Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Window of Immunologic Responses and Horizon of Biological Therapies
Abstract
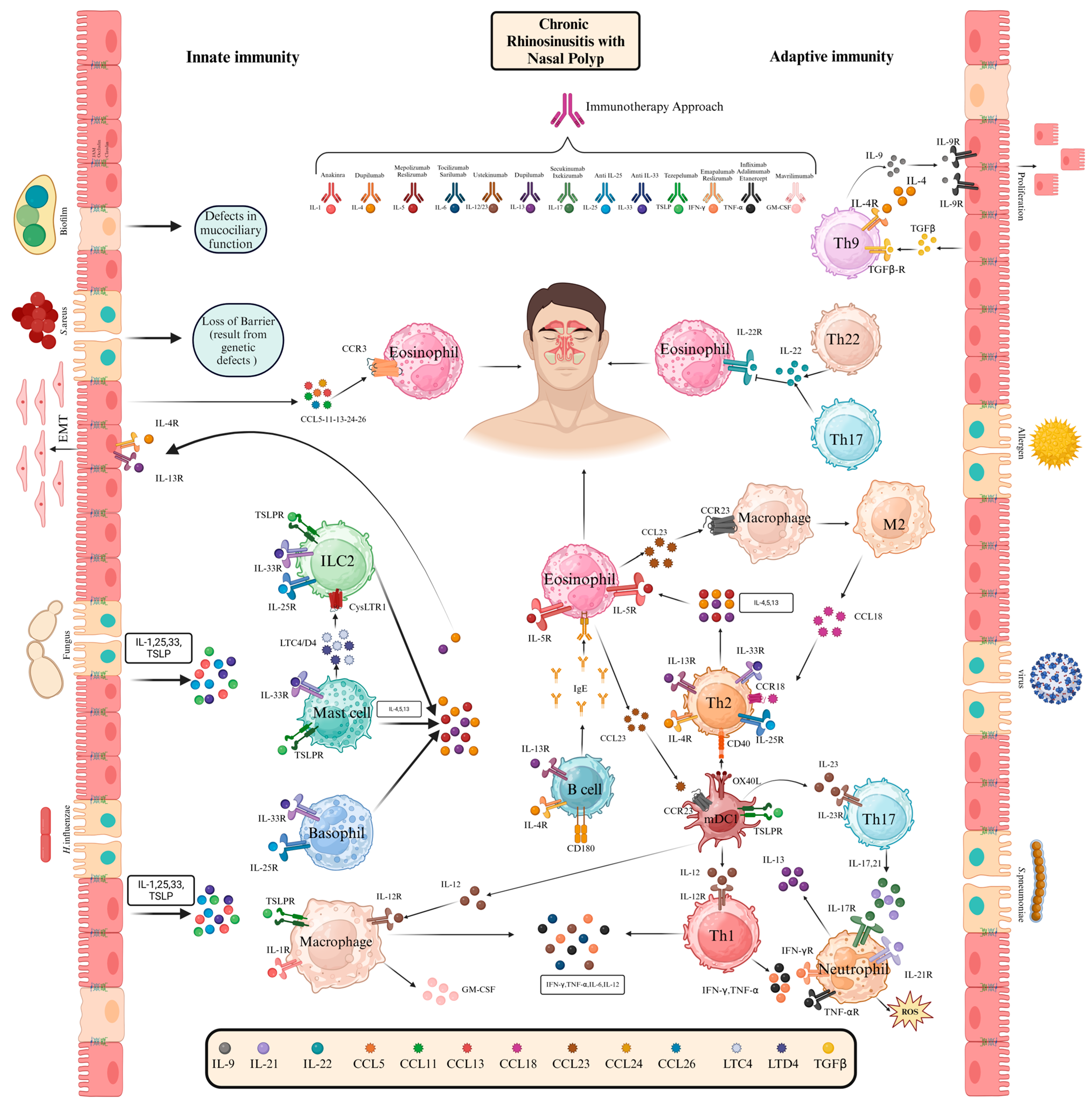
1. Introduction
2. Immunopathogenesis of CRSwNP
2.1. Innate Immunity in CRSwNP
| Category | Component | Function | Dysregulation in CRSwNP | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barrier Integrity | Epithelial Barrier | Prevents entry of antigens. | Increased permeability, EMT, and tissue remodeling driven by IL-4 and IL-13. | [18,19] |
| Mucociliary Clearance | Clears mucus and microbes from nasal passages. | Ciliary dysfunction and abnormal ciliogenesis allow bacterial proliferation and biofilm formation. | [22] | |
| Pattern Recognition Receptor | Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) | Recognize microbial patterns and initiate inflammatory responses. | Inconsistent expression levels, leading to variable immune responses. | [20,21] |
| Bitter Taste Receptors (T2R38) | Detect quorum-sensing molecules and trigger mucociliary clearance and antimicrobial peptide release. | Nonfunctional T2R38 alleles linked to severe disease and reduced antimicrobial responses. | [22] | |
| LBP-BPI-PLUNC Proteins | Bind LPS and disrupt bacterial biofilms. | Reduced PLUNC levels in eosinophilic polyps, correlating with colonization by S. aureus and P. aeruginosa. | [22] | |
| Acyloxyacyl Hydrolase (AOAH) | Degrades bacterial LPS and modulates inflammation. | Genetically linked to CRS and asthma. | [24] | |
| Antimicrobial Defense | S100 Proteins | Exhibit antimicrobial and inflammatory-modulating properties. | Decreased levels of S100A7 and S100A8/9 in CRS patients, leading to impaired epithelial defense. | [25] |
| Lysozyme and Lactoferrin | Protect against bacterial infections. | Reduced in nasal polyp tissues due to submucosal gland loss, compromising local defense. | [25] | |
| Resident Immune Cells | Neutrophils | Combat pathogens through NETs and enzymatic activity. | Contribute to biofilm resistance and chronic inflammation in non-eosinophilic CRS. | [14] |
| ILC2s | Produce IL-5 and IL-13, driving type 2 inflammation. | Increased numbers of eosinophilic CRS, amplifying inflammation and eosinophil recruitment. | [26] | |
| Alarmins | IL-33, HMGB1 | Activate mast cells, dendritic cells, and ILC2s to amplify immune responses. | Elevated levels drive type 2 inflammation and epithelial damage. | [26] |
| Complement System | Complement Proteins | Enhance pathogen clearance through opsonization and MAC formation. | Dysregulation may contribute to chronic inflammation and impaired microbial control. | [13] |
| Biofilms | Pathogenic Biofilms | Protect bacteria from host defenses and antibiotics. | Biofilms by S. aureus and P. aeruginosa perpetuate inflammation and treatment resistance. | [13] |
2.1.1. Eosinophils
2.1.2. Mast Cells
2.1.3. ILC2 Cells
2.1.4. NK Cells
2.2. Adaptive Immunity in CRSwNP
2.2.1. T Helper Cells
2.2.2. B Cells
2.2.3. Dendritic Cells
| Category | Component | Function | Dysregulation in CRSwNP | Therapeutic Implications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T Cells | Th1 Cells | Produce IFN-γ, driving cell-mediated immunity and antimicrobial responses. | Reduced activity in eosinophilic CRSwNP, but may contribute to neutrophilic inflammation in non-eosinophilic CRSwNP. | Targeting IFN-γ pathways for non-eosinophilic CRSwNP. | [77] |
| Th2 Cells | Release IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, promoting type 2 inflammation and eosinophilic infiltration. | Dominant in eosinophilic CRSwNP; linked to tissue damage, mucus production, and epithelial barrier dysfunction. | Biologic therapies targeting IL-4Rα (dupilumab), IL-5 (mepolizumab, reslizumab). | [77] | |
| Th17 Cells | Secrete IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22, driving neutrophilic recruitment and tissue remodeling. | Elevated in non-eosinophilic CRSwNP; IL-21 alterations may impact allergic inflammation. | Anti-IL-17 therapies (e.g., secukinumab) for neutrophilic inflammation. | [100] | |
| Th9 Cells | Produce IL-9, promoting epithelial growth and inflammatory cell infiltration. | Increased IL-9 and IL-9R expression in epithelial and submucosal cells in CRSwNP. | Targeting IL-9 to reduce epithelial overgrowth and inflammation. | [100] | |
| Th22 Cells | Secrete IL-22, contributing to epithelial repair and inflammation. | Elevated IL-22 levels linked to eosinophilic inflammation and reduced IL-22 receptor expression in CRSwNP. | Modulation of IL-22 pathways for epithelial repair and inflammation control. | [77,100] | |
| T Regulatory (Treg) Cells | Suppress immune responses, maintain tolerance, and regulate inflammation. | Reduced Treg populations, impaired migration, and overexpression of SOCS3 inhibiting FoxP3 expression. | SOCS3 inhibitors and TGF-β supplementation to restore Treg function. | [89,90] | |
| Dendritic Cells | Myeloid DCs (mDC1, mDC2) | Present antigens, modulate Th responses (mDC1: Th2 polarization; mDC2: Th17 polarization). | mDC2 abundance promotes Th2 dominance; mDC1s in lamina propria enhance type 2 cytokine production via OX40L. | Blocking TSLP-OX40L pathways to reduce Th2 inflammation. | [97] |
| Plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) | Regulate type 1 and type 2 immune responses and antiviral defense. | Limited role identified in CRSwNP but may regulate inflammation balance. | Enhancing pDC function to counteract type 2 inflammation. | [99] | |
| B Cells | BAFF (B cell-activating factor) | Supports B cell survival, differentiation, and Ig production. | Elevated BAFF levels in nasal polyps, promoting plasma cell differentiation and IgE production. | Targeting BAFF to suppress B cell activity and Ig production. | [94] |
| Plasma Cells | Fully differentiated B cells that secrete immunoglobulins. | Increased plasma cells producing IgE, IgA, IgM, and soluble IgD in nasal polyps. | Suppression of local IgE and antibody production. | [94] | |
| IgE | Amplifies type 2 inflammation via mast cell activation and eosinophilic recruitment. | Elevated IgE levels correlate with eosinophilic CRSwNP severity. | Anti-IgE therapies (e.g., omalizumab) to reduce type 2 inflammation. | [95] | |
| IgD+ Plasmablasts | Contribute to local inflammation via soluble IgD production. | Increased levels in non-eosinophilic CRSwNP; role in local immune responses. | Investigation of IgD-targeted therapies for non-eosinophilic CRSwNP. | [95] |
2.3. Therapeutic Approaches for CRSwNP: Past, Ongoing, and Future Clinical Directions
2.4. Targeting Key Cytokines with Monoclonal Antibodies
2.4.1. IgE Blockade
2.4.2. IL-4 and IL-13 Blockade
2.4.3. Anti-IL-5 Blockade
2.4.4. IL-17 Blockade
2.4.5. TSLP Blockade
| Generic Name | Trade Name | Mechanism of Action | Indication/Current Status | Comments | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omalizumab | Xolair | Anti-IgE via FcεRI receptor blockade | FDA-approved for CRSwNP | Reduces nasal polyp size and symptoms, particularly effective in patients with comorbid severe asthma | [106] |
| Mepolizumab | Nucala | Anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody | FDA-approved for CRSwNP | Shown to reduce surgery needs and eosinophil levels in severe eosinophilic CRSwNP | [58] |
| Benralizumab | Fasenra | Anti-IL-5 via IL-5Rα receptor blockade | Phase III clinical trials | Efficacy in reducing eosinophilic inflammation and nasal polyps under investigation | [120] |
| Dupilumab | Dupixent | Anti-IL-4 and IL-13 via IL-4Rα receptor blockade | FDA-approved for CRSwNP | Demonstrated significant improvement in quality of life, olfactory function, and symptom control | [108] |
| Reslizumab | Cinqair | Anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody | Phase II clinical trials | Reduces eosinophil counts; requires further study for full CRSwNP approval | [121] |
| Brodalumab | Siliq | Anti-IL-17 via IL-17RA receptor blockade | Preclinical/research stage | Limited efficacy in asthma; potential exploration in CRSwNP | [116] |
| Tezepelumab | Tezspire | TSLP blockade; upstream inhibition of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 | Phase III clinical trials | Promising results in asthma; potential for reducing type 2 inflammation in CRSwNP | [117] |
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takahashi, H.; Matsuyama, T.; Kawabata-Iwakawa, R.; Morishita, Y.; Kawamoto, T.; Chikamatsu, K. ADGRB3-High and POSTN-High Fibroblasts Are Markers of Endotypic Traits in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Immuno 2024, 4, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, F.; Ghalehbaghi, B.; Aazami, H.; Mohebbi, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Falak, R.; Babaheidarian, P.; Najafi, M.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Ghalehbaghi, S.; et al. Frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in Iranian chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldajani, A.; Alroqi, A.; Alramyan, R.; Alhejin, N.; Alswayyed, M.; Alrajban, W.A.; Alromaih, S.; Aloulah, M.O.; Alrasheed, A.S.; Aldousary, S.; et al. Prevalence of type 2 inflammation in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Saudi Arabia. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1421140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokane, S.; Kawasumi, T.; Takeno, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Miyamoto, S.; Fujita, R.; Ishikawa, C.; Oda, T.; Horibe, Y.; Ishino, T.; et al. Impaired Coordination of the Ciliary Movement in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: The Role of Decreased Planar Cell Polarity Protein Expression. Immuno 2024, 4, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, J.R.; Lee, R.J. Taste receptors in the upper airway. World J. Otorhinolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2018, 4, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challapalli, S.D.; McKee, S.; Luong, A.U. The role of fungus in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 30, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalehbaghi, B.; Aazami, H.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Mohebbi, A.; Babaheidarian, P.; Rashidi, N.; Mokhtarian, K.; Ahmadi, R.; Kamali, M.; Ponour, M.; et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins 3 and 5 potentially delineate polarization of Th cells in chronic rhinosinusitis. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2024, 97, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helman, S.N.; Barrow, E.; Edwards, T.; DelGaudio, J.M.; Levy, J.M.; Wise, S.K. The role of allergic rhinitis in chronic rhinosinusitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2020, 40, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Bui, D.V.; Yun, Y.; Nguyen, L.M.; Mitani, A.; Suzuki, K.; Asako, M.; Kanda, A.; Iwai, H.; et al. CCL4 regulates eosinophil activation in eosinophilic airway inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, M.; Sahin, M.; Yenisey, C. Increased TSLP, IL-33, IL-25, IL-19, IL 21 and amphiregulin (AREG) levels in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapurin, N.; Wu, J.; Labby, A.B.; Chandra, R.K.; Chowdhury, N.I.; Turner, J.H. Current insight into treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis: Phenotypes, endotypes, and implications for targeted therapeutics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Meese, T.; Van Nevel, S.; Holtappels, G.; Vanhee, S.; Bröker, B.M.; Li, Z.; De Meester, E.; De Ruyck, N.; et al. The multi-omics single-cell landscape of sinus mucosa in uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 256, 109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hao, H.; Wang, L.-E. Bioinformatics analysis and verification of key candidate genes influencing the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 710. [Google Scholar]
- Kagoya, R.; Kondo, K.; Kishimoto-Urata, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Kikuta, S.; Yamasoba, T. A murine model of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis using the topical application of a vitamin D3 analog. Allergy 2021, 76, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazami, H.; Seif, F.; Ghalehbaghi, B.; Babaheidarian, P.; Mohebbi, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Ghalehbaghi, S.; Behnam, B.; Entezami, K.Z.; et al. Local eosinophils are associated with increased IgA subclass levels in the sinonasal mucosa of chronic rhinosinusitis with polyp patients. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatello, L.G.; Tonon, S.; Mele, V.; Santini, S.; Miani, C.; Pucillo, C.E.M. Update on the Biological and Clinical Relevance of Mast Cells in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viksne, R.J.; Sumeraga, G.; Pilmane, M. Antimicrobial and defense proteins in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Medicina 2023, 59, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, R.R.; Kingdom, T.T.; Hwang, P.H.; Smith, T.L.; Alt, J.A.; Baroody, F.M.; Batra, P.S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Chandra, R.K.; et al. (Eds.) International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Rhinosinusitis. In International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Čábalová, L.; Čabanová, K.; Bielniková, H.; Kukutschová, J.; Dvořáčková, J.; Zeleník, K.; Komínek, P. Solid Anorganic Particles and Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Histopathology Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleimer, R.P. Immunopathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A.; Deshpande, P.; Campbell, C.N.; Krantz, M.S.; Mukherjee, E.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Pirmohamed, M.; Palubinsky, A.M.; Phillips, E.J. Updates on the immunopathology and genomics of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 289–300.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaodong, X.; Tao, L.; Jianmin, L.; Jing, Z.; Bing, Z.; Jintao, D.; Bachert, C.; Luo, B. Crocin Inhibits the Type 2 Inflammatory Response Produced by ILC2s in Eosinophilic Nasal Polyps. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2023, 37, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, J.; Sun, Y. Relationship between eosinophilic and neutrophilic inflammation in Chinese chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 184, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, J.; Canziani, K.E.; Guzmán, L.; Bernedo, V.; García, M.; Altamirano, E.M.; Feregotti, E.; Curciarello, R.; Muglia, C.I.; Docena, G.H.; et al. Type-2 cytokines promote the secretion of the eosinophil–attractant CCL26 by intestinal epithelial cells in food-sensitized patients. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 909896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Cheng, W.; Li, Z.; Yao, M.; Sun, K. Clinical associations of bitter taste perception and bitter taste receptor variants and the potential for personalized healthcare. Pharmacogenom. Pers. Med. 2023, 31, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idler, B.M.; Iijima, K.; Ochkur, S.I.; Jacobsen, E.A.; Rank, M.A.; Kita, H.; Lal, D. Eosinophil peroxidase: A biomarker for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis agnostic of polyp status. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Cooksley, C.; Suzuki, T.; Ramezanpour, M.; Nakazono, A.; Nakamaru, Y.; Homma, A.; Vreugde, S. TLR signals in epithelial cells in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 780425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, J.; Seyfert, H.-M. (Eds.) The first line of defence: Insights into mechanisms and relevance of phagocytosis in epithelial cells. In Seminars in Immunopathology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Lv, W.; Yu, H. The NLRP3 inflammasome in allergic diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, C.E.; Rude, K.M.; Gareau, M.G. Role of pattern recognition receptors and the microbiota in neurological disorders. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.; Kwak, J.; Han, M.; Kim, T.H. Different Roles of Dendritic Cells for Chronic Rhinosinusitis Treatment According to Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, P.-J.; Gysemans, C.; Verstuyf, A.; Mathieu, C. Vitamin D’s effect on immune function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, D.-Q.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.-B.; Song, J.; Liang, Y.; Ruan, J.-W.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Li, J.-X.; Pan, L. Defective STING expression potentiates IL-13 signaling in epithelial cells in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska-Bliźniewska, H.; Paprocka-Zjawiona, M.; Merecz-Sadowska, A.; Zajdel, R.; Bliźniewska-Kowalska, K.; Malinowska, K. Serum IL-5, POSTN and IL-33 levels in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis correlate with clinical severity. BMC Immunol. 2022, 23, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perić, A.; Gaćeša, D.; Cvetković, G.; Vojvodić, D. Inflammatory mediators in nasal secretions of patients with nasal polyposis with and without aspirin sensitivity. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledda, A.G.; Costanzo, G.; Sambugaro, G.; Caruso, C.; Bullita, M.; Di Martino, M.L.; Serra, P.; Firinu, D.; Del Giacco, S. Eosinophil Cationic Protein Variation in Patients with Asthma and CRSwNP Treated with Dupilumab. Life 2023, 13, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, M.; Menzella, F.; Altieri, E.; Bargagli, E.; Bracciale, P.; Brussino, L.; Caiaffa, M.F.; Canonica, G.W.; Caruso, C.; Centanni, S.; et al. Benralizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma with and without chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: An ANANKE study post-hoc analysis. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 881218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.; Hull, L.; McLachlan, R.; Snidvongs, K.; Chin, D.; Pratt, E.; Kalish, L.; Sacks, R.; Earls, P.; Sewell, W.; et al. (Eds.) Clinical severity and epithelial endotypes in chronic rhinosinusitis. In International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Miljkovic, D.; Bassiouni, A.; Cooksley, C.; Ou, J.; Hauben, E.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. Association between group 2 innate lymphoid cells enrichment, nasal polyps and allergy in chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy 2014, 69, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, S.; Kondo, K.; Kanaya, K.; Suzukawa, K.; Ushio, M.; Urata, S.; Asakage, T.; Kakigi, A.; Suzukawa, M.; Ohta, K.; et al. Expression of IL-33 and its receptor ST2 in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, E115–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, H.; Luo, W. The PI3K-Akt-HIF-1α pathway reducing nasal airway inflammation and remodeling in nasal polyposis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, NP43–NP49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G.T.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Liao, B.; Lu, X.; Liu, Z. Increased accumulation of CD30 ligand-positive mast cells associates with eosinophilic inflammation in nasal polyps. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, E110–E117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, L.; Förster-Ruhrmann, U.; Olze, H.; Beule, A.G.; Chaker, A.M.; Hagemann, J.; Huppertz, T.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Dazert, S.; Deitmer, T.; et al. Evaluation of ongoing mepolizumab treatment in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Explor. Asthma Allergy 2024, 2, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Chang, L.-H.; Huang, W.-Q.; Wu, H.-T.; Wu, X.-F.; Huang, Z.-Z.; Zhang, G.-H. Effects and clinical significance of NLRP3 inflammasome activated by IL-17A in CRSwNP. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi Chin. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 58, 690–698. [Google Scholar]
- Tantilipikorn, P.; Sookrung, N.; Muangsomboon, S.; Lumyongsatien, J.; Bedavanija, A.; Suwanwech, T. Endotyping of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without polyp using transcription factor analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelardi, M.; Giancaspro, R.; Duda, L.; Quaranta, V.N.; Pizzulli, C.; Maiorano, E.; Di Canio, F.M.; Ruzza, A.; Iannuzzi, L.; Quaranta, N.A.A.; et al. Eosinophil-mast cell pattern of intraepithelial infiltration as a marker of severity in CRSwNP. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Laidlaw, T.M.; Cho, S.H.; Mullol, J.; Swanson, B.N.; Naimi, S.; Classe, M.; Harel, S.; Jagerschmidt, A.; Laws, E.; et al. Effect of dupilumab on type 2 biomarkers in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: SINUS-52 study results. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2023, 132, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.-J.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Ma, M.-C.; Wu, C.-K.; Luo, S.-D.; Wu, W.-B. Transcriptomic analysis of genes associated with oxidative stress in chronic rhinosinusitis patients with nasal polyps: Identifying novel genes involved in nasal polyposis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Th17/Treg cells regulated by interleukin 6 in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 279, 3493–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Tu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Shen, L.; Luo, Q.; Ye, J. Diagnostic value and underlying mechanism of nasal nitric oxide in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 159, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braile, M.; Fiorelli, A.; Sorriento, D.; Di Crescenzo, R.M.; Galdiero, M.R.; Marone, G.; Santini, M.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S. Human lung-resident macrophages express and are targets of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in the tumor microenvironment. Cells 2021, 10, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Xing, Q.L.; Yang, H.W.; Yang, F.; Luo, Y.; Kong, W.J.; Wang, Y.J. Construction and analysis of a ceRNA network and patterns of immune infiltration in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: Based on data mining and experimental verification. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.A.; Gupta, G.; Afzal, M.; Thapa, R.; Ali, H.; Alqahtani, S.M.; almalki, W.H.; Kazmi, I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Saleem, S.; et al. Polyphenol-loaded nano-carriers for breast cancer therapy: A comprehensive review. BioNanoScience 2024, 14, 4219–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiong, Y.; Tu, J.; Tang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Shen, L.; Luo, Q.; Ye, J. Hypoxia disrupts the nasal epithelial barrier by inhibiting PTPN2 in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, A.M.; El-Badaway, O.; Elsayh, I.K.; Osman, M.M. Delineation of T cell subsets in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022, 42, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, A.D.; Kohanski, M.A.; Cohen, N.A. Biomarkers in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Immunol. Allergy Clin. 2018, 38, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, P.; Han, J.K.; Smith, S.G.; Sousa, A.R.; Howarth, P.H.; Yancey, S.W.; Chan, R.; Bachert, C. (Eds.) The roles of eosinophils and interleukin-5 in the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. In International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Tsilioni, I.; Ren, H. Recent advances in our understanding of mast cell activation–or should it be mast cell mediator disorders? Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Maurer, M.; Palomares, O.; Busse, W.W. What is the contribution of IgE to nasal polyposis? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrani, J.H.; Strohm, A.N.; Haung, Y.-A.; Doherty, T.A. Monitoring Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Biology in Models of Lung Inflammation. Bio-Protocol 2023, 13, e4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, N.; Smole, U.; Yong, H.-M.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Yao, N.; Singh, A.; Gabrielson, E.; Wills-Karp, M.; Lajoie, S. C3a is required for ILC2 function in allergic airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretzki, A.; Lin, Y.J.; Schülke, S. Immune metabolism in allergies, does it matter?—A review of immune metabolic basics and adaptations associated with the activation of innate immune cells in allergy. Allergy 2021, 76, 3314–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.Y.; Bartemes, K.R.; Bachman, K.A.; Hagan, J.B.; Kita, H. In vitro culture with cytokines provides a tool to assess the effector functions of ilc2s in peripheral blood in asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 11, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, S.; He, Y.; Yin, Y.; Xu, W. Mast cell degranulation impairs pneumococcus clearance in mice via IL-6 dependent and TNF-α independent mechanisms. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, Z.; Chen, X.; Lai, X.; Zheng, R.; et al. IL-21 induces pyroptosis of Treg cells via Akt–mTOR–NLRP3–caspase 1 axis in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 641–655.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, T.; Pesic, J.; Pardali, K.; Gaestel, M.; Arthur, J.S.C. p38 MAPK signalling regulates cytokine production in IL-33 stimulated Type 2 Innate Lymphoid cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata, H.; Moro, K.; Koyasu, S. The group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC 2) regulatory network and its underlying mechanisms. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 286, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathä, L.; Krabbendam, L.; Martinez Høyer, S.; Heesters, B.A.; Golebski, K.; Kradolfer, C.; Ghaedi, M.; Ma, J.; Stadhouders, R.; Bachert, C.; et al. Human CD127 negative ILC2s show immunological memory. J. Exp. Med. 2024, 221, e20231827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Takahashi, H.; Tada, H.; Chikamatsu, K. Circulating T cell subsets and ILC2s are altered in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps after dupilumab treatment. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2023, 37, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglivo, I.; Quaranta, V.N.; Dragonieri, S.; Colantuono, S.; Menzella, F.; Selvaggio, D.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Caruso, C. The New Paradigm: The Role of Proteins and Triggers in the Evolution of Allergic Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkiewicz, D.; Kupczyk, M.; Brożek-Mądry, E.; Rapiejko, P. Biologicals in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps–position of the Polish Society of Otorhinolaryngologists–Head and Neck Surgeons and the Polish Society of Allergology experts. Pol. J. Otolaryngol. 2023, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Taheri, M.; Javan, F.; Poudineh, M.; Athari, S.S. Beyond CAR-T: The rise of CAR-NK cell therapy in asthma immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakushina, E.V.; Popova, L.I.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr.; Werner, J.; Mikhailovsky, N.V.; Bazhin, A.V. The advantages and challenges of anticancer dendritic cell vaccines and NK cells in adoptive cell immunotherapy. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Peters, A.T.; Stevens, W.W.; Schleimer, R.P.; Tan, B.K.; Kern, R.C. Endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: Relationships to disease phenotypes, pathogenesis, clinical findings, and treatment approaches. Allergy 2022, 77, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, M.; Abbasi, L.; Ghanbari Naeini, L.; Kokabian, P.; Nameh Goshay Fard, N.; Givtaj, N. Dendritic cells and natural killer cells: The road to a successful oncolytic virotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 950079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Lan, C.; Benlagha, K.; Camara, N.O.S.; Miller, H.; Kubo, M.; Heegaard, S.; Lee, P.; Yang, L.; Forsman, H.; et al. The interaction of innate immune and adaptive immune system. MedComm 2024, 5, e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Zhang, N.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, L. (Eds.) Highlights of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in definition, prognosis, and advancement. In International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Pan, S.; Lin, S. IL-33 expression in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and its relationship with clinical severity. Orl 2018, 79, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, T.; Nakayama, K.; Utsumi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Yanagisawa, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Minagawa, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Hara, H.; Araya, J.; et al. Efficacy of mepolizumab for patients with severe asthma and eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Bu, X.; Luan, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Distinct type 2-high inflammation associated molecular signatures of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps with comorbid asthma. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2020, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, M.A.; Corredera, E.; Banerjee, H.; Moore, J.; Wang, L.; Kane, L.P.; Lee, S.E. Association of mast cell burden and tim-3 expression with recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 130, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchagina, A.A.; Koroleva, E.; Tumanov, A.V. Innate lymphoid cells in response to intracellular pathogens: Protection versus immunopathology. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 775554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.T.; Gottschalk, T.A.; Tsantikos, E.; Hibbs, M.L. The role of innate lymphoid cells in chronic respiratory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 733324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Jo, A.; Lim, H.-S.; Kim, J.Y.; Eun, K.M.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.K.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, D.W. Enhanced type 2 immune reactions by increased IL-22/IL-22Ra1 signaling in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Eun, K.M.; Kim, M.-K.; Cho, D.; Han, S.A.; Han, S.-Y.; Seo, Y.; Lee, D.-H.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Comparison between signature cytokines of nasal tissues in subtypes of chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 11, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.J.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.L.; Kweon, M.-N.; Kim, J.H. Enhanced interferon-β response contributes to eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Shu, L.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Ke, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y. YES-associated protein-regulated Smad7 worsen epithelial barrier injury of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.; Bae, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.H.; Lyu, L.; Chung, Y.J.; Mo, J.H. Role of IL-17A in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regateiro, F.; Botelho Alves, P.; Moura, A.; Azevedo, J.; Regateiro, F.S. The diverse roles of T cell subsets in asthma. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 53, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, J.; Shahba, F.; Jafariaghdam, N.; Mohebbi, S.; Arshi, S.; Bemanian, M.H.; Fallahpour, M.; Shokri, S.; Atashrazm, F.; Amini, S.; et al. Immune endotyping and gene expression profile of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in the aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) and the non-AERD subgroups. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2024, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyawasam, H.H.; James, L.K. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: Eosinophils versus B lymphocytes in disease pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 24, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, N.; Piazzetta, G.L.; Lobello, N.; Cicala, G.; Patafi, M.; Benincasa, A.T.; Pelaia, C.; Chiarella, E.; Pelaia, G. Real-Life Effects of Omalizumab on Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Z.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J.-X.; Xiao, Q.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.-X.; Liu, Z. B cell–activating factor promotes B cell survival in ectopic lymphoid tissues in nasal polyps. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 625630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Guo, C.-L.; Xiang, W.-X.; Li, J.-X.; Huang, K.; Schleimer, R.P. Aberrant follicular regulatory T cells associate with immunoglobulin hyperproduction in nasal polyps with ectopic lymphoid tissues. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, F.; Tsuboi, H.; Ono, Y.; Abe, S.; Takahashi, H.; Ito, K.; Yamada, K.; Kawano, M.; Kondo, Y.; Asano, K.; et al. Pathogenic roles and therapeutic potential of the CCL8–CCR8 axis in a murine model of IgG4-related sialadenitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlBloushi, S.; Al-Ahmad, M. Exploring the immunopathology of type 2 inflammatory airway diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1285598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbecki, J.; Kojder, K.; Simińska, D.; Bohatyrewicz, R.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. CC chemokines in a tumor: A review of pro-cancer and anti-cancer properties of the ligands of receptors CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, and CCR4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soklic, T.K.; Rijavec, M.; Silar, M.; Koren, A.; Kern, I.; Hocevar-Boltezar, I.; Korosec, P. Transcription factors gene expression in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley-Yates, P.T.; Larenas-Linnemann, D.; Bhargave, C.; Verma, M. Intranasal corticosteroids: Topical potency, systemic activity and therapeutic index. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Jimenez, D.; Moreno-Luna, R.; Cuvillo, A.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.; Maza-Solano, J.; Sanchez-Gomez, S. Endoscopic extended sinus surgery for patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, the choice of mucoplasty: A systematic review. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023, 23, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Tsai, M.-H.; Su, Y.-Y.; Huang, S.-C. Comparison of cytokine expression and disease severity between plasma cell-dominant and eosinophil-dominant patients in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2024, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Heffler, E.; Crimi, C.; Maglio, A.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W. Interleukins 4 and 13 in asthma: Key pathophysiologic cytokines and druggable molecular targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 851940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishino, T.; Takeno, S.; Takemoto, K.; Yamato, K.; Oda, T.; Nishida, M.; Horibe, Y.; Chikuie, N.; Kono, T.; Taruya, T.; et al. Distinct gene set enrichment profiles in eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps by bulk RNA barcoding and sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzella, F.; Just, J.; Sauerbeck, I.S.; Mailaender, C.; Saccheri, F.; Thonnelier, C.; Jaumont, X.; Mala, L. Omalizumab for the treatment of patients with severe allergic asthma with immunoglobulin E levels above >1500 IU/mL. World Allergy Organ. J. 2023, 16, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Tan, B.K.; Klingler, A.I.; Poposki, J.A.; Hulse, K.E.; Grammer, L.C.; Welch, K.C.; Smith, S.S.; Conley, D.B.; et al. Associations between inflammatory endotypes and clinical presentations in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2812–2820.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.R.; Kosloski, M.P.; Xu, C.; Davis, J.D.; Kamal, M.A. Dupilumab: Mechanism of action, clinical, and translational science. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Song, X.; Wang, D.; Hu, L.; Yu, H.; Sun, X.; et al. Comparative short-term efficacy of endoscopic sinus surgery and biological therapies in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A network meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2023, 13, e12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantone, E.; De Corso, E.; Ricciardiello, F.; Di Nola, C.; Grimaldi, G.; Allocca, V.; Motta, G. Olfaction recovery following dupilumab is independent of nasal polyp reduction in CRSwNP. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, B.; Shen, S.; Song, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of CM310 in severe eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CROWNS-1): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 61, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Granata, F.; Pucino, V.; Pecoraro, A.; Heffler, E.; Loffredo, S.; Scadding, G.W.; Varricchi, G. The intriguing role of interleukin 13 in the pathophysiology of asthma. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, S.; Wang, C.; Yoshikawa, M.; Asako, M.; Suzaki, I.; Bachert, C.; Han, J.; Fuller, A.; Baylis, L.; Su, L.; et al. Mepolizumab in CRSwNP/ECRS and NP: The phase III randomised MERIT trial in Japan, China, and Russia. Rhinology 2024, 62, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredero-Jung, D.H.; Elena-Pérez, S.; García-Sánchez, A.; Estravís, M.; Isidoro-García, M.; Sanz, C.; Dávila, I. Interleukin 5 Receptor Subunit Alpha Expression as a Potential Biomarker in Patients with Nasal Polyposis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, P.; Desrosiers, M.; Cornet, M.; Mullol, J.; De Corso, E.; Turel, N.K.; Maspero, J.; Fujieda, S.; Zhang, L.; Sousa, A.R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of twice per year depemokimab in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (ANCHOR-1 and ANCHOR-2): Phase 3, randomised, double-blind, parallel trials. Lancet 2025, 405, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, S.; Tasnin, F.M.; Islam, M.N.; Rauf, A.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Ahmed Khalil, A.; Aljohani, A.S.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; et al. Role of Th17 and IL-17 Cytokines on Inflammatory and Auto-immune Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panettieri, R., Jr.; Lugogo, N.; Corren, J.; Ambrose, C.S. Tezepelumab for severe asthma: One drug targeting multiple disease pathways and patient types. J. Asthma Allergy 2024, 31, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipworth, B.J.; Han, J.K.; Desrosiers, M.; Hopkins, C.; Lee, S.E.; Mullol, J.; Pfaar, O.; Li, T.; Chen, C.; Almqvist, G.; et al. Tezepelumab in adults with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yan, H.; Chen, L.; Hou, Q.; Chen, B.; et al. Translational Investigation of CM326 from Preclinical Studies to Randomized Phase I Clinical Trials in Healthy Adults. BioDrugs 2025, 39, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandikattu, H.K.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Mishra, A. Synergy of Interleukin (IL)-5 and IL-18 in eosinophil mediated pathogenesis of allergic diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 47, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virchow, J.C.; McDonald, M.; Garin, M.; Korn, S. Reslizumab as add-on therapy in patients with refractory asthma. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2020, 7, e000494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farokhi, S.; Tabaie, S.M.; Fakouri, A.; Manshouri, S.; Emtiazi, N.; Sanaei, A.; Mahjoor, M.; Akbari, A.M.; Daneshvar, A.; Seif, F. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Window of Immunologic Responses and Horizon of Biological Therapies. Immuno 2025, 5, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030026
Farokhi S, Tabaie SM, Fakouri A, Manshouri S, Emtiazi N, Sanaei A, Mahjoor M, Akbari AM, Daneshvar A, Seif F. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Window of Immunologic Responses and Horizon of Biological Therapies. Immuno. 2025; 5(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarokhi, Simin, Seyed Mehdi Tabaie, Arshia Fakouri, Shirin Manshouri, Nikoo Emtiazi, Ayda Sanaei, Mohammad Mahjoor, Amir Mohammad Akbari, Ali Daneshvar, and Farhad Seif. 2025. "Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Window of Immunologic Responses and Horizon of Biological Therapies" Immuno 5, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030026
APA StyleFarokhi, S., Tabaie, S. M., Fakouri, A., Manshouri, S., Emtiazi, N., Sanaei, A., Mahjoor, M., Akbari, A. M., Daneshvar, A., & Seif, F. (2025). Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Window of Immunologic Responses and Horizon of Biological Therapies. Immuno, 5(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030026






