; Tarach, K.; Góra-Marek, K.; Ryczkowski, J.; Chmielarz, L. Mesoporous silica materials modified with alumina polycations as catalysts for the synthesis of dimethyl ether from methanol. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, O.; Yasyerli, S.; Dogu, G.; Dogu, T. Structural variations of MCF and SBA-15-like mesoporous materials as a result of differences in synthesis solution pH. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 131, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, E.M.; Córdoba, J.M.; Odén, M. The effects on pore size and particle morphology of heptane additions to the synthesis of mesoporous silica SBA-15. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 133, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Hampsey, J.E.; Hu, Q.; He, J.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y. Mesoporous Silica-Reinforced Polymer Nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3656–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Koutsoumpis, S.; Zidropoulos, S.; Kripotou, S.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kyritsis, A.; Pissis, P. Rigid amorphous fraction and segmental dynamics in nanocomposites based on poly(L–lactic acid) and nano-inclusions of 1–3D geometry studied by thermal and dielectric techniques. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittigstein, P.; Priestley, R.D.; Broadbelt, L.J.; Torkelson, J.M. Model polymer nanocomposites provide an understanding of confinement effects in real nanocomposites. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.; Klonos, P.A.; Kyritsis, A.; Tziolas, A.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Interfacial interactions, crystallization and molecular mobility in nanocomposites of Poly(lactic acid) filled with new hybrid inclusions based on graphene oxide and silica nanoparticles. Polymer (Guildf.) 2019, 166, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, L.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Vlachopoulos, A.; Klonos, P.A.; Kyritsis, A.; Tzetzis, D.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D. Synthesis and characterization of novel polymer/clay nanocomposites based on poly(butylene 2,5-furan dicarboxylate). Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobdeedamrong, A.; Jenjob, R.; Crespy, D. Encapsulation and Release of Essential Oils in Functional Silica Nanocontainers. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13235–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, U.T.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.-S.; Jeong, M.Y. Nanostructured Multifunctional Surface with Antireflective and Antimicrobial Characteristics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar-Mohammadi, M.; Bahrami, S.H.; Joghataei, M.T. Fabrication of novel nanofiber scaffolds from gum tragacanth/poly(vinyl alcohol) for wound dressing application: In vitro evaluation and antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4935–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, M.N.; Liang, E.I.; Rodriguez, L.A.; Vollereaux, N.; Yee, A.F. Nanopatterned polymer surfaces with bactericidal properties. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
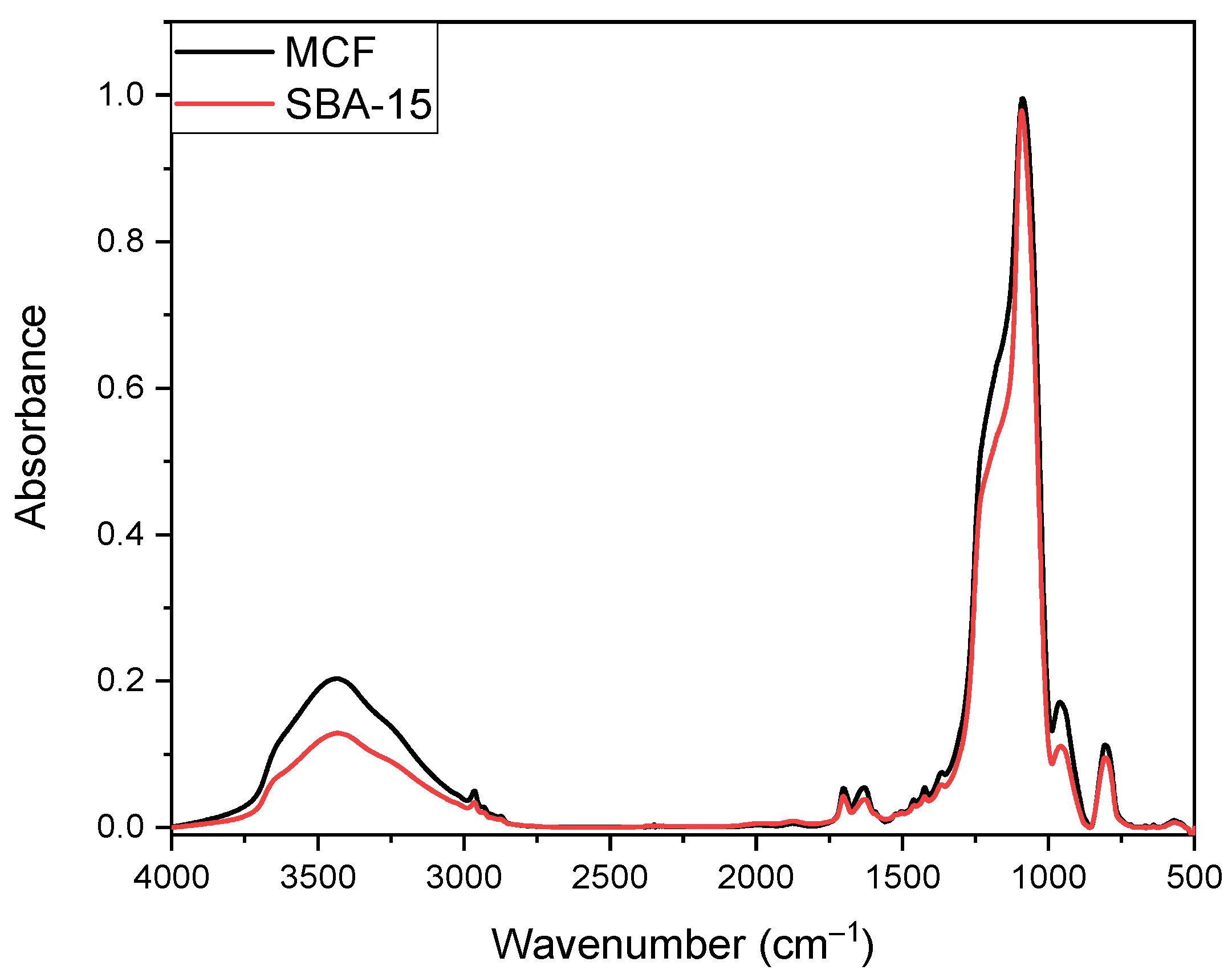

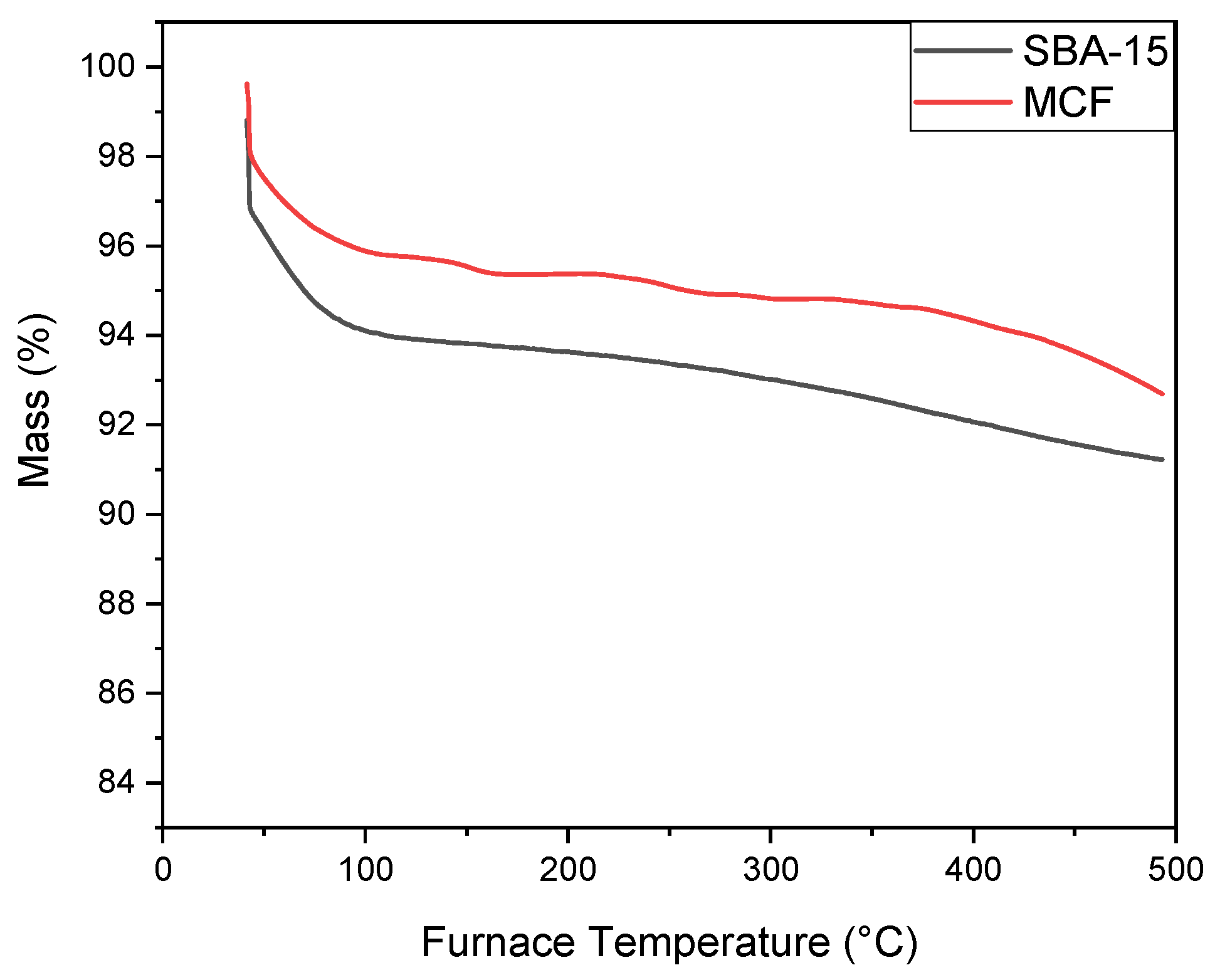
| Material | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume P/Po = 0.99 (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Window Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15 | 619 | 0.5 | 4 | - |
| MCF | 837 | 1.56 | 18.5 | 6.1 |
| Sample | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | ΔHcc (J/g) | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLLA | 62 | 126 | 17.1 | 156 | 18.9 |
| PLLA/MCF 1% | 64 | 122 | 23.1 | 153 | 23.6 |
| PLLA/MCF 2.5% | 64 | 118 | 21.6 | 153 | 23 |
| PLLA/MCF 5% | 65 | 119 | 22.4 | 154 | 24.7 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 1% | 64 | 120 | 23.3 | 153 | 25.4 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 2.5% | 63 | 112 | 20.8 | 152 | 24 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 5% | 65 | 115 | 24.2 | 155 | 26.1 |
| Sample | Td,5% (°C) | Td,10% (°C) | Td,max (°C) | R500 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLLA | 350 | 361 | 413 | 1.8 |
| PLLA/MCF 1% | 355 | 365 | 419 | 3.4 |
| PLLA/MCF 2.5% | 360 | 369 | 423 | 4.5 |
| PLLA/MCF 5% | 361 | 369 | 426 | 7.8 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 1% | 356 | 365 | 420 | 2 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 2.5% | 358 | 366 | 423 | 6.1 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 5% | 358 | 366 | 426 | 8 |
| Sample | Hardness (MPa) | St Dev | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | St Dev |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLLA | 108 | 2 | 4580 | 188 |
| PLLA/MCF 1% | 193 | 20 | 6974 | 390 |
| PLLA/MCF 2.5% | 201 | 23 | 7035 | 366 |
| PLLA/MCF 5% | 85 | 7 | 4285 | 156 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 1% | 105 | 17 | 5125 | 371 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 2.5% | 126 | 13 | 5890 | 54 |
| PLLA/SBA-15 5% | 110 | 21 | 5720 | 135 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psochia, E.; Papadopoulos, L.; Gkiliopoulos, D.J.; Francone, A.; Grigora, M.-E.; Tzetzis, D.; de Castro, J.V.; Neves, N.M.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Torres, C.M.S.; et al. Bottom-Up Development of Nanoimprinted PLLA Composite Films with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for Smart Packaging Applications. Macromol 2021, 1, 49-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1010005
Psochia E, Papadopoulos L, Gkiliopoulos DJ, Francone A, Grigora M-E, Tzetzis D, de Castro JV, Neves NM, Triantafyllidis KS, Torres CMS, et al. Bottom-Up Development of Nanoimprinted PLLA Composite Films with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for Smart Packaging Applications. Macromol. 2021; 1(1):49-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1010005
Chicago/Turabian StylePsochia, Eleni, Lazaros Papadopoulos, Dimitrios J. Gkiliopoulos, Achille Francone, Maria-Eirini Grigora, Dimitrios Tzetzis, Joana Vieira de Castro, Nuno M. Neves, Konstantinos S. Triantafyllidis, Clivia M. Sotomayor Torres, and et al. 2021. "Bottom-Up Development of Nanoimprinted PLLA Composite Films with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for Smart Packaging Applications" Macromol 1, no. 1: 49-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1010005
APA StylePsochia, E., Papadopoulos, L., Gkiliopoulos, D. J., Francone, A., Grigora, M.-E., Tzetzis, D., de Castro, J. V., Neves, N. M., Triantafyllidis, K. S., Torres, C. M. S., Kehagias, N., & Bikiaris, D. N. (2021). Bottom-Up Development of Nanoimprinted PLLA Composite Films with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties for Smart Packaging Applications. Macromol, 1(1), 49-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol1010005