Identification of Novel Can Manipulation Behaviour in the Common Raven (Corvus corax)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
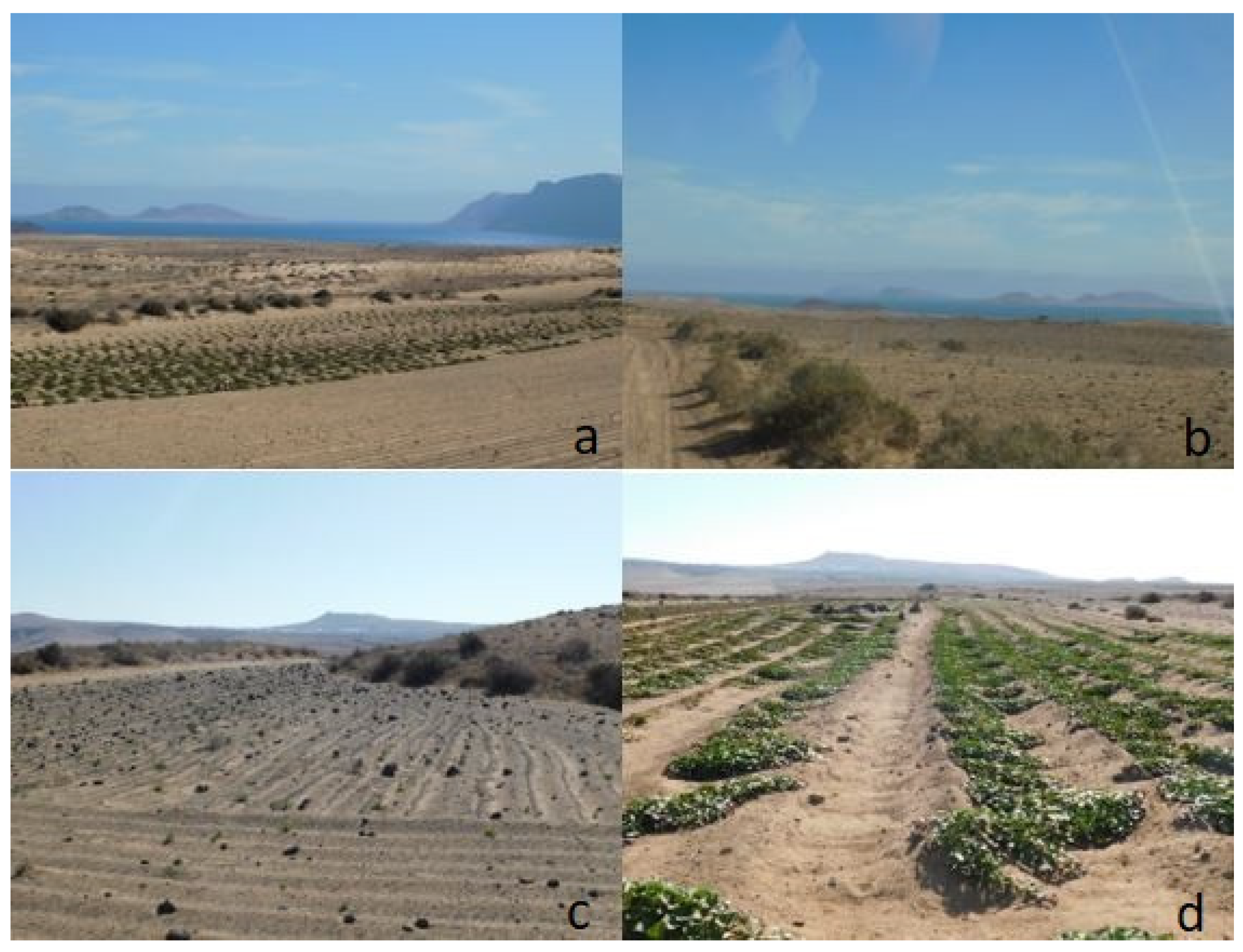
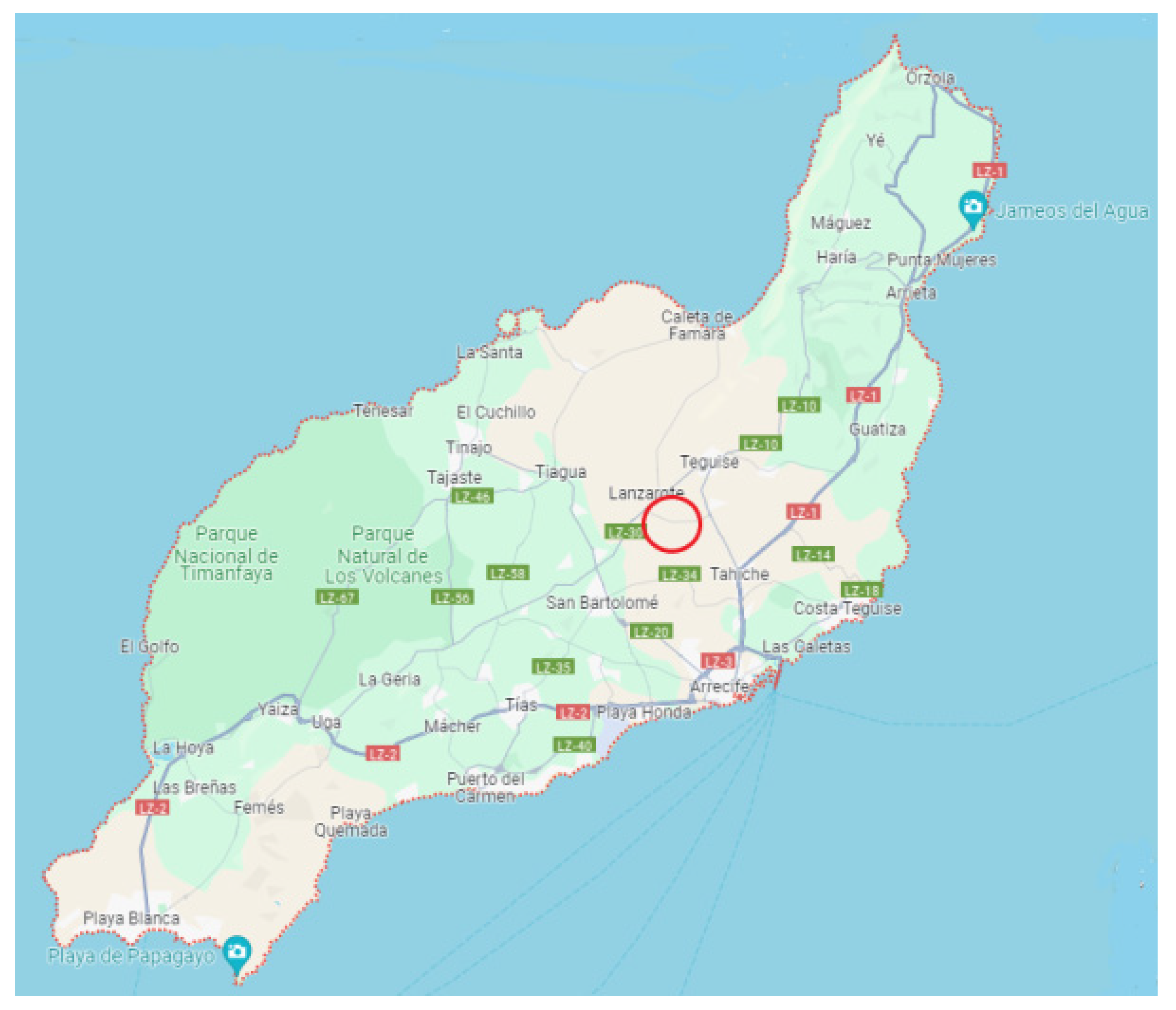
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Species
2.3. Data Collection and Field Methods
2.3.1. Pilot Study
2.3.2. Field Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Observation Locations and Recording
3.2. Camera Trap Observation
3.3. Human Observation
3.4. Comparing Camera Trap and Human Observational Data
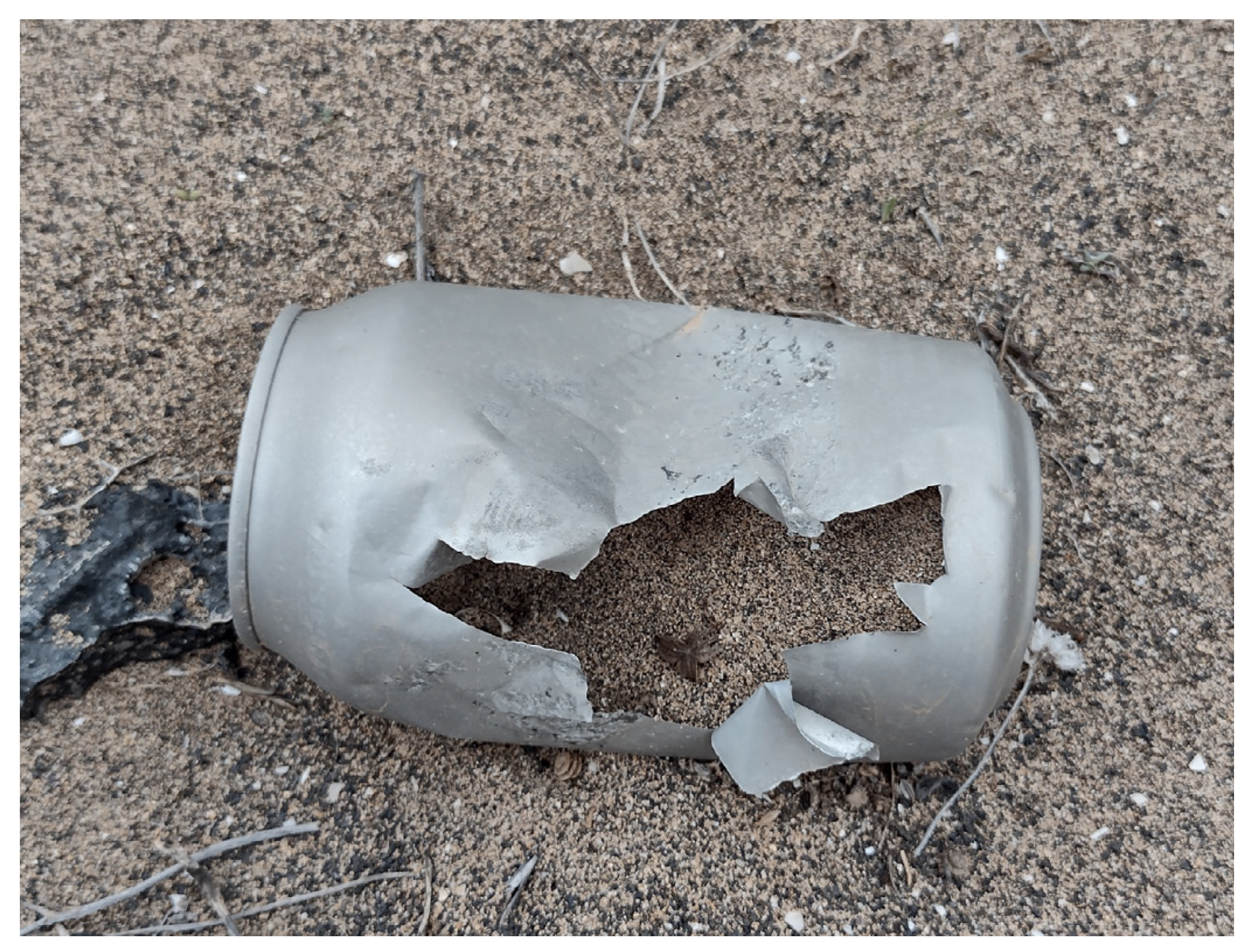
3.5. Can Piercing Behaviour Identified in Desert Clear Ups
4. Discussion
4.1. Camera Trapping Technology vs. Human Observation
4.2. Camera Traps Showing Raven Behaviour
4.3. Human Observations of Raven Behaviour
4.4. GPS Location of Ravens
4.5. Ravens’ Manipulation of Cans
4.6. Can Perforation Strategies
4.7. Study Limitations
4.8. Further Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraser, O.N.; Bugnyar, T. The quality of social relationships in ravens. Anim. Behav. 2010, 79, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BirdLife International. Corvus Corax. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22706068/113271893 (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Benmazouz, I.; Jokimäki, J.; Lengyel, S.; Juhász, L.; Kaisanlahti-Jokimäki, M.L.; Kardos, G.; Kövér, L. Corvids in urban environments: A systematic global literature review. Animals 2021, 11, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley-Turner, G. Common Raven; The Cornell Lab, Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/common_Raven/lifehistory (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Overington, S.E.; Griffin, A.S.; Sol, D.; Lefebvre, L. Are innovative species ecological generalists? A test in North American birds. Behav. Ecol. 2011, 22, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Range, F.; Bugnyar, T.; Kotrschal, K. The performance of Ravens on simple discrimination tasks: A preliminary study. Acta Ethol. 2008, 11, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siverio, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Siverio, F. Population Size and Status of Common Raven (Corvus corax) on the Central-western Islands of the Canarian Archipelgo. Vieraea 2010, 38, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWF. Conservation Technology. World Wildlife Fund. 2020. Available online: https://www.wwf.org.uk/project/conservationtechnology (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Trolliet, F.; Huynen, M.; Vermeulen, C.; Hambucker, A. Use of Camera Traps for Wildlife Studies: A Review. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. 2014, 18, 446–454. Available online: https://popups.uliege.be/1780-4507/ (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Santangeli, A.; Pakanen, V.; Bridgeford, P.; Boorman, M.; Kolberg, H.; Sanz-Agular, A. The Relative Contribution of Camera Trap Technology and Citizen Science for Estimating Survival of an Endangered African Vulture. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 246, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, D.; Campbell, K.; Holmes, N. Using digital data collection tools to improve overall cost-efficiency and provide timely analysis for decision making during invasive species eradication campaigns. Wildl. Res. 2015, 41, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B. The Science of Sense; Tongi University: Shangai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, S. Business Communication for Success; California State University: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rovero, F.; Zimmerman, F. Camera Trapping for Wildlife Research; Pelagic Publishing: Exeter, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Caravaggi, A.; Banks, P.; Burton, A.; Finlay, C.; Haswell, P.; Hayward, M.; Rowcliffe, M.; Wood, M. A review of camera trapping for conservation behaviour research. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 3, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newey, S.; Davidson, P.; Nazir, S.; Fairhurst, G.; Verdicchio, F.; Irvine, R.; Van der Wal, R. Limitations of recreational camera traps for wildlife management and conservation research: A Practionars perspective. Ambio 2015, 44, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palencia, P.; Vincente, J.; Soriguer, R.; Acebado, P. Towards a best-practices guide for camera trapping: Assessing differences among camera trap models and settings under field conditions. J. Zool. 2021, 316, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearn, O.; Glover-Kapfer, P. Snap Happy: Camera traps are an effective sampling tools when compared with alternative methods. Roy. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis-Desormeaux, M.; Davidson, Z.; Mwololo, M.; Kisio, E. Comparing motion captures cameras versus human observer monitoring of mammal through fence gaps: A case study from Kenya. Afr. J. Ecol. 2016, 54, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desert Watch. El Jable. Desert Watch. 2020. Available online: https://desertwatch.org (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- UNESCO. Lanzarote Biosphere Reserve, Lanzarote. UNESCO. 2019. Available online: https://en.unesco.org/biosphere/eu-na/lanzarote (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Martin, J.; Martinez, J.; Moreno, V.; Rodriguez, A. An Analysis of the Tourist Mobility in the Island of Lanzarote: Car Rental Versus More Sustainable Transportation Alternatives. Sustainability 2019, 11, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centro de Datos Lanzarote. Legal Population of Lanzarote According to Municipality (1 January 2023). 2023. Available online: https://www.datosdelanzarote.com/item/poblacion-de-derecho-de-lanzarote-segun-municipio-1-de-enero-de-2023-comparacion-con-2022 (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Vilet, K.; Moore, C. Citizen Science Initiatives: Engaging the Public and Demystifying Science. J. Microbiol. Biol. Ed. 2016, 17, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K. Lanzarote’s Lunar-Like Landscape. NASA Earth Observatory. 2019. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/146057/lanzarotes-lunar-like-landscape (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Ecoturismo. Ornithological Tourism in Lanzarote. Revivir Lanzarote. 2016. Available online: https://ecotourism.lanzarotebiosfere.org/en/turismo-ornitologico-en-lanzarote (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Ecoturismo. El Jable: Much More than Sand. Revivir Lanzarote. 2021. Available online: https://ecotourism.lanzarotebiosfere.org/en/portfolio/el-jable (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Manuel, N.; HernÁndez, E.C.; ValdÉs, F. Seed dispersal by common ravens Corvus corax among island habitats (Canarian Archipelago). Ecoscience 1999, 6, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Schwan, M. Common Ravens; Alaska Department of Fish and Game: Juneau, AK, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, T. Corvids: Husbandry and Management; AZA 2003 Eastern Regional: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Peebles, L.; Spencer, J. Common Ravens. In Wildlife Damage Management Technical Series; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guilherme, J.; Burnside, R.; Collar, N.; Dolman, P. Consistent Nest-site Selections Across Habitats Increases Fitness in Asian Houbara. Auk 2018, 135, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, B.; Marzluff, J.; Adams, W. Fear and Food Recognition in Naïve Common Ravens. Auk 1995, 112, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desert Watch. Cleaning the Deserts. Desert Watch. 2022. Available online: https://desertwatch.org/cleaning-the-desert (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Nettle, D. Cutting through the Forest of Statistical Tests. In Modelling and Visualising Data Using R: A Practical Introduction. 2019. Available online: https://www.danielnettle.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/funwithR3.0.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Kissel, R.; Poserina, J. (Eds.) Chi-Squared Distribution. In Optimal Sports Math, Statistics, and Fantasy; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 103–135. [Google Scholar]
- Fontúrbel, F.E.; Rodríguez-Gómez, G.B.; Fernández, N.; García, B.; Orellana, J.I.; Castaño-Villa, G.J. Sampling understory birds in different habitat types using point counts and camera traps. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 119, 106863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwerts, J.A.; Stephenson, P.J.; Maisels, F.; Rowcliffe, M.; Astaras, C.; Jansen, P.A.; van Der Waarde, J.; Sterck, L.E.; Verweij, P.A.; Bruce, T.; et al. Methods for wildlife monitoring in tropical forests: Comparing human observations, camera traps, and passive acoustic sensors. Conserv. Sci. Prac. 2021, 3, e568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, S.L.; Roberts, D.G.; Phillips, R.D.; Edwards, C. Effectiveness of camera traps for quantifying daytime and nighttime visitation by vertebrate pollinators. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 9304–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, P.M.; Buette, J.C.; Brook, B.W. Investigating avian behaviour using opportunistic camera-trap imagery reveals an untapped data source. Ornithol. Sci. 2022, 21, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Juricic, E.; O’Rourke, C.; Pitlik, T. Visual coverage and scanning behaviour in two corvid species: American crow and Western scrub jay. J. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 196, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugnyar, T. Social Cognition in Ravens. Compar. Cogn. Beh. Rev. 2013, 8, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Lawick-Goodall, J. Tool-using in Primates, and other vertebrates. Adv. Study Behav. 1971, 3, 195–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amant, R.; Horton, T. Revisiting the Definition of Animal Tool Use. NC State Repository. 2007. Available online: https://repository.lib.ncsu.edu/bitstream/handle/1840.4/1112/TR-2007-16.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Jonsson, K.; Fabre, P.; Irestedt, M. Brains, tools, innovation and biogeography in crows and Ravens. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover-Kapfer, P.; Soto-Navarro, C.; Wearn, O. Camera-trapping version 3.0: Current constraints and future priorities for development. Rem. Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 5, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; Massen, J.; Bugnyar, T.; Osvath, M. Ravens remember the nature of a single reciprocal interaction sequence over 2 days and even a month. Anim. Behav. 2017, 128, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andren, H. Corvid Density and Nest Predation in Relation to Forest Fragmentation: A landscape perspective. Ecology 2017, 73, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlem, G.; Souttou, K.; Derboukh, W.; Mokhtar, G. Role of Common Raven, Corvus corax, in reducing crop pests populations in some agricultural areas in Algeria. J. Environ. Biol. 2017, 38, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeDecker, J. Crows and Ravens; North Central IPM Centre: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.J.; Maro, A.; Weaver, V.; Dudley, R. Dietary ethanol ingestion by free-ranging spider monkeys (Ateles geoffroyi). R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 211729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryjanowski, P.; Hetman, M.; Czechowski, P.; Grzywaczewski, G.; Sklenicka, P.; Ziemblińska, K.; Sparks, T.H. Birds drinking alcohol: Species and relationship with people. A review of information from scientific literature and social media. Animals 2020, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wascher, C.; Heiss, R.; Baglione, V.; Canestrari, D. Behavioural response to olfactory cues in carrion crows. Behav. Proc. 2015, 111, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrimen, A.; Berger, R. Olfactory acuity in the common Raven (Corvus corax). Phys. Behav. 1986, 36, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, T.; Gouagna, L.; Dabiré, K.; Elguero, E.; Fontenille, D.; Renaud, F.; Costantini, C.; Thomas, F. Beer Consumption Increases Human Attractiveness to Malaria Mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arroyo, M.; Gómez-Martínez, M.A.; MacGregor-Fors, I. Litter buffet: On the use of trash bins by birds in six boreal urban settlements. Avian Res. 2023, 1, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Osorio, D. Vision in Birds; Elsevier: Birmingham, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jelbert, S.A.; Hosking, R.J.; Taylor, A.H.; Gray, R.D. Mental template matching is a potential cultural transmission mechanism for New Caledonian crow tool manufacturing traditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, C.; Hunt, G.R.; St Clair, J.J.H. Corvid Technologies: How Do New Caledonian Crows Get Their Tool Designs? Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R1109–R1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Álvarez, M.J.; Clayton, N.S. Neural processes underlying tool use in humans, macaques, and corvids. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 560669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, A.; Emery, N.; Clayton, N. Intelligence in corvids and apes: A case of convergent evolution? Ethology 2009, 115, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, B. Raven tool use? Condor 1987, 90, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabadayi, C.; Osvath, M. Ravens parallel great apes in flexible planning for tool-use and bartering. Science 2017, 357, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, I.; Osvath, M. Tool use and tooling in Ravens (Corvus corax): A review and novel observations. Ethology 2022, 129, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignatio, A. Home Range and Habitat Use of Breeding Common Ravens in Redwood National and State Parks. Master’s Thesis, Facility of Humboldt State University, Arcata, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harel, R.; Duriez, O.; Spiegel, O.; Fluhr, J.; Horvitz, N.; Getz, W.; Bouten, W.; Sarrazin, F.; Hatzofe, O.; Nathan, R. Decision-making by a scaring birds: Time, energy and risk considerations at different spatio-temporal scales. Philosoph. Trans. R. Soc. 2016, 371, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. A Vending Machine for Crows. Ph.D. Thesis, New York University, Interactive Telecommunication Program, New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vahl, W.; Van der Meer, J.; Weissing, F.; Van Dullemen, D.; Piersma, T. The mechanisms of interference competition: Two experiments on foraging waders. Behav. Ecol. 2005, 16, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, J.; Losos, J.; Cruz, F.; Nunez, H. The relationship between morphology, escape behaviour and microhabitat occupation in the lizard clade Liolaemus (Iguanidae: Tropidurinae: Liolaemini). J. Evol. Biol. 2004, 17, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zug, G.; Dowling, H. Chemoreception. Britannica. 2002. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/animal/reptile/Chemoreception (accessed on 10 March 2023).







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dickinson, R.; Loftus, L. Identification of Novel Can Manipulation Behaviour in the Common Raven (Corvus corax). Birds 2024, 5, 155-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds5010011
Dickinson R, Loftus L. Identification of Novel Can Manipulation Behaviour in the Common Raven (Corvus corax). Birds. 2024; 5(1):155-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds5010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleDickinson, Rebecca, and Loni Loftus. 2024. "Identification of Novel Can Manipulation Behaviour in the Common Raven (Corvus corax)" Birds 5, no. 1: 155-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds5010011
APA StyleDickinson, R., & Loftus, L. (2024). Identification of Novel Can Manipulation Behaviour in the Common Raven (Corvus corax). Birds, 5(1), 155-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds5010011




