Immunopathogenesis of Nipah Virus Infection and Associated Immune Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiological and Clinical Perspectives
2.1. Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
2.2. Human Transmission of Henipaviruses
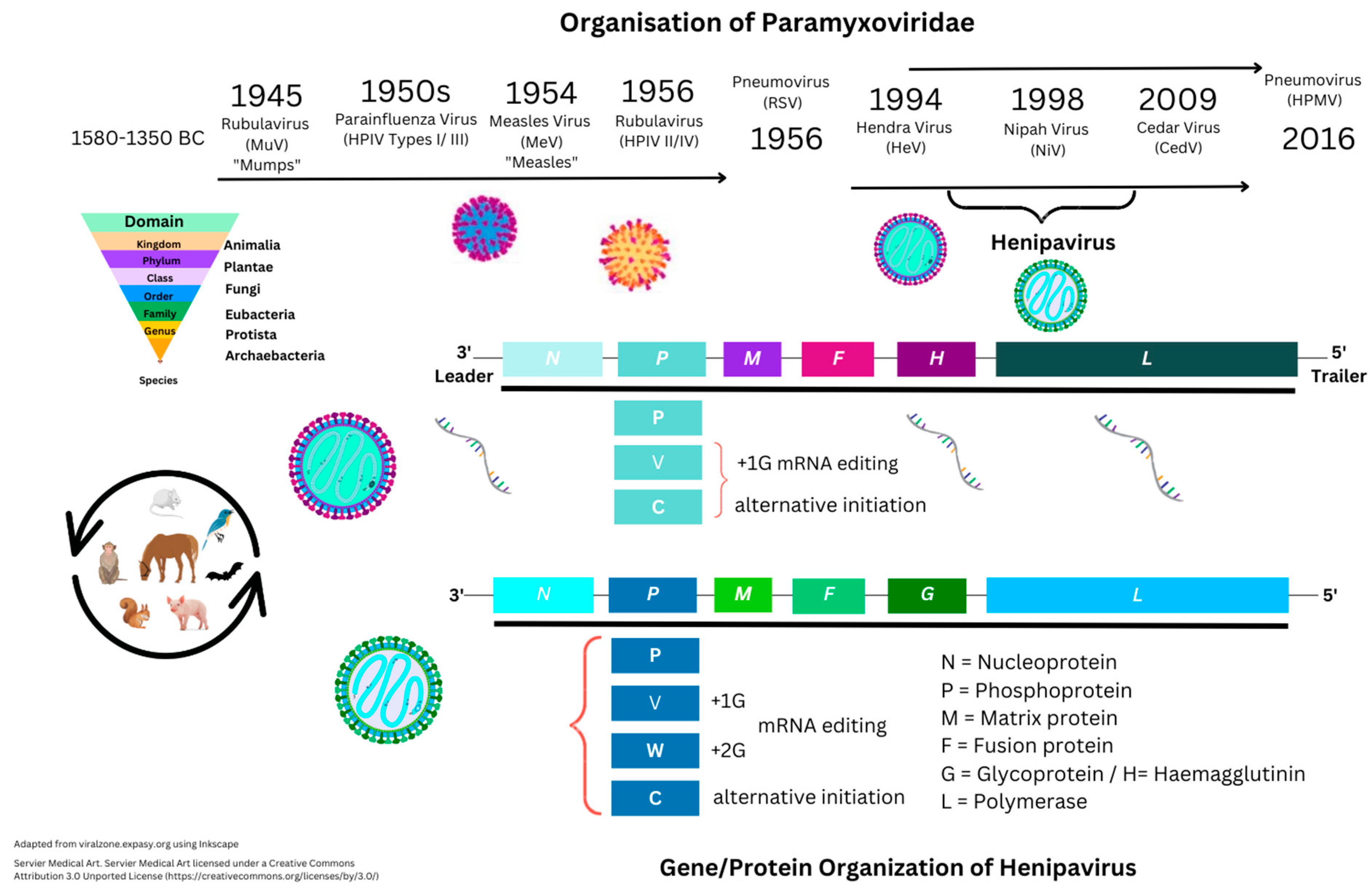
2.3. Animal Host Reservoirs of Henipaviruses
3. Henipavirus Pathogenesis
3.1. Introduction to Nipah Virus Proteins and Genes
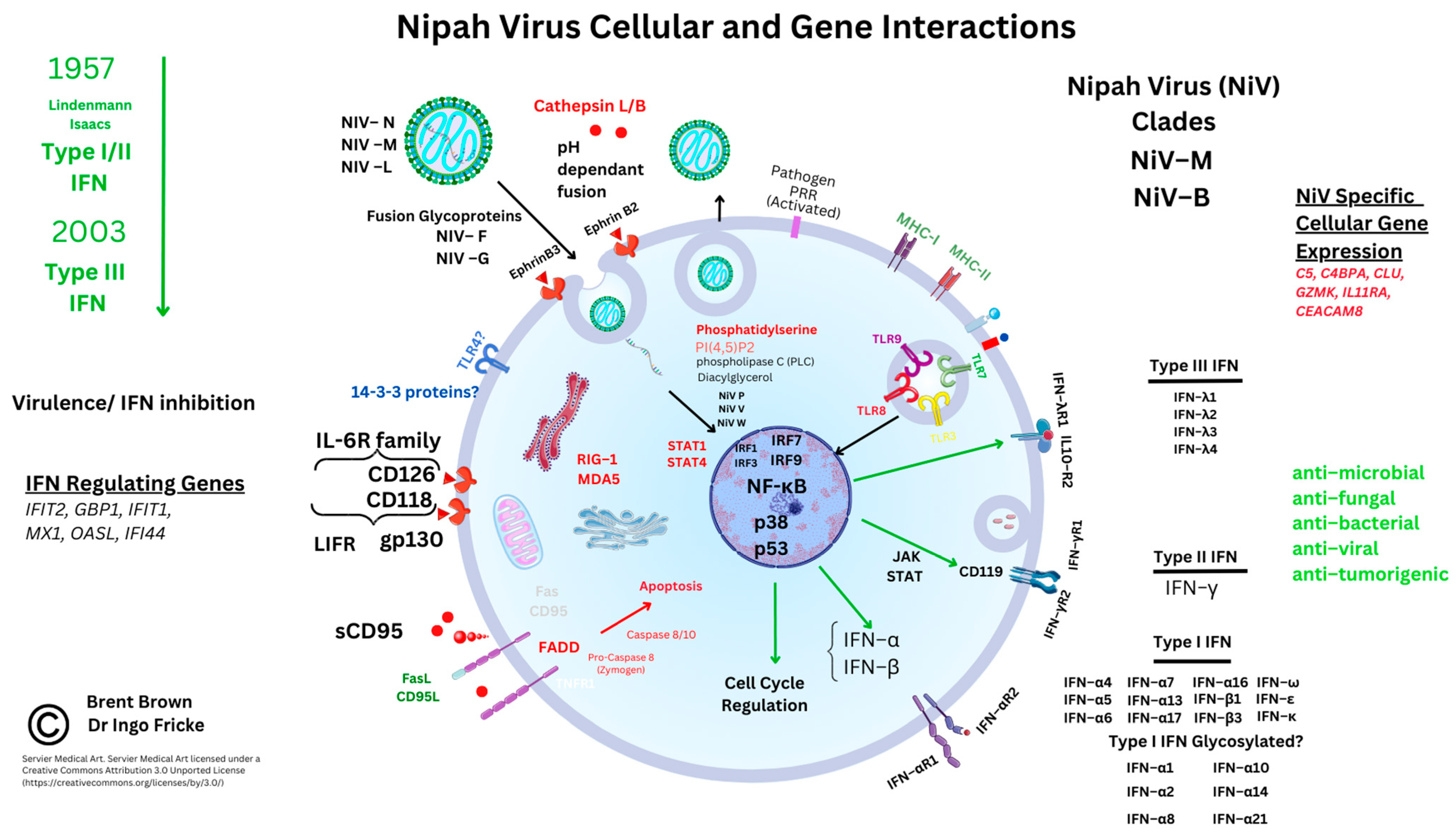
3.2. Nipah Virus Viral Protein Factors
3.3. Receptor-Mediated Nipah Virus Entry
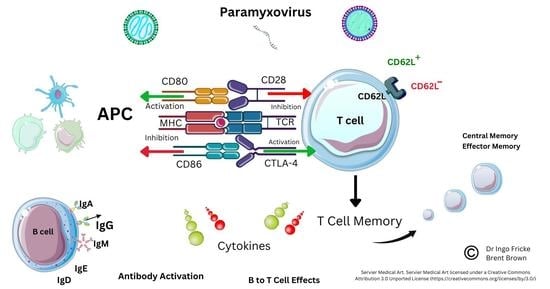
3.4. Cellular Immunomodulatory Properties of Nipah Virus Infection
4. Current Therapeutics
4.1. Clinical Trials
4.2. Henipavirus Monoclonal Antibodies and Vaccines in Development
4.3. Current Antiviral Therapeutics
4.4. Diagnostic Methods and Future Prospects
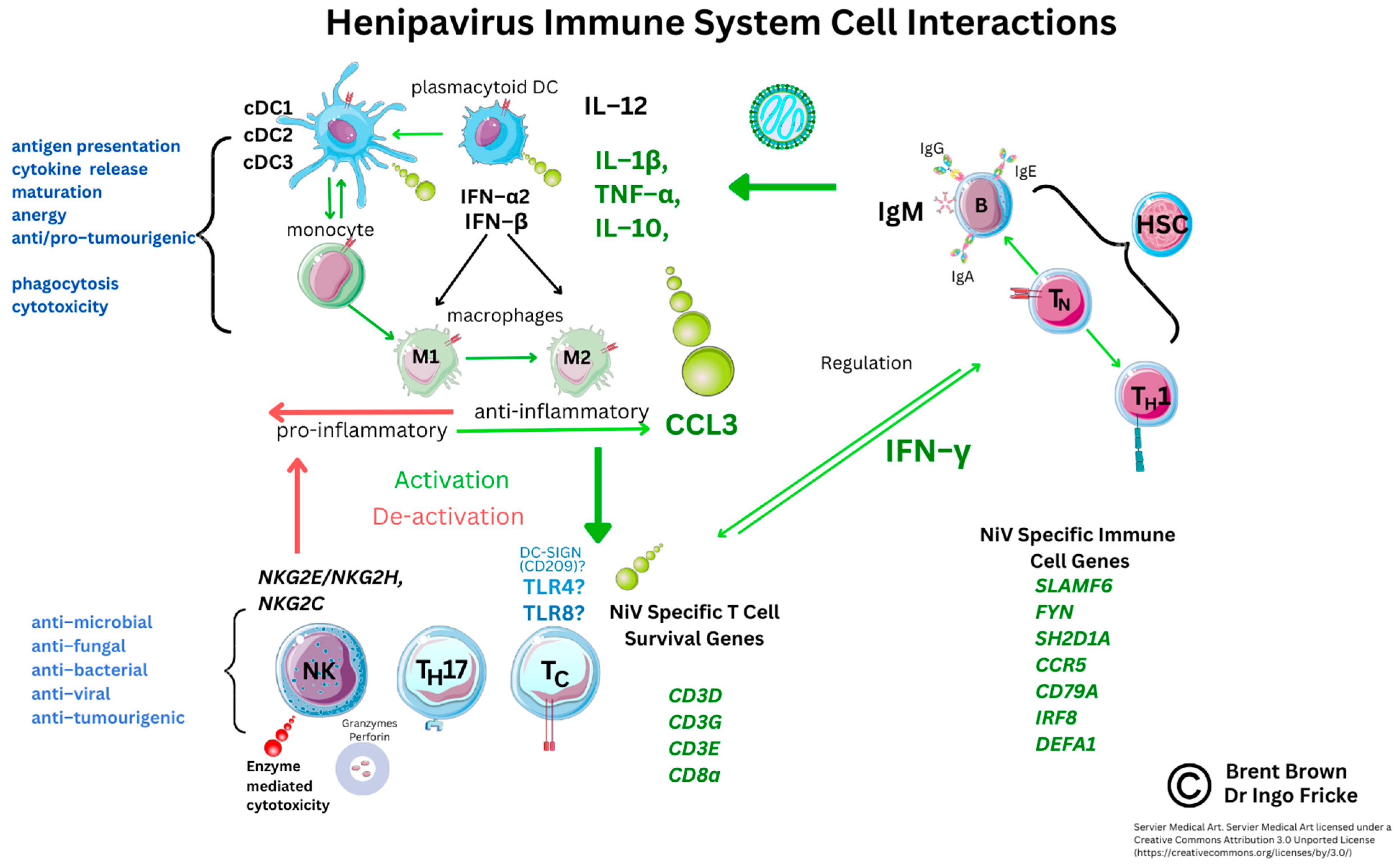
5. Current Known Immunological Perspectives of Nipah Virus Infection
5.1. Background
5.2. Analysis of Cellular Nipah Virus Immunogen Responses
5.3. Current Implications and Immunological Research
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; Ayllón, M.A.; Bào, Y.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briese, T.; Brown, P.A.; Bukreyev, A.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the Order Mononegavirales: Update 2019. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, V.; Mattenberger, F.; Geller, R. Chaperoning the Mononegavirales: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Viruses 2018, 10, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.G.; Hur, S. Cellular Origins of DsRNA, Their Recognition and Consequences. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Etten, J.L.; Lane, L.C.; Dunigan, D.D. DNA Viruses: The Really Big Ones (Viruses). Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.; Rogers, R.; Selvey, L.; Selleck, P.; Hyatt, A.; Gould, A.; Gleeson, L.; Hooper, P.; Westbury, H. A Novel Morbillivirus Pneumonia of Horses and Its Transmission to Humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1995, 1, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J.J. Nipah-Virus Encephalitis—Investigation of a New Infection. Lancet 1999, 354, 1222–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Müller, M.A.; Maganga, G.D.; Vallo, P.; Binger, T.; Gloza-Rausch, F.; Cottontail, V.M.; Rasche, A.; Yordanov, S.; et al. Bats Host Major Mammalian Paramyxoviruses. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, K.; Young, P.L.; Field, H.; Mackenzie, J.S. Newly Discovered Viruses of Flying Foxes. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 68, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, G.A.; de Jong, C.; Barr, J.A.; Tachedjian, M.; Smith, C.; Middleton, D.; Yu, M.; Todd, S.; Foord, A.J.; Haring, V.; et al. Cedar Virus: A Novel Henipavirus Isolated from Australian Bats. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, H.; Young, P.; Yob, J.M.; Mills, J.; Hall, L.; Mackenzie, J. The Natural History of Hendra and Nipah Viruses. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, V.P.; Hossain, M.J.; Parashar, U.D.; Ali, M.M.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Kuzmin, I.; Niezgoda, M.; Rupprecht, C.; Bresee, J.; Breiman, R.F. Nipah Virus Encephalitis Reemergence, Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, N.; Liu, B.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, L.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, F. Genetic Characteristics of Human Parainfluenza Virus Types 1-4 From Patients With Clinical Respiratory Tract Infection in China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 679246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Pang, J.; Ma, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y. Global Magnitude of Encephalitis Burden and Its Evolving Pattern over the Past 30 Years. J. Infect. 2022, 84, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, A.; Herrmann, J.L.; Morand, P.; Buzelé, R.; Crabol, Y.; Stahl, J.P.; Mailles, A. Epidemiology of Infectious Encephalitis Causes in 2016. Med. Mal. Infect. 2017, 47, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackhurst, B.M.; Funk, K.E. Viral pathogens increase risk of neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Ojha, V.; Fricke, I.; Al-Sheboul, S.A.; Imarogbe, C.; Gravier, T.; Green, M.; Peterson, L.; Koutsaroff, I.P.; Demir, A.; et al. Innate and Adaptive Immunity during SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Biomolecular Cellular Markers and Mechanisms. Vaccines 2023, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, M.S.; Comer, J.A.; Lowe, L.; Rota, P.A.; Rollin, P.E.; Bellini, W.J.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Mishra, A.C. Nipah Virus-Associated Encephalitis Outbreak, Siliguri, India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.L.; Defres, S.; Solomon, T. Measles-Induced Encephalitis. QJM 2015, 108, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Keum, H.R.; Kim, S.W.; Baek, H.S.; Byun, J.C.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.M. Seasonal Trends in the Prevalence, and Incidence of Viral Encephalitis in Korea (2015–2019). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Autoimmune Encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunkel, A.R.; Glaser, C.A.; Bloch, K.C.; Sejvar, J.J.; Marra, C.M.; Roos, K.L.; Hartman, B.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Scheld, W.M.; Whitley, R.J. The Management of Encephalitis: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sejvar, J.J.; Hossain, J.; Saha, S.K.; Gurley, E.S.; Banu, S.; Hamadani, J.D.; Faiz, M.A.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Mohammad, Q.D.; Mollah, A.H.; et al. Long-Term Neurological and Functional Outcome in Nipah Virus Infection. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumanes, D.; Falsey, A.R.; Quataert, S.; Secor-Socha, S.; Lee, F.E.-H.; Yang, H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Topham, D.J.; Walsh, E.E. T-Cell Responses in Adults During Natural Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fülöp, T.; Larbi, A.; Pawelec, G. Human T Cell Aging and the Impact of Persistent Viral Infections. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassoun, F.; Goldeck, D.; Pera, A.; van Heemst, D.; Slagboom, P.E.; Pawelec, G.; Solana, R. Functional Changes of T-Cell Subsets with Age and CMV Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Sazzad, H.M.S.; Satter, S.M.; Sultana, S.; Hossain, M.J.; Hasan, M.; Rahman, M.; Campbell, S.; Cannon, D.L.; Ströher, U.; et al. Nipah Virus Transmission from Bats to Humans Associated with Drinking Traditional Liquor Made from Date Palm Sap, Bangladesh, 2011–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arankalle, V.A.; Bandyopadhyay, B.T.; Ramdasi, A.Y.; Jadi, R.; Patil, D.R.; Rahman, M.; Majumdar, M.; Banerjee, P.S.; Hati, A.K.; Goswami, R.P.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Nipah Virus, West Bengal, India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, K.; Hyatt, A.D.; Fogarty, R.; Middleton, D.; Bingham, J.; Epstein, J.H.; Rahman, S.A.; Hughes, T.; Smith, C.; Field, H.E.; et al. Henipavirus Ecology Research Group. Pteropid bats are confirmed as the reservoir hosts of henipaviruses: A comprehensive experimental study of virus transmission. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.E.; Islam, A.; Crameri, G.; Todd, S.; Islam, A.; Khan, S.U.; Foord, A.; Rahman, M.Z.; Mendenhall, I.H.; Luby, S.P.; et al. Isolation and Full-Genome Characterization of Nipah Viruses from Bats, Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.Z.; Sazzad, H.M.S.; Luby, S.P.; Sturm-Ramirez, K.; Bhuiyan, M.U.; Rahman, M.Z.; Islam, M.M.; Ströher, U.; Sultana, S.; Kafi, M.A.H.; et al. Nipah Virus Contamination of Hospital Surfaces during Outbreaks, Bangladesh, 2013–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Hickey, A.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Han, Z.; McEachern, J.; et al. Antibodies to Nipah or Nipah-like Viruses in Bats, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1974–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudeep, A.B.; Yadav, P.D.; Gokhale, M.D.; Balasubramanian, R.; Gupta, N.; Shete, A.; Jain, R.; Patil, S.; Sahay, R.R.; Nyayanit, D.A.; et al. Detection of Nipah Virus in Pteropus Medius in 2019 Outbreak from Ernakulam District, Kerala, India. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.D.; Sahay, R.R.; Balakrishnan, A.; Mohandas, S.; Radhakrishnan, C.; Gokhale, M.D.; Balasubramanian, R.; Abraham, P.; Gupta, N.; Sugunan, A.P.; et al. Nipah Virus Outbreak in Kerala State, India Amidst of COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Gyamfi, E.; Kim, L.S.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Lamb, R.A. Mutagenesis of Paramyxovirus Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Membrane-Proximal Stalk Region Influences Stability, Receptor Binding, and Neuraminidase Activity. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7778–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranadheera, C.; Proulx, R.; Chaiyakul, M.; Jones, S.; Grolla, A.; Leung, A.; Rutherford, J.; Kobasa, D.; Carpenter, M.; Czub, M. The Interaction between the Nipah Virus Nucleocapsid Protein and Phosphoprotein Regulates Virus Replication. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossart, K.N.; Fusco, D.L.; Broder, C.C. Paramyxovirus entry. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 790, 95–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.J.; Wang, L.-F.; Horvath, C.M. Hendra Virus V Protein Inhibits Interferon Signaling by Preventing STAT1 and STAT2 Nuclear Accumulation. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11842–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabukarski, F.; Lawrence, P.; Tarbouriech, N.; Bourhis, J.-M.; Delaforge, E.; Jensen, M.R.; Ruigrok, R.W.H.; Blackledge, M.; Volchkov, V.; Jamin, M. Structure of Nipah Virus Unassembled Nucleoprotein in Complex with Its Viral Chaperone. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Kliemke, V.; Liu, Q.; Chou, K.C. The Nanoscale Organization of Nipah Virus Matrix Protein Revealed by Super-Resolution Microscopy. Biophys. J. 2022, 121, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, M.; Maisner, A. Nipah Virus Fusion Protein: Importance of the Cytoplasmic Tail for Endosomal Trafficking and Bioactivity. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 94, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterfield, B.A.; Cross, R.W.; Fenton, K.A.; Borisevich, V.; Agans, K.N.; Deer, D.J.; Graber, J.; Basler, C.F.; Geisbert, T.W.; Mire, C.E. Nipah Virus C and W Proteins Contribute to Respiratory Disease in Ferrets. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6326–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.-S.; Shaw, M.L.; Muñoz-Jordan, J.; Cros, J.F.; Nakaya, T.; Bouvier, N.; Palese, P.; García-Sastre, A.; Basler, C.F. Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV)-Based Assay Demonstrates Interferon-Antagonist Activity for the NDV V Protein and the Nipah Virus V, W, and C Proteins. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowiak, B.; Weingartl, H.M. Nipah Virus Infects Specific Subsets of Porcine Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, Z.; Tang, W.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kwok, H.F.; Sun, F.; Cao, Z. P38 Activation and Viral Infection. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2022, 24, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.J.; Husby, M.L.; Kiosses, W.B.; Yin, J.; Saxena, R.; Rennick, L.J.; Heiner, A.; Harkins, S.S.; Pokhrel, R.; Schendel, S.L.; et al. Measles and Nipah Virus Assembly: Specific Lipid Binding Drives Matrix Polymerization. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.T.; Broder, C.C.; Middleton, D.; Wang, L.-F. Hendra and Nipah Viruses: Different and Dangerous. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, P.; Dutta, D.; Ghosh, E.; Bose, I.; Bhattacharjee, S. Molecular Pathogenesis of Nipah Virus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 2451–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, M.L.; Yusoff, K.; Othman, S.; Chia, S.L. V Protein, the Virulence Factor across the Family Paramyxoviridae: A Review. Asia Pac. J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 27, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaparte, M.I.; Dimitrov, A.S.; Bossart, K.N.; Crameri, G.; Mungall, B.A.; Bishop, K.A.; Choudhry, V.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Wang, L.-F.; Eaton, B.T.; et al. Ephrin-B2 Ligand Is a Functional Receptor for Hendra Virus and Nipah Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10652–10657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.J.W.; Young, T.A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Leser, G.P.; Komives, E.A.; Lamb, R.A.; Zhou, Z.H.; Salafsky, J.; Jardetzky, T.S. Monomeric EphrinB2 Binding Induces Allosteric Changes in Nipah Virus G That Precede Its Full Activation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochenek, M.L.; Dickinson, S.; Astin, J.W.; Adams, R.H.; Nobes, C.D. Ephrin-B2 Regulates Endothelial Cell Morphology and Motility Independently of Eph-Receptor Binding. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawatsky, B.; Grolla, A.; Kuzenko, N.; Weingartl, H.; Czub, M. Inhibition of Henipavirus Infection by Nipah Virus Attachment Glycoprotein Occurs without Cell-Surface Downregulation of Ephrin-B2 or Ephrin-B3. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradel-Tretheway, B.G.; Liu, Q.; Stone, J.A.; McInally, S.; Aguilar, H.C. Novel Functions of Hendra Virus G N-Glycans and Comparisons to Nipah Virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7235–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stone, J.A.; Nicola, A.V.; Baum, L.G.; Aguilar, H.C. Multiple Novel Functions of Henipavirus O-Glycans: The First O-Glycan Functions Identified in the Paramyxovirus Family. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, R.R.; Muth, A.; Schneider, I.C.; Friedel, T.; Hartmann, J.; Plückthun, A.; Maisner, A.; Buchholz, C.J. Receptor-Targeted Nipah Virus Glycoproteins Improve Cell-Type Selective Gene Delivery and Reveal a Preference for Membrane-Proximal Cell Attachment. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, O.A.; Wolf, M.C.; Aguilar, H.C.; Enterlein, S.; Wang, W.; Mühlberger, E.; Su, S.V.; Bertolotti-Ciarlet, A.; Flick, R.; Lee, B. Two Key Residues in EphrinB3 Are Critical for Its Use as an Alternative Receptor for Nipah Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratnarajah, C.K.; Generous, A.R.; Yousaf, I.; Cattaneo, R. Receptor-Mediated Cell Entry of Paramyxoviruses: Mechanisms, and Consequences for Tropism and Pathogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 2771–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.L.; Schountz, T.; Wang, L.-F. Antiviral Immune Responses of Bats: A Review. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. IFNγ: Signalling, Epigenetics and Roles in Immunity, Metabolism, Disease and Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenborn, J.R.; Wilson, C.B. Regulation of interferon-gamma during innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv. Immunol. 2007, 96, 41–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, S.; Horie, R.; Sato, H.; Kai, C.; Yoneda, M. Possible Role of the Nipah Virus V Protein in the Regulation of the Interferon Beta Induction by Interacting with UBX Domain-Containing Protein1. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; O’Boyle, K.; Auer, J.; Raju, S.; You, F.; Wang, P.; Fikrig, E.; Sutton, R.E. Multiple UBXN Family Members Inhibit Retrovirus and Lentivirus Production and Canonical NFκΒ Signaling by Stabilizing IκBα. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Baker, M.L.; Kulcsar, K.; Misra, V.; Plowright, R.; Mossman, K. Novel Insights Into Immune Systems of Bats. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanelli, G.; Pagnini, U.; Iovane, G.; García-Sastre, A. Type I and Type II Interferon Antagonism Strategies Used by Paramyxoviridae: Previous and New Discoveries, in Comparison. Viruses 2022, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iampietro, M.; Aurine, N.; Dhondt, K.P.; Dumont, C.; Pelissier, R.; Spanier, J.; Vallve, A.; Raoul, H.; Kalinke, U.; Horvat, B. Control of Nipah Virus Infection in Mice by the Host Adaptors Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein (MAVS) and Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response 88 (MyD88). J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, S401–S406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.L.; Woolsey, C.; Borisevich, V.; Agans, K.N.; Prasad, A.N.; Deer, D.J.; Geisbert, J.B.; Dobias, N.S.; Fenton, K.A.; Cross, R.W.; et al. A recombinant VSV-vectored vaccine rapidly protects nonhuman primates against lethal Nipah virus. disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200065119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Guillaume, V.; Sato, H.; Fujita, K.; Georges-Courbot, M.-C.; Ikeda, F.; Omi, M.; Muto-Terao, Y.; Wild, T.F.; Kai, C. The Nonstructural Proteins of Nipah Virus Play a Key Role in Pathogenicity in Experimentally Infected Animals. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Yi, H. Toll-like Receptor 3 (TLR3) Regulation Mechanisms and Roles in Antiviral Innate Immune Responses. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2021, 22, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, A.T.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, P.-S.; Luko, K.; Rozario, P.; Wen, M.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, P.; Ng, J.H.J.; Sobota, R.M.; et al. Interferon Regulatory Factors IRF1 and IRF7 Directly Regulate Gene Expression in Bats in Response to Viral Infection. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Gao, Y.; Dozmorov, I.; Malladi, V.; Saha, I.; McDaniel, M.M.; Parameswaran, S.; Liang, C.; Arana, C.; Zhang, B.; et al. IRF1 Governs the Differential Interferon-Stimulated Gene Responses in Human Monocytes and Macrophages by Regulating Chromatin Accessibility. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharaj, P.; Wang, Y.E.; Dawes, B.E.; Yun, T.E.; Park, A.; Yen, B.; Basler, C.F.; Freiberg, A.N.; Lee, B.; Rajsbaum, R. The Matrix Protein of Nipah Virus Targets the E3-Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM6 to Inhibit the IKKε Kinase-Mediated Type-I IFN Antiviral Response. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran Satyanarayanan, S.; El Kebir, D.; Soboh, S.; Butenko, S.; Sekheri, M.; Saadi, J.; Peled, N.; Assi, S.; Othman, A.; Schif-Zuck, S.; et al. IFN-β Is a Macrophage-Derived Effector Cytokine Facilitating the Resolution of Bacterial Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Rouzaut, A.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Le Bon, A.; Melero, I. Direct Effects of Type I Interferons on Cells of the Immune System. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiffer, T.R.; Ciancanelli, M.J.; Edwards, M.R.; Basler, C.F. Interactions of the Nipah Virus P, V, and W Proteins across the STAT Family of Transcription Factors. mSphere 2020, 5, e00449-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torpey, N.; Maher, S.E.; Bothwell, A.L.M.; Pober, J.S. Interferon α but Not Interleukin 12 Activates STAT4 Signaling in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26789–26796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, K.; Graham, K.; Durr, P.A. Sero-Monitoring of Horses Demonstrates the Equivac® HeV Hendra Virus Vaccine to Be Highly Effective in Inducing Neutralising Antibody Titres. Vaccines 2021, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, V.; Contamin, H.; Loth, P.; Georges-Courbot, M.-C.; Lefeuvre, A.; Marianneau, P.; Chua, K.B.; Lam, S.K.; Buckland, R.; Deubel, V.; et al. Nipah Virus: Vaccination and Passive Protection Studies in a Hamster Model. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartl, H.M.; Berhane, Y.; Caswell, J.L.; Loosmore, S.; Audonnet, J.-C.; Roth, J.A.; Czub, M. Recombinant Nipah Virus Vaccines Protect Pigs against Challenge. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7929–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playford, E.G.; Munro, T.; Mahler, S.M.; Elliott, S.; Gerometta, M.; Hoger, K.L.; Jones, M.L.; Griffin, P.; Lynch, K.D.; Carroll, H.; et al. Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Immunogenicity of a Human Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the G Glycoprotein of Henipaviruses in Healthy Adults: A First-in-Human, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 1 Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya, M.; Broder, C.C. Vaccines to Emerging Viruses: Nipah and Hendra. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020, 7, 447–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mire, C.E.; Satterfield, B.A.; Geisbert, J.B.; Agans, K.N.; Borisevich, V.; Yan, L.; Chan, Y.-P.; Cross, R.W.; Fenton, K.A.; Broder, C.C.; et al. Pathogenic Differences between Nipah Virus Bangladesh and Malaysia Strains in Primates: Implications for Antibody Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Bobb, K.; Borisevich, V.; Geisbert, J.B.; Agans, K.N.; Cross, R.W.; Prasad, A.N.; Fenton, K.A.; Yu, H.; Fouts, T.R.; et al. A Single Dose Investigational Subunit Vaccine for Human Use against Nipah Virus and Hendra Virus. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.K.; Graham, S.P. Vaccine Development for Nipah Virus Infection in Pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicks, M.D.J.; Spencer, A.J.; Edwards, N.J.; Wadell, G.; Bojang, K.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hill, A.V.S.; Cottingham, M.G. A Novel Chimpanzee Adenovirus Vector with Low Human Seroprevalence: Improved Systems for Vector Derivation and Comparative Immunogenicity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warimwe, G.M.; Gesharisha, J.; Carr, B.V.; Otieno, S.; Otingah, K.; Wright, D.; Charleston, B.; Okoth, E.; Elena, L.-G.; Lorenzo, G.; et al. Chimpanzee Adenovirus Vaccine Provides Multispecies Protection against Rift Valley Fever. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, V.J.; Wells, D.; Lambe, T.; Wright, D.; Fischer, R.J.; Bushmaker, T.; Saturday, G.; van Doremalen, N.; Gilbert, S.C.; de Wit, E.; et al. Protective Efficacy of a Novel Simian Adenovirus Vaccine against Lethal MERS-CoV Challenge in a Transgenic Human DPP4 Mouse Model. NPJ Vaccines 2017, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Doremalen, N.; Lambe, T.; Sebastian, S.; Bushmaker, T.; Fischer, R.; Feldmann, F.; Haddock, E.; Letko, M.; Avanzato, V.A.; Rissanen, I.; et al. A Single-Dose ChAdOx1-Vectored Vaccine Provides Complete Protection against Nipah Bangladesh and Malaysia in Syrian Golden Hamsters. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, E.; Harrington-Kandt, R.; Beglov, J.; Bull, N.; Pinpathomrat, N.; Swarbrick, G.M.; Lewinsohn, D.A.; Lewinsohn, D.M.; McShane, H. Identification and Evaluation of Novel Protective Antigens for the Development of a Candidate Tuberculosis Subunit Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00014-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doremalen, N.; Avanzato, V.A.; Goldin, K.; Feldmann, F.; Schulz, J.E.; Haddock, E.; Okumura, A.; Lovaglio, J.; Hanley, P.W.; Cordova, K.; et al. ChAdOx1 NiV Vaccination Protects against Lethal Nipah Bangladesh Virus Infection in African Green Monkeys. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, V. In Silico Identification of Epitope-Based Peptide Vaccine for Nipah Virus. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangacharya, O.; Parab, A.; Adkine, S.; Nagargoje, R. A Study on the Design of an in Silico Self-Amplifying MRNA Vaccine against Nipah Virus Using Immunoinformatics. J. Biomol. Struct Dyn. 2023, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalodimou, G.; Veit, S.; Jany, S.; Kalinke, U.; Broder, C.C.; Sutter, G.; Volz, A. A Soluble Version of Nipah Virus Glycoprotein G Delivered by Vaccinia Virus MVA Activates Specific CD8 and CD4 T Cells in Mice. Viruses 2019, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Georges-Courbot, M.-C.; Ikeda, F.; Ishii, M.; Nagata, N.; Jacquot, F.; Raoul, H.; Sato, H.; Kai, C. Recombinant Measles Virus Vaccine Expressing the Nipah Virus Glycoprotein Protects against Lethal Nipah Virus Challenge. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.-T.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Tan, C.-T.; Goh, K.-J.; Thayaparan, T.; Kunjapan, S.R.; Chew, N.-K.; Chua, K.-B.; Lam, S.-K. Treatment of Acute Nipah Encephalitis with Ribavirin. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 49, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, K.; Daikoku, T. Favipiravir, an Anti-Influenza Drug against Life-Threatening RNA Virus Infections. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 209, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, B.E.; Kalveram, B.; Ikegami, T.; Juelich, T.; Smith, J.K.; Zhang, L.; Park, A.; Lee, B.; Komeno, T.; Furuta, Y.; et al. Favipiravir (T-705) Protects against Nipah Virus Infection in the Hamster Model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.K.; Feldmann, F.; Gary, J.M.; Jordan, R.; Bannister, R.; Cronin, J.; Patel, N.R.; Klena, J.D.; Nichol, S.T.; Cihlar, T.; et al. Remdesivir (GS-5734) Protects African Green Monkeys from Nipah Virus Challenge. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Gall, F.M.; Mathieu, C.; Hierweger, M.M.; Brügger, M.; Alves, M.P.; Vesin, J.; Banfi, D.; Kalbermatter, D.; Horvat, B.; et al. Highly Potent Host-Specific Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Paramyxovirus and Pneumovirus Replication with High Resistance Barrier. mBio 2021, 12, e0262121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhu, W.; Truong, T.; Pickering, B.; Babiuk, S.; Kobasa, D.; Banadyga, L. Detection of Nipah and Hendra Viruses Using Recombinant Human Ephrin B2 Capture Virus in Immunoassays. Viruses 2022, 14, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, N.M.; Olsson, M.; Marsh, G.A.; Macdonald, J.; McMillan, D. Evaluation of Three Rapid Low-Resource Molecular Tests for Nipah Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1101914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.d.M.; Puspo, J.A.; Adib, A.A.; Hossain, M.E.; Alam, M.M.; Sultana, S.; Islam, A.; Klena, J.D.; Montgomery, J.M.; Satter, S.M.; et al. An Immunoinformatics Prediction of Novel Multi-Epitope Vaccines Candidate Against Surface Antigens of Nipah Virus. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mass, E.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Kierdorf, K.; Schlitzer, A. Tissue-specific macrophages: How they develop and choreograph tissue biology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Verma, S.; Kamthania, M.; Saxena, A.K.; Pandey, K.C.; Pande, V.; Kolbe, M. Exploring the Structural Basis to Develop Efficient Multi-Epitope Vaccines Displaying Interaction with HLA and TAP and TLR3 Molecules to Prevent NIPAH Infection, a Global Threat to Human Health. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, N.I.; Leo, Y.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Auchus, A.P.; Lee, K.E.; Ling, A.E.; Chew, S.K.; Ang, B.; Rollin, P.E.; Umapathi, T.; et al. Outbreak of Nipah-Virus Infection among Abattoir Workers in Singapore. Lancet 1999, 354, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, P.; Ksiazek, T.; Eaton, B.T. Laboratory Diagnosis of Nipahand Hendra Virus Infections. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, Y.; Weingartl, H.M.; Lopez, J.; Neufeld, J.; Czub, S.; Embury-Hyatt, C.; Goolia, M.; Copps, J.; Czub, M. Bacterial Infections in Pigs Experimentally Infected with Nipah Virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2008, 55, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, R.; Wosik, K.; Berard, J.L.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Ifergan, I.; Kebir, H.; Haqqani, A.S.; Kreymborg, K.; Krug, S.; Moumdjian, R.; et al. Activated Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule Promotes Leukocyte Trafficking into the Central Nervous System. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.A. The Role of CD6 in Autoimmune Diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 1001–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuo, H.; Ono, N.; Yanagi, Y. Morbilliviruses Use Signaling Lymphocyte Activation Molecules (CD150) as Cellular Receptors. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5842–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorenko, S.P.; Clark, E.A. The Dual-Function CD150 Receptor Subfamily: The Viral Attraction. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolsey, C.; Borisevich, V.; Fears, A.C.; Agans, K.N.; Deer, D.J.; Prasad, A.N.; O’Toole, R.; Foster, S.L.; Dobias, N.S.; Geisbert, J.B.; et al. Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus–Vectored Vaccine Induces Long-Lasting Immunity against Nipah Virus Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e164946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ni, Y.A.; Song, Z.; Yi, Z.; Wang, F. Identification of pathogenic genes and transcription factors in respiratory syncytial virus. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fensterl, V.; Sen, G.C. The ISG56/IFIT1 Gene Family. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, D.; Lin, R.; Lv, Q.; Wang, W. IFI44 Is an Immune Evasion Biomarker for SARS-CoV-2 and Staphylococcus Aureus Infection in Patients with RA. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1013322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, X. Functions and Clinical Significance of KLRG1 in the Development of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Immunotherapy. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, N.; Ji, N.; Tan, X.; Chen, C.; Noel, O.D.V.; Rodriguez-Padron, M.; Lin, C.; Alonzo, D.G.; Huang, T.H.; Svatek, R.S. KLRF1, a novel marker of CD56bright NK cells, predicts improved survival for patients with locally advanced bladder cancer. Cancer Med. 2022, 00, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, A.; Gao, G. KLRK1 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, K.-L.; Schlickeiser, S.; Vogt, K.; Boës, D.; Stanko, K.; Appelt, C.; Streitz, M.; Grütz, G.; Stobutzki, N.; Meisel, C.; et al. Killer-like Receptors and GPR56 Progressive Expression Defines Cytokine Production of Human CD4+ Memory T Cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocher-Demske, A.M.; Cui, J.; Szymczak-Workman, A.L.; Vignali, K.M.; Latini, J.N.; Pieklo, G.P.; Kimball, J.C.; Avery, L.; Cipolla, E.M.; Huckestein, B.R.; et al. IFNγ-induction of TH1-like regulatory T cells controls antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, J.; He, F.; Ma, X.; Fan, F.; Meng, M.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhang, L. CD96, a New Immune Checkpoint, Correlates with Immune Profile and Clinical Outcome of Glioma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, G.; Devadiga, S.; McElroy, A.K.; Prabhu, S.; Sheik, S.; Abdulmajeed, J.; Robin, S.; Sushama, A.; Jayaram, A.; Nittur, S.; et al. Adaptive Immune Responses in Humans During Nipah Virus Acute and Convalescent Phases of Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Swartzlander, D.B.; Ghosh, A.; Fryer, J.D.; Wang, B.; Zheng, H. Clusterin Secreted from Astrocyte Promotes Excitatory Synaptic Transmission and Ameliorates Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supino, D.; Minute, L.; Mariancini, A.; Riva, F.; Magrini, E.; Garlanda, C. Negative Regulation of the IL-1 System by IL-1R2 and IL-1R8: Relevance in Pathophysiology and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.N.; Woolsey, C.; Geisbert, J.B.; Agans, K.N.; Borisevich, V.; Deer, D.J.; Mire, C.E.; Cross, R.W.; Fenton, K.A.; Broder, C.C.; et al. Resistance of Cynomolgus Monkeys to Nipah and Hendra Virus Disease Is Associated With Cell-Mediated and Humoral Immunity. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, S436–S447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G. Advances in Understanding the Roles of CD244 (SLAMF4) in Immune Regulation and Associated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 648182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pende, D.; Meazza, R.; Marcenaro, S.; Aricò, M.; Bottino, C. 2B4 Dysfunction in XLP1 NK Cells: More than Inability to Control EBV Infection. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 204, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, J.; Zijlstra-Willems, E.; Koen, G.; Kootstra, N.A.; Wolthers, K.C.; Geijtenbeek, T.B. Transmission of Zika virus by dendritic cell subsets in skin and vaginal mucosa. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1125565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.H.; Kwon, D.S.; Torensma, R.; van Vliet, S.J.; van Duijnhoven, G.C.F.; Middel, J.; Cornelissen, I.L.M.H.A.; Nottet, H.S.L.M.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Littman, D.R.; et al. DC-SIGN, a Dendritic Cell–Specific HIV-1-Binding Protein That Enhances Trans-Infection of T Cells. Cell 2000, 100, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Stegmann, F.; Gnanapragassam, V.S.; Lepenies, B. From Structure to Function—Ligand Recognition by Myeloid C-Type Lectin Receptors. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 5790–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzaioli, V.; Canavan, M.; Floudas, A.; Flynn, K.; Mullan, R.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. CD209/CD14+ Dendritic Cells Characterization in Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients: Activation, Synovial Infiltration, and Therapeutic Targeting. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 722349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asao, H. Interleukin-21 in Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiong, V.; Shu, M.H.; Wong, W.F.; AbuBakar, S.; Chang, L.Y. Nipah Virus Infection of Immature Dendritic Cells Increases Its Transendothelial Migration Across Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, D.N.J.; McKenzie, J.L. Interstitial Dendritic Cells. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1990, 6, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, C.; Bell, T.M.; Facemire, P.; Zeng, X.; Briese, T.; Lipkin, W.I.; Shamblin, J.D.; Esham, H.L.; Donnelly, G.C.; Johnson, J.C.; et al. Detailed Analysis of the Pathologic Hallmarks of Nipah Virus (Malaysia) Disease in the African Green Monkey Infected by the Intratracheal Route. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Yang, K. Role of CD68 in Tumor Immunity and Prognosis Prediction in Pan-Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carow, B.; Rottenberg, M.E. SOCS3, a Major Regulator of Infection and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Ramasamy, K.; Pillai, S.M.A.; Santhamma, B.; Konda, S.; Pitta Venkata, P.; Blankenship, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Altwegg, K.A.; et al. LIF/LIFR Oncogenic Signaling Is a Novel Therapeutic Target in Endometrial Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadhapalli, S.; Dileep, K.V.; Zhang, K.Y.J.; Nair, H.B.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Targeting LIF/LIFR Signaling in Cancer. Genes Dis. 2022, 9, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabé, S.; Guay-Giroux, A.; Tormo, A.J.; Duluc, D.; Lissilaa, R.; Guilhot, F.; Mavoungou-Bigouagou, U.; Lefouili, F.; Cognet, I.; Ferlin, W.; et al. The IL-27 P28 Subunit Binds Cytokine-Like Factor 1 to Form a Cytokine Regulating NK and T Cell Activities Requiring IL-6R for Signaling. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7692–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamins, A.O.; Restif, O.; Ntiamoa-Baidu, Y.; Suu-Ire, R.; Hayman, D.T.S.; Cunningham, A.A.; Wood, J.L.N.; Rowcliffe, J.M. Uncovering the Fruit Bat Bushmeat Commodity Chain and the True Extent of Fruit Bat Hunting in Ghana, West Africa. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 3000–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamins, A.O.; Rowcliffe, J.M.; Ntiamoa-Baidu, Y.; Cunningham, A.A.; Wood, J.L.N.; Restif, O. Characteristics and Risk Perceptions of Ghanaians Potentially Exposed to Bat-Borne Zoonoses through Bushmeat. Ecohealth 2015, 12, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anti, P.; Owusu, M.; Agbenyega, O.; Annan, A.; Badu, E.K.; Nkrumah, E.E.; Tschapka, M.; Oppong, S.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; Drosten, C. Human–Bat Interactions in Rural West Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1418–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.; Lam, T.T.Y.; Wu, J.T. Controlling avian influenza. BMJ 2023, 380, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, K.; Xiao, S.; Hu, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Hong, J.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Animal Influenza Infections with Explicit Virus Subtypes until 2016: A Spatio-Temporal Descriptive Analysis. One Health 2023, 16, 100514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Song, D.; Yuan, Z. Evaluation and Comparison of Three Virucidal Agents on Inactivation of Nipah Virus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smither, S.J.; Eastaugh, L.S.; O’Brien, L.M.; Phelps, A.L.; Lever, M.S. Aerosol Survival, Disinfection and Formalin Inactivation of Nipah Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.H.; Anthony, S.J.; Islam, A.; Kilpatrick, A.M.; Ali Khan, S.; Balkey, M.D.; Ross, N.; Smith, I.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Tao, Y.; et al. Nipah Virus Dynamics in Bats and Implications for Spillover to Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29190–29201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, M.J.; Kula, T.; Leng, Y.; Li, M.; de Vries, R.D.; Knip, M.; Siljander, H.; Rewers, M.; Choy, D.F.; Wilson, M.S.; et al. Measles Virus Infection Diminishes Preexisting Antibodies That Offer Protection from Other Pathogens. Science 2019, 366, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.N.; Sawatsky, B.; Han, A.X.; Laksono, B.M.; Walz, L.; Parker, E.; Pieper, K.; Anderson, C.A.; de Vries, R.D.; Lanzavecchia, A.; et al. Incomplete genetic reconstitution of B cell pools contributes to prolonged immunosuppression after measles. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaay6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein Names | Gene Names | Length (Amino Acids) |
|---|---|---|
| RNA–directed RNA polymerase L (Protein L) | L | 2244 |
| Non–structural protein V | P/V/C | 456 |
| Glycoprotein G | G | 602 |
| Fusion glycoprotein F0 (Protein F) | F | 546 |
| Matrix protein (Protein M) | M | 352 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) | P/V/C | 709 |
| Nucleoprotein (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein) | N | 532 |
| Protein W | P/V/C | 450 |
| Protein Names | Gene Names | Length (Amino Acids) |
|---|---|---|
| Fusion glycoprotein F0 (Protein F) | F | 546 |
| RNA–directed RNA polymerase L (Protein L) | L | 2244 |
| Non–structural protein V | P/V/C | 457 |
| Phosphoprotein (Protein P) | P/V/C | 707 |
| Nucleoprotein (Protein N) (Nucleocapsid protein) | N | 532 |
| Matrix protein (Protein M) | M | 352 |
| Glycoprotein G | G | 604 |
| Protein C | P/V/C | 166 |
| Protein W | P/V/C | 448 |
| NCT ID | Title | Locations |
|---|---|---|
| NCT04199169 | Safety and immunogenicity of a Nipah virus vaccine | OH, USA |
| NCT05178901 | Phase 1: evaluate safety and immunogenicity PHV02 | KS, USA |
| NCT05398796 | Dose-escalation evaluation of the safety and immunogenicity of mRNA-1215 | NIH, MD, USA |
| NCT01811784 | Community intervention to prevent Nipah spillover | Bangladesh |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, B.; Gravier, T.; Fricke, I.; Al-Sheboul, S.A.; Carp, T.-N.; Leow, C.Y.; Imarogbe, C.; Arabpour, J. Immunopathogenesis of Nipah Virus Infection and Associated Immune Responses. Immuno 2023, 3, 160-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno3020011
Brown B, Gravier T, Fricke I, Al-Sheboul SA, Carp T-N, Leow CY, Imarogbe C, Arabpour J. Immunopathogenesis of Nipah Virus Infection and Associated Immune Responses. Immuno. 2023; 3(2):160-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno3020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Brent, Tanya Gravier, Ingo Fricke, Suhaila A. Al-Sheboul, Theodor-Nicolae Carp, Chiuan Yee Leow, Chinua Imarogbe, and Javad Arabpour. 2023. "Immunopathogenesis of Nipah Virus Infection and Associated Immune Responses" Immuno 3, no. 2: 160-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno3020011
APA StyleBrown, B., Gravier, T., Fricke, I., Al-Sheboul, S. A., Carp, T.-N., Leow, C. Y., Imarogbe, C., & Arabpour, J. (2023). Immunopathogenesis of Nipah Virus Infection and Associated Immune Responses. Immuno, 3(2), 160-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno3020011