Immunophenotypic Characterization of LAMP-1 on Cytotoxic T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Its Correlation with Disease Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Biochemical Analysis
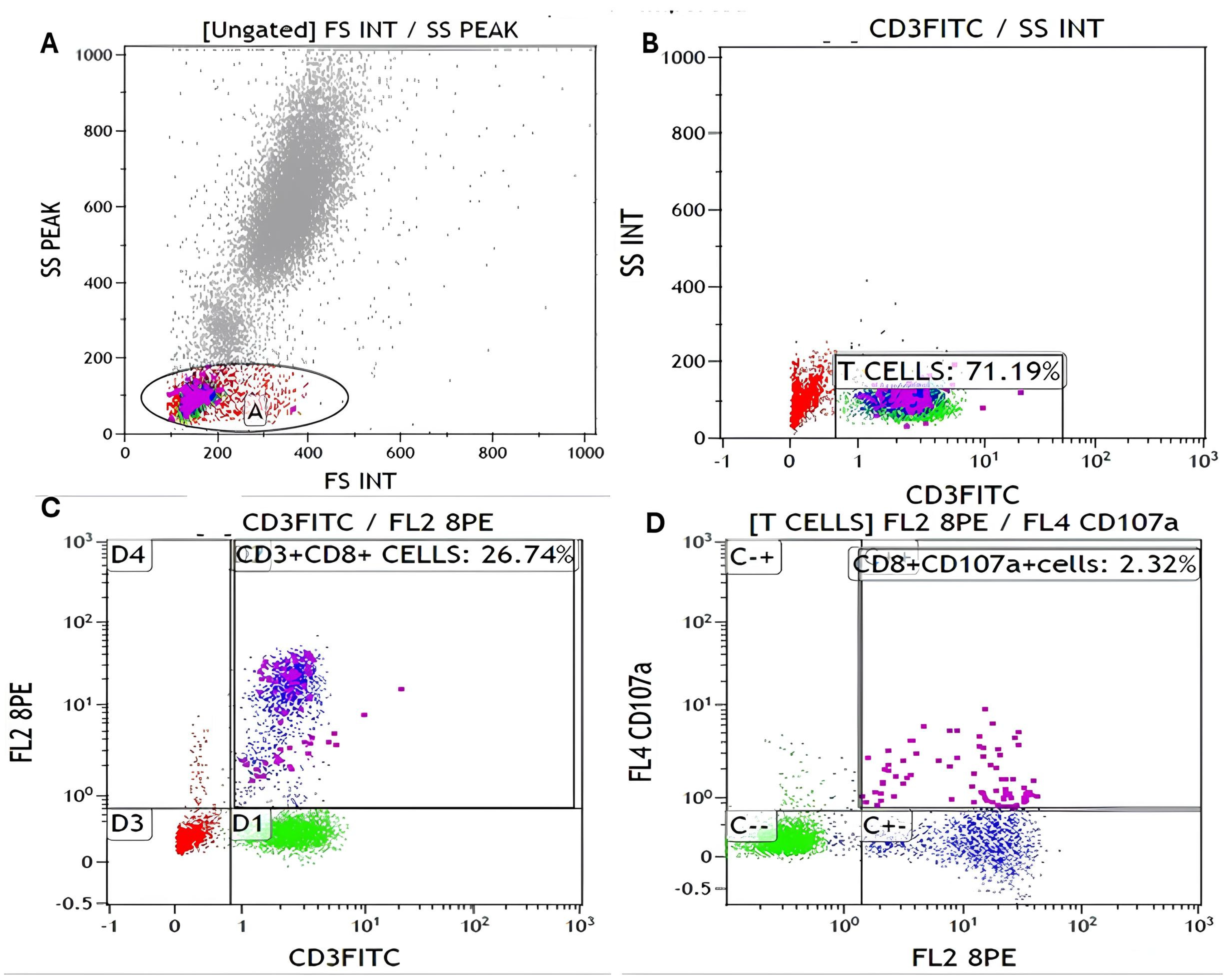
2.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.5. Selection of the Pathway
2.6. In Silico Enrichment Bioinformatics Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Data Analysis
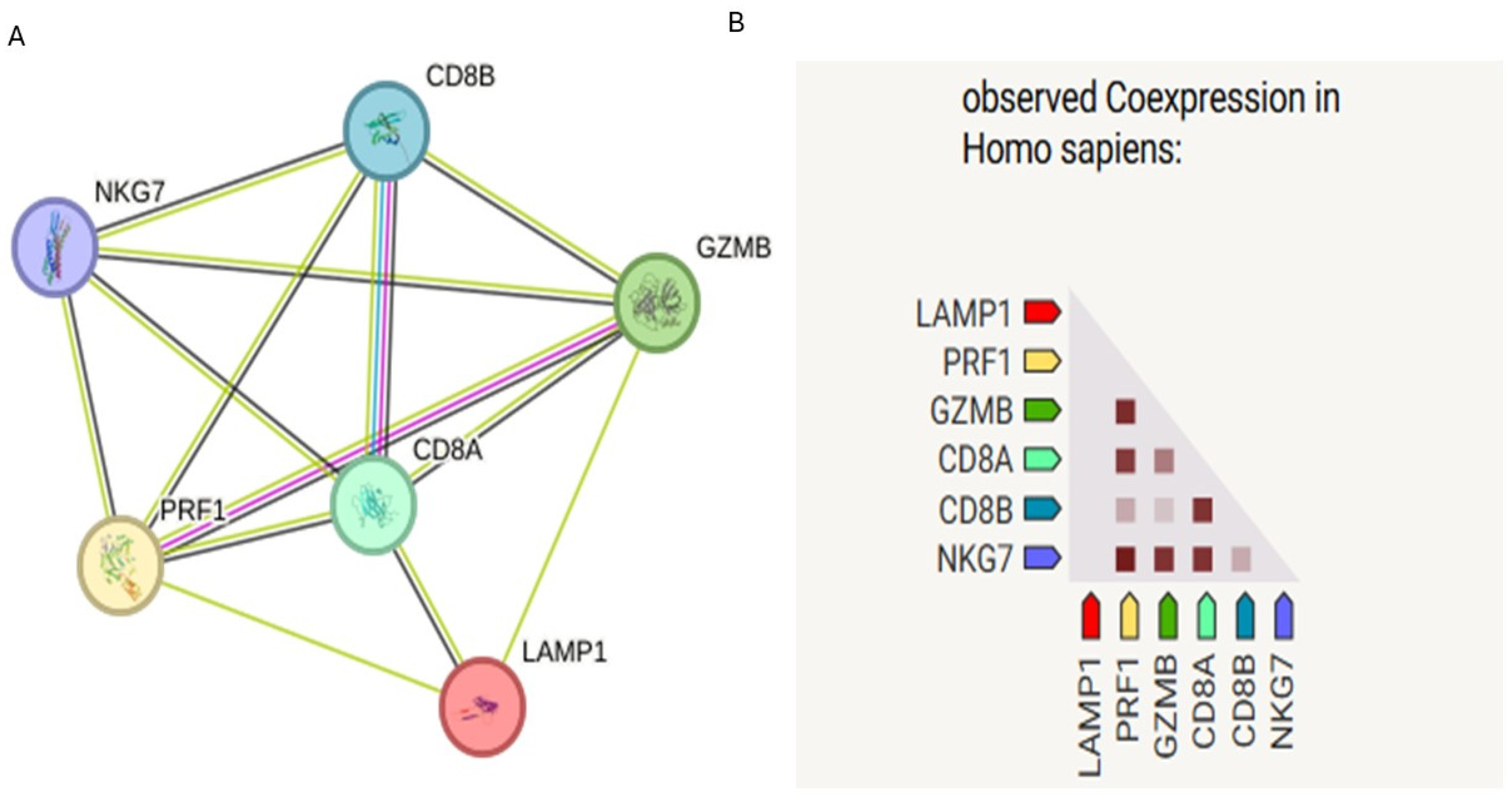
3.1.1. KEGG and Reactome Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.1.2. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
3.2. Flow Cytometry Gating Strategy
3.3. Demographic Characteristics of SLE Patients and Controls, and Baseline
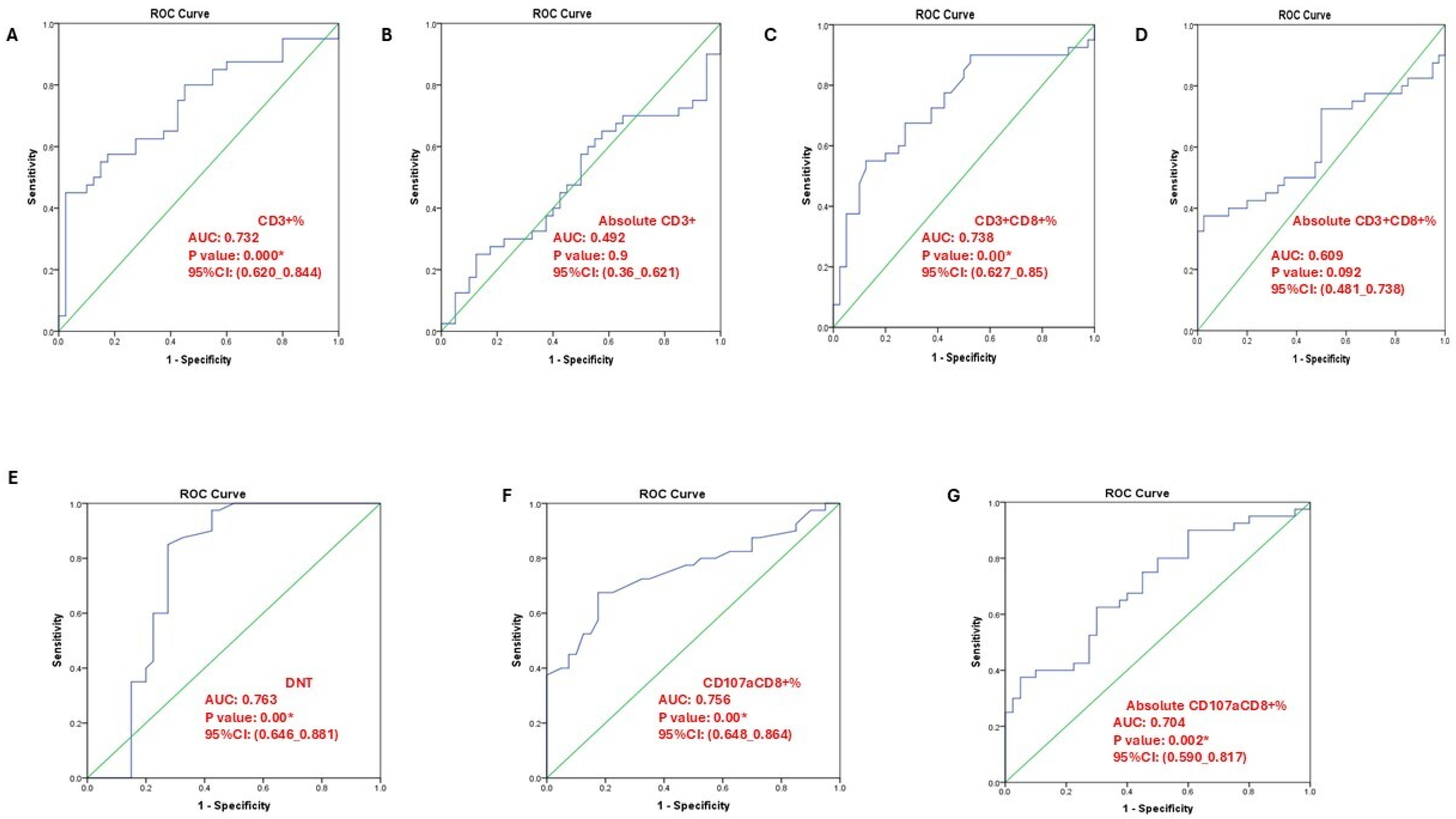
3.4. T-Cell Subsets and CD107a+CD8+ Expression in SLE Patients and Controls
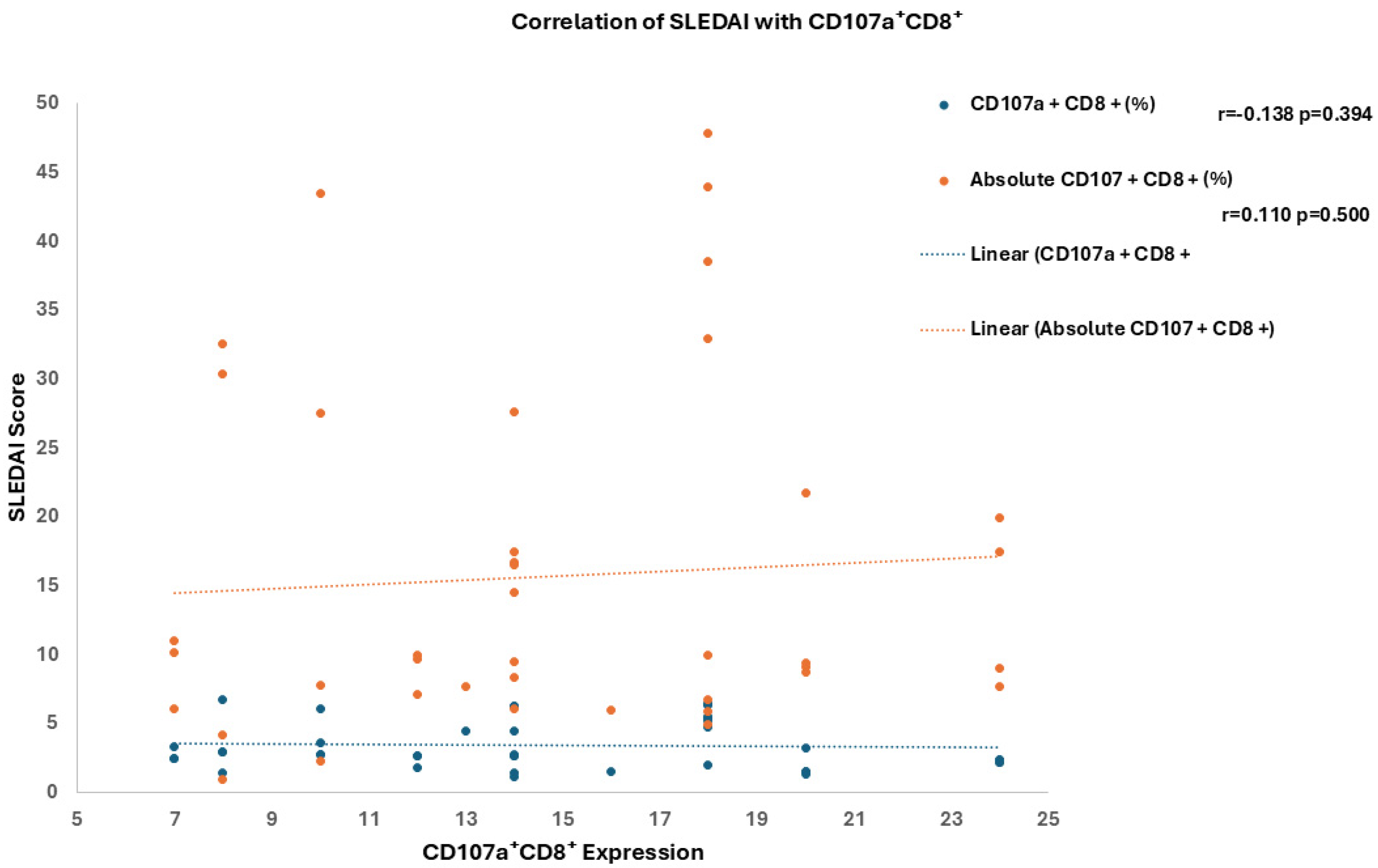
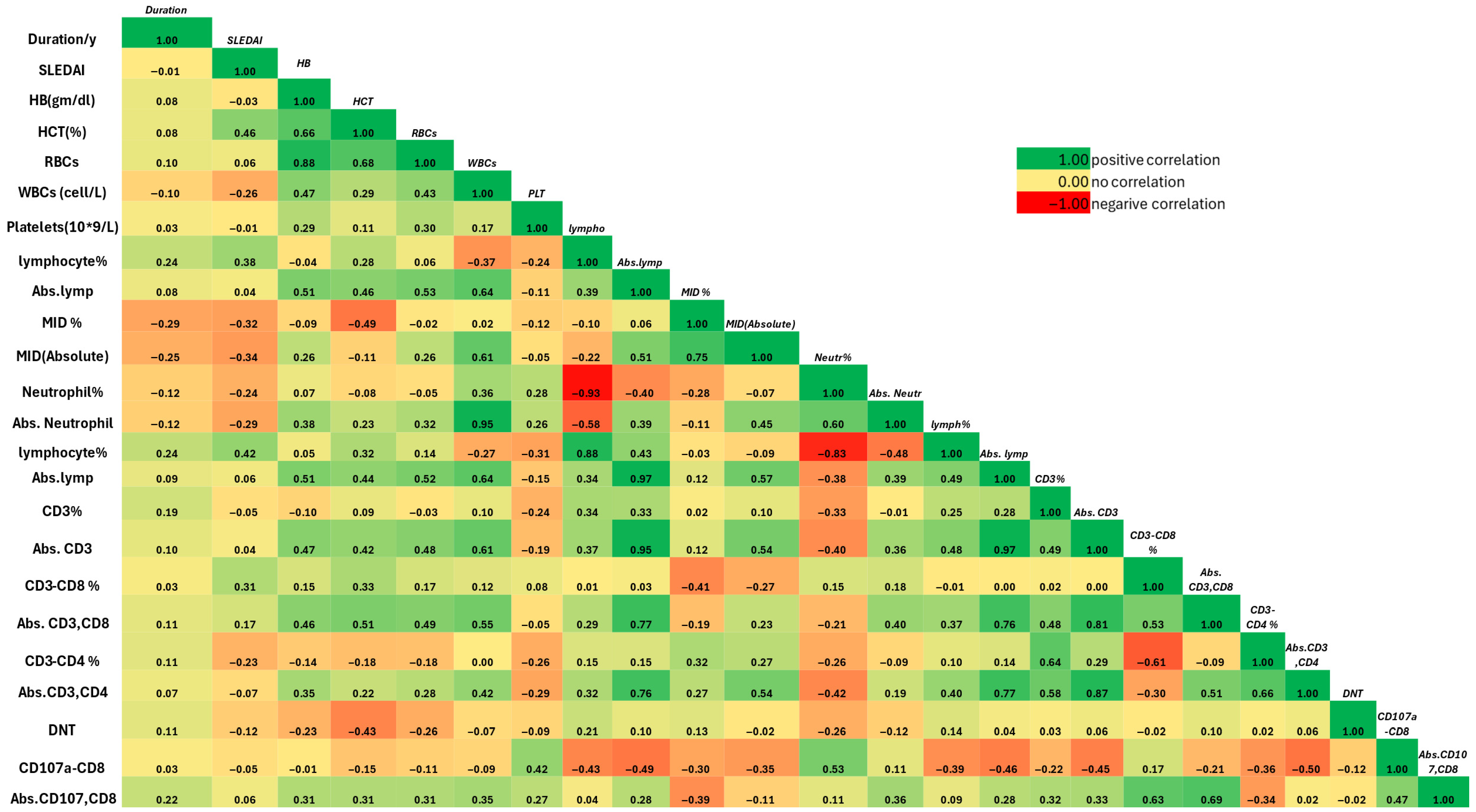
3.5. Association of T-Cell Subsets with Clinical and Laboratory Features of SLE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| NK cell | Natural Killer Cell |
| Reactome | Database of Curated Biological Pathways |
| CD28 | Cluster of Differentiation 28 |
| RAP1 | RAS-related Protein 1 |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte |
| CD107a (LAMP-1) | Lysosomal-Associated Membrane Protein 1 |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| ALK | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| CD8A/CD8B | CD8 Alpha and Beta Chains (Co-receptor Molecules on Cytotoxic T Cells) |
| PRF1 | Perforin 1 |
| GZMB | Granzyme B |
| NKG7 | Natural Killer Cell Granule Protein 7 |
| STRING | Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins |
| FS | Forward Scatter |
| SS | Side Scatter |
| ANA | Antinuclear Antibody |
| Anti-dsDNA | Anti–double-stranded DNA Antibody |
| RBC | Red Blood Cell |
| WBC | White Blood Cell |
| MID | Monocytes, Eosinophils, and Basophils: Intermediate Cell Population |
| CD3 | Cluster of Differentiation 3 |
| CD4 | Cluster of Differentiation 4 |
| CD8 | Cluster of Differentiation 8 |
| DNT | Double-Negative T Cell |
| SLEDAI | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DAMPs | Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| IL-17 | Interleukin-17 |
| CTLs | Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (plural form of CTL) |
| DNTs | Double-Negative T Cells (plural form of DNT) |
References
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Goyal, A.; Varacallo, M.A. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gheita, T.A.; Noor, R.A.; Abualfadl, E.; Abousehly, O.S.; El-Gazzar, I.I.; El Shereef, R.R.; Senara, S.; Abdalla, A.M.; Khalil, N.M.; ElSaman, A.M.; et al. Adult systemic lupus erythematosus in Egypt: The nation-wide spectrum of 3661 patients and world-wide standpoint. Lupus 2021, 30, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Miedany, Y.; Elhadidi, K.; Mahmoud, G.A.; Abu-Zaid, M.H.; Mahmoud, A.A.; El Gaafary, M.; Kamel, N.; Fathi, N.A.; Nasser, A.A.; Hassan, W.; et al. Egyptian recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: A consensus, evidence-based, clinical practice guidelines for treat-to-target management. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabil. 2023, 50, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eesa, N.N.; Nabi, H.A.; El Owaidy, R.; Khalifa, I.; Radwan, A.R.; NourEl-Din, A.M.; Amer, M.A.; ElShereef, R.R.; Hassan, E.; Ismail, F.; et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus children in Egypt: Homeland spectrum amid the global situation. Lupus 2021, 30, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadidi, K.T.; Medhat, B.M.; Baki, N.M.A.; Kafy, H.A.; Abdelrahaman, W.; Yousri, A.Y.; Attia, D.H.; Eissa, M.; El Dessouki, D.; Elgazzar, I.; et al. Characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus in a sample of the Egyptian population: A retrospective cohort of 1109 patients from a single center. Lupus 2018, 27, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzi, L.; Merville, P.; Deminière, C.; Moreau, J.; Combe, C.; Pellegrin, J.; Viallard, J.; Blanco, P. Predominance of CD8+ T lymphocytes among periglomerular infiltrating cells and link to the prognosis of class III and class IV lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohnen, A.; Chiang, S.C.; Stojanovic, A.; Schmidt, H.; Claus, M.; Saftig, P.; Janßen, O.; Cerwenka, A.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Watzl, C. Surface CD107a/LAMP-1 protects natural killer cells from degranulation-associated damage. Blood 2013, 122, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzewski, K.; Gil-Krzewska, A.; Nguyen, V.; Peruzzi, G.; Coligan, J.E. LAMP1/CD107a is required for efficient perforin delivery to lytic granules and NK-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 2013, 121, 4672–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiechmann, A.; Wilde, B.; Tyczynski, B.; Amann, K.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Kribben, A.; Lang, K.S.; Witzke, O.; Dolff, S. CD107a+ (LAMP-1) Cytotoxic CD8+ T-Cells in Lupus Nephritis Patients. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 556776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Zaki, H.; Hosny, M.; Fouad, M.; Moneim, N. Association of interleukin-36α gene expression in Egyptian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with organ involvement and disease activity. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2021, 28, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, M.; Orbai, A.; Alarcón, G.S.; Gordon, C.; Merrill, J.T.; Fortin, P.R.; Bruce, I.N.; Isenberg, D.; Wallace, D.J.; Nived, O.; et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Merrill, J.T.; Bombardieri, S. Assessment of Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Companion to Rheumatology; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Isenberg, D.A.; Castrejon, I. Measures of Adult Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Disease Activity and Damage. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiezzi, F.; Parker-Gaddis, K.L.; Cole, J.B.; Clay, J.S.; Maltecca, C. Pathways Identified by the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID Version 6.7) in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). 2015. Available online: https://datasetcatalog.nlm.nih.gov/dataset?q=0001923133 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Blanco, P.; Pitard, V.; Viallard, J.; Taupin, J.; Pellegrin, J.; Moreau, J. Increase in activated CD8+ T lymphocytes expressing perforin and granzyme B correlates with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispín, J.C.; Oukka, M.; Bayliss, G.; Cohen, R.A.; Van Beek, C.A.; Stillman, I.E.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Juang, Y.-T.; Tsokos, G.C. Expanded double negative T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus produce IL-17 and infiltrate the kidneys. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8761–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, H.; Rock, K.L. How dying cells alert the immune system to danger. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, M.R.; Koup, R. A Detection of T-cell degranulation: CD107a and b. Methods Cell Biol. 2004, 75, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buang, N.; Tapeng, L.; Gray, V.; Sardini, A.; Whilding, C.; Lightstone, L.; Cairns, T.D.; Pickering, M.C.; Behmoaras, J.; Ling, G.S.; et al. Type I interferons affect the metabolic fitness of CD8+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J. T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, M.R.; Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; De Rosa, S.C.; Douek, D.C.; Roederer, M.; Koup, R.A. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 281, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-M.; Tsokos, G.C. The role of CD8+ T-cell systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaech, S.M.; Wherry, E.J. Heterogeneity and cell-fate decisions in effector and memory CD8+ T cell differentiation during viral infection. Immunity 2007, 27, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, V.R.; Suarez-Fueyo, A.; Meidan, E.; Li, H.; Mizui, M.; Tsokos, G.C. Pathogenesis of Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cellular Perspective. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, N.; Niazy, M.H.; Kamal, A. Lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: Is it more than a laboratory finding? Egypt. Rheumatol. 2020, 42, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, L.; Palucka, A.K.; Arce, E.; Cantrell, V.; Borvak, J.; Banchereau, J.; Pascual, V. Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirou, K.A.; Kalliolias, G.D. A new tool for detection of type I interferon activation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaul, A.; Gordon, C.; Crow, M.K.; Touma, Z.; Urowitz, M.B.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hughes, G. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, A.; Gordon, C.; Crow, M.K.; Touma, Z.; Urowitz, M.B.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hughes, G. T-cell subsets in lesions of systemic and discoid lupus erythematosus. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1985, 12, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Qin, H.; Wu, H. Single-Cell Transcriptome Reveals the Heterogeneity of T Cells in Mice with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Neuronal Inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 11375–11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehar-Belaid, D.; Hong, S.; Marches, R.; Chen, G.; Bolisetty, M.; Baisch, J.; Walters, L.; Punaro, M.; Rossi, R.J.; Chung, C.-H.; et al. Mapping systemic lupus erythematosus heterogeneity at the single-cell level. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1094–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaks, Z.; Winans, T.; Caza, T.; Fernandez, D.; Liu, Y.; Landas, S.K.; Banki, K.; Perl, A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Liver and Antiphospholipid Antibody Production Precede Disease Onset and Respond to Rapamycin in Lupus-Prone Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2728–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; He, Z.; Ye, J.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; et al. Phenotypical changes and clinical significance of CD4+/CD8+ T cells in SLE. Lupus Sci. Med. 2022, 9, e000660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, E.F.; Lee, J.C.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Lyons, P.A.; Smith, K.G. T-cell exhaustion, co-stimulation and clinical outcome in autoimmunity and infection. Nature 2015, 523, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Variable | Cases (n = 40) | Controls (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | Age mean ± SD | 35.28 ± 7.18 | 32.90 ± 8.86 | 0.192 |
| Sex (M/F) | (6/34) | (4/36) | 0.499 | |
| Family history, (yes/no) | 27/13 | – | ||
| Disease duration (years), mean ± SD | 7.81 ± 4.15 | – | ||
| Disease activity | SLEDAI score, mean ± SD 2 3 4 | 14.75 ± 5.12 6 24 10 | – | |
| Clinical manifestations | Nephritis | 27 (67.5%) | – | – |
| Photosensitivity | 23 (57.5%) | – | – | |
| Hair loss | 20 (50.0%) | – | – | |
| Oral ulcers | 27 (67.5%) | – | – | |
| Discoid rash | 4 (10.0%) | – | – | |
| Malar rash | 32 (80.0%) | – | – | |
| Musculoskeletal involvement | 28 (70.0%) | – | – | |
| CNS involvement | 5 (12.5%) | – | – | |
| Visual manifestations | 1 (2.5%) | – | – | |
| Serous membranes involvement | 7 (17.5%) | – | – | |
| Vasculitis | 3 (7.5%) | – | – | |
| Proteinuria | 25 (62.5%) | – | – | |
| Hematological abnormality | 18 (45.0%) | – | – | |
| Anemia | 20 (50.0%) | – | – | |
| Leucopenia | 6 (15.0%) | – | – | |
| Thrombocytopenia | 9 (22.5%) | – | – | |
| Serology | ANA positivity | 40 (100.0%) | – | – |
| Anti-dsDNA | 32 (80.0%) | – | – | |
| Anti-phospholipid antibodies | 5 (12.5%) | – | – | |
| C3 consumed | 29 (72.5%) | – | – | |
| C4 consumed | 32 (80.0%) | – | – | |
| Treatment | Steroids | 40 (100.0%) | – | – |
| Hydroxychloroquine | 40 (100.0%) | – | – | |
| Azathioprine | 24 (60.0%) | – | – | |
| Mycophenolate | 10 (25.0%) | – | – | |
| Cyclophosphamide | 6 (15.0%) | – | – |
| Category (Mean ± SD) | Variable | Cases (n = 40) | Controls (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBC parameters | Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.92 ± 1.21 | 12.69 ± 0.72 | 0.001 * |
| HCT (%) | 38.06 ± 4.08 | 38.09 ± 2.27 | 0.965 | |
| RBC count (×106/µL) | 4.12 ± 0.51 | 4.30 ± 0.25 | 0.049 * | |
| WBC count (×103/µL) | 7.31 ± 2.98 | 7.81 ± 1.83 | 0.314 | |
| Platelets (×103/µL) | 240.9 ± 102.5 | 296.9 ± 89.38 | 0.011 * | |
| Lymphocyte Lymphocytes (%) | 1 (AO) | 27.21 ± 10.45 | 31.0 ± 8.88 | 0.07 |
| 2 (AV) | 26.09 ± 10.64 | 28.45 ± 8.60 | 0.227 | |
| Absolute Lymphocytes | 1 (AP) | 1875.8 ± 817.9 | 2339.8 ± 701.7 | 0.028 * |
| 2 (AW) | 1822.9 ± 855.2 | 2143.6 ± 672.3 | 0.108 | |
| Differential count | MID (%) | 8.15 ± 4.09 | 8.15 ± 3.48 | 0.847 |
| Absolute MID cell/L | 597.9 ± 336.5 | 632.1 ± 311.7 | 0.722 | |
| Neutrophil (%) | 64.64 ± 10.82 | 60.85 ± 9.53 | 0.214 | |
| Absolute Neutrophil | 4836.3 ± 2358.0 | 4858.7 ± 1594.8 | 0.644 |
| Parameter (Mean ± SD) | Cases (n = 40) | Control (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD3 (%) | 75.05 ± 11.85 | 64.93 ± 11.33 | <0.001 * |
| Absolute CD3 | 1395.4 ± 722.2 | 1425.4 ± 579.7 | 0.9 |
| CD3+CD8+ (%) | 34.62 ± 12.34 | 26.91 ± 6.72 | 0.001 * |
| Absolute CD3+CD8+ | 483.4 ± 270.4 | 390.5 ± 181.6 | <0.001 * |
| CD3+CD4+ (%) | 31.92 ± 14.42 | 68.78 ± 7.56 | <0.001 * |
| Absolute CD3+CD4+ | 474.4 ± 370.1 | 5.01 ± 3.88 | <0.001 * |
| DNT | 6.42 ± 1.80 | 4.31 ± 3.91 | <0.001 * |
| CD107a+CD8+ (%) | 3.45 ± 1.77 | 2.03 ± 0.59 | <0.001 * |
| Absolute CD107a+CD8+ | 15.69 ± 12.46 | 7.90 ± 4.48 | 0.002 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AbdelMaogood, A.K.K.; Tawfik, M.G.; Khattab, S.; Attea, H.A.; Abdellatif, H.A.A.; Hosny, N.; Askar, A.M. Immunophenotypic Characterization of LAMP-1 on Cytotoxic T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Its Correlation with Disease Activity. Immuno 2025, 5, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040056
AbdelMaogood AKK, Tawfik MG, Khattab S, Attea HA, Abdellatif HAA, Hosny N, Askar AM. Immunophenotypic Characterization of LAMP-1 on Cytotoxic T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Its Correlation with Disease Activity. Immuno. 2025; 5(4):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040056
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelMaogood, Asmaa K. K., Marwa G. Tawfik, Sally Khattab, Heba A. Attea, Hidi A. A. Abdellatif, Nora Hosny, and Aya Mohamed Askar. 2025. "Immunophenotypic Characterization of LAMP-1 on Cytotoxic T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Its Correlation with Disease Activity" Immuno 5, no. 4: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040056
APA StyleAbdelMaogood, A. K. K., Tawfik, M. G., Khattab, S., Attea, H. A., Abdellatif, H. A. A., Hosny, N., & Askar, A. M. (2025). Immunophenotypic Characterization of LAMP-1 on Cytotoxic T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Its Correlation with Disease Activity. Immuno, 5(4), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040056






