CIDP: Current Treatments and Identification of Targets for Future Specific Therapeutic Intervention
Abstract
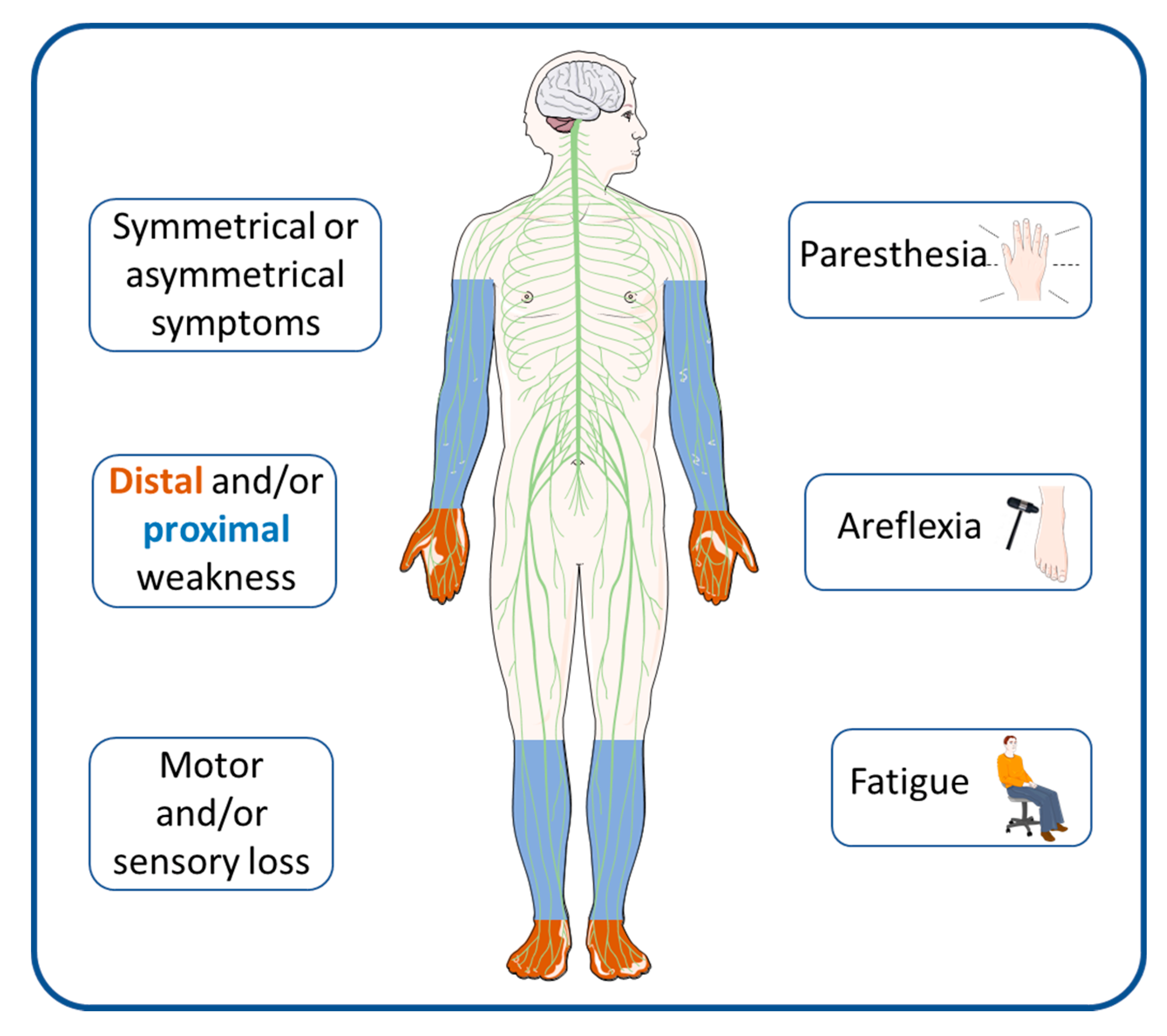
1. Introduction
2. Prognosis
3. Current Treatments
4. Animal Models
5. Novel Therapeutic Options
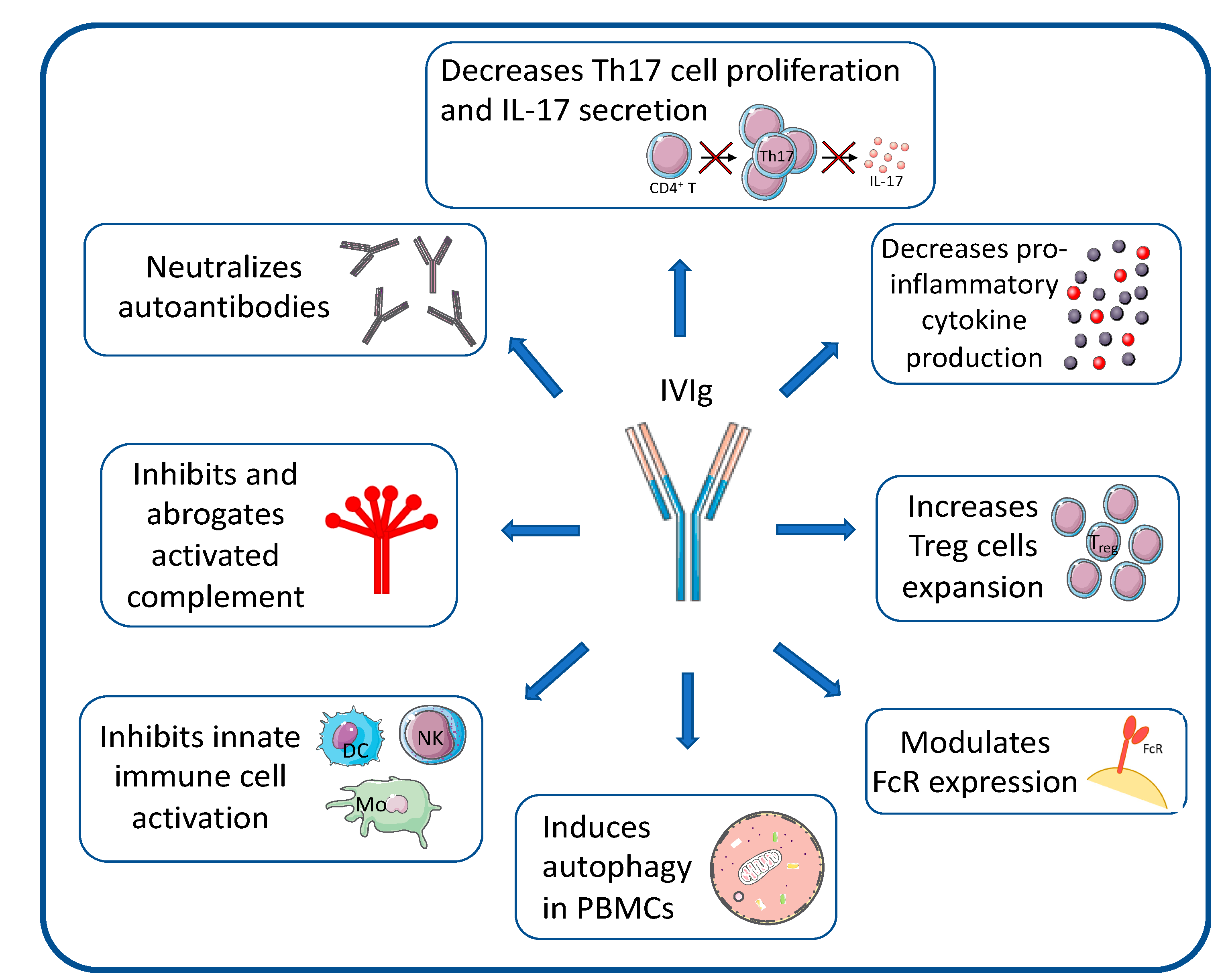
5.1. IVIG and SCIg
5.2. B Cell-Targeted Strategies
5.3. T Cell-Targeted Strategies
5.4. Ig-Targeted Strategies
5.5. Complement-Targeted Strategies
5.6. Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs) and Autophagy-Targeted Strategies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eftimov, F.; van Schaik, I. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: Update on clinical features, phenotypes and treatment options. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafsteinsdottir, B.; Olafsson, E. Incidence and Natural History of Idiopathic Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: A Population-Based Study in Iceland. Eur. Neurol. 2016, 75, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi-Rogers, M.; Hughes, R.A.C. Epidemiology of chronic inflammatory neuropathies in southeast England. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiò, A.; Cocito, D.; Bottacchi, E.; Buffa, C.; Leone, M.; Plano, F.; Mutani, R.; Calvo, A.; Parcidp, T. Idiopathic chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: An epidemiological study in Italy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mygland, A.; Monstad, P. Chronic polyneuropathies in Vest-Agder, Norway. Eur. J. Neurol. 2001, 8, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, M.; Nakashima, K.; Nakayama, H.; Takahashi, K. Epidemiology of inflammatory neurological and inflammatory neuromuscular diseases in Tottori Prefecture, Japan. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1995, 49, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, R.S.; Dyck, P.J.; Melton, L.J.; Leibson, C.; Ransom, J.; Dyck, P.J.B. Incidence and prevalence of CIDP and the association of diabetes mellitus. Neurology 2009, 73, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefter, S.; Hardiman, O.; Ryan, A.M. A population-based epidemiologic study of adult neuromuscular disease in the Republic of Ireland. Neurology 2017, 88, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Burke, D.; Kuwabara, S. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: Update on diagnosis, immunopathogenesis and treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabally, Y.A.; Sarasamma, P.; Abbott, R.J. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy after Campylobacter jejuni infection mimicking vasculitic mononeuritis multiplex in a diabetic. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2004, 9, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Vásquez, C.; Redford, J.; Choudhary, P.P.; Gray, I.A.; Maitland, P.; Gregson, N.A.; Smith, K.J.; Hughes, R.A. Immunological investigation of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 73, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrizaila, N.; Lehmann, H.C.; Kuwabara, S. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet 2021, 397, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, Y.; Vatti, N.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Chang, C.; Mancera-Páez, O.; Gershwin, M.E.; Anaya, J.-M. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy as an autoimmune disease. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 102, 8–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vaccine-induced autoimmunity: The role of molecular mimicry and immune crossreaction. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Taki, T.; Inagaki, F.; Kasama, T.; Takahashi, M.; Saito, K.; Handa, S.; Miyatake, T. A bacterium lipopolysaccharide that elicits Guillain-Barré syndrome has a GM1 ganglioside-like structure. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 178, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafer-Macko, C.; Hsieh, S.T.; Li, C.Y.; Ho, T.W.; Sheikh, K.; Cornblath, D.R.; McKhann, G.M.; Asbury, A.K.; Griffin, J.W. Acute motor axonal neuropathy: An antibody-mediated attack on axolemma. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 40, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Katsuno, M. Pathophysiology of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: Insights into Classification and Therapeutic Strategy. Neurol. Ther. 2020, 9, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Katsuno, M. Macrophages and Autoantibodies in Demyelinating Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, M.; Suzuki, S.; Takada, K.; Kusunoki, S. Antibodies to LM1 and LM1-containing ganglioside complexes in Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 239, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vural, A.; Doppler, K.; Meinl, E. Autoantibodies Against the Node of Ranvier in Seropositive Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: Diagnostic, Pathogenic, and Therapeutic Relevance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, K.M.; Ousman, S.S. The immune response and aging in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, S.; Misawa, S.; Mori, M.; Tamura, N.; Kubota, M.; Hattori, T. Long term prognosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: A five year follow up of 38 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftimov, F.; Vermeulen, M.; van Doorn, P.A.; Brusse, E.; van Schaik, I.N. Long-term remission of CIDP after pulsed dexamethasone or short-term prednisolone treatment. Neurology 2012, 78, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallat, J.-M.; Sommer, C.; Magy, L. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges for a treatable condition. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mygland, A.; Monstad, P.; Vedeler, C. Onset and course of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2005, 31, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köller, H.; Kieseier, B.C.; Jander, S.; Hartung, H.-P. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Lais, A.C.; Ohta, M.; Bastron, J.A.; Okazaki, H.; Groover, R.V. Chronic inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1975, 50, 621–637. [Google Scholar]
- Dyck, P.J.; O’Brien, P.C.; Oviatt, K.F.; Dinapoli, R.P.; Daube, J.R.; Bartleson, J.D.; Mokri, B.; Swift, T.; Low, P.A.; Windebank, A.J. Prednisone improves chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy more than no treatment. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.; Mehndiratta, M.M.; Rajabally, Y.A. Corticosteroids for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD002062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivity, S.; Katz, U.; Daniel, N.; Nussinovitch, U.; Papageorgiou, N.; Shoenfeld, Y. Evidence for the use of intravenous immunoglobulins--a review of the literature. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 38, 201–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.; Shoenfeld, Y. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: Revisiting the role of intravenous immmunoglobulins. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2013, 15, 293–294. [Google Scholar]
- Markvardsen, L.K.; Carstens, A.-K.R.; Knak, K.L.; Overgaard, K.; Vissing, J.; Andersen, H. Muscle Strength and Aerobic Capacity in Patients with CIDP One Year after Participation in an Exercise Trial. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 6, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garssen, M.P.J.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Schmitz, P.I.M.; Zandbergen, A.; Welter, T.G.; Merkies, I.S.J.; Stam, H.J.; van Doorn, P.A. Physical training and fatigue, fitness, and quality of life in Guillain-Barré syndrome and CIDP. Neurology 2004, 63, 2393–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lieverloo, G.G.A.; Peric, S.; Doneddu, P.E.; Gallia, F.; Nikolic, A.; Wieske, L.; Verhamme, C.; Van Schaik, I.N.; Nobile-Orazio, E.; Basta, I.; et al. Corticosteroids in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: A retrospective, multicentre study, comparing efficacy and safety of daily prednisolone, pulsed dexamethasone, and pulsed intravenous methylprednisolone. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Engel, W.K. Chronic relapsing (dysimmune) polyneuropathy: Pathogenesis and treatment. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 9, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile-Orazio, E.; Cocito, D.; Jann, S.; Uncini, A.; Beghi, E.; Messina, P.; Antonini, G.; Fazio, R.; Gallia, F.; Schenone, A.; et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin versus intravenous methylprednisolone for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, S.R.M.; Zambreanu, L.; Abbas, A.; Rajabally, Y.A.; Hadden, R.D.M.; de Haan, R.J.; de Borgie, C.A.J.M.; Lunn, M.P.; van Schaik, I.N.; Eftimov, F.; et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin and intravenous methylprednisolone as optimal induction treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: Protocol of an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (OPTIC). Trials 2021, 22, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrichem, M.E.; Bus, S.R.; Wieske, L.; Mohammed, H.; Verhamme, C.; Hadden, R.; Van Schaik, I.N.; Eftimov, F. Combined intravenous immunoglobulin and methylprednisolone as induction treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (OPTIC protocol): A prospective pilot study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.; Bensa, S.; Willison, H.; Van den Bergh, P.; Comi, G.; Illa, I.; Nobile-Orazio, E.; Van Doorn, P.; Dalakas, M.; Bojar, M.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin versus oral prednisolone in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehndiratta, M.M.; Hughes, R.A.C.; Pritchard, J. Plasma exchange for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD003906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, R.D.M.; Bensa, S.; Lunn, M.P.T.; Hughes, R.A.C. Immunoadsorption inferior to plasma exchange in a patient with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Hartung, H.-P. Plasma exchange and intravenous immunoglobulins: Mechanism of action in immune-mediated neuropathies. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 231, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnson, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Amital, H. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity 2009, 42, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.F.; Bolton, C.F.; Zochodne, D.; Feasby, T.E. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. Brain J. Neurol. 1996, 119 Pt 4, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.R.; Barohn, R.J.; Freimer, M.L.; Kissel, J.T.; King, W.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Rice, R.; Campbell, W.; Donofrio, P.; Jackson, C.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of IVIg in untreated chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 2001, 56, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftimov, F.; Winer, J.B.; Vermeulen, M.; de Haan, R.; van Schaik, I.N. Intravenous immunoglobulin for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 12, CD001797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.C.; Donofrio, P.; Bril, V.; Dalakas, M.C.; Deng, C.; Hanna, K.; Hartung, H.-P.; Latov, N.; Merkies, I.S.; van Doorn, P.A. Intravenous immune globulin (10% caprylate-chromatography purified) for the treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (ICE study): A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalem, D.; Shemer, A.; Shovman, O.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Kivity, S. The Efficacy of Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Guillain-Barré Syndrome: The Experience of a Tertiary Medical Center. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2018, 20, 754–760. [Google Scholar]
- Harel, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Intravenous immunoglobulin and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 29, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debs, R.; Reach, P.; Cret, C.; Demeret, S.; Saheb, S.; Maisonobe, T.; Viala, K. A new treatment regimen with high-dose and fractioned immunoglobulin in a special subgroup of severe and dependent CIDP patients. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbach, H.; Katz, U.; Sherer, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y. Intravenous immunoglobulin: Adverse effects and safe administration. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 29, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schaik, I.N.; Bril, V.; van Geloven, N.; Hartung, H.-P.; Lewis, R.A.; Sobue, G.; Lawo, J.-P.; Praus, M.; Mielke, O.; Durn, B.L.; et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin for maintenance treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (PATH): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, S.R.; Sharma, K.R.; Bassam, B.A.; Pulley, M.T.; Shije, J.Z.; Kafal, A. Individualizing Therapy in CIDP: A Mini-Review Comparing the Pharmacokinetics of Ig with SCIg and IVIg. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 638816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, L.; Mazzeo, A.; Russo, M.; Arimatea, I.; Vita, G.; Toscano, A. Long-term treatment with subcutaneous immunoglobulin in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: A follow-up period up to 7 years. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querol, L.; Nogales-Gadea, G.; Rojas-Garcia, R.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Diaz-Manera, J.; Suárez-Calvet, X.; Navas, M.; Araque, J.; Gallardo, E.; Illa, I. Antibodies to contactin-1 in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, J.J.; Miura, Y.; Fukami, Y.; Inoue, T.; Manso, C.; Belghazi, M.; Sekiguchi, K.; Kokubun, N.; Ichikawa, H.; Wong, A.H.Y.; et al. Neurofascin-155 IgG4 in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 2016, 86, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, Y.; Devaux, J.J.; Fukami, Y.; Manso, C.; Belghazi, M.; Wong, A.H.Y.; Yuki, N. Contactin 1 IgG4 associates to chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with sensory ataxia. Brain J. Neurol. 2015, 138, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomelli, R.; Afeltra, A.; Bartoloni, E.; Berardicurti, O.; Bombardieri, M.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Carubbi, F.; Caso, F.; Cervera, R.; Ciccia, F.; et al. The growing role of precision medicine for the treatment of autoimmune diseases; results of a systematic review of literature and Experts’ Consensus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, K.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Fritzler, M.J. Precision health: A pragmatic approach to understanding and addressing key factors in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.A.; Berger, M.; Querol, L.; Kuitwaard, K.; Hadden, R.D. Individualized immunoglobulin therapy in chronic immune-mediated peripheral neuropathies. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2018, 23, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafflick, D.; Kieseier, B.C.; Wiendl, H.; Zu, M.; Horste, G. Novel pathomechanisms in inflammatory neuropathies. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, B.H.; Adams, R.D. Allergic neuritis: An experimental disease of rabbits induced by the injection of peripheral nervous tissue and adjuvants. J. Exp. Med. 1955, 102, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.P.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Levi, M.; Nennesmo, I.; Wahren, B.; Mix, E.; Winblad, B.; Schalling, M.; Zhu, J. P0 protein peptide 180–199 together with pertussis toxin induces experimental autoimmune neuritis in resistant C57BL/6 mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 62, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalvez, D.G.; Yoo, S.; Craig, G.A.; Wood, R.J.; Fletcher, J.L.; Murray, S.S.; Xiao, J. Myelin Protein Zero180-199 Peptide Induced Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis in C57BL/6 Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1791, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calida, D.M.; Kremlev, S.G.; Fujioka, T.; Hilliard, B.; Ventura, E.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Lavi, E.; Rostami, A. Experimental allergic neuritis in the SJL/J mouse: Induction of severe and reproducible disease with bovine peripheral nerve myelin and pertussis toxin with or without interleukin-12. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 107, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-J.; Wei, Y.-J.; Ao, Q.; Gong, K.; Wang, J.-Y.; Sun, Q.-S.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Z.-C.; Chen, L. Myelin ultrastructure of sciatic nerve in rat experimental autoimmune neuritis model and its correlation with associated protein expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7849–7858. [Google Scholar]
- Sheremata, W.A.; Behan, P.O. Experimental allergic neuritis: A new experimental approach. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1973, 36, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspary, E.A.; Field, E.J. Antibody response to central and peripheral nerve antigens in rat and guinea-pig. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1965, 28, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.H.; Stone, S.H.; Raine, C.S. Attempts to induce chronic experimental allergic neuritis in strain 13 and Hartley guinea pigs. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1977, 36, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletic, H.; Utermöhlen, O.; Wedekind, C.; Hermann, M.; Stenzel, W.; Lassmann, H.; Schlüter, D.; Deckert, M. P0(106–125) is a neuritogenic epitope of the peripheral myelin protein P0 and induces autoimmune neuritis in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brostoff, S.W.; Levit, S.; Powers, J.M. Induction of experimental allergic neuritis with a peptide from myelin P2 basic protein. Nature 1977, 268, 752–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, A.; Gregorian, S.K.; Brown, M.J.; Pleasure, D.E. Induction of severe experimental autoimmune neuritis with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the 53–78 amino acid sequence of the myelin P2 protein. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C.M.; Hughes, R.A.; Moore, S.E.; Smith, K.J.; Walsh, F.S. Induction of experimental autoimmune neuritis with peripheral myelin protein-22. Brain J. Neurol. 1998, 121 Pt 10, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suzumura, A.; Sobue, G.; Sugimura, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Sobue, I. Chronic experimental allergic neuritis (EAN) in juvenile guinea pigs: Immunological comparison with acute EAN in adult guinea pigs. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1985, 71, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, G.K.; Pollard, J.D.; Schindhelm, K.; Antony, J. Chronic experimental allergic neuritis. An electrophysiological and histological study in the rabbit. J. Neurol. Sci. 1987, 81, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shy, M.E.; Arroyo, E.; Sladky, J.; Menichella, D.; Jiang, H.; Xu, W.; Kamholz, J.; Scherer, S.S. Heterozygous P0 knockout mice develop a peripheral neuropathy that resembles chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Gaupp, S.; Korn, T.; Köllner, G.; Hartung, H.-P.; Toyka, K.V. Biphasic form of experimental autoimmune neuritis in dark Agouti rats and its oral therapy by antigen-specific tolerization. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 75, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, B.; Rhee, L.; Bour-Jordan, H.; Hsin, H.; Montag, A.; Soliven, B.; Arcella, J.; Girvin, A.M.; Miller, S.D.; Bluestone, J.A. Development of spontaneous autoimmune peripheral polyneuropathy in B7-2-deficient NOD mice. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliven, B. Autoimmune neuropathies: Insights from animal models. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2012, 17 (Suppl. S2), 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubogu, E.E.; Yosef, N.; Xia, R.H.; Sheikh, K.A. Behavioral, electrophysiological, and histopathological characterization of a severe murine chronic demyelinating polyneuritis model. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2012, 17, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, S.; Beaino, W.; Kremer, L.; Taleb, O.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.G.; Lam, C.D.; Greer, J.M.; de Seze, J.; Trifilieff, E. Characterization of a new rat model for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 278, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sèze, J.; Kremer, L.; Alves do Rego, C.; Taleb, O.; Lam, D.; Beiano, W.; Mensah-Nyagan, G.; Trifilieff, E.; Brun, S. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: A new animal model for new therapeutic targets. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, S.; Schall, N.; Bonam, S.R.; Bigaut, K.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.-G.; de Sèze, J.; Muller, S. An autophagy-targeting peptide to treat chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 92, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, L.; Taleb, O.; Boehm, N.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.G.; Trifilieff, E.; de Seze, J.; Brun, S. FTY720 controls disease severity and attenuates sciatic nerve damage in chronic experimental autoimmune neuritis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Brun, S.; René, F.; de Sèze, J.; Loeffler, J.-P.; Jeltsch-David, H. Autophagy in neuroinflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 856–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, S.; Schall, N.; Jeltsch-David, H.; Sèze, J.; de Muller, S. Assessing Autophagy in Sciatic Nerves of a Rat Model that Develops Inflammatory Autoimmune Peripheral Neuropathies. Cells 2017, 6, E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinas, D.; Katz, J.; Nisbet, P.; England, J.D. Current practice patterns in CIDP: A cross-sectional survey of neurologists in the United States. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 397, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, H.I.; Knoers, N.V.A.M.; van Haelst, M.M.; van Haaften, G. Drug Repurposing for Rare Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, E.W. Differences between IGIV products: Impact on clinical outcome. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.J.; Wilkinson, J.; Coventry, B.J. Therapeutic options for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: A systematic review. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casertano, S.; Signoriello, E.; Rossi, F.; Di Pietro, A.; Tuccillo, F.; Bonavita, S.; Lus, G. Ocrelizumab in a case of refractory chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with anti-rituximab antibodies. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 2673–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Dou, Y.-C.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.-W.; Cao, L.-L.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhu, J.; Duan, R.-S. Atorvastatin ameliorates experimental autoimmune neuritis by decreased Th1/Th17 cytokines and up-regulated T regulatory cells. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 271, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Fauser, U.; Schluesener, H.J. FTY720 ameliorates experimental autoimmune neuritis by inhibition of lymphocyte and monocyte infiltration into peripheral nerves. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat, J.-M.; Mathis, S.; Ghorab, K.; Milor, M.-A.; Richard, L.; Magy, L. Natalizumab as a Disease-Modifying Therapy in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy—A Report of Three Cases. Eur. Neurol. 2015, 73, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Greathouse, K.M.; Beacham, R.L.; Palladino, S.P.; Helton, E.S.; Ubogu, E.E. Fibronectin connecting segment-1 peptide inhibits pathogenic leukocyte trafficking and inflammatory demyelination in experimental models of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 292, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, V.; Benatar, M.; Andersen, H.; Vissing, J.; Brock, M.; Greve, B.; Kiessling, P.; Woltering, F.; Griffin, L.; Bergh, P.V.D. Efficacy and Safety of Rozanolixizumab in Moderate to Severe Generalized Myasthenia Gravis: A Phase 2 Randomized Control Trial. Neurology 2021, 96, e853–e865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbers, M.G.; Plomp, J.J.; van Es, I.E.; Fillié-Grijpma, Y.E.; Kamar-Al Majidi, S.; Ulrichts, P.; de Haard, H.; Hofman, E.; van der Maarel, S.M.; Verschuuren, J.J. Efgartigimod improves muscle weakness in a mouse model for muscle-specific kinase myasthenia gravis. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 317, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrichts, P.; Guglietta, A.; Dreier, T.; van Bragt, T.; Hanssens, V.; Hofman, E.; Vankerckhoven, B.; Verheesen, P.; Ongenae, N.; Lykhopiy, V.; et al. Neonatal Fc receptor antagonist efgartigimod safely and sustainably reduces IgGs in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4372–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, S.K.; Zitman, F.M.P.; Humphreys, P.D.; Greenshields, K.; Verschuuren, J.J.; Jacobs, B.C.; Rother, R.P.; Plomp, J.J.; Willison, H.J. Eculizumab prevents anti-ganglioside antibody-mediated neuropathy in a murine model. Brain J. Neurol. 2008, 131, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer zu Hörste, G.; Mausberg, A.K.; Korth, C.; Stüve, O.; Kieseier, B.C. Quinpramine--a promising compound for treating immune-mediated demyelination of the nervous system. Drug News Perspect. 2010, 23, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, N.; Gros, F.; Schall, N.; Décossas, M.; Bagnard, D.; Briand, J.-P.; Muller, S. HSC70 blockade by the therapeutic peptide P140 affects autophagic processes and endogenous MHCII presentation in murine lupus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, N.; Gros, F.; Schall, N.; Briand, J.-P.; Muller, S. A therapeutic peptide in lupus alters autophagic processes and stability of MHCII molecules in MRL/lpr B cells. Autophagy 2011, 7, 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macri, C.; Wang, F.; Tasset, I.; Schall, N.; Page, N.; Briand, J.-P.; Cuervo, A.M.; Muller, S. Modulation of deregulated chaperone-mediated autophagy by a phosphopeptide. Autophagy 2015, 11, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, F.; Schall, N.; Muller, S. Rescue of autophagy and lysosome defects in salivary glands of MRL/lpr mice by a therapeutic phosphopeptide. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 90, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, M.; Wang, F.; Schall, N.; Kleinmann, J.-F.; Faludi, M.; Nashi, E.P.; Sibilia, J.; Martin, T.; Schaeffer, E.; Muller, S. Lupus Regulator Peptide P140 Represses B Cell Differentiation by Reducing HLA Class II Molecule Overexpression. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schall, N.; Page, N.; Macri, C.; Chaloin, O.; Briand, J.-P.; Muller, S. Peptide-based approaches to treat lupus and other autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, R.; Scherbarth, H.R.; Rillo, O.L.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Muller, S. Lupuzor/P140 peptide in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIb clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voynova, E.; Lefebvre, F.; Qadri, A.; Muller, S. Correction of autophagy impairment inhibits pathology in the NOD.H-2h4 mouse model of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 108, 102418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubeuf, F.; Schall, N.; Petit-Demoulière, N.; Frossard, N.; Muller, S. An Autophagy Modulator Peptide Prevents Lung Function Decrease and Corrects Established Inflammation in Murine Models of Airway Allergy. Cells 2021, 10, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tasset, I.; Cuervo, A.M.; Muller, S. In Vivo Remodeling of Altered Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway by a Phosphopeptide in Lupus. Cells 2020, 9, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, F.; Arnold, J.; Page, N.; Décossas, M.; Korganow, A.-S.; Martin, T.; Muller, S. Macroautophagy is deregulated in murine and human lupus T lymphocytes. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, F.M.; Fleming, A.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Compromised autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.-Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, G. Autophagy and its implication in human oral diseases. Autophagy 2017, 13, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Elazar, Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sowers, J.R.; Ren, J. Targeting autophagy in obesity: From pathophysiology to management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 356–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonam, S.R.; Wang, F.; Muller, S. Lysosomes as a therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2019, 18, 923–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Shin, Y.K.; Park, S.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Rha, S.-H.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, H.J.; Park, H.T. Autophagy is involved in the reduction of myelinating Schwann cell cytoplasm during myelin maturation of the peripheral nerve. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Xue, R.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, P.; Ouyang, X.; Dai, T.; Zhu, W.; Tian, S. Autophagy is involved in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune neuritis in rats. Neuroreport 2016, 27, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C. Potential biomarkers for monitoring therapeutic response in patients with CIDP. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2011, 16 (Suppl. S1), 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Animals | Antigen | Model of Disease | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult guinea pigs | MBP | Acute | [67] |
| Rabbits | Sciatic nerve tissue | Acute | [62] |
| C57BL6 mice | P0(180–199) | Acute | [63,64] |
| C57BL6 mice | P0(106–125) | Acute | [70] |
| SJL mice | P2 protein | Acute | [71] |
| SJL mice | BPNM | Acute | [65] |
| Lewis rats | P2(53–78) | Acute | [72] |
| Lewis rats | P0(180–199) | Acute | [66] |
| Lewis rats | PMP22 | Acute | [73] |
| Juvenile guinea pigs | BPN homogenate | Chronic | [74] |
| Rabbits | BPNM | Chronic | [75] |
| Heterozygous KO (P0+/-) mice | Inherited | Chronic | [76] |
| Dark Agouti rats | BPNM | Chronic | [77] |
| B7-2 KO NOD mice | Spontaneous | Chronic | [78] |
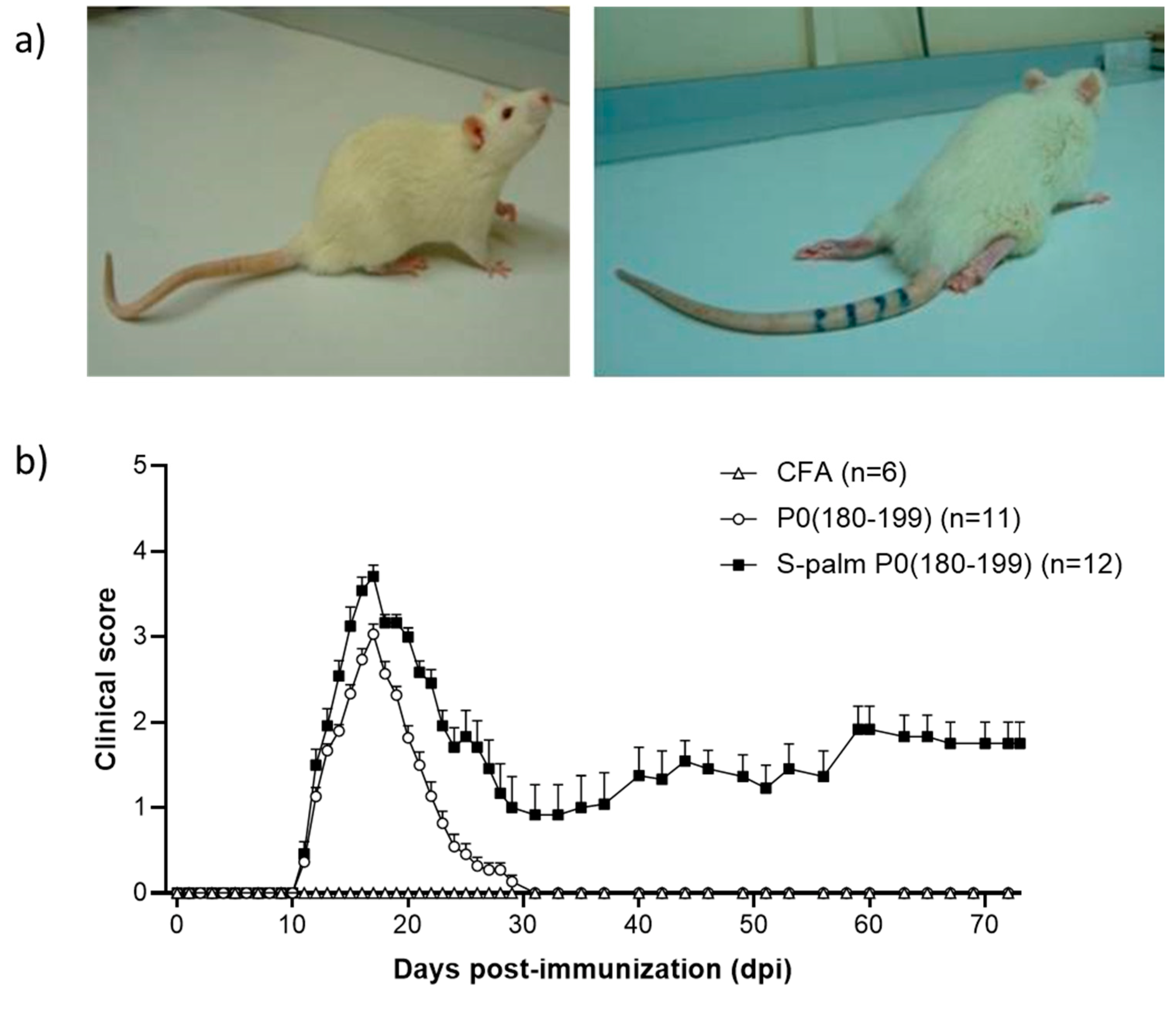
| Lewis rats | S-palm P0(180–199) | Chronic | [81] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brun, S.; de Sèze, J.; Muller, S. CIDP: Current Treatments and Identification of Targets for Future Specific Therapeutic Intervention. Immuno 2022, 2, 118-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010009
Brun S, de Sèze J, Muller S. CIDP: Current Treatments and Identification of Targets for Future Specific Therapeutic Intervention. Immuno. 2022; 2(1):118-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrun, Susana, Jérôme de Sèze, and Sylviane Muller. 2022. "CIDP: Current Treatments and Identification of Targets for Future Specific Therapeutic Intervention" Immuno 2, no. 1: 118-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010009
APA StyleBrun, S., de Sèze, J., & Muller, S. (2022). CIDP: Current Treatments and Identification of Targets for Future Specific Therapeutic Intervention. Immuno, 2(1), 118-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2010009







