Combined Effect of Viscosity Ratio and Interfacial Tension on Residual Saturations: Implications for CO2 Geo-Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Core Flooding Experiments
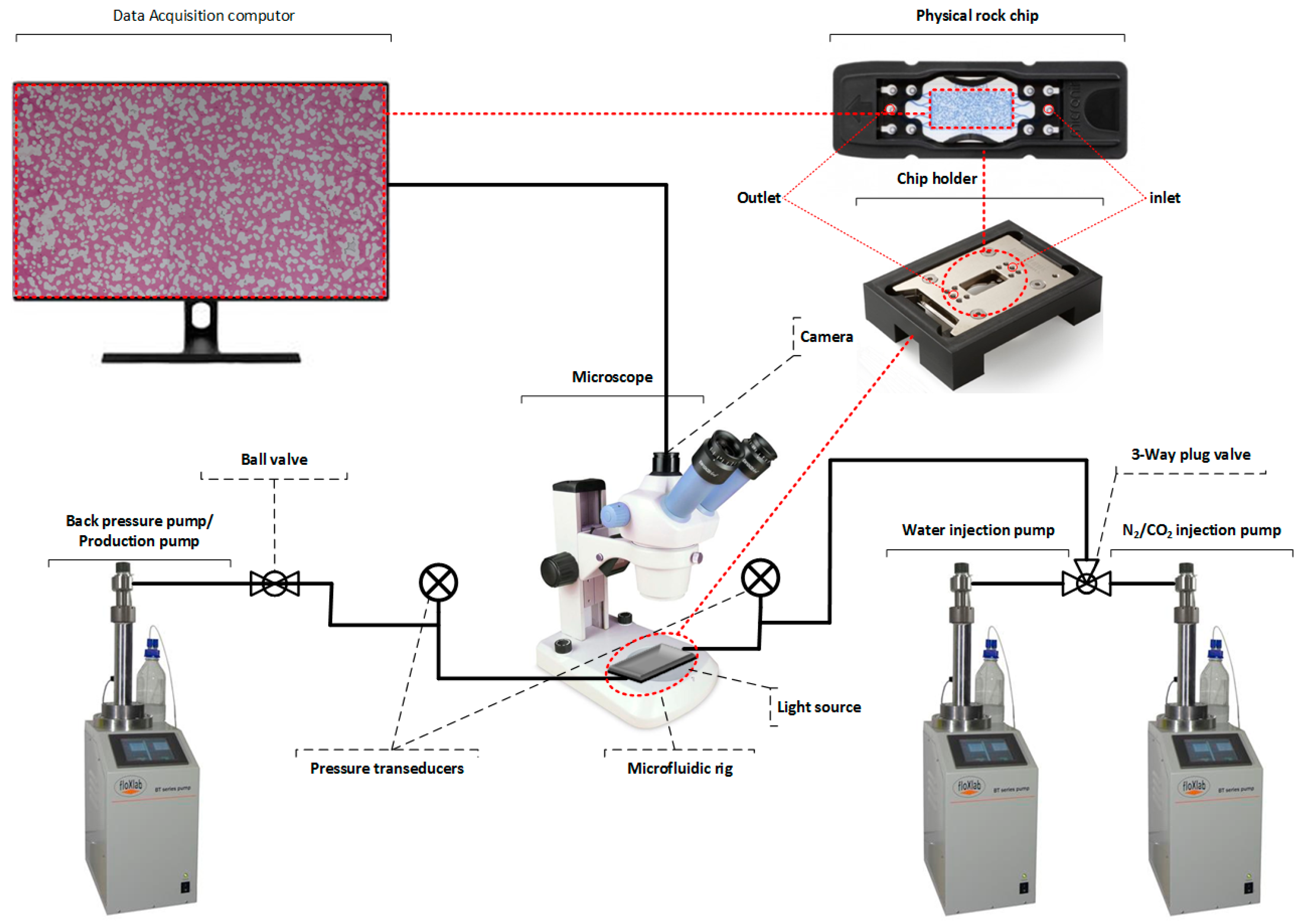
2.1.1. Methodology and Equipment
2.1.2. Core Flooding Process
2.2. Microfluidic Experiments
2.2.1. Fluid Composition and Properties
2.2.2. Microfluidic Chip Properties and Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
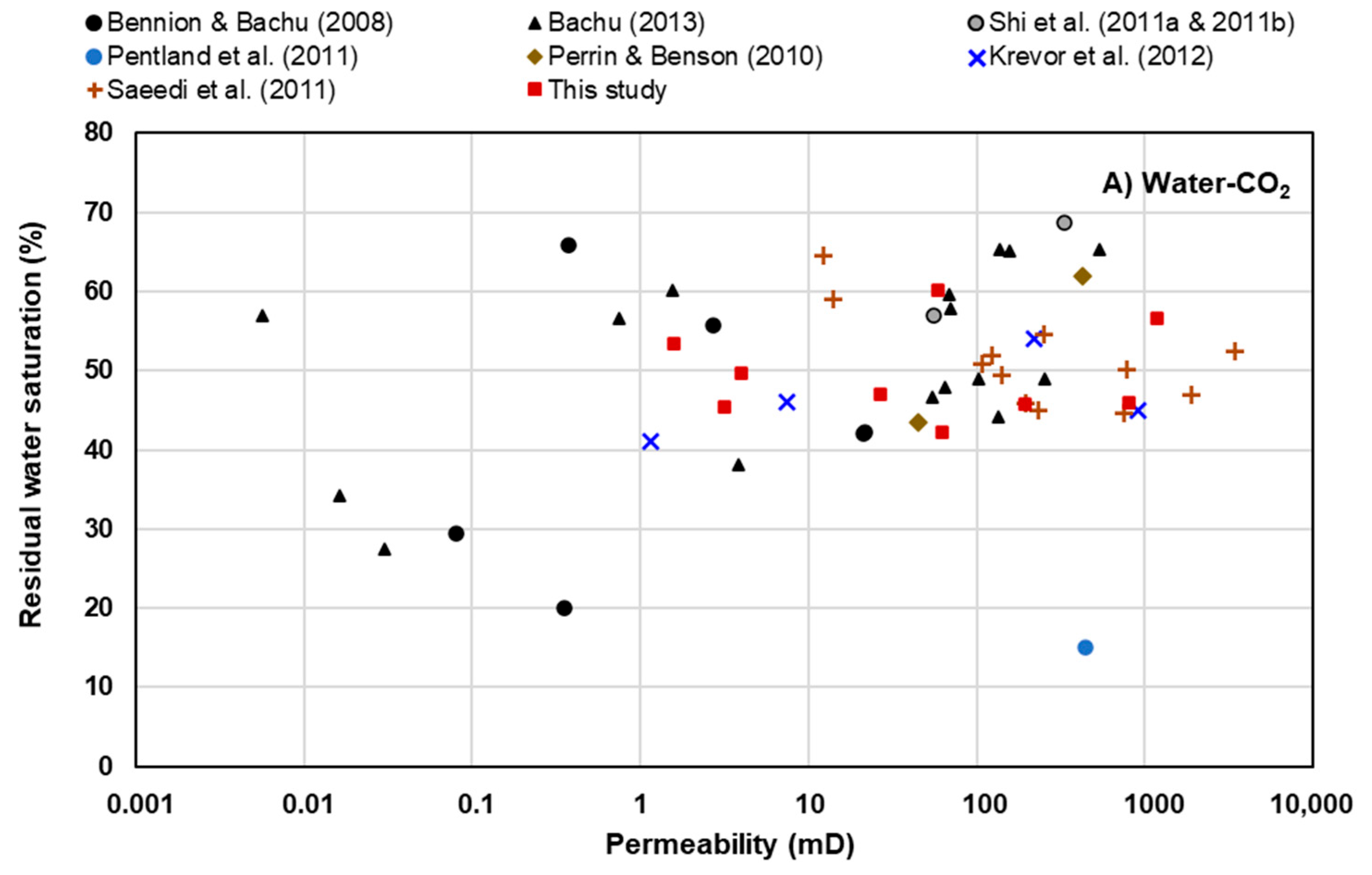
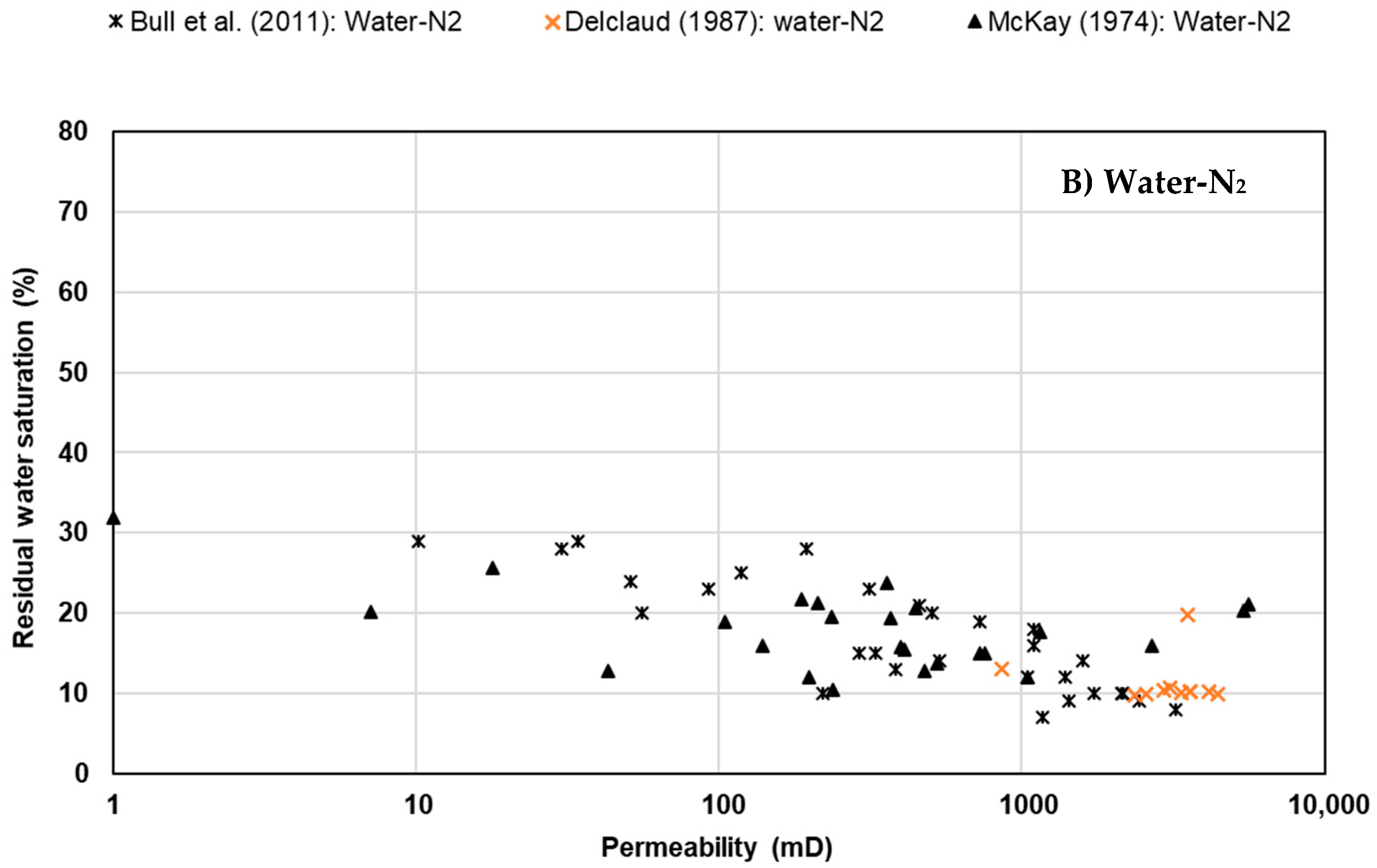
3.1. Core Flooding; Residual Saturation Data
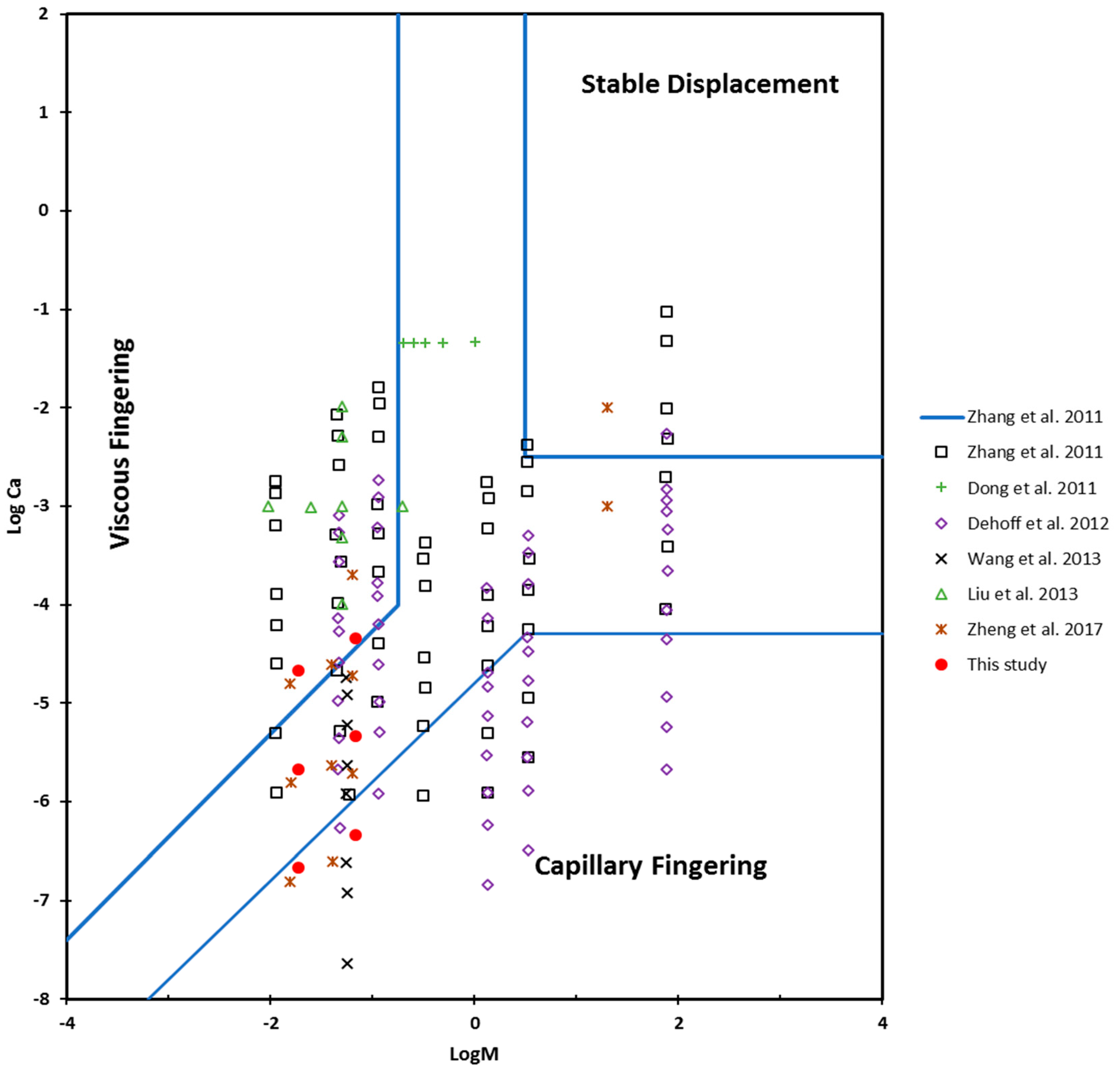
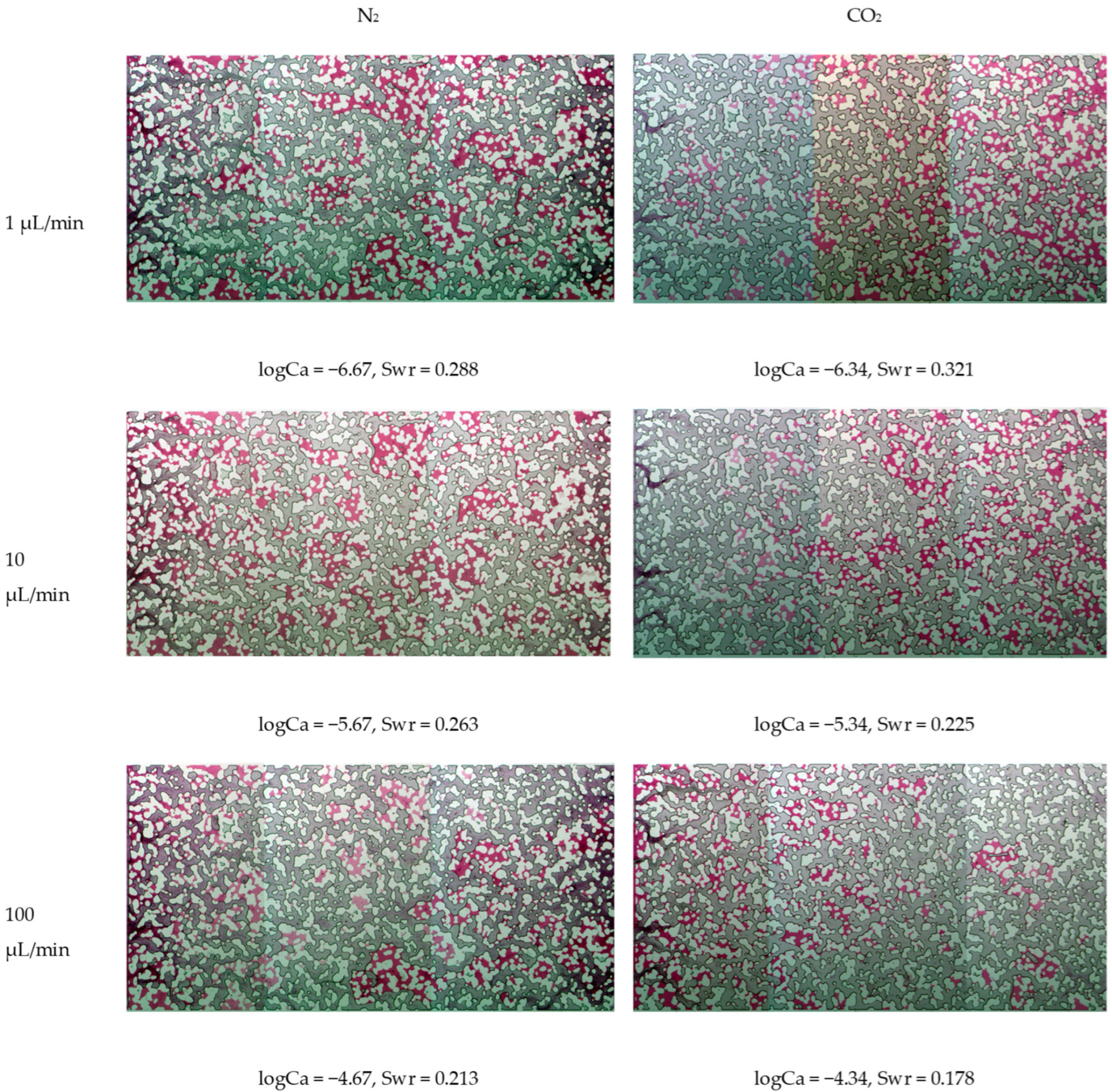
3.2. Microfluidic Device Experiments and Residual Saturation Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lackner, K.S. A Guide to CO2 Sequestration. Science 2003, 300, 1677–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalbaud, C.; Robin, M.; Lombard, J.M.; Martin, F.; Egermann, P.; Bertin, H. Interfacial Tension Measurements and Wettability Evaluation for Geological CO2 Storage. Adv. Water Res. 2009, 32, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Peterson, M.P.; Yan, H.; Filonchyk, M.; Gusev, A. Greenhouse gas emissions and reduction strategies for the world’s largest greenhouse gas emitters. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 944, 173895. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khdheeawi, E.A.; Mahdi, D.S.; Yuan, Y.; Iglauer, S. Influence of Clay Content on CO2-Rock Interaction and Mineral-Trapping Capacity of Sandstone Reservoirs. Energies 2023, 16, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassinari, C.C.G.; Kumar, N.; Ali, M.; Blunt, M.J.; Sampaio, M.A.; Izadpanahi, A. A review of carbon storage in saline aquifers: Mechanisms, prerequisites, and key considerations. Fuel 2024, 369, 131744. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, M.; Saeedi, A.; Al-Bayati, D. Pore-Scale Displacement Experiments Using Microfluidic Device to Investigate Fingering Mechanisms Using Both CO2 and N2: Implications for EOR and CO2 Geo-Storage. Pet. Chem. 2024, 64, 756–761. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Cardenas, M.B.; Bennett, P.C. Extended Roof Snap-Off for a Continuous Non-Wetting Fluid and an Example Case for Supercritical CO2. Adv. Water Res. 2014, 64, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Jiang, R.; Ma, C.; Jing, Y.; Chen, K.; Lu, Y. CO2 Oil Displacement and Geological Storage Status and Prospects. Energy Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 475–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, D.B.; Thomas, F.B.; Jamaluddin, A.; Ma, T. The Effect of Trapped Critical Fluid Saturations on Reservoir Permeability and Conformance; Hycal Energy Research Laboratories Ltd.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, S. Experimental Study of Multiphase Flow in Porous Media During CO2 Geo-Sequestration Processes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Iglauer, S. CO2–Water–Rock Wettability: Variability, Influencing Factors, and Implications for CO2 Geostorage. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-bayati, A.; Saeedi, A.; White, C.; Xie, Q.; Myers, M. The Effects of Crossflow and Permeability Variation on Different Miscible CO2 Injection Schemes Performance in Layered Sandstone Porous Media. In Proceedings of the IOR 2019—20th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Pau, France, 8–11 April 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Al-bayati, A.; Saeedi, A.; Myers, M.; White, C.; Xie, Q.; Hossain, M.M. Immiscible Water Alternating CO2 Displacement Efficiency in Layered Water Wet Porous Media. In Proceedings of the 82nd EAGE Annual Conference & Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khdheeawi, E.A. Optimizing CO2-Water Injection Ratio in Heterogeneous Reservoirs: Implications for CO2 Geo-Storage. Energies 2024, 17, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenormand, R.; Touboul, E.; Zarcone, C. Numerical Models and Experiments on Immiscible Displacements in Porous Media. J. Fluid Mech. 1988, 189, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, S.R.; Salino, P.A.; Sorbie, K.S. The Effect of Interfacial Tension Upon Gas-Oil Relative Permeability Measurements: Interpretation Using Pore-Scale Models. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–8 October 1997; Society of Petroleum Engineers: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dullien, F.A.L. Porous Media: Fluid Transport and Pore Structure; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferer, M.; Ji, C.; Bromhal, G.S.; Cook, J.; Ahmadi, G.; Smith, D.H. Crossover from Capillary Fingering to Viscous Fingering for Immiscible Unstable Flow: Experiment and Modeling. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 016303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Tsai, J.P.; Shan, H.Y.; Chen, H.H. Experimental Study on Imbibition Displacement Mechanisms of Two-Phase Fluid Using Micro Model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, P.; Bodiguel, H.; Colin, A. Drainage in Two-Dimensional Porous Media: From Capillary Fingering to Viscous Flow. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 046315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Oostrom, M.; Wietsma, T.W.; Grate, J.W.; Warner, M.G. Influence of Viscous and Capillary Forces on Immiscible Fluid Displacement: Pore-Scale Experimental Study in a Water-Wet Micromodel Demonstrating Viscous and Capillary Fingering. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3493–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Aryana, M. An Experimental Investigation of Flow Regimes in Imbibition and Drainage Using a Microfluidic Platform. Energies 2019, 12, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, P.G.; Taylor, G.I. The Penetration of a Fluid into a Porous Medium or Hele-Shaw Cell Containing a More Viscous Liquid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1958, 245, 312–329. [Google Scholar]
- DeHoff, R.T.; Oostrom, M.; Zhang, C.; Grate, J.W. Evaluation of Two-Phase Relative Permeability and Capillary Pressure Relations for Unstable Displacements in a Pore Network. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11, vzj2012-0024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Mahabadi, N.; Yun, T.S.; Jang, J. Effect of Capillary and Viscous Force on CO2 Saturation and Invasion Pattern in the Microfluidic Chip. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Yan, Y.Y.; Li, W.Z. LBM Simulation of Viscous Fingering Phenomenon in Immiscible Displacement of Two Fluids in Porous Media. Transp. Porous Media 2011, 88, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Valocchi, A.J.; Kang, Q.; Werth, C. Pore-Scale Simulations of Gas Displacing Liquid in a Homogeneous Pore Network Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Transp. Porous Media 2013, 99, 555–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabadi, N. Multiphase Fluid Flow Through Porous Media: Conductivity and Geomechanics. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, D.B.; Bachu, S. Supercritical CO2 and H2S-Brine Drainage and Imbibition Relative Permeability Relationships for Intercrystalline Sandstone and Carbonate Formations. In Proceedings of the SPE Europec/EAGE Annual Conference and Exhibition, Vienna, Austria, 12–15 June 2006; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, M.J.; King, M.J.; Scher, H. Simulation and Theory of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, 7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, M.J. Pore Level Modeling of the Effects of Wettability. SPE J. 1997, 2, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvatne, P.H.; Blunt, M.J. Predictive Pore-Scale Modeling of Two-Phase Flow in Mixed Wet Media. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krevor, S.; Blunt, M.J.; Benson, S.M.; Pentland, C.H.; Reynolds, C.; Al-Menhali, A.; Niu, B. Capillary Trapping for Geologic Carbon Dioxide Storage—From Pore Scale Physics to Field Scale Implications. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2015, 40, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, C.A.; Bray, J.M.; Seymour, J.D.; Codd, S.L. NMR Study Comparing Capillary Trapping in Berea Sandstone of Air, Carbon Dioxide, and Supercritical Carbon Dioxide After Imbibition of Water. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, N.; Oostrom, M.; Wietsma, T.W.; Li, X.; Bonneville, A. Experimental Study of Crossover from Capillary to Viscous Fingering for Supercritical CO2–Water Displacement in a Homogeneous Pore Network. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, A.; Rezaee, R.; Evans, B.; Clennell, B. Multiphase Flow Behaviour During CO2 Geo-Sequestration: Emphasis on the Effect of Cyclic CO2–Brine Flooding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2011, 79, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, D.B.; Bachu, S. Drainage and Imbibition Relative Permeability Relationships for Supercritical CO2/Brine and H2S/Brine Systems in Intergranular Sandstone, Carbonate, Shale, and Anhydrite Rocks. SPE Reserv. Evaluation Eng. 2008, 11, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachu, S. Drainage and Imbibition CO2/Brine Relative Permeability Curves at in Situ Conditions for Sandstone Formations in Western Canada. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 4428–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-Q.; Xue, Z.; Durucan, S. Supercritical CO2 core flooding and imbibition in Tako sandstone—Influence of sub-core scale heterogeneity. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2011, 5, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-Q.; Xue, Z.; Durucan, S. Supercritical CO2 core flooding and imbibition in Berea sandstone—CT imaging and numerical simulation. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 5001–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentland, C.H.; El-Maghraby, R.; Iglauer, S.; Blunt, M.J. Measurements of the capillary trapping of super-critical carbon dioxide in Berea sandstone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L06401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentland, C.; El-Maghraby, R.; Georgiadis, A.; Iglauer, S.; Blunt, M. Immiscible Displacements and Capillary Trapping in CO2 Storage. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-W.; Perrin, J.-C.; Benson, S.M. Effect of gravity, flow rate, and small scale heterogeneity on multiphase flow of CO2 and brine. In Proceedings of the SPE Western Regional Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 27–29 May 2010. SPE-132607. [Google Scholar]
- Krevor, S.C.M.; Pini, R.; Zuo, L.; Benson, S.M. Relative permeability and trapping of CO2 and water in sandstone rocks at reservoir conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W02532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, Ø.; Bratteli, F.; Ringen, J.K.; Melhuus, K.; Bye, A.L.; Iversen, J.E. The quest for the true residual gas saturation–an experimental approach. In Proceedings of the International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts, Austin, TX, USA, 18–21 September 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Delclaud, J.; Rochon, J.; Nectoux, A. Investigation of gas/oil relative permeabilities: High-permeability oil reservoir application. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, TX, USA, 27–30 September 1987. SPE-16966. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, B.A. Laboratory Studies of Sandstone Reservoirs Gas Displacement from Having Strong Water Drive. APPEA J. 1974, 14, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, A.; Rezaee, R. Effect of Residual Natural Gas Saturation on Multiphase Flow Behaviour During CO2 Geo-Sequestration in Depleted Natural Gas Reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 82, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, C.S. Calculation of Imbibition Relative Permeability for Two- and Three-Phase Flow from Rock Properties. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1968, 8, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, D.N.; Santamarina, J.C. Water-CO2-Mineral Systems: Interfacial Tension, Contact Angle, and Diffusion—Implications to CO2 Geological Storage. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Zou, P.; Gao, K.; Xu, X.; Pu, W.; Wood, C. Pore-Scale Monitoring of CO2 and N2 Flooding Processes in a Tight Formation Under Reservoir Conditions Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): A Case Study. Fuel 2019, 246, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, W.R. Snap-Off in Constricted Tubes and Porous Media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 166, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bayati, D.; Saeedi, A.; Ktao, I.; Myers, M.; White, C.; Mousavi, A.; Xie, Q.; Lagat, C. X-Ray Computed Tomography Assisted Investigation of Flow Behaviour of Miscible CO2 to Enhance Oil Recovery in Layered Sandstone Porous Media. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 21–23 March 2022; p. D011S004R004. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.D.; Honarpour, M.M. Capillary End Effects in Coreflood Calculations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1998, 19, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample ID | Geological Location | Water Salinity (ppm NaCl) | Porosity (%) | Gas Permeability (mD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPB1 | Southern Perth Basin | 30,000 | 16.5 | 3.15 |
| SPB2 | Southern Perth Basin | 30,000 | 20.1 | 27 |
| SB1 | Surat Basin | 1000 | 20.4 | 62 |
| SB2 | Surat Basin | 1000 | 22.9 | 800 |
| GB1 | Gippsland Basin | 2000 | 18.29 | 4 |
| GB2 | Gippsland Basin | 2000 | 25.4 | 1180 |
| GB3 | Gippsland Basin | 30,000 | 18.4 | 193 |
| GB4 | Gippsland Basin | 10,000 | 10.2 | 1.6 |
| GB4 | Gippsland Basin | 2000 | 18 | 59 |
| Phase | N2 | CO2 |
|---|---|---|
| Contact angle [deg] | 30 ± 10 | 45 ± 10 |
| Interfacial tension at CO2-H2O [mN/m] | 69.3 | 34.9 |
| Capillary number [logCa] | ||
| 1 μL/min | −6.67 | −6.34 |
| 10 μL/min | −5.67 | −5.34 |
| 100 μL/min | −4.67 | −4.34 |
| Density [kg/m3] | 69.4 | 782.7 |
| Viscosity [mPa·s] | 1.9 × 10−2 | 6.8 × 10−2 |
| Viscosity ratio [log(/)] | −1.73 | −1.17 |
| Injection Fluid | Pressure (MPa) | Temperature (°C) | IFT when in Contact with Water (mN·m) | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Residual Water Saturation—End of Drainage Flood (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2S | 8.6 | 35 | 12.2 | 0.134 | 48.1 |
| CO2 | 32.12 | 0.047 | 42.3 | ||
| H2S | 17.4 | 56 | 12.3 | 0.121 | 54.5 |
| CO2 | 34.56 | 0.058 | 49.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Bayati, D.; Mahdi, D.S.; Al-Khdheeawi, E.A.; Myers, M.; Saeedi, A. Combined Effect of Viscosity Ratio and Interfacial Tension on Residual Saturations: Implications for CO2 Geo-Storage. Gases 2025, 5, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases5030013
Al-Bayati D, Mahdi DS, Al-Khdheeawi EA, Myers M, Saeedi A. Combined Effect of Viscosity Ratio and Interfacial Tension on Residual Saturations: Implications for CO2 Geo-Storage. Gases. 2025; 5(3):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases5030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Bayati, Duraid, Doaa Saleh Mahdi, Emad A. Al-Khdheeawi, Matthew Myers, and Ali Saeedi. 2025. "Combined Effect of Viscosity Ratio and Interfacial Tension on Residual Saturations: Implications for CO2 Geo-Storage" Gases 5, no. 3: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases5030013
APA StyleAl-Bayati, D., Mahdi, D. S., Al-Khdheeawi, E. A., Myers, M., & Saeedi, A. (2025). Combined Effect of Viscosity Ratio and Interfacial Tension on Residual Saturations: Implications for CO2 Geo-Storage. Gases, 5(3), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases5030013