Abstract
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) is a ligand-activated transcription factor expressed in dendritic cells (DCs), where it exerts anti-inflammatory responses against TLR4-induced inflammation. Recently, microRNA-511 (miR-511) has also emerged as a key player in controlling TLR4-mediated signalling and in regulating the function of DCs. Interestingly, PPARγ has been previously highlighted as a putative target of miR-511 activity; however, the link between miR-511 and PPARγ and its influence on human DC function within the context of LPS-induced inflammatory responses is unknown. Using a selection of miR-511-3p-specific inhibitors and mimics, we demonstrate for the first time that knockdown or overexpression of miR-511-3p inversely correlates with PPARγ mRNA levels and affects its transcriptional activity following treatment with rosiglitazone (RSG; PPARγ agonist), in the presence or absence of LPS. Additionally, we show that PPARγ-mediated suppression of DC activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in miR-511-3p knockdown DCs is abrogated following overexpression of miR-511-3p. Lastly, PPARγ activation suppressed LPS-mediated induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity in DCs, most likely due to changes in miR-511-3p expression. Our data thus suggests that PPARγ-induced modulation of DC phenotype and function is influenced by miR-511-3p expression, which may serve as a potential therapeutic target against inflammatory diseases.
1. Introduction
The innate immune system rapidly responds to endotoxin exposure through the induction of acute inflammatory responses [1]. Endotoxins such as LPS, a major cell wall component of Gram-negative bacteria, can induce potent inflammatory responses through the release of an array of mediators such as cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. However, when uncontrolled, inflammatory responses can lead to tissue damage and chronic inflammatory diseases [2]. Dendritic cells (DCs) are the most efficient antigen-presenting cells (APCs) capable of initiating and maintaining primary immune responses and are key players in regulating inflammatory responses [3]. DCs are highly sensitive to even low concentrations of LPS in the environment and detect the presence of LPS (for instance, during bacterial infection) via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). This triggers downstream signalling pathways, which coordinate the expression of genes required to initiate or control inflammation [4].
Recently, the role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in modulating inflammatory responses has been of particular interest. PPARγ is a lipid-activated transcription factor expressed in a variety of cell types, including DCs, where it regulates genes associated with adipogenesis, lipid metabolism and inflammation [5]. In DCs, PPARγ regulates other cellular processes, including maturation and migration, activation, antigen presentation and cytokine production [6,7,8]. Moreover, PPARγ activation in DCs in the presence of LPS resulted in decreased IL-12 expression [9], suggesting that PPARγ ligands may promote anti-inflammatory responses. Studies by us and others have also demonstrated a key role for the tryptophan-metabolising enzyme IDO in controlling LPS-mediated inflammatory responses [10,11,12,13]. Interestingly, the recent finding that PPARγ promotes IDO activity and subsequent immune suppression in the tumour microenvironment highlights the complexity of PPARγ-induced regulatory mechanisms [14]. Nevertheless, the overall immunosuppressive effect of PPARγ and the underlying mechanisms, particularly during LPS-induced inflammation in DCs, are not fully understood.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of gene regulators that bind the 3′UTR of target genes and cause translational inhibition or mRNA degradation [15]. Due to their role in regulating biological processes, miRNAs represent crucial regulators in human health and disease. Recently, miR-511-3p, the functional miRNA of the mature miR-511 strand (located at the 3 end of miR-511), has been identified as an important regulator of human DC and macrophage development and function. For example, miR-511-3p expression is increased following DC differentiation from monocytes [16] and has been shown to be a key regulator of TLR4 expression in DCs [17]. Additionally, transcriptional products associated with inflammation and wound healing in alternatively activated macrophages (AAMs) were found to be altered by miR-511 expression [18]. Recently, miR-511-3p has been shown to suppress cockroach allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and lung inflammation in mice. Interestingly, PPARγ has also been highlighted as a putative target of miR-511 activity, affecting human myeloid cell differentiation and function [17,19]. Here, we sought to investigate the potential relationship between miR-511-3p expression and PPARγ activity and how this influences LPS-mediated inflammatory responses in human DCs. Better understanding of the mechanisms regulating PPARγ activity could pave the way for the rational design of therapies against inflammatory disorders.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells (DCs)
This was done as previously described [20,21]. Buffy coats were obtained from healthy donors (National Blood Service, Sheffield, UK) after obtaining informed written consent and following ethics committee approval (Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Nottingham; BT08052013-160-1701). PBMCs were separated by density gradient centrifugation on Histopaque (Sigma-Aldrich, Dorset, UK), and monocytes were purified by positive selection using the MACS CD14 isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Woking, UK). Briefly, PBMCs were washed twice with MACS buffer (2 mM EDTA with 0.5% FBS in PBS) and incubated with CD14+ magnetic beads for 15 min at 4 °C. Subsequently, labelled cells were allowed to bind to LS columns (Miltenyi Biotec), washed three times with MACS buffer before eluting positively bound fraction. Monocytes were then cultured in 24-well plates using RPMI medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 U/mL streptomycin and 2 mM L-glutamine (all from Sigma). Cells were incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. The purity of CD14+ cells was always above 90%, as measured by flow cytometry. DC differentiation was carried out over 6 days with 250 U/mL IL-4 and 50 ng/mL GM-CSF (Miltenyi Biotec).
2.2. Flow Cytometry Analysis
Mouse monoclonal antibodies against human CD86 (clone FM95) and DC-SIGN (clone DCN47.5) were purchased from Miltenyi Biotec. Antibodies against human CD83 (clone HB15e) was purchased from eBioscience, Hartfield, UK. Anti-PDL1 (clone MIH1) antibody was purchased from BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA, USA), and the anti-CD206 antibody (clone 15-2) was purchased from Biolegend (San Diego, CA, USA). Briefly, cells were collected and washed twice in cold PBA (PBS buffer containing 0.5% BSA and 0.1% sodium azide (Sigma Aldrich)). Staining with labelled antibodies was then carried out in the dark at 4 °C for 20 min according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Unless otherwise stated, specific antibodies were conjugated to Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC), Phycoerythrin (PE) or Phycoerythrin Cyanine 5.1 (PE/Cy5). Following staining, samples were washed twice with PBA buffer and fixed in 0.5% formaldehyde solution before analysis. Non-reactive, isotype-matched antibodies were used as controls. Flow cytometry was carried out on the FC500 Flow Cytometer (Beckman Coulter, London, UK), and data were analysed using Weasel Software for Windows.
2.3. Quantification of IDO Activity
IDO activity was determined as described before [20,22]. Briefly, DCs (2.5 × 105 cells/mL) were seeded in a 24-well plate with complete RPMI media, supplemented with 100 μM L-tryptophan (TRP) (Sigma Aldrich). Cells were then stimulated with PPARγ agonist and antagonist RSG and GW9662 (5 µM), respectively, for 24 h, in the presence and absence of LPS (0.1 µg/mL) and culture supernatant was harvested and stored at −20 °C until analysis. A colourimetric assay for IDO activity was performed by measuring the levels of L-kynurenine (KYN) produced in culture supernatant. The concentration of L-KYN was then calculated from a standard curve of defined concentrations from 0 to 200 μM. Rosiglitazone (RSG) and GW9662 were purchased from Cayman chemicals (Cambridge, UK), and L-KYN was obtained from Sigma Aldrich, UK.
2.4. Live/Dead Assay
Cell viability following treatment with RSG and GW9662 was determined using the LIVE/DEAD assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Leicester, UK) as described previously [23]. Cells were imaged using the Etaluma LS720 Microscope (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Data were analysed using Image J software v1.51 for Windows.
2.5. RNA Interference
Pre-designed miR-511-3p inhibitors and mimics were purchased from Qiagen, and transfection was carried out using the HiPerFect Transfection Reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Qiagen). The miRNA targeted sequence was 5′-AAUGUGUAGCAAAAGACAGA-3′. Briefly, CD14+ monocytes were suspended in Opti-MEM® reduced serum media (Gibco) and seeded. Prior to transfection, miR-511-3p inhibitor or mimic was diluted in serum-free media with transfection reagent in separate tubes for 10 min at room temperature before adding dropwise unto cells. The miScript Inhibitor Negative Control and the AllStars Negative Control siRNA (Qiagen) were used as scrambled controls (CT) for inhibitors and mimics, respectively. All transfections were carried out at a final concentration of 50 nM, as determined during optimisations. Monocytes were differentiated into DCs after 6 h of incubation, with fresh Opti-MEM® media supplemented with IL-4 and GM-CSF. Transfection efficiency was determined using the fluorescently labelled siGLO RISC-free control siRNA (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA), and miRNA and/or mRNA expression was assessed afterwards.
2.6. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
Dendritic cells treated with miR-511-3p inhibitors and mimics as well as controls were stimulated on day 6 with RSG in the presence or absence of LPS (Sigma Aldrich) for 24 h before harvesting. Cell samples were then washed twice with cold PBS and stored in RNA later before RNA isolation. Total RNA, including small RNAs, was isolated with Trizol Reagent using the miRNeasy Mini kit, according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen). The concentration of purified RNA was measured using a NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Leicester, UK). First-strand cDNA was then generated with the SuperScript III Reverse Transcription kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Leicester, UK) or the miScript Reverse Transcription (RT) II kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Reverse transcription was done with the T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, Watford, UK) and the 5X HiFlex buffer was used for parallel qRT-PCR quantification of mature miRNA and mRNA.
2.7. Real Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Comparative real-time PCR for miR-511-3p expression was carried out on the MxPro 3005P qRT-PCR system (Stratagene, CA, USA) using the miScript SYBR Green PCR kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, 12.5 µL 2X QuantiTect SYBR-Green Master Mix, 2.5 µL 10X Universal Primer and 2.5 µL Primer Assay (forward primer) was mixed with 3 ng of reverse transcription product. qRT-PCR cycling was initiated at 95 °C for 15 min, followed by 40 cycles of 94 °C for 15 s, 55 °C for 30 s and 70 °C for 30 s. Mature miR-511-3p-specific primers were obtained from Qiagen, and relative expression was normalised to U6 (RNU6-2) small nuclear RNAs. qRT-PCR for mRNA expression was done with the Brilliant III Ultra-Fast SYBR Green qRT-PCR Master Mix (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), as previously described [20]. The two-step cycling reaction was initiated at 95 °C for 3 min followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 20 s and 60 °C for 20 s. PPARG and FABP4 mRNA expression levels were normalised GAPDH and calculated using the comparative Delta Ct method, which determines the difference in Ct values between the gene of interest and the housekeeping gene. All experimental procedures were done in triplicate. Forward and reverse mRNA primers were selected using Roche Universal Probes Library and purchased from Eurofins Scientific, Wolverhampton, UK (Table 1).

Table 1.
Primers for real-time PCR.
2.8. Cytokine ELISA
Culture supernatants were collected and stored at −20 °C before analysis. The levels of TNF-α, IL-10 and IL-6 were measured by sandwich ELISA using the Duo Set ELISA kit (R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK) [24] according to manufacturer’s instructions.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Data were analysed using GraphPad Prism v7.02 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) and values expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments unless otherwise stated. Statistical differences were determined using Student’s t-test (to compare two groups) or one/two-way ANOVA (to compare three or more groups) with Tukey’s post-hoc testing. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in miR-511-3p Expression Affect PPARγ Expression and Activity in Human DCs
We first examined PPARγ regulation in human DCs after changes in miR-511-3p expression. For this purpose, we differentiated monocyte-derived DCs in the presence of miR-511-3p-specific inhibitors and mimics, which resulted in a significant downregulation and/or increase in miR-511-3p miRNA expression, respectively (Figure 1). Subsequently, we measured the expression of PPARγ by comparative qRT-PCR and showed for the first time that knockdown of miR-511-3p (henceforth referred to as miR-511-3p-inhibitor), resulted in a significant increase in PPARγ mRNA levels (Figure 1A), whereas a significant decrease in PPARγ expression was observed in miR-511-3p overexpressed cells (i.e., miR-511-3p-mimic) (Figure 1B). As demonstrated in Figure 1C, there is a strong inverse association between the level of PPARγ relative to miR-511-3p, indicated by an increase in PPARγ expression when miR-511-3p is low, and vice versa when miR-511-3p expression is high. It is important to note that transfection with either miR-511-3p inhibitors or mimics did not result in loss of cell viability, as determined by Annexin-V staining (Figure S1), and did not impact monocyte-to-DC differentiation, as we have previously demonstrated [16].
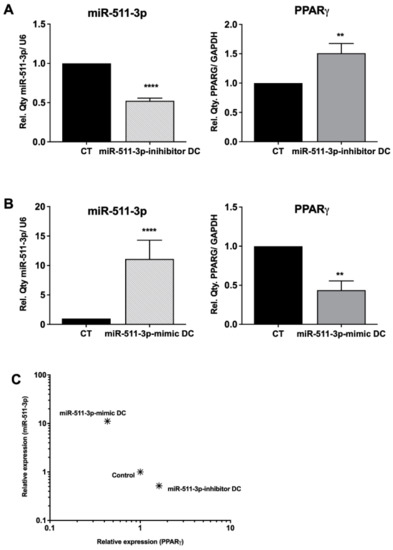
Figure 1.
Analysis of PPARγ mRNA levels in response to up- or downregulation of miR-511-3p expression. Relative expression of miR-511-3p and PPARγ, respectively, in (A) miR-511-3p-inhibitor and (B) miR-511-3p-mimic DCs. (C) Scatter plot showing the relationship between miR-511-3p and PPARγ expression. Monocytes were differentiated in the presence of 50 nM miR-511-3p-specific inhibitors and mimics. Gene expression was assessed on day 6 and normalised to U6 and GAPDH for miRNA and mRNA, respectively. (One representative data is shown out of three). ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.
Several natural (e.g., 15d-PGJ2) as well as synthetic agonists (also known as thiazolidinediones (TZDs)) have been shown to induce PPARγ activation in a variety of cell types [25,26]. Following up- or downregulation of miR-511-3p and its effect on PPARγ expression, we treated DCs with LPS and the synthetic agonist rosiglitazone (RSG) in order to determine the influence of these ligands on PPARγ activity. PPARγ activity was assessed by measuring the expression of one of its target genes (i.e., FABP4) by qRT-PCR. Interestingly, we found that PPARγ activity was downregulated in control and miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs following LPS treatment but was significantly increased after RSG stimulation alone and in the presence of LPS (LPS + RSG) (Figure 2A), suggesting that lack of miR-511-3p expression promotes the effects of PPARγ activity in DCs. In line with this, PPARγ mRNA expression was also downregulated in miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs following LPS treatment (data not shown). In contrast, we found a decrease in PPARγ activity in miR-511-3p-mimic DCs treated with LPS + RSG, highlighting the immune regulatory control of miR-511-3p overexpression on PPARγ activity (Figure 2B).
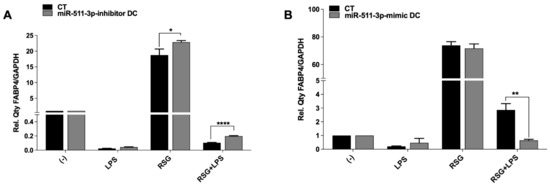
Figure 2.
PPARγ activity is affected by changes in miR-511-3p expression. Relative FABP4 expression in (A) miR-511-3p-inhibitor and (B) miR-511-3p-mimic DCs treated with RSG and LPS. Monocyte-derived DCs were transfected with 50 nM inhibitor and mimic for 6 days and stimulated with 5 uM RSG and 0.1 ug/mL LPS for 24 h. Gene expression was normalised to GAPDH. (One representative experiment out of three). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.
Studies indicate that RSG treatment affects DC maturation and downstream activation [27]. In line with this, we found that RSG-downregulated LPS induced the expression of the CD83 maturation marker but not CD86 in untransfected DCs. Moreover, there were no changes to the expression of mannose receptor (MR) as well as PDL-1, with the exception of DC-SIGN, which was significantly upregulated following LPS-induced DC maturation (Figure 3A). As expected, miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs downregulated CD83 expression following LPS stimulation in the presence of RSG (LPS/RSG) but was rescued following the addition of GW9662. Conversely, CD83 expression in miR-511-3p-mimic DCs after LPS treatment remained unchanged either in the presence of RSG or its antagonist GW9662, which is indicative of suppression of PPARγ activity by miR-511-3p-mimic cells (Figure 3B). Although LPS-induced CD86 expression was not affected in the miR-511-3p-inhibitor cells after PPARγ stimulation with RSG, we observed a decrease in CD86 expression following the addition of GW9662 (Figure 3C). Taken together, our data support the notion that increased miR-511-3p expression could downregulate PPARγ activity and promote LPS-induced DC maturation and activation.
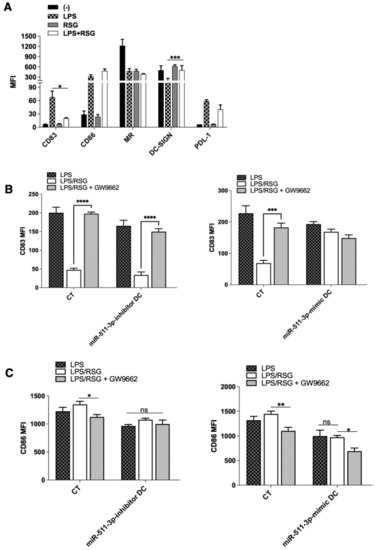
Figure 3.
LPS-induced DC maturation and activation is affected by PPARγ activity. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of human DC maturation, activation and exhaustion markers (CD83, CD86 and PDL-1) following treatment with LPS and RSG. Receptors for antigen capture, including MR and DC-SIGN, are also shown (n = 4). (B,C) MFI ratios for CD83 and CD86, respectively, in human miR-511-3p-inhibitor and miR-511-3p-mimic DCs. Monocyte-derived DCs were transfected with 50 nM miRNA inhibitor and mimic and stimulated with 0.1 µg/mL LPS and 5 µM RSG in the presence or absence of 5 µM GW9662 for 24 h (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
3.2. PPARγ Activation Modulates Cytokine Production in miR-511-3p-Transfected DCs
It has been previously described that PPARγ activation is able to modulate LPS-induced cytokine production in cells such as macrophages and DCs from humans and mice [28,29,30]. Having demonstrated the influence of miR-511-3p expression on PPARγ activity in human DCs, we examined the levels of IL-6 and IL-10, cytokines produced by miR-511-3p-inhibitor and miR-511-3p-mimic DCs in culture supernatant. miR-511-3p-inhibitor and miR-511-3p-mimic DCs were treated with RSG, LPS or both for 24 h in the presence or absence of PPARγ antagonist GW9662. As shown in Figure 4, IL-6 production in miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs was significantly downregulated in LPS/RSG conditions compared to LPS alone; however, in the presence of the PPARγ antagonist GW9662, IL-6 was significantly increased, abrogating the suppressive influence of RSG in these conditions (Figure 4A). In untransfected DCs, we found no significant changes in RSG-mediated suppression of IL-6 and TNF-α production (induced by LPS treatment) following treatment with GW9662 (Figure S2). Conversely, miR-511-3p-mimic DCs showed a significant increase in IL-6 after LPS treatment alone and in the presence of RSG but not after GW9662 treatment. The downregulation in PPARγ expression and activity resulting from miR-511-3p overexpression could account for an increase in IL-6 production, suggesting that PPARγ is a potent suppressor of LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses. Interestingly, the production of IL-10 was increased in all conditions following knockdown of miR-511-3p (i.e., miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs) compared to CT, with the exception of LPS/RSG condition, which showed no statistically significant difference with CT samples (Figure 4B). As expected, miR-511-3p-mimic DCs downregulated IL-10 production following treatment with LPS in the presence or absence of RSG, compared to scrambled controls (CT), whereas no significant changes were seen in IL-10 secretion between LPS alone or LPS/RSG conditions.
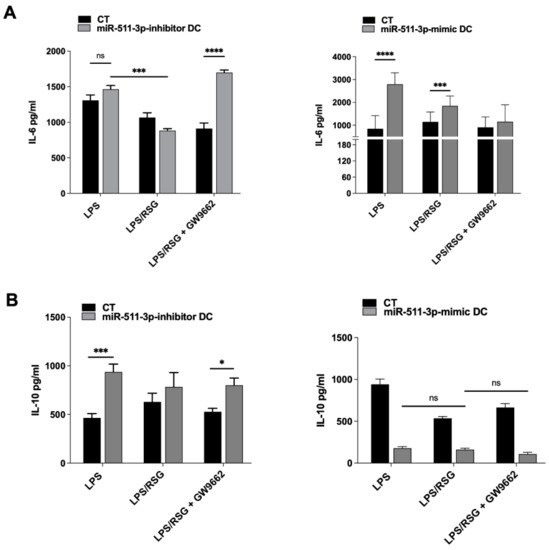
Figure 4.
Cytokine secretion is modulated by PPARγ activity in miR-511-3p transfected DCs. (A) IL-6 pro- and (B) IL-10 anti-inflammatory cytokine production by miR-511-3p-inhibitor and miR-511-3p-mimic DCs, respectively, stimulated with 5 µM RSG and 0.1 µg/mL LPS for 24 h in the presence or absence of 5 µM GW9662. Culture supernatants were collected, and cytokine levels were quantified by ELISA (n = 3). * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, ns: not significant.
3.3. PPARγ Modulation of LPS-Induced IDO Activity Is Influenced by miR-511-3p Expression in Human DCs
Under steady-state conditions, induction of the tryptophan-metabolising pathway by IDO acts as an immune regulatory mechanism in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli such as IFN-γ and TNF-α [31,32]. Under certain conditions, IDO induction can also be mediated through an IFN-γ-independent pathway, such as the presence of LPS during bacterial infection [10,33]. Recently, PPARγ was also shown to promote IDO activity and generation of local tolerogenic DCs within solid tumours [14]; nonetheless, the relationship between PPARγ and IDO in DCs within the context of LPS-induced inflammation is unknown. In order to investigate this, we first treated untransfected DCs with LPS, RSG and GW9662 alone to determine the influence of these ligands on IDO activity (Figure S3). Subsequently, we determined IDO activity following treatment with LPS in the presence or absence of these ligands. IDO activity was measured by colourimetric determination of kynurenine (KYN) produced in culture supernatant. As summarised in Figure 5, RSG alone had no influence on IDO activity but significantly downregulated LPS-induced IDO activity in DCs. Additionally, there were no significant changes to IDO activity following the addition of the PPARγ antagonist (LPS/RSG + GW9662) (Figure 5A). Next, we examined whether changes in miR-511-3p expression in DCs could affect IDO activity following treatment with LPS and RSG. Again, RSG stimulation alone had no effect on IDO activity (data not shown) but was able to significantly downregulate LPS-induced IDO activity in miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs (Figure 5B). Interestingly, IDO activity was markedly reduced in the miR-511-3p-mimic cells after treatment with LPS and LPS/RSG, similar to observations with IL-10, suggesting that IDO activity in DC could be potentially regulated by miR-511-3p in a PPARγ-independent fashion. Furthermore, we found an inverse correlation between miR-511-3p regulation and IDO activity after treatment with GW9662, indicating that PPARγ may play a key role in IDO downregulation induced by RSG in human DCs (Figure 5C). These data suggest that PPARγ activation is able to downregulate IDO activity in human DCs partly due to changes in miR-511-3p expression. As indicated in the LIVE/DEAD stain, DC viability was comparable in all conditions tested (Figure S4).
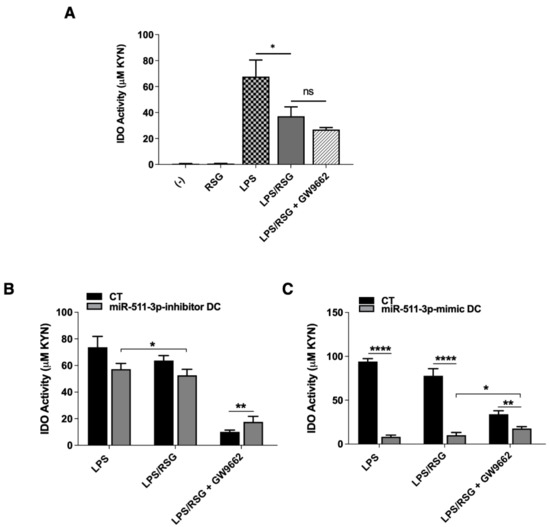
Figure 5.
IDO regulation by human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. (A) IDO activity in human DCs treated with 5 µM RSG and 0.1 µg/mL LPS for 24 h in the presence or absence of 5 µM GW9662 (n = 3). (B,C) IDO activity in miR-511-3p-inhibitor and miR-511-3p-mimic DCs, respectively, following treatment with 5 µM RSG and 0.1 µg/mL LPS for 24 h in the presence or absence of 5 µM GW9662. Culture supernatant was collected and examined for IDO activity (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001, ns: not significant.
4. Discussion
The PPAR receptors, which belong to the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily, were originally identified as key players in controlling the oxidation of lipids and fatty acids. Among the three members, PPARγ is essential for controlling adipocyte differentiation and glucose metabolism [34], and, presently, several reports have demonstrated the importance of PPARγ agonists as treatment against inflammatory diseases [35,36,37]. MicroRNAs are crucial players in mammalian gene regulation and their role in fine-tuning gene expression, particularly through dysregulated expression, has been reported in several infectious and inflammatory diseases. In this study, the role of miR-511-3p in modulating PPARγ activity in human DCs was investigated within the context of LPS-induced inflammatory responses.
We performed a prediction of miR-511-3p target genes using two independent miRNA databases, TargetScan 8.0 and Targetspy, and found PPARGC1A and PPARGC1B as putative targets, similar to studies by Tserel et al. [17]. In line with this, data presented in Figure 1 show that overexpression of miR-511-3p significantly downregulated PPARγ expression, as quantified by qRT-PCR. Recently, miRNAs have been shown to mediate pathways decreasing PPARγ expression during the onset of inflammation. For instance, miR-27b was shown to decrease PPARγ mRNA levels as mutation or deletion of the miR-27b start site completely abolished the reduction of luciferase activity in THP1 macrophages [38]. Additionally, they showed that miR-27b inhibitors prevented LPS-dependent PPARγ mRNA reduction in a concentration-dependent manner. It is noteworthy, however, that while our functional data corroborates changes in miR-511-3p expression level following inhibition or overexpression, the need for confirming PPARγ expression levels at the protein level is also crucial.
In line with previous reports, our data show that treatment of DCs with the PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone (RSG) induced PPARγ activity, whereas LPS treatment alone completely abrogates PPARγ activity (Figure 2). Two isoforms of PPARγ have been identified (PPARγ1 and 2), and studies show that both isoforms are downregulated in monocyte and macrophage cell lines following treatment with LPS [38]. However, prolonged exposure to LPS in these studies enabled recovery of PPARγ mRNA levels to almost basal levels after 24 h [38]. Notably, Samokhvalov et al. demonstrated that although LPS downregulates PPARγ activity, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which are biologically active metabolites of arachidonic acids, act as PPARγ agonists to suppress LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses [39]. This could explain the increase in PPARγ activity following LPS/RSG treatment in miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs seen in the present study (Figure 2A). Similarly, in a rat model of sepsis, infusion of low-dose LPS was shown to significantly decrease hepatic PPARγ protein levels, but administration of the LPS-binding agent (polymyxin B) reduced the plasma endotoxin level and prevented PPARγ downregulation in the septic animals [40], thus highlighting the complex mechanisms underlying the regulation of PPARγ during LPS-induced inflammation.
Several reports have indicated that induction of the IDO pathway of tryptophan metabolism contributes towards immune-modulatory events [41]. Within the context of inflammation, IDO induction leads to the suppression of T-cell effector responses [42]. A role for LPS in IDO induction has also been demonstrated by our group and others [20,43], which explains why IDO activity and expression is increased following LPS treatment. In this study, we show that LPS-induced IDO activity is significantly reduced in the presence of RSG compared to LPS alone. Interestingly, IDO activity following treatment with RSG and/or LPS in miR-511-3p-mimic DCs was also significantly reduced when compared to CT cells only. It is likely that transfection with miRNA mimics resulted in repression of other cell responses or miRNA target genes, as previously reported [44]. This could account for the decrease in IDO activity as well as IL-10 secretion in miR-511-3p-mimic cells. Recently, it has been demonstrated that fatty acid oxidisation by PPARγ in melanomas positively regulates IDO in DCs by promoting a switch towards a tolerogenic state to enable immune evasion [14]. In contrast, our data indicate that PPARγ activation negatively regulates IDO activity in DCs within the context of LPS-induced inflammation. A schematic representation of the relationship between miR-511-3p and PPARγ in modulating DC function is shown in Figure 6.
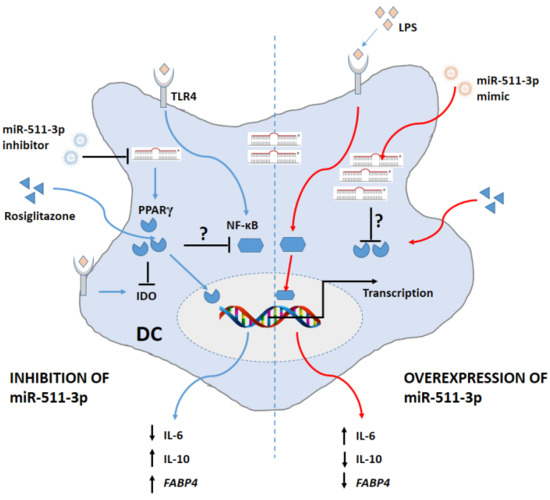
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the relationship between miR-511-3p and PPARγ in modulating human DC function. Downregulation of miR-511-3p promotes PPARγ expression and activity (FABP4) and subsequently suppresses LPS-induced inflammation. In contrast, overexpressing miR-511-3p reverses the effects of PPARγ and promotes transcription of pro-inflammatory genes.
The anti-inflammatory effect of PPARγ ligands in regulating immune responses is well documented. In particular, high dose 15d-PGJ2 or TZD (PPARγ agonists) treatment of monocytes and macrophages was shown to inhibit secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β) [26] and suppress IFN-γ-dependent inducible genes [25,45]. Additionally, it has been shown that IL-10 is induced by RSG in experimental models of colitis and Parkinson’s disease [46,47]. In the present study, we highlight the dynamics of IL-6 and IL-10 production by miR-511-3p-modified DCs, which further demonstrates the role of PPARγ supporting an anti-inflammatory profile in miR-511-3p-inhibitor DCs. Interestingly, a number of potential links between PPARγ and c-type lectins, particularly the mannose receptor (MR), have also been suggested. These include data showing that interaction between MR and Man-LAM from Mycobacterium tuberculosis can induce PPARγ activation [48]. Considering that changes in miR-511-3p expression are associated with changes in MR expression as well as IDO activity, as demonstrated previously [16], it is likely that miR-511-3p may play a role in regulating MR expression and DC function through PPARγ. These studies, therefore, suggest that PPARγ and signalling molecules/pathways controlling its expression or activity may serve as a target for anti-inflammatory therapy. In recent years, the therapeutic potential of microRNAs has been accumulating, particularly due to the development of small molecule analogues or inhibitors, which aim to suppress miRNA expression in human disease or block specific inflammatory pathways. However, clinical use of miRNA is dependent on the successful delivery of drugs to diseased organs. For instance, analogues of miR-511-3p in combination with other small molecule drugs could potentially block immune pathways that exacerbate inflammatory responses and enhance quality of life. Collectively, these data highlight the potential immune-regulatory role of miR-511-3p on PPARγ activity in human DCs. The roles of miRNAs and PPARγ in immune regulation are still being investigated, and this transcription factor is emerging as a key player in various stages of the resolution of inflammation.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/immuno2010008/s1, Figure S1: Apoptotic effect of miR-511-3p transfection on Mo-DCs. Figure S2: PPARγ activation by rosiglitazone (RSG) downregulates TNF-α production in human DC. Figure S3: IDO activity in untransfected DCs. Figure S4: Dendritic cell viability title.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, D.A. and A.M.G.; methodology, D.A., A.R., M.A. and C.M.; software, D.A. and A.R.; validation, D.A., A.R. and A.M.G.; formal analysis, D.A., A.R., M.A. and C.M.; investigation, D.A., A.R., M.A. and C.M.; resources, D.A. and A.M.G.; data curation, A.R., M.A. and C.M.; writing—original draft D.A., A.R. and A.M.G.; writing—review and editing, D.A., A.R., M.A., C.M. and A.M.G.; project administration, D.A. and A.M.G.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
D.A. is a recipient of the Vice Chancellor’s Ph.D Scholarship at the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the declaration of Helsinki, and the study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Nottingham; BT08052013-160-1701.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all donors involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge support from the flow cytometry facility (School of Life Sciences, University of Nottingham).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
References
- Rosenfeld, Y.; Shai, Y. Lipopolysaccharide (Endotoxin)-host defense antibacterial peptides interactions: Role in bacterial resistance and prevention of sepsis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilroy, D.; Lawrence, T. The resolution of acute inflammation: A ‘tipping point’ in the development of chronic inflammatory diseases. In The Resolution of Inflammation; Rossi, A.G., Sawatzky, D.A., Eds.; Birkhäuser Basel: Basel, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, T.; Fong, C. The resolution of inflammation: Anti-inflammatory roles for NF-κB. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The Nuclear Factor NF-κB Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadian, M.; Suh, J.M.; Hah, N.; Liddle, C.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: The good, the bad and the future. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klotz, L.; Dani, I.; Edenhofer, F.; Nolden, L.; Evert, B.; Paul, B.; Kolanus, W.; Klockgether, T.; Knolle, P.; Diehl, L. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma control of dendritic cell function contributes to development of CD4+ T cell anergy. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2122–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nencioni, A.; Grunebach, F.; Zobywlaski, A.; Denzlinger, C.; Brugger, W.; Brossart, P. Dendritic cell immunogenicity is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, V.; Hammad, H.; Staels, B.; Capron, M.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Trottein, F. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibits the migration of dendritic cells: Consequences for the immune response. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5295–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faveeuw, C.; Fougeray, S.; Angeli, V.; Fontaine, J.; Chinetti, G.; Gosset, P.; Delerive, P.; Maliszewski, C.; Capron, M.; Staels, B.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activators inhibit interleukin-12 production in murine dendritic cells. FEBS Lett. 2000, 486, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, F.; Awuah, D.; Negm, O.H.; Shakib, F.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. The role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway in the TLR4-induced tolerogenic phenotype in human DCs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallarino, F.; Grohmann, U.; Vacca, C.; Bianchi, R.; Orabona, C.; Spreca, A.; Fioretti, M.C.; Puccetti, P. T cell apoptosis by tryptophan catabolism. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tas, S.W.; Vervoordeldonk, M.J.; Hajji, N.; Schuitemaker, J.H.N.; van der Sluijs, K.F.; May, M.J.; Ghosh, S.; Kapsenberg, M.L.; Tak, P.P.; de Jong, E.C. Noncanonical NF-κB signaling in dendritic cells is required for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) induction and immune regulation. Blood 2007, 110, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mbongue, J.C.; Nicholas, D.A.; Torrez, T.W.; Kim, N.-S.; Firek, A.F.; Langridge, W.H.R. The Role of Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase in Immune Suppression and Autoimmunity. Vaccines 2015, 3, 703–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Xiao, C.; Evans, K.S.; Theivanthiran, T.; DeVito, N.; Holtzhausen, A.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Boczkowski, D.; Nair, S.; et al. Paracrine Wnt5a-β-Catenin Signaling Triggers a Metabolic Program that Drives Dendritic Cell Tolerization. Immunity 2018, 48, 147–160.e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bentwich, I.; Avniel, A.; Karov, Y.; Aharonov, R.; Gilad, S.; Barad, O.; Barzilai, A.; Einat, P.; Einav, U.; Meiri, E.; et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awuah, D.; Alobaid, M.; Latif, A.; Salazar, F.; Emes, R.D.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. The Cross-Talk between miR-511-3p and C-Type Lectin Receptors on Dendritic Cells Affects Dendritic Cell Function. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tserel, L.; Runnel, T.; Kisand, K.; Pihlap, M.; Bakhoff, L.; Kolde, R.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, P.; Rebane, A. MicroRNA expression profiles of human blood monocyte-derived dendritic cells and macrophages reveal miR-511 as putative positive regulator of Toll-like receptor 4. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26487–26495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karo-Atar, D.; Itan, M.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Munitz, A. MicroRNA profiling reveals opposing expression patterns for miR-511 in alternatively and classically activated macrophages. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2015, 52, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, K.K.; Pagel, P.; von Frowein, J.; Magg, T.; Roscher, A.A.; Schmid, I. The leukemogenic fusion gene MLL-AF9 alters microRNA expression pattern and inhibits monoblastic differentiation via miR-511 repression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar, F.; Hall, L.; Negm, O.H.; Awuah, D.; Tighe, P.J.; Shakib, F.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. The mannose receptor negatively modulates the Toll-like receptor 4-aryl hydrocarbon receptor-indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase axis in dendritic cells affecting T helper cell polarization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1841–1851 e1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Nieto, S.; Johal, R.K.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Emara, M.; Royer, P.J.; Chau, D.Y.; Shakib, F.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. Laminin and fibronectin treatment leads to generation of dendritic cells with superior endocytic capacity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldajani, W.A.; Salazar, F.; Sewell, H.F.; Knox, A.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. Expression and regulation of immune-modulatory enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) by human airway epithelial cells and its effect on T cell activation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57606–57617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donaldson, A.R.; Tanase, C.E.; Awuah, D.; Vasanthi Bathrinarayanan, P.; Hall, L.; Nikkhah, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Rose, F.; Alexander, C.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. Photocrosslinkable Gelatin Hydrogels Modulate the Production of the Major Pro-inflammatory Cytokine, TNF-α, by Human Mononuclear Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaemmaghami, A.M.; Shakib, F. Human T cells that have been conditioned by the proteolytic activity of the major dust mite allergen Der p 1 trigger enhanced immunoglobulin E synthesis by B cells. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricote, M.; Li, A.C.; Willson, T.M.; Kelly, C.J.; Glass, C.K. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature 1998, 391, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Ting, A.T.; Seed, B. PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines. Nature 1998, 391, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, I.; Gogolak, P.; Im, J.S.; Dezso, B.; Rajnavolgyi, E.; Nagy, L. Activation of PPARγ Specifies a Dendritic Cell Subtype Capable of Enhanced Induction of iNKT Cell Expansion. Immunity 2004, 21, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Shi, L.; Xin, W.; Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Yao, W.; et al. Activation of PPARγ inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines production by upregulation of miR-124 in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, S.; Mirakaj, V.; Bringmann, A.; Weck, M.M.; Grünebach, F.; Brossart, P. PPAR-γ agonists inhibit toll-like receptor-mediated activation of dendritic cells via the MAP kinase and NF-κB pathways. Blood 2005, 106, 3888–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, K.; Sasaki, S.; Suda, T.; Chida, K.; Nakamura, H. Antiinflammatory Roles of Peroxisome Proliferator–activated Receptor γ in Human Alveolar Macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, C.M.; Hale, P.T.; Carlin, J.M. The Role of IFN-γ and TNF-α-Responsive Regulatory Elements in the Synergistic Induction of Indoleamine Dioxygenase. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005, 25, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.M.; Shirey, K.A.; Carlin, J.M. Synergistic transcriptional activation of indoleamine dioxygenase by IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Interferon Cytokine Res 2003, 23, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujigaki, S.; Saito, K.; Sekikawa, K.; Tone, S.; Takikawa, O.; Fujii, H.; Wada, H.; Noma, A.; Seishima, M. Lipopolysaccharide induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is mediated dominantly by an IFN-gamma-independent mechanism. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, T.; Nagy, L. Nuclear receptors, transcription factors linking lipid metabolism and immunity: The case of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 38, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Delfín, J.; Morales, M.; Caelles, C. Hypoglycemic Action of Thiazolidinediones/Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor γ by Inhibition of the c-Jun NH2-Terminal Kinase Pathway. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landreth, G. Therapeutic use of agonists of the nuclear receptor PPARgamma in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2007, 4, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D.; Lichtenstein, G.R.; Deren, J.J.; Sands, B.E.; Hanauer, S.B.; Katz, J.A.; Lashner, B.; Present, D.H.; Chuai, S.; Ellenberg, J.H.; et al. Rosiglitazone for active ulcerative colitis: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jennewein, C.; von Knethen, A.; Schmid, T.; Brüne, B. MicroRNA-27b Contributes to Lipopolysaccharide-mediated Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ (PPARγ) mRNA Destabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 11846–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samokhvalov, V.; Vriend, J.; Jamieson, K.; Akhnokh, M.; Manne, R.; Falck, J.; Seubert, J. PPARγ signaling is required for mediating eets protective effects in neonatal cardiomyocytes exposed to LPS. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, R.; Dong, W.; Jacob, A.; Wang, P. Endotoxin downregulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ via the increase in TNF-α release. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R84–R92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bubnoff, D.; Bieber, T. The indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) pathway controls allergy. Allergy 2012, 67, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.E.; Astola, N.; Cribbs, A.P.; Goddard, M.E.; Park, I.; Green, P.; Davies, A.H.; Williams, R.O.; Feldmann, M.; Monaco, C. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 is protective in atherosclerosis and its metabolites provide new opportunities for drug development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13033–13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curti, A.; Trabanelli, S.; Salvestrini, V.; Baccarani, M.; Lemoli, R.M. The role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in the induction of immune tolerance: Focus on hematology. Blood 2009, 113, 2394–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.Y.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Miletic, A.V.; Lai, M.; Knight, S.; Sabouri-Ghomi, M.; Head, S.R.; Macauley, M.S.; Rickert, R.C.; Xiao, C. Transfection of microRNA Mimics Should Be Used with Caution. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chawla, A.; Barak, Y.; Nagy, L.; Liao, D.; Tontonoz, P.; Evans, R.M. PPAR-γ dependent and independent effects on macrophage-gene expression in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celinski, K.; Dworzanski, T.; Korolczuk, A.; Piasecki, R.; Slomka, M.; Madro, A.; Fornal, R. Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-gamma ligands on dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2011, 62, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Pisanu, A.; Lecca, D.; Mulas, G.; Wardas, J.; Simbula, G.; Spiga, S.; Carta, A.R. Dynamic changes in pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in microglia after PPAR-gamma agonist neuroprotective treatment in the MPTPp mouse model of progressive Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 71, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, M.V.; Brooks, M.N.; Morris, J.D.; Torrelles, J.B.; Azad, A.K.; Schlesinger, L.S. Mycobacterium tuberculosis activates human macrophage peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma linking mannose receptor recognition to regulation of immune responses. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).