Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis in Greek Patients with Predominantly Antibody Deficiencies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic and Genetic Analysis
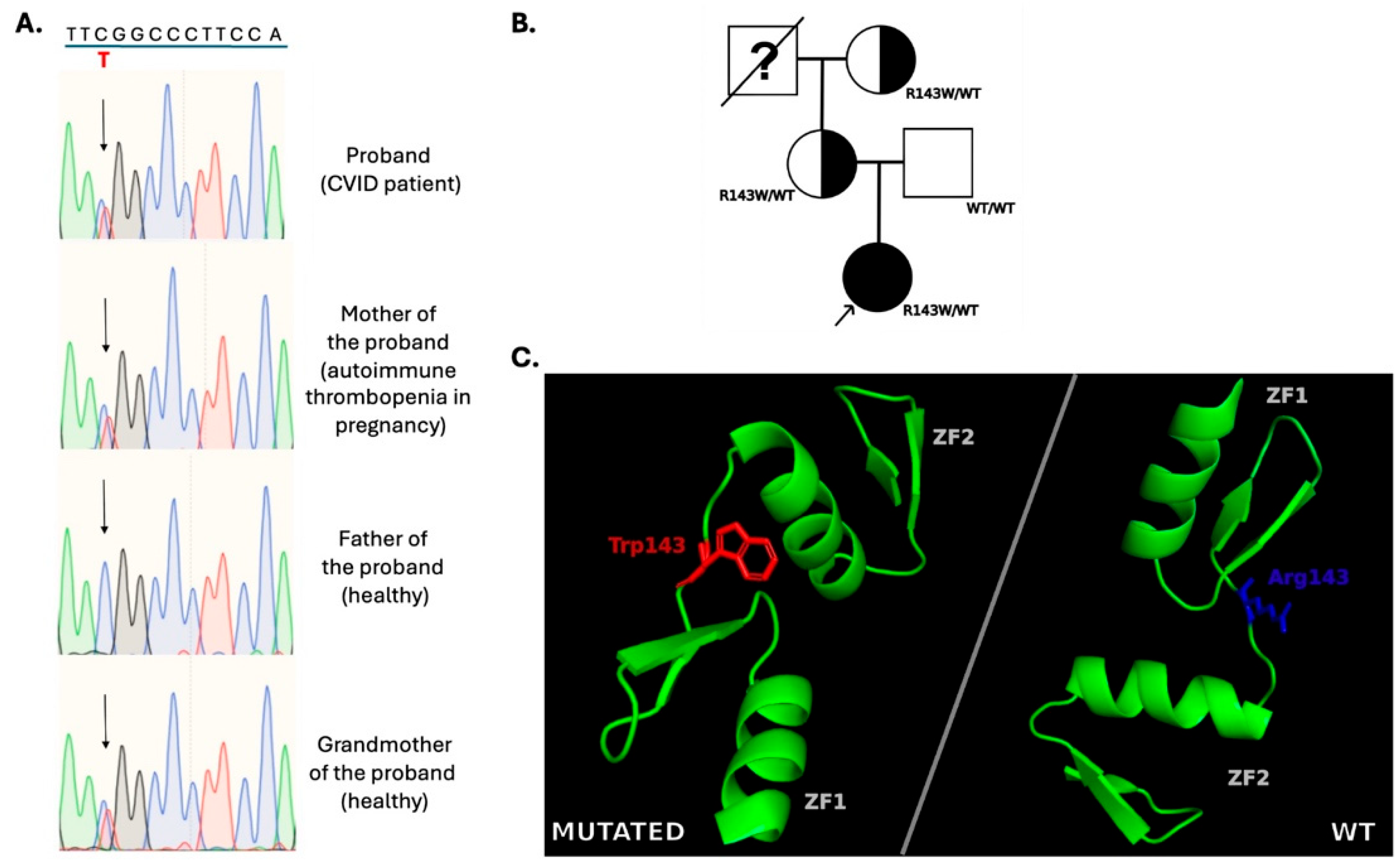
2.4. Sanger Sequencing Validation and Family Testing
3. Results
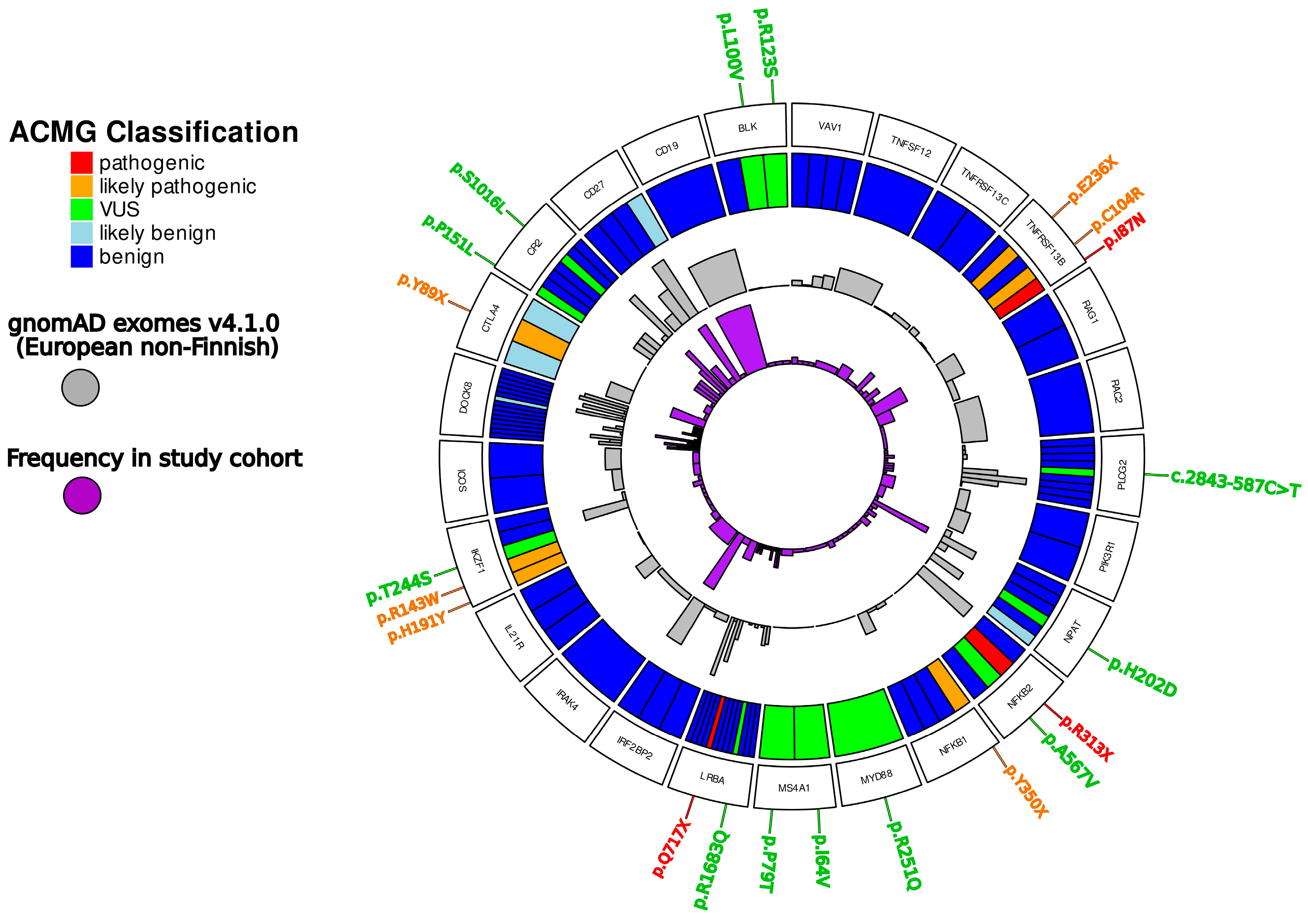
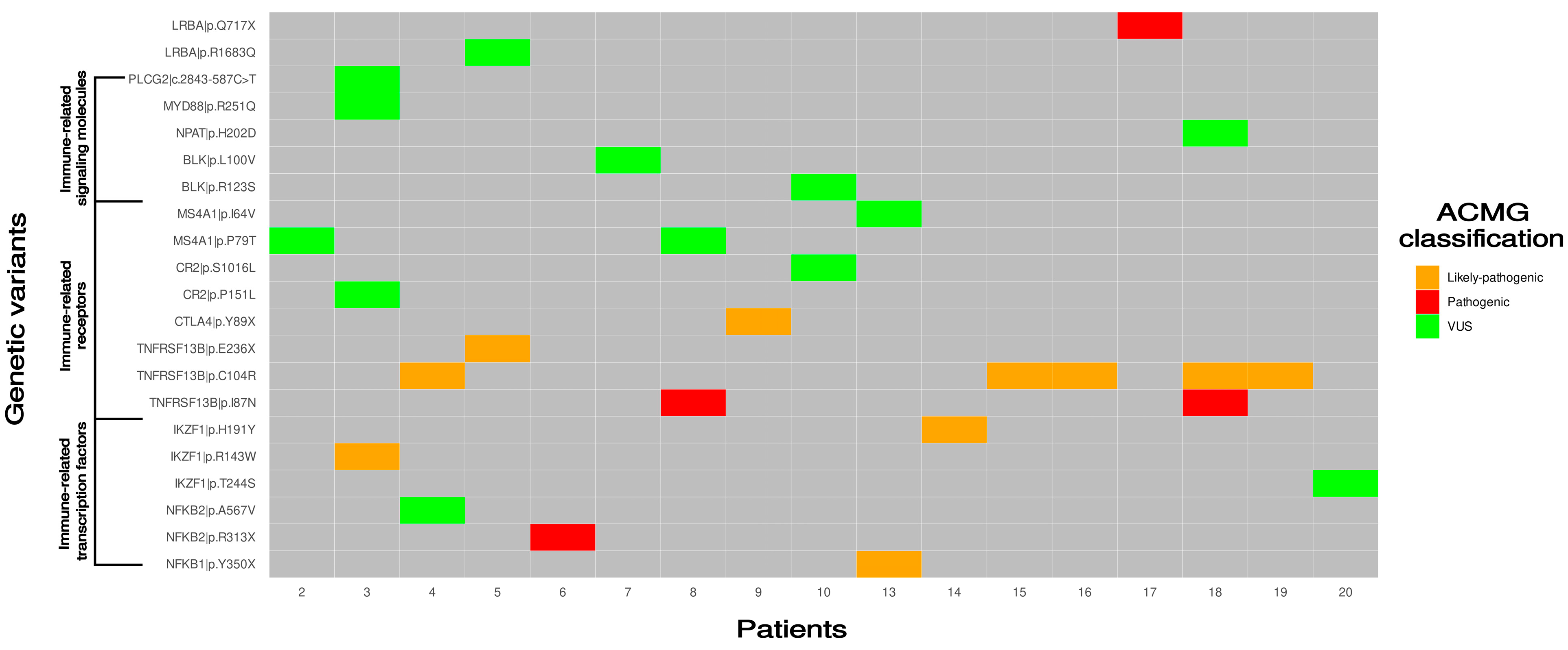
3.1. Genetic Defects Identified in the Study
3.2. Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic Variants Detected in Transcription Factors Involved in Immune System
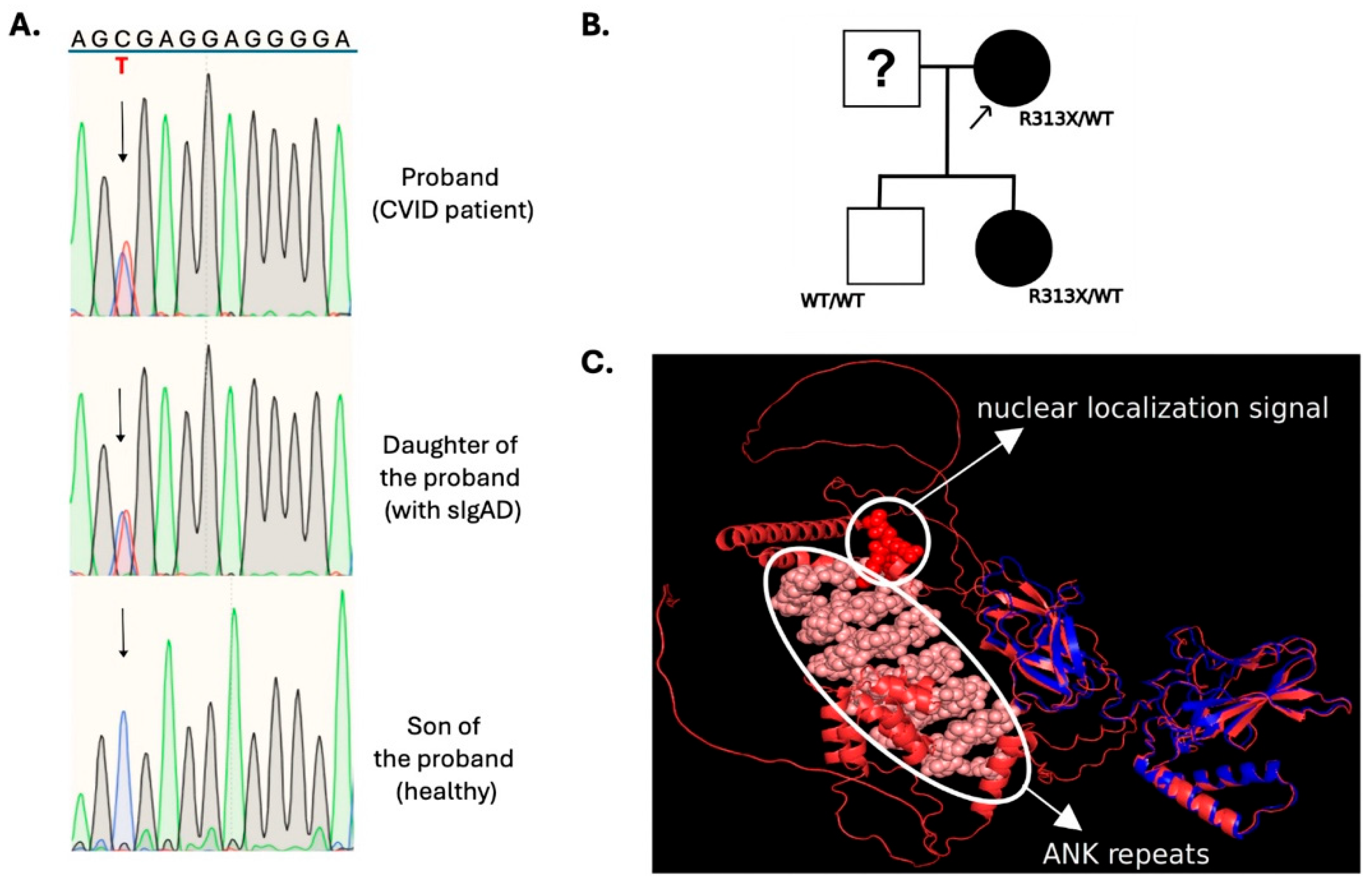
3.2.1. NFKB2
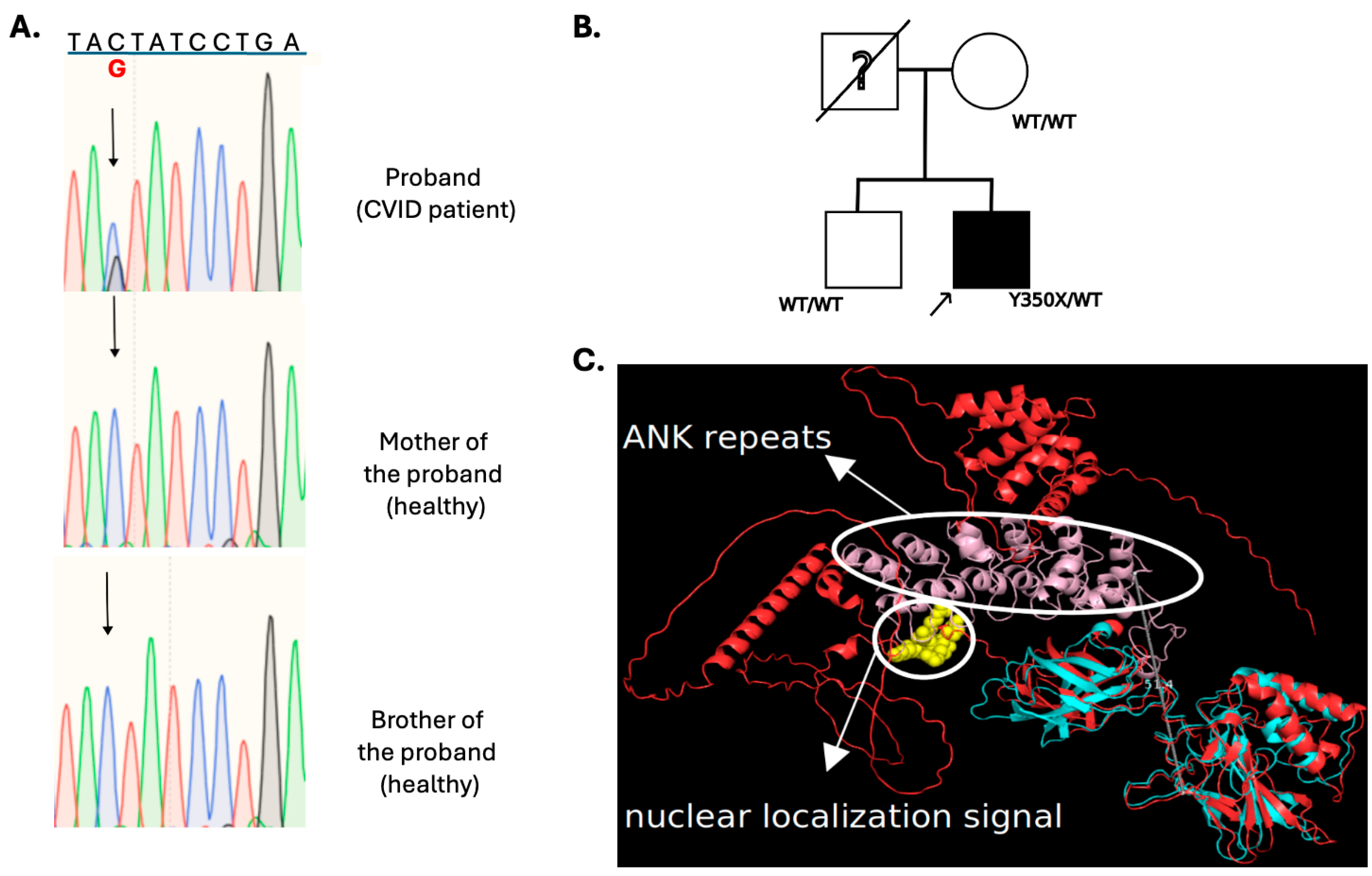
3.2.2. NFKB1
3.2.3. IKZF1
3.2.4. LRBA
3.3. Variants of Unknown Significance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Notarangelo, L.D.; Bacchetta, R.; Casanova, J.-L.; Su, H.C. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: An Expanding Universe. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabb1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geha, R.S.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Casanova, J.-L.; Chapel, H.; Conley, M.E.; Fischer, A.; Hammarström, L.; Nonoyama, S.; Ochs, H.D.; Puck, J.M.; et al. International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification Committee. Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: An Update from the International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification Committee. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 776–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyts, I.; Bousfiha, A.; Duff, C.; Singh, S.; Lau, Y.L.; Condino-Neto, A.; Bezrodnik, L.; Ali, A.; Adeli, M.; Drabwell, J. Primary Immunodeficiencies: A Decade of Progress and a Promising Future. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 625753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapousouzi, A.; Kalala, F.; Sarrou, S.; Farmaki, E.; Antonakos, N.; Kakkas, I.; Kourakli, A.; Labropoulou, V.; Kelaidi, C.; Tsiouma, G.; et al. A Nationwide Study of the Delayed Diagnosis and the Clinical Manifestations of Predominantly Antibody Deficiencies and CTLA4-Mediated Immune Dysregulation Syndrome in Greece. Medicina 2024, 60, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayry, J.; Hermine, O.; Webster, D.A.; Lévy, Y.; Kaveri, S.V. Common Variable Immunodeficiency: The Immune System in Chaos. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gereige, J.D.; Maglione, P.J. Current Understanding and Recent Developments in Common Variable Immunodeficiency Associated Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, R.; Habibi, S.; Sharifi, L.; Azizi, G.; Abolhassani, H.; Olbrich, P.; Aghamohammadi, A. Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Classification, and Management. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 30, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhassani, H.; Hammarström, L.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Current Genetic Landscape in Common Variable Immune Deficiency. Blood 2020, 135, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Coonrod, E.M.; Kumánovics, A.; Franks, Z.F.; Durtschi, J.D.; Margraf, R.L.; Wu, W.; Heikal, N.M.; Augustine, N.H.; Ridge, P.G.; et al. Germline Mutations in NFKB2 Implicate the Noncanonical NF-κB Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskandarian, Z.; Fliegauf, M.; Bulashevska, A.; Proietti, M.; Hague, R.; Smulski, C.R.; Schubert, D.; Warnatz, K.; Grimbacher, B. Assessing the Functional Relevance of Variants in the IKAROS Family Zinc Finger Protein 1 (IKZF1) in a Cohort of Patients With Primary Immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzer, U.; Chapel, H.M.; Webster, A.D.B.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Schlesier, M.; Peter, H.H.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Schneider, P.; Schäffer, A.A.; et al. Mutations in TNFRSF13B Encoding TACI Are Associated with Common Variable Immunodeficiency in Humans. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poodt, A.E.J.; Driessen, G.J.A.; de Klein, A.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; van der Burg, M.; de Vries, E. TACI Mutations and Disease Susceptibility in Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 156, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, V.; Sevdali, E.; Recher, M.; Abolhassani, H.; Hammarstrom, L.; Smulski, C.R.; Baronio, M.; Plebani, A.; Proietti, M.; Speletas, M.; et al. CVID-Associated B Cell Activating Factor Receptor Variants Change Receptor Oligomerization, Ligand Binding, and Signaling Responses. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevdali, E.; Block, V.; Lataretu, M.; Li, H.; Smulski, C.R.; Briem, J.-S.; Heitz, Y.; Fischer, B.; Ramirez, N.-J.; Grimbacher, B.; et al. BAFFR Activates PI3K/AKT Signaling in Human Naive but Not in Switched Memory B Cells through Direct Interactions with B Cell Antigen Receptors. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 111019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Herrera, G.; Tampella, G.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; Herholz, P.; Trujillo-Vargas, C.M.; Phadwal, K.; Simon, A.K.; Moutschen, M.; Etzioni, A.; Mory, A.; et al. Deleterious Mutations in LRBA Are Associated with a Syndrome of Immune Deficiency and Autoimmunity. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Nalda, A.; Fortuny, C.; Rey, L.; Bunney, T.D.; Alsina, L.; Esteve-Solé, A.; Bull, D.; Anton, M.C.; Basagaña, M.; Casals, F.; et al. Severe Autoinflammatory Manifestations and Antibody Deficiency Due to Novel Hypermorphic PLCG2 Mutations. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speletas, M.; Mamara, A.; Papadopoulou-Alataki, E.; Iordanakis, G.; Liadaki, K.; Bardaka, F.; Kanariou, M.; Germenis, A.E. TNFRSF13B/TACI Alterations in Greek Patients with Antibody Deficiencies. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieudonné, Y.; Guffroy, A.; Vollmer, O.; Carapito, R.; Korganow, A.-S. IKZF1 Loss-of-Function Variant Causes Autoimmunity and Severe Familial Antiphospholipid Syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.R.; Eng, C.M. Next-Generation Sequencing to Diagnose Suspected Genetic Disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Garcia, E.; Vega, H.A.-d.l. (Eds.) Translational Research and Onco-Omics Applications in the Era of Cancer Personal Genomics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-24100-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinkšel, M.; Writzl, K.; Maver, A.; Peterlin, B. Improving Diagnostics of Rare Genetic Diseases with NGS Approaches. J. Community Genet. 2021, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorsteveld, E.E.; Hoischen, A.; van der Made, C.I. Next-Generation Sequencing in the Field of Primary Immunodeficiencies: Current Yield, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 61, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudilla, F.; Franco-Jarava, C.; Martínez-Gallo, M.; Garcia-Prat, M.; Martín-Nalda, A.; Rivière, J.; Aguiló-Cucurull, A.; Mongay, L.; Vidal, F.; Solanich, X.; et al. Expanding the Clinical and Genetic Spectra of Primary Immunodeficiency-Related Disorders With Clinical Exome Sequencing: Expected and Unexpected Findings. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnosis Criteria—ESID. Available online: https://esid.org/working-parties/registry-working-party/diagnosis-criteria/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Kakkas, I.; Tsinti, G.; Kalala, F.; Farmaki, E.; Kourakli, A.; Kapousouzi, A.; Dimou, M.; Kalaitzidou, V.; Sevdali, E.; Peristeri, A.-M.; et al. TACI Mutations in Primary Antibody Deficiencies: A Nationwide Study in Greece. Medicina 2021, 57, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sic, H.; Speletas, M.; Cornacchione, V.; Seidl, M.; Beibel, M.; Linghu, B.; Yang, F.; Sevdali, E.; Germenis, A.E.; Oakeley, E.J.; et al. An Activating Janus Kinase-3 Mutation Is Associated with Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen-4-Dependent Immune Dysregulation Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM®. McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University. (Baltimore, MD). Available online: https://omim.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Xu, C.; Gu, X.; Padmanabhan, R.; Wu, Z.; Peng, Q.; DiCarlo, J.; Wang, Y. smCounter2: An Accurate Low-Frequency Variant Caller for Targeted Sequencing Data with Unique Molecular Identifiers. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingolani, P. Variant Annotation and Functional Prediction: SnpEff. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2493, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting Amino Acid Changes That Affect Protein Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting Functional Effect of Human Missense Mutations Using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Rödelsperger, C.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster Evaluates Disease-Causing Potential of Sequence Alterations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate Structure Prediction of Biomolecular Interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB Family of Transcription Factors and Its Regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Demissie, E.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Mambole, A.; O’Garra, A.; Tomczak, M.F.; Erdman, S.E.; Fox, J.G.; et al. NF-κB1 Inhibits TLR-Induced IFN-β Production in Macrophages through TPL-2-Dependent ERK Activation. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, H.S.; Bernasconi, A.; Niemela, J.E.; Almejun, M.B.; Gallego, W.A.F.; Goel, S.; Stoddard, J.L.; Sánchez, R.G.P.; Franco, C.A.A.; Oleastro, M.; et al. A Nonsense N -Terminus NFKB2 Mutation Leading to Haploinsufficiency in a Patient with a Predominantly Antibody Deficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, A.; Lagos, M.; Vargas-Hernández, A.; Posey, J.E.; Coban-Akdemir, Z.; Jhangiani, S.; Mace, E.M.; Reyes, A.; King, A.; Cavagnaro, F.; et al. Novel Heterozygous Mutation in NFKB2 Is Associated With Early Onset CVID and a Functional Defect in NK Cells Complicated by Disseminated CMV Infection and Severe Nephrotic Syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuijnenburg, P.; Lango Allen, H.; de Bree, G.J.; Savic, S.; Jansen, M.H.; Stockdale, C.; Simeoni, I.; Ten Berge, I.J.M.; van Leeuwen, E.M.M.; NIHR BioResource; et al. Pathogenic NFKB2 Variant in the Ankyrin Repeat Domain (R635X) Causes a Variable Antibody Deficiency. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 203, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.-C. Non-Canonical NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fliegauf, M.; Krüger, R.; Steiner, S.; Hanitsch, L.G.; Büchel, S.; Wahn, V.; von Bernuth, H.; Grimbacher, B. A Pathogenic Missense Variant in NFKB1 Causes Common Variable Immunodeficiency Due to Detrimental Protein Damage. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 621503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fliegauf, M.; Bryant, V.L.; Frede, N.; Slade, C.; Woon, S.-T.; Lehnert, K.; Winzer, S.; Bulashevska, A.; Scerri, T.; Leung, E.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of the NF-κB1 Subunit P50 in Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, L.B.; Ward, A.C. The Ikaros Gene Family: Transcriptional Regulators of Hematopoiesis and Immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Nichogiannopoulou, A.; Wu, L.; Sun, L.; Sharpe, A.H.; Bigby, M.; Georgopoulos, K. Selective Defects in the Development of the Fetal and Adult Lymphoid System in Mice with an Ikaros Null Mutation. Immunity 1996, 5, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, B.S.; Morales-Alcelay, S.; Kleiger, G.; Brown, K.E.; Fisher, A.G.; Smale, S.T. Targeting of Ikaros to Pericentromeric Heterochromatin by Direct DNA Binding. Genes. Dev. 2000, 14, 2146–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papathanasiou, P.; Perkins, A.C.; Cobb, B.S.; Ferrini, R.; Sridharan, R.; Hoyne, G.F.; Nelms, K.A.; Smale, S.T.; Goodnow, C.C. Widespread Failure of Hematolymphoid Differentiation Caused by a Recessive Niche-Filling Allele of the Ikaros Transcription Factor. Immunity 2003, 19, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, K.; Moore, D.D.; Derfler, B. Ikaros, an Early Lymphoid-Specific Transcription Factor and a Putative Mediator for T Cell Commitment. Science 1992, 258, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.; Kuehn, H.S.; Odakir, E.; Niemela, J.E.; Ozcan, A.; Eken, A.; Rohlfs, M.; Cansever, M.; Gok, V.; Aydin, F.; et al. Common Variable Immunodeficiency, Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia, and Pancytopenia Associated with a Defect in IKAROS. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 43, e351–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezen, E.; Çatak, M.C.; Çatak, F.B.; Piepoli, S.; Zahedimaram, P.; Ultanır, E.; Barış, S.; Erman, B. Structure and Function of the LRBA Protein. TJI 2024, 12 (Suppl. 1), 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Sex | Year of Birth | Age of Onset | Clinical Presentation | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 1980 | 4 | Recurrent respiratory infections; COPD/CRPD; splenomegaly | CVID |
| 2 | M | 1970 | 7 | Recurrent respiratory infections; COPD; bronchiectasis; meningitis | CVID |
| 3 | F | 2002 | 14 | Recurrent respiratory infections; hypothyroidism | CVID |
| 4 | M | 1962 | 38 | Recurrent respiratory and urinary infections; lymphadenopathy; granulomatous disease; CNS myelitis; lymphomas (Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin) | CVID * |
| 5 | M | 1976 | 8 | Recurrent respiratory infections; AIT; lymphoproliferation (lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly) | IgA + sGD |
| 6 | F | 1980 | 26 | Recurrent respiratory and urinary infections, arthralgias, eczema | CVID |
| 7 | M | 1997 | 4 | Recurrent respiratory infections, hypothyroidism, non-Hodgkin lymphoma | CVID * |
| 8 | M | 2004 | 15 | Recurrent AIT, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy | CVID |
| 9 | F | 1995 | 14 | Recurrent respiratory infections, Crohn-like disease, hypothyroidism, pernicious anemia, tonsillar hypertrophy | IDS |
| 10 | M | 1975 | 20 | Recurrent malaria infections, AΙΤ, splenomegaly, Hodgkin lymphoma, recurrent, eczema | CVID * |
| 11 | F | 1958 | 18 | Recurrent respiratory infections, hypothyroidism, optic nerve atrophy | CVID ** |
| 12 | F | 1949 | 50 | Recurrent respiratory infections, granulomatous disease, hypothyroidism | CVID ** |
| 13 | M | 1976 | 32 | Recurrent respiratory infections, recurrent Evans syndrome | CVID |
| 14 | M | 1998 | 1 | Recurrent skin infections, refractory AIT | CVID |
| 15 | M | 1965 | 39 | Recurrent attacks of AIT and AHA, splenomegaly, enteropathy | CVID |
| 16 | M | 1985 | 10 | Recurrent respiratory infections, bronchiectasis, vitiligo | CVID |
| 17 | F | 1972 | 27 | Recurrent respiratory infections, CVID-ILD, AIT | CVID |
| 18 | M | 1946 | 48 | Recurrent respiratory infections, hypothyroidism, pernicious anemia, AHA, non-Hodgkin lymphoma | CVID * |
| 19 | M | 2003 | 3 | Recurrent respiratory infections, refractory AIT, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy | IgA + sGD |
| 20 | F | 1986 | 35 | PBC, incidental diagnosis after recurrent abortions | CVID |
| No. | Gene, OMIM | Pathway Function | Associated Diseases | Clinical Manifestations | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ICOS, 604558 | T-cell stimulation, immune response regulation | CVID | Recurrent infections | AR |
| 2 | TACI, 604907 | B-cell activation, Ab production | CVID, sIgAD | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AD/AR |
| 3 | CD19, 107265 | BCR signaling and B-cell development | CVID | Recurrent infections | AR |
| 4 | BAFFR, 606269 | B-cell survival and maturation | CVID, autoimmune diseases | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AR |
| 5 | MS4A1, 112210 | BCR signaling and B-cell development | CVID | Recurrent infections | AR |
| 6 | CD81, 186845 | T-cell development, B-cell signaling | CVID | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AR |
| 7 | CR2, 120650 | Complement receptor, B-cell activation | CVID, SLE | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AR |
| 8 | LRBA, 606453 | Vesicle trafficking, immune regulation | IDS, autoimmune diseases | Recurrent infections autoimmunity, lymphoproliferation, hypogamma | AR |
| 9 | PRKCD, 176977 | Apoptosis, BCR signaling | CVID, ALPS | Lymphoproliferation, autoimmunity | AR |
| 10 | NFKB2, 164012 | Transcription factor, immune response regulation | CVID, autoimmune diseases | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AD |
| 11 | IL21, 605384 | Immune responses regulation | CVID, autoimmune diseases | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AR |
| 12 | NFKB1, 164011 | Transcription factor, immune response regulation | CVID, autoimmune diseases | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AD |
| 13 | IKZF1, 603023 | Transcription factor, regulation of cell differentiation | CVID, ALL | Recurrent infections, leukemia | AD |
| 14 | CD27, 186711 | TNF receptor superfamily, T- and B-cell activation | Lymphoproliferative syndrome, combined immunodeficiency | Recurrent infections, lymphoproliferation | AR |
| 15 | RAG1, 179615 | V(D)J recombination, B- and T-cell development | SCID, Omenn syndrome | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AR |
| 16 | RAG2, 179616 | V(D)J recombination, B- and T-cell development | SCID, Omenn syndrome | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity | AR |
| 17 | PIK3CD, 602839 | PI3K signaling, B-cell and T-cell function | APDS | Lymphoproliferation, recurrent infections | AD, AR |
| 18 | PIK3R1, 171833 | PI3K signaling, B-cell and T-cell function | APDS | Lymphoproliferation, recurrent infections | AD, AR |
| 19 | RAC2, 602049 | Small GTPase, neutrophil function | Immunodeficiency | Recurrent infections, neutropenia | AD |
| 20 | BLK, 191305 | BCR signaling, B-cell development | SLE, MODY11 | SLE, diabetes | AD |
| 21 | PLCG2, 600220 | B-cell activation | PLAID, APLAID | Cold urticaria, autoimmunity, recurrent infections | AD |
| 22 | VAV1, 164875 | T- and B-cell activation | Myasthenia Gravis susceptibility, CVID | Recurrent infections, bone marrow failure | AD |
| 23 | IRF2BP2, 615332 | Transcriptional repressor, B-cell differentiation | CVID | Immunodeficiency | AD |
| 24 | NPAT, 601448 | Histone and cyclin E transcription, cell cycle regulation | Ataxia, lymphoma susceptibility | Ataxia, lymphomagenesis | AD |
| 25 | MYD88, 602170 | TLR signaling, NFkB activation | Immunodeficiency, WM | Pyogenic bacterial infections | AR |
| 26 | IRAK4, 606883 | TLR signaling, NFkB activation | Immunodeficiency | Recurrent bacterial infections | AR |
| 27 | TWEAK, 602695 | Apoptosis, NFkB activation | Immunodeficiency, cardiomyopathy | recurrent infections, hypogamma | AD |
| 28 | IL21R, 605383 | Immune responses regulation | Immunodeficiency | Recurrent infections | AR |
| 29 | CTLA4, 123890 | Immune checkpoint, T-cell regulation | IDS, autoimmune diseases | Recurrent infections autoimmunity, lymphoproliferation, hypogamma | AD |
| 30 | DOCK8, 611432 | Immune cell function, migration and survival | Hyper-IgE syndrome, combined immunodeficiency | Recurrent infections, eczema, skin lesions, asthma | AR |
| Gene | Target Variant | Primers | PCR Product | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFKB1 | NM_003998.4: c.1050C>G, p.Y350X | F | 5′-GCCATTGTCTTCAAAACTCCAAAGTAT-3′ | 150 bp. |
| R | 5′-AACAACTGACTTACCTTTGATTTCAGGA-3′ | |||
| NFKB2 | NM_001322934.2: c.937C>T, p.R313X | F | 5′-GGGCACCAAGGACATCGAGTAT-3′ | 497 bp. |
| R | 5′-CCACATCTAGCTCTTGGGACCTTCT-3′ | |||
| IKZF1 | NM_006060.6: c.427C>T, p.R143W | F | 5′-CTCGTAGCATCGTCCTCATGT-3′ | 174 bp. |
| R | 5′-TGGCATTTGAAGGGCTTCTCC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galanopoulos, A.P.; Raftopoulou, S.; Sarrou, S.; Matziri, A.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Stratakos, G.; Mouchtouri, V.A.; Hölzer, M.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Kalala, F.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis in Greek Patients with Predominantly Antibody Deficiencies. Immuno 2025, 5, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030027
Galanopoulos AP, Raftopoulou S, Sarrou S, Matziri A, Papoutsopoulou S, Stratakos G, Mouchtouri VA, Hölzer M, Hadjichristodoulou C, Kalala F, et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis in Greek Patients with Predominantly Antibody Deficiencies. Immuno. 2025; 5(3):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalanopoulos, Achilleas P., Sofia Raftopoulou, Styliani Sarrou, Alexia Matziri, Stamatia Papoutsopoulou, Grigorios Stratakos, Varvara A. Mouchtouri, Martin Hölzer, Christos Hadjichristodoulou, Fani Kalala, and et al. 2025. "Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis in Greek Patients with Predominantly Antibody Deficiencies" Immuno 5, no. 3: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030027
APA StyleGalanopoulos, A. P., Raftopoulou, S., Sarrou, S., Matziri, A., Papoutsopoulou, S., Stratakos, G., Mouchtouri, V. A., Hölzer, M., Hadjichristodoulou, C., Kalala, F., & Speletas, M. (2025). Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis in Greek Patients with Predominantly Antibody Deficiencies. Immuno, 5(3), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030027








