Impact of Major Pelvic Ganglion Denervation on Prostate Histology, Immune Response, and Serum Prolactin and Testosterone Levels in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Groups and Surgical Procedures
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Tissue Collection
2.5. Dissociation of Prostate Tissue
2.6. Quantification of Serum Interleukins, Prolactin, and Testosterone
2.7. Characterization of Immune Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
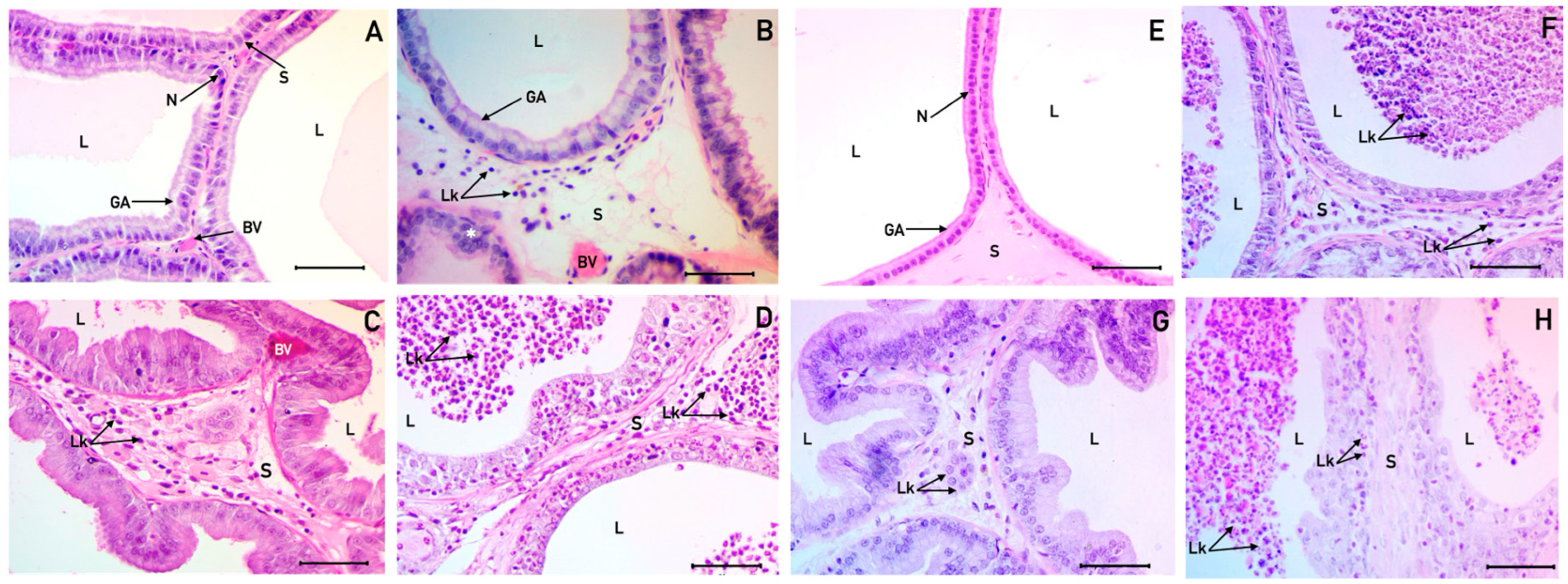
3.1. Histological Description of the Ventral and Dorsolateral Prostate
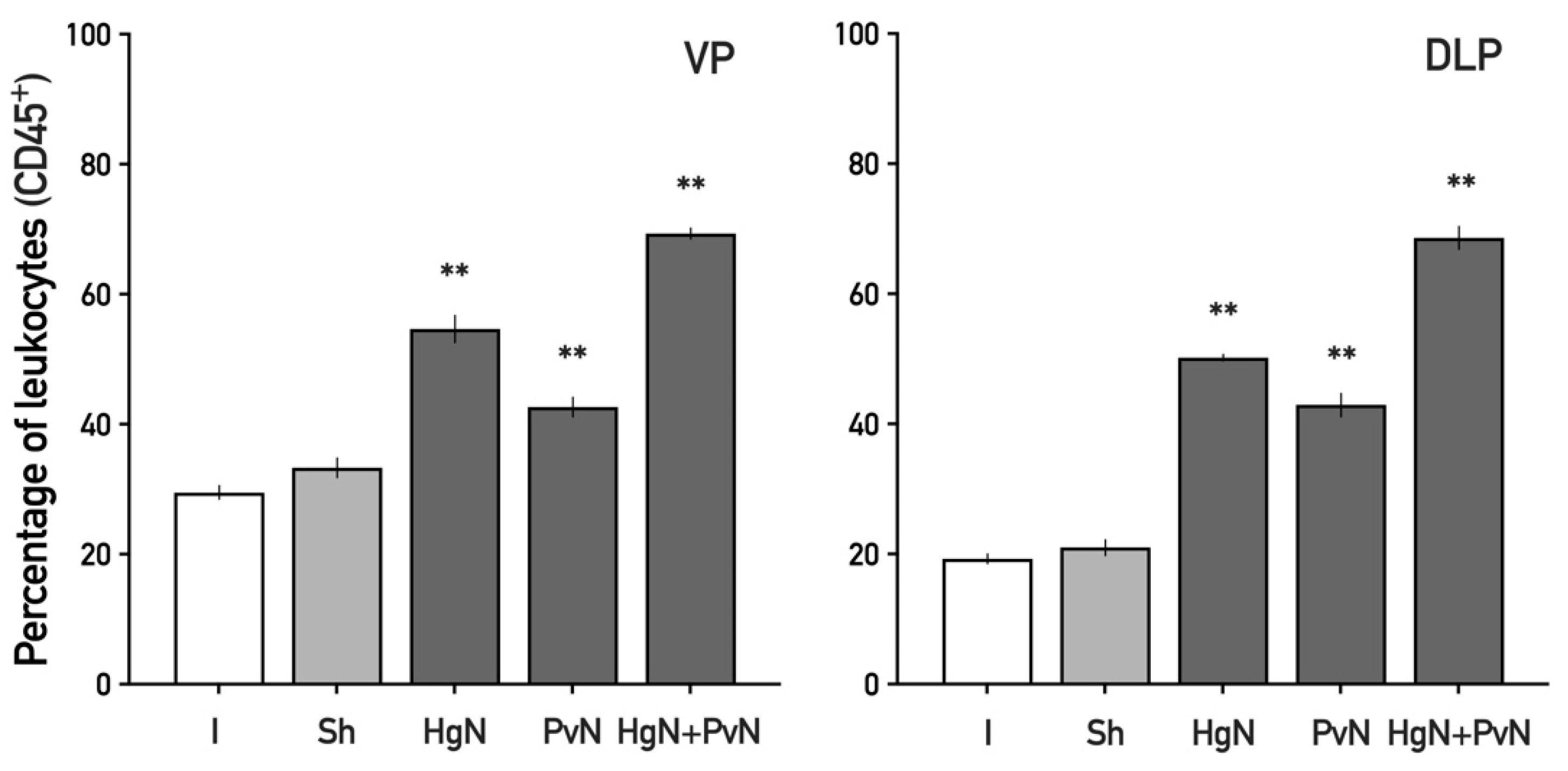
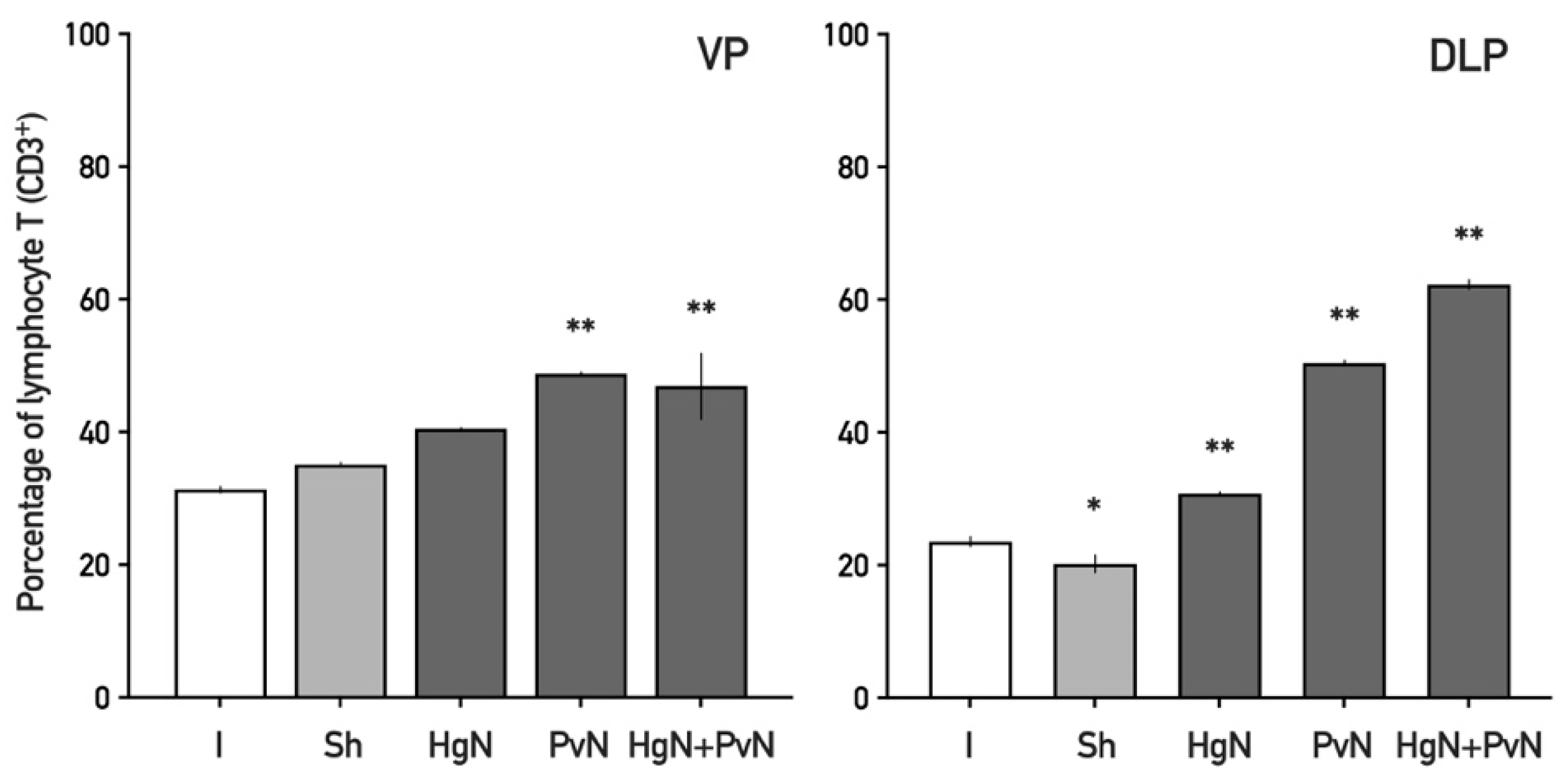
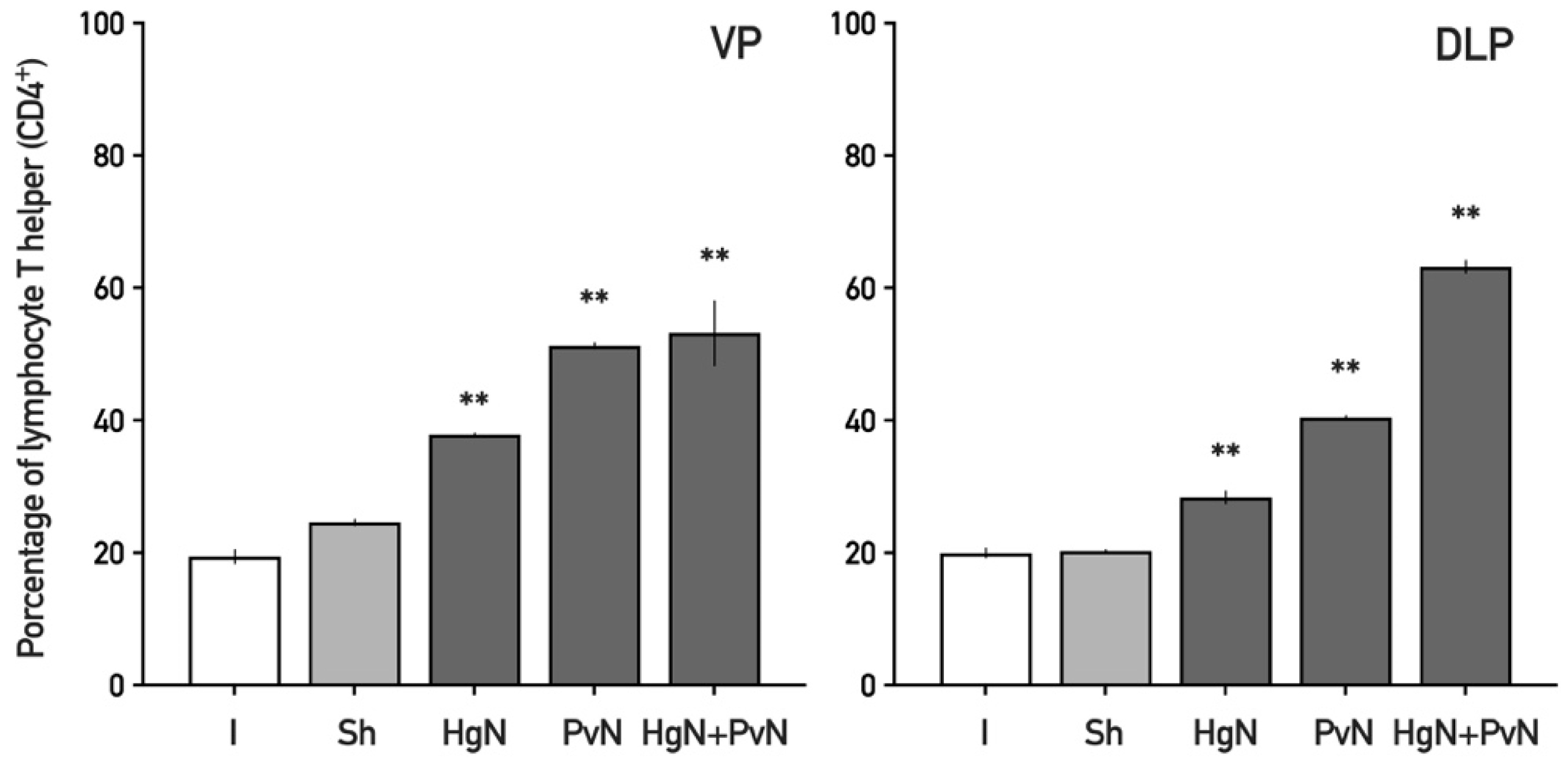
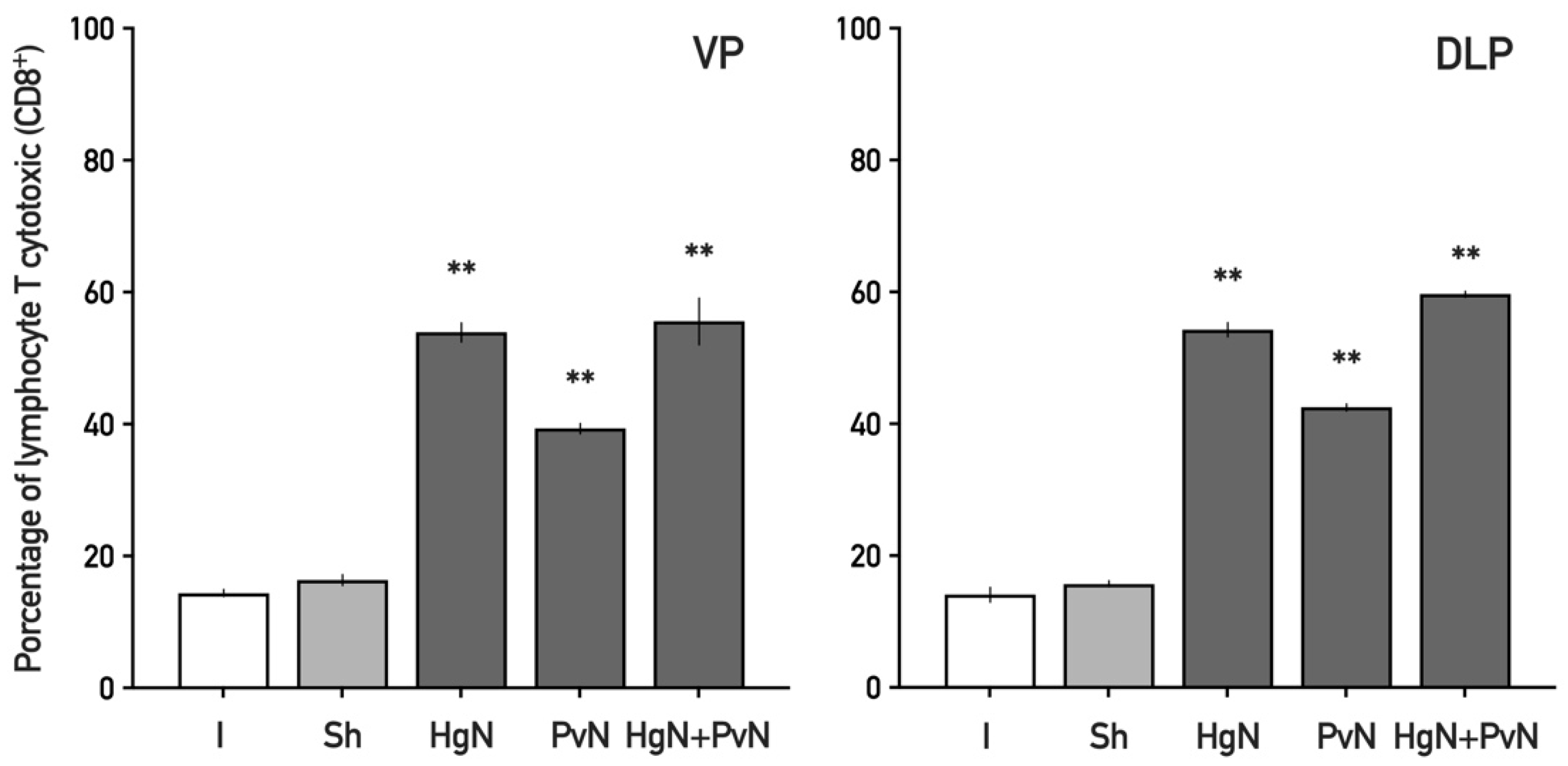
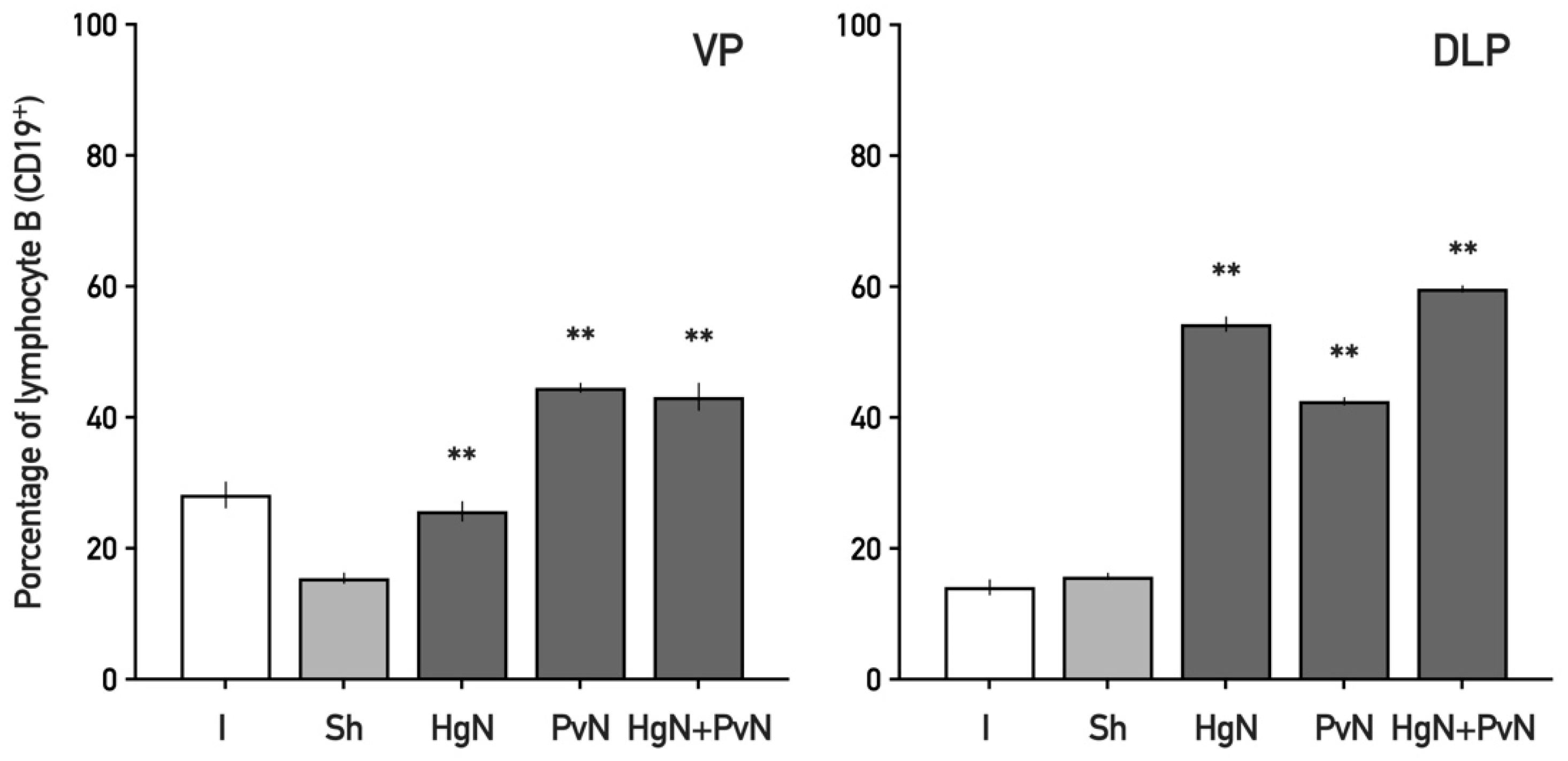
3.2. Immune Cell Infiltration in the Ventral and Dorsolateral Prostate
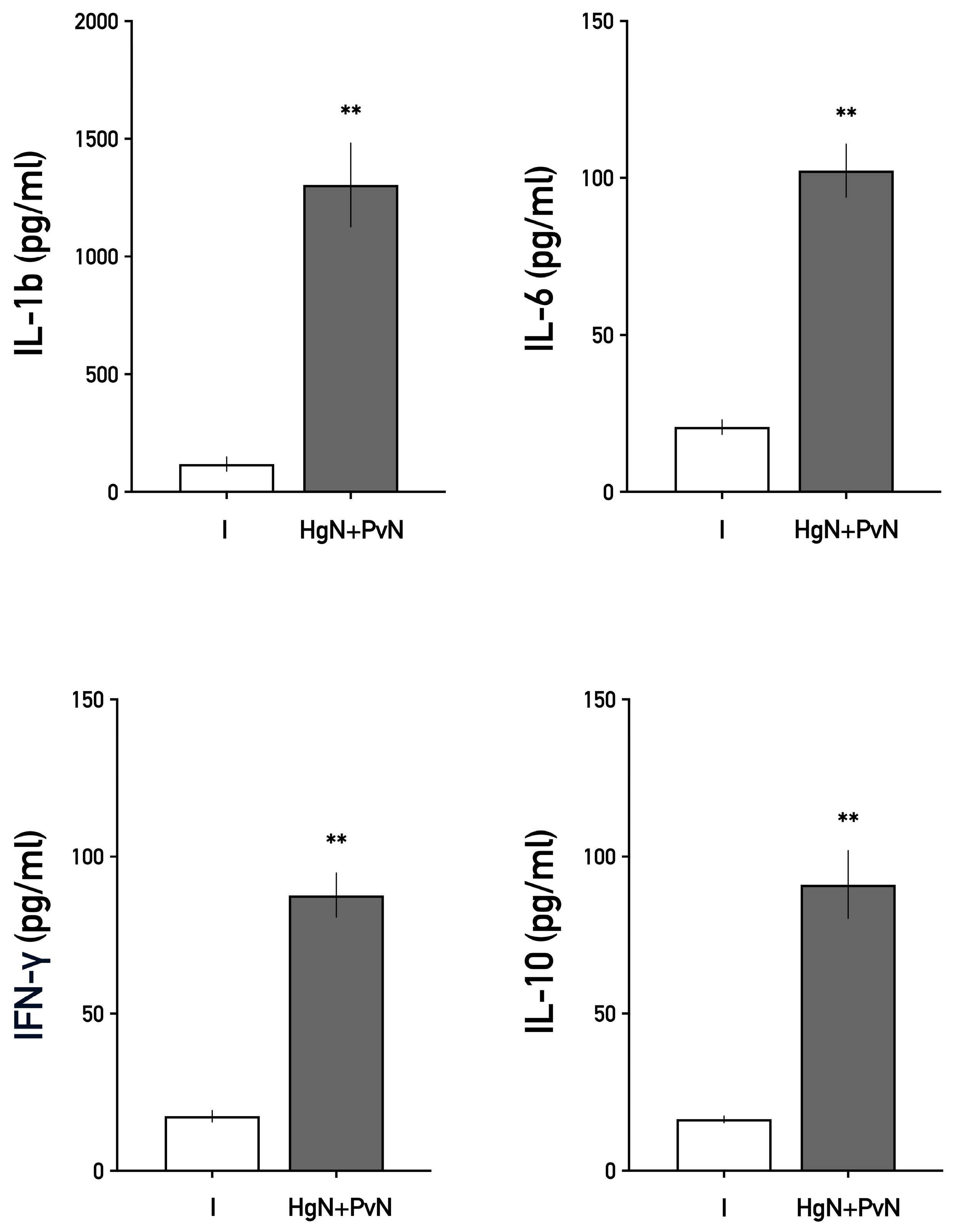
3.3. Systemic Levels of Interleukins
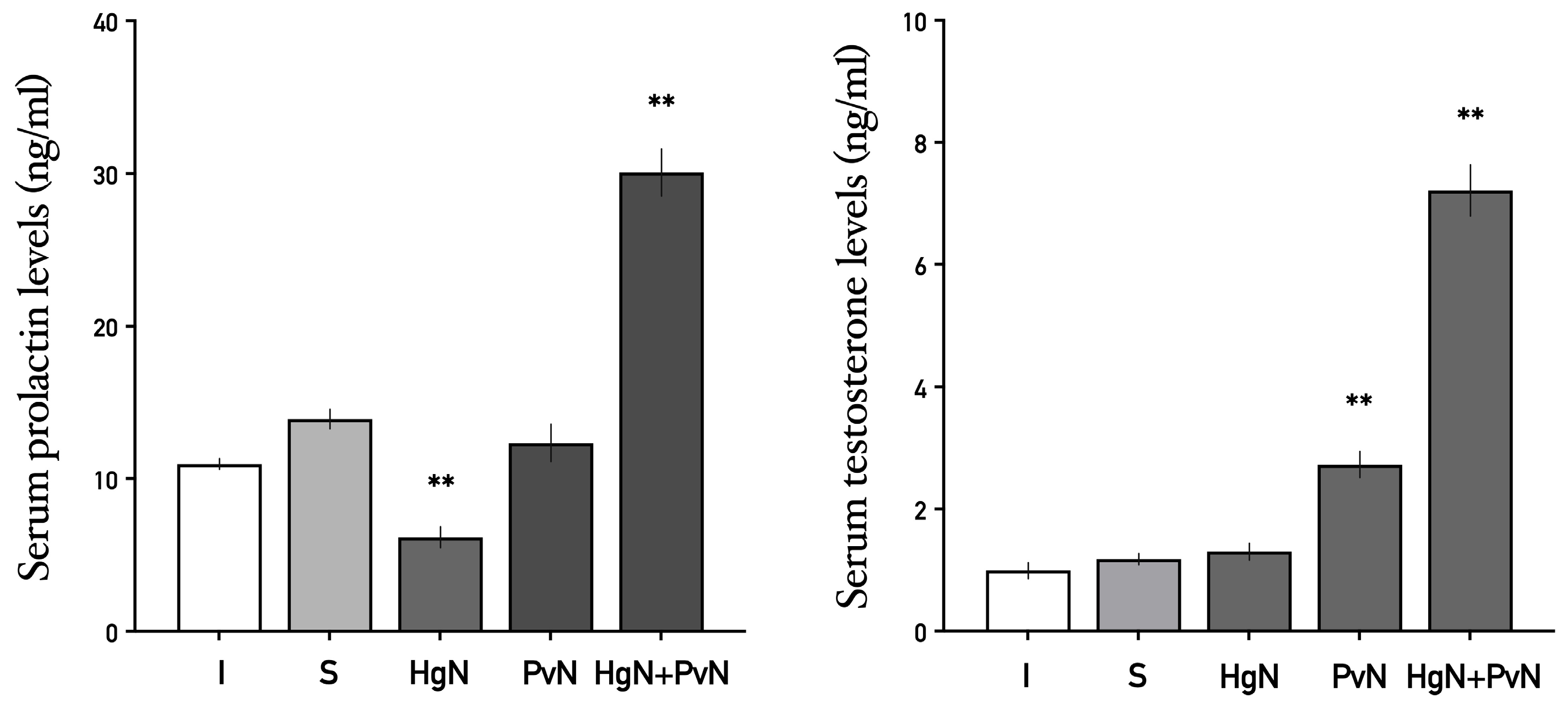
3.4. Systemic Levels of Prolactin and Testosterone
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Denervation on Prostate Histology
4.2. Enhanced Immune Cell Infiltration and Inflammatory Response
4.3. Elevated Systemic Cytokine Levels
4.4. Alterations in Serum Prolactin and Testosterone Levels
4.5. Interplay Between Neural Regulation, Hormones, and Immune Responses
4.6. Implications for Prostate Diseases and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPH | Bening Prostatic Hyperplasia |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| CICUAL | Comité Interno para el Uso y Cuidado de Animales de Laboratorio |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunoabsorbent Assay |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| Hg | Hypogastric Nerve |
| MPG | Mayor Pelvic Ganglion |
| Pv | Pelvic Nerve |
| INF-γ | Interferon Gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
References
- Lotti, F.; Maggi, M. Sexual dysfunction and male infertility. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landa-García, J.N.; Palacios-Arellano, M.d.l.P.; Morales, M.A.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Toledo-Cárdenas, M.R.; Suárez-Medellín, J.M.; Coria-Avila, G.A.; Manzo, J.; et al. The Anatomy, Histology, and Function of the Major Pelvic Ganglion. Animals 2024, 14, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hérnandez-Aguilar, M.E.; Aranda-Abreu, G.; Rojas-Durán, F. Neuroendocrine and molecular aspects of the physiology and pathology of the prostate. In Behavioral Neuroendocrinology, 1st ed.; Komisaruk, B., González-Mariscal, G., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 263–277. ISBN 9781498731911. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Zavaleta, V.; Mateos-Moreno, A.; Cruz-Rivas, V.H.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Vázquez-Narváez, E.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Suárez-Medellín, J.; Manzo-Denes, J.; Toledo-Cárdenas, M.R.; et al. Contribución del sistema nervioso autónomo y la conducta sexual en la fisiopatología de la próstata. eNeurobiologia 2021, 12, 180221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, K.M. Male Accessory Sex Glands. In Boorman’s Pathology of the Rat: Reference Atlas; Suttie, A.W., Boorman, G.A., Leininger, J.R., Eustis, S.L., Elwell, M.R., MacKenzie, W.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, D. The fine structure and histochemistry of prostatic glands in relation to sex hormones. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1966, 20, 207–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darras, F.S.; Lee, C.; Huprikar, S.; Rademaker, A.W.; Grayhack, J.T. Evidence for a non-androgenic role of testis and epididymis in androgen-supported growth of the rat ventral prostate. J. Urol. 1992, 148, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, W.C.; Hamilton, D.W. The effect of experimentally induced diabetes on the metabolism of glucose by seminiferous tubules and epididymal spermatozoa from the rat. Endocrinology 1984, 115, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriole, G.; Bruchovsky, N.; Chung, L.W.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Rittmaster, R.; Roehrborn, C.; Russell, D.; Tindall, D. Dihydrotestosterone and the prostate: The scientific rationale for 5alpha-reductase inhibitors in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.W.; Cunha, G.R. Stromal-epithelial interactions: II. Regulation of prostatic growth by embryonic urogenital sinus mesenchyme. Prostate 1983, 4, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindblom, J.; Dillner, K.; Ling, C.; Törnell, J.; Wennbo, H. Progressive prostate hyperplasia in adult prolactin transgenic mice is not dependent on elevated serum androgen levels. Prostate 2002, 53, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevalainen, M.T.; Valve, E.M.; Ingleton, P.M.; Nurmi, M.; Martikainen, P.M.; Harkonen, P.L. Prolactin and prolactin receptors are expressed and functioning in human prostate. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Aguilar, M.E.; Serrano, M.K.; Pérez, F.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E.; Sanchez, V.; Mateos, A.; Manzo, J.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Cruz-Gomez, Y.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D. Quantification of neural and hormonal receptors at the prostate of long-term sexual behaving male rats after lesion of pelvic and hypogastric nerves. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 222, 112915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Moreno, A.; Sánchez-Zavaleta, V.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Manzo, J.; Suárez-Medellín, J.; Toledo, M.R.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E. Effect of preganglionar denervation on the expression of adrenergic, muscarinic, androgen, and prolactin receptors at the major pelvic ganglion of long-term sexual behaving male rats. eNeurobiologia 2021, 12, 050321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyprianou, N.; Tu, H.; Jacobs, S.C. Apoptotic versus proliferative activities in human benign prostatic hyperplasia. Hum. Pathol. 1996, 27, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marzo, A.M.; Nakai, Y.; Nelson, W.G. Inflammation, atrophy, and prostate carcinogenesis. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2007, 25, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfanos, K.S.; Isaacs, W.B.; Marzo, A.M. Infections and inflammation in prostate cancer. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2013, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sfanos, K.S.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Nelson, W.G.; De Marzo, A.M. The inflammatory microenvironment and microbiome in prostate cancer development. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 15, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, M.T.; Möller, A.; Smyth, M.J. Inflammation and immune surveillance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 2012, 608406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fibbi, B.; Penna, G.; Morelli, A.; Adorini, L.; Maggi, M. Chronic inflammation in the pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haverkamp, J.; Charbonneau, B.; Ratliff, T.L. Prostate inflammation and its potential impact on prostate cancer: A current review. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 3, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Goldstein, A.S. Inflammation promotes prostate differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1666–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, G.; Fibbi, B.; Amuchastegui, S.; Cossetti, C.; Aquilano, F.; Laverny, G.; Gacci, M.; Crescioli, C.; Maggi, M.; Adorini, L. Human Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Stromal Cells as Inducers and Targets of Chronic Immuno-Mediated Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4056–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfanos, K.S.; De Marzo, A.M. Prostate cancer and inflammation: The evidence. Histopathology 2012, 60, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Yu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Fan, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q.; et al. The inflammation patterns of different inflammatory cells in histological structures of hyperplasic prostatic tissues. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 13, 842008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolnik, M.D.; Servandio, C.; Abramovici, A. Comparative studyof experimental induced bening and atypical hyperplasia in the ventral prostate of different rat strains. J. Od Androl. 1994, 15, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; McKenna, K.E.; McVary, K.T.; Lee, C. Requirement of Innervation for Maintenance of Structural and Functional Integrity in the Rat Prostate. Biol. Reprod. 1991, 44, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Piñeiro, L.; Dahiya, R.; Nunes, L.L.; Tanagho, E.A.; Schmidt, R.A. Pelvic Plexus Denervation in Rats Causes Morphologic and Functional Changes of the Prostate. J. Urol. 1993, 150, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVary, K.T.; McKenna, K.E.; Lee, C. Prostate innervation. Prostate 1998, 36, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Huang, J.T. Neuroendocrine cells of prostate cancer: Biologic functions and molecular mechanisms. Asian J. Androl. 2019, 21, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luján, M.; Páez, A.; Llanes, L.; Angulo, J.; Berenguer, A. Role of autonomic innervation in rat prostatic structure maintenance: A morphometric analysis. J. Urol. 1998, 160, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomb, E.; Kruglikova, A.; Dvir, D.; Parnes, N.; Abramovici, A. Induction of atypical prostatic hyperplasia in rats by sympathomimetic stimulation. Prostate 1998, 34, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, D.E. Tensegrity II. How structural networks influence cellular information processing networks. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulou, V.; Pediaditakis, I.; Alkahtani, S.; Alarifi, S.A.; Schmidt, E.M.; Lang, F.; Gravanis, A.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Stournaras, C. Differential effects of dehydroepiandrosterone and testosterone in prostate and colon cancer cell apoptosis: The role of nerve growth factor (NGF) receptors. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2446–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulombe, P.A.; Wong, P. Cytoplasmic intermediate filaments revealed as dynamic and multipurpose scaffolds. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetzl, A.C.; Montico, F.; Kido, L.A.; Cagnon, V.H. Prolactin, EGFR, vimentin and α-actin profiles in elderly rat prostate subjected to steroid hormonal imbalance. Tissue Cell 2016, 48, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Thraves, P.; Kuettel, M.; Dritschilo, A. Cytoskeletal and adhesion protein changes during neoplastic progression of human prostate epithelial cells. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 1998, 1, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.H.; Frame, F.M.; Collins, A.T. Prostate cancer stem cells. J. Pathol. 2009, 217, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.L.; Scarth, J.A.; Patterson, M.R.; Wasson, C.W.; Hemingway, G.C.; Barba-Moreno, D.; Macdonald, A. E6-mediated activation of JNK drives EGFR signalling to promote proliferation and viral oncoprotein expression in cervical cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1669–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sadacharan, S.; Su, S.; Belldegrun, A.; Persad, S.; Singh, G. Overexpression of vimentin: Role in the invasive phenotype in an androgen-independent model of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2306–2311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, C.; Cui, K.; Xiong, T.; Chen, Z. Chronic inflammation promotes proliferation in the prostatic stroma in rats with experimental autoimmune prostatitis: Study for a novel method of inducing benign prostatic hyperplasia in a rat model. World J. Urol. 2020, 11, 2933–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Kwon, O.-J.; Henry, G.; Malewska, A.; Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; Brinkley, W.; Zhang, Y.; Castro, P.D.; Titus, M.; et al. Non-Cell-Autonomous Regulation of Prostate Epithelial Homeostasis by Androgen Receptor. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leenders, G.J.; Gage, W.R.; Hicks, J.L.; van Balken, B.; Aalders, T.W.; Schalken, J.A.; De Marzo, A.M. Intermediate cells in human prostate epithelium are enriched in proliferative inflammatory atrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anim, J.T.; Udo, C.; John, B. Characterisation of inflammatory cells in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Acta Histochem. 1998, 100, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, G.; Mitteregger, D.; Marberger, M. Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) an Immune Inflammatory Disease? Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindborg, J.A.; Niemi, J.P.; Howarth, M.A.; Liu, K.W.; Moore, C.Z.; Mahajan, D.; Zigmond, R.E. Molecular and cellular identification of the immune response in peripheral ganglia following nerve injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vykhovanets, E.V.; Resnick, M.I.; Marengo, S.R. The healthy rat prostate contains high levels of natural killer-like cells and unique subsets of cd4+ helper-inducer t cells: Implications for prostatitis. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrogeorgiou, M.; Chatzikalil, E.; Theocharis, S.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Peoc’h, M.; Mobarki, M.; Karpathiou, G. The immune microenvironment of cancer of the uterine cervix. Histol. Histopathol. 2024, 39, 1245–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinger, D.L.; Lorton, D. Autonomic regulation of cellular immune function. Auton. Neurosci. 2014, 182, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourshargh, S.; Alon, R. Leukocyte Migration into Inflamed Tissues. Immunity 2014, 41, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.J. Inflammation: Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat. Res. 2008, 659, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunkel, S.L.; Standiford, T.; Kasahara, K.; Strieter, R.M. Interleukin-8 (IL-8): The major neutrophil chemotactic factor in the lung. Exp. Lung Res. 1991, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neveu, B.; Moreel, X.; Deschênes-Rompré, M.P.; Bergeron, A.; LaRue, H.; Ayari, C.; Fradet, Y.; Fradet, V. IL-8 secretion in primary cultures of prostate cells is associated with prostate cancer aggressiveness. Res. Rep. Urol. 2014, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kooten, G.; Banchereau, J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beadling, C.; Slifka, M.K. Regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by the related cytokines IL-12, IL-23, and IL-27. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2006, 54, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, Q.; Ding, Y.; Tang, Z.; Tan, P.; Lin, T.; Guo, D.; Qiu, S. Toll-like receptor 10 (TLR10) exhibits suppressive effects on inflammation of prostate epithelial cells. Asian J. Androl. 2019, 21, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambara, G.; De Cesaris, P.; De Nunzio, C.; Ziparo, E.; Tubaro, A.; Filippini, A.; Riccioli, A. Toll-like receptors in prostate infection and cancer between bench and bedside. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintar, A.A.; Roth, F.D.; De Paul, A.L.; Aoki, A.; Maldonado, C.A. Toll-Like Receptor 4 in Rat Prostate: Modulation by Testosterone and Acute Bacterial Infection in Epithelial and Stromal Cells. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 75, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.G.; Xu, Z.Q. Impact of immune inflammation on the proliferation and apoptosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia cells. Nat. J. Androl. 2021, 27, 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, T.; Livas, L.; Kyprianou, N. Inflammation in prostate cancer progression and therapeutic targeting. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voronov, E.; Shouval, D.S.; Krelin, Y.; Cagnano, E.; Benharroch, D.; Iwakura, Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; Apte, R.N. IL-1 is required for tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Zhang, X. Interleukin-10: New perspectives on an old cytokine. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 226, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzrock, R. Cytokine deregulation in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2001, 55, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiñska, J.; Kowalska, M.M.; Nowacki, M.P.; Chwaliñski, M.G.; Rysiñska, A.; Fuksiewicz, M. CRP, TNFα, IL-1ra, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-30 in blood serum of colorectal cancer patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2000, 6, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiró, N.; Bermudez-Fernandez, S.; Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Atienza, S.; Beridze, N.; Escaf, S.; Vizoso, F.J. Analysis of the expression of interleukins, interferon β, and nuclear factor-κ B in prostate cancer and their relationship with biochemical recurrence. J. Immunother. 2014, 37, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlot, E.; Moze, E.; Dantzer, R.; Neveu, P.J. Cytokine Production by Spleen Cells after Social Defeat in Mice: Activation of T Cells and Reduced Inhibition by Glucocorticoids. Stress 2004, 7, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, B.; Zoccali, C. Spleen IL-10, a key player in obesity-driven renal risk. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borba, V.V.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. Prolactin and autoimmunity: The hormone as an inflammatory cytokine. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, M.; Basaria, S.; Ceda, G.P.; Ble, A.; Ling, S.M.; Bandinelli, S.; Valenti, G.; Ferrucci, L. The relationship between testosterone and molecular markers of inflammation in older men. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2005, 28, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zermann, D.H.; Ishigooka, M.; Doggweiler, R.; Schubert, J.; Schmidt, R.A. Central nervous system neurons labeled following the injection of pseudorabies virus into the rat prostate gland. Prostate 2000, 44, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Giuliano, F.; Yaici, E.; Conrath, M.; Trassard, O.; Benoit, G.; Vergé, D. Identification of lumbar spinal neurons controlling simultaneously the prostate and the bulbospongiosus muscles in the rat. Neuroscience 2006, 138, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaïci, E.D.; Rampin, O.; Tang, Y.; Calas, A.; Jestin, A.; Leclerc, P.; Benoit, G.; Giuliano, F. Catecholaminergic projections onto spinal neurons destined to the pelvis including the penis in rat. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2002, 14, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, M.E.; Clapp, C.; de la Escalera, G.M.; Torner, L.M. Dopamine escape potentiation of prolactin release may involve the activation of calcium channels by protein kinases A y C. Neuroendocrinology 1994, 2, 779–786. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- De Marzo, A.M.; Platz, E.A.; Sutcliffe, S.; Xu, J.; Grönberg, H.; Drake, C.G.; Nakai, Y.; Isaacs, W.B.; Nelson, W.G. Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becerra-Romero, P.S.; Fernández-Pomares, C.; Rodríguez-Alba, J.C.; Manzo, J.; Aranda-Abreu, G.E.; Rojas-Durán, F.; Herrera-Covarrubias, D.; Toledo-Cárdenas, M.R.; Coria-Ávila, G.A.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.E. Impact of Major Pelvic Ganglion Denervation on Prostate Histology, Immune Response, and Serum Prolactin and Testosterone Levels in Rats. Immuno 2025, 5, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030033
Becerra-Romero PS, Fernández-Pomares C, Rodríguez-Alba JC, Manzo J, Aranda-Abreu GE, Rojas-Durán F, Herrera-Covarrubias D, Toledo-Cárdenas MR, Coria-Ávila GA, Hernández-Aguilar ME. Impact of Major Pelvic Ganglion Denervation on Prostate Histology, Immune Response, and Serum Prolactin and Testosterone Levels in Rats. Immuno. 2025; 5(3):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecerra-Romero, Pabeli Saraí, Cynthia Fernández-Pomares, Juan Carlos Rodríguez-Alba, Jorge Manzo, Gonzalo E. Aranda-Abreu, Fausto Rojas-Durán, Deissy Herrera-Covarrubias, María Rebeca Toledo-Cárdenas, Genaro Alfonso Coria-Ávila, and Maria Elena Hernández-Aguilar. 2025. "Impact of Major Pelvic Ganglion Denervation on Prostate Histology, Immune Response, and Serum Prolactin and Testosterone Levels in Rats" Immuno 5, no. 3: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030033
APA StyleBecerra-Romero, P. S., Fernández-Pomares, C., Rodríguez-Alba, J. C., Manzo, J., Aranda-Abreu, G. E., Rojas-Durán, F., Herrera-Covarrubias, D., Toledo-Cárdenas, M. R., Coria-Ávila, G. A., & Hernández-Aguilar, M. E. (2025). Impact of Major Pelvic Ganglion Denervation on Prostate Histology, Immune Response, and Serum Prolactin and Testosterone Levels in Rats. Immuno, 5(3), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030033










