Abstract
Only survey studies have linked specific individual psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression and schizophrenia to Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS), Periodic Limb Movements in Sleep (PLMS) or both. We therefore aim to polysomnographically characterize sleep in a sample of physician-based, newly diagnosed cases of RLS with various ICD-10 psychiatric diagnoses. Retrospective analysis of data from a convenience sample of psychiatric patients (n = 43) per standard clinical sleep disorder cut-offs was conducted. Next, a cluster analysis was performed on the sleep data, taking into account the psychiatric diagnosis, comorbid non-psychiatric somatic problems and medication. We found that 37.2% of our sample showed clinically significant PLMS ≥ 15 and 76.5% exhibited an apnea hypopnea index (AHI) ≥ 5. Sleep structure was unaltered apart from the PLMS-related parameters. Two clusters were statistically identified: Cluster 1 primarily representing recurrent major depressive issues and Cluster 2 representing present but not predominant mood symptomatology as well as mixed disorders with personality problems. The known confounders were controlled. A PLMS index ≥ 15 was differentially distributed among the two clusters with Cluster 1: 10 out of 17 with PLMS index ≥ 15; Cluster 2: 1 out of 16 with PLMS index ≥15; whilst AHI was not different. Patients in Cluster 1 have a higher rate of periodic leg movements than patients in Cluster 2. This suggests that the high association with PLMS is primarily driven by affective disorders. Our findings warrant questioning of RLS symptomatology in patients with psychiatric conditions.
1. Introduction
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is characterized by four obligatory features: (a) an urge to move the legs usually associated with leg discomfort; (b) symptoms are worse at rest, e.g., lying or sitting; (c) symptoms are worse later in the day or evening; and (d) there is at least partial and temporary relief by activity such as walking or stretching or bending the legs. RLS is a common neurological, sensorimotor disorder, with a prevalence rate of about 2–3% of adults suffering from clinically significant symptoms [1,2]. The leg discomfort in RLS leads to significant sleep-onset difficulties or insomnia [3,4]. Patients with RLS may sleeplessly pace the floor at night in order to get rid of the leg discomfort so that they can go back to sleep. Some studies have indicated that the quality of life of patients with RLS is as bad as that experienced in patients with diabetes or in osteoarthritis with hypertension [1]. Eighty to eighty-seven per cent of patients with RLS may also have Periodic Limb Movements of Sleep (PLMS) > 5/h, which are large flexions of the hips, knees and thighs that recur multiple times throughout the night during sleep at frequencies of every 5 to 90 s [5].
Previous studies have shown that various psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and schizophrenia have a higher prevalence of RLS, PLMS or both [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. More specifically, RLS occurred in 20% of adults with ADHD and more severe ADHD symptomatology was associated with RLS [12]. Whilst patients with schizophrenia may complain of insomnia and poor sleep, 21.4% had RLS and in 47.8% at least one of the RLS diagnostic criteria was met [6]. Motor dysfunction, such as muscle twitch bursts during sleep or PLMS, were described in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder [9,10]. Depression is co-occurring in these patients. Depression is also co-occurring in individuals with sleep-related disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It was demonstrated that depressed OSA patients have a higher PLM index [11,13], and in depressed RLS patients, insomnia complaints were described. Overall, in depressed patients, odds ratios as high as 9.7 indicate the strong association with RLS and PLM disorder [11,13]. A high risk of suicide and self-harm independent of most identified diseases and conditions has been reported in RLS patients [14].
There is a potential risk of misdiagnosis, underdiagnosis and non-diagnosis of the unpleasant leg sensation or RLS across psychological conditions. In addition, given that a dopaminergic abnormality has been described in RLS, the sensorimotor signs and enhanced arousal in RLS might be more disturbed in psychiatric patients where dopaminergic abnormalities have also been described [15]. If RLS is associated with more severe psychiatric symptoms this would warrant improved awareness amongst clinicians [16]. There are a few reports in the literature exploring the role of RLS in selective individual psychiatric conditions, but there have been no previous polysomnographic (PSG) studies of a general grouping of psychiatric patients with a variety of psychiatric disorders, all of whom had RLS. Our objective was to describe the co-occurrence and association of symptomatology of sleep disordered breathing and periodic leg movements in a psychiatric sample with newly diagnosed RLS patients, as reported in the literature based on surveys. In this retrospective study, we therefore aim to polysomnographically characterize sleep in a sample of physician-based cases of RLS with various psychiatric diagnoses. To our knowledge, this is also the first study to employ a cluster analysis as an analytic tool to characterize the relationship between psychiatric state and PSG parameters in RLS patients.
In this study, we explore the underlying associations in terms of PSG features between the psychiatric state, the comorbid non-psychiatric somatic problems and medication in RLS patients. All patients were diagnosed per the ICD-10. Given the survey literature, we hypothesize that subgroups in relation to the psychiatric state exist.
2. Materials and Methods
We describe a retrospective analysis of clinical data, which will include a standard clinical approach (2.3.1.) and a datamining approach (2.3.2.) on the data that was available in the records (Supplementary Materials Figure S1).
2.1. Procedure
Seventy-one physician-based cases of RLS meeting the ICD-10 criteria (International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision) G25.81 were contacted as per the IRB-MR004 approved protocol by the Centre Hospitalier Le Vinatier. Patients received an individual information document explaining the retrospective analysis of their data and were provided an opposition form to using their data for research purposes. Returning this form precluded using their data per French law (Délibération n. 2018–155 du 3 mai 2018 CNIL.fr). The study was registered on a national public registry database—MR-411-422-019 (www.indsante.fr, accessed on 1 June 2021).
The design of the study is a descriptive within-subjects effect where all participants underwent the same ‘experimental’ manipulation: i.e., a clinical sleep study. Because there is no dependent variable under potential influence by an extraneous variable, a control group is not needed [17]. Subjects of whom the sleep study was performed between 2016 to 2019 were contacted safeguarding simple randomization. This retrospective study reports on data collected on two consecutive overnight polysomnography (PSG) recordings of subjects with psychiatric issues, having a (or multiple) (comorbid) psychiatric diagnosis. Psychiatric diagnoses met ICD-10 criteria as assessed by clinical interview per Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview.
All subjects had an initial complaint of restlessness or restless sleep and are newly diagnosed physician-based cases of RLS (i.e., inclusion criterion). No RLS severity measurement was applied, but diagnosis was made based on clinical description: the need to move the legs accompanied to varying degrees by unpleasant sensations, predominantly during the evening and improved by movement, excluding mimics [2,18]. That is, in this convenience sample of psychiatric patients, patients were interviewed about the symptoms of RLS. Those who met the criteria for RLS of the International RLS study group [2] underwent two nights of PSG study for clinical purposes in a specialized unit of the psychiatric hospital (CH Le Vinatier, Bron, France).
We retrieved sleep data, psychiatric diagnoses and other information such as somatic conditions and medications. Of the 71 contacted, 55 subjects gave their consent to use their data, which was subsequently retrieved from the hospital records.
2.2. Polysomnography (PSG)
All subjects underwent two nights of PSG, which were scored in accordance to AASM 2007 criteria [19]. All recordings included at least six leads of EEG (F3-A2, F4-A1, C3-A2, C4-A1, O1-A2, O2-A1), a surface electromyogram recordings from the mentalis and bilateral anterior tibialis, an electrocardiogram and a vertical and horizontal electrooculogram. Respiration was monitored using a nasal cannula and with thoracic and abdominal strain gauges, whereas blood oxygen saturation was continuously recorded by cutaneous finger pulse oximetry.
Video-PSG was recorded on an OSG BrainRT PSG device (OSG 2840 Rumst, Belgium; http://www.osg.be, accessed on 1 June 2021). Standard PSG parameters were reported: Total Sleep Time (TST), Sleep Onset Latency (SOL), Rapid Eye Movement SOL (SOREM), Sleep Efficiency Index (SEI), Sleep Quality (SWS + REM/TST), Wake After Sleep Onset (WASO), Stages N1 to N3 and REM (calculated per TST). Leg movements were identified per the stipulated criteria of the World Association of Sleep Medicine (WASM) 2016 guidelines [20].
2.2.1. The Apnea–Hypopnea Index (AHI)
Sleep disordered breathing (SDB) was diagnosed based on the apnea–hypopnea index (AHI); i.e., AHI ≥ 5 events/h TST and scored per the recommendation of Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force [19,21]. The first-night PSG was with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for five subjects of which two did continue CPAP on the second night.
2.2.2. The Periodic Limb Movements of Sleep (PLMS) Index
The Periodic Limb Movements of Sleep (PLMS) index of ≥15 times/h TST was chosen as cut-off based upon the AASM cut-off for PLMS severity [22].
PLMS were scored as repetitive leg movements lasting from 0.5 to 10 s, separated by an intermovement interval (defined as the time between onsets of consecutive leg movements) ranging from 5 to 90 s, organized in series of at least 4 leg movements [19,23]. PLMS associated with respiratory events were not excluded, but supplementarily analyzed per the WASM criteria (WASM old: within ± 0.5 s of the end of a respiratory event; WASM new: from 2.0 s before to 10.25 s after the end of a respiratory event) and AASM (within ±0.5 s of the beginning/end of a respiratory event) were conducted [20]. As generated per BrainRT software, the percentage of the different sleep stages associated with PLM were reported as percentage of PLMS series [PLMS series stage, %; calculated as (PLM series period (in min)/number of min in that sleep stage N1) × 100]. In addition, the periodicity index was calculated [24].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
We examined the available clinical data, prior to the standard clinical approach and cluster analysis, (Supplementary Materials Figure S1). That is, the two overnight PSG’s were compared using t-test for dependent samples. For the comparison of the first- and second-night AHI, we applied the Wilcoxon matched pairs test.
2.3.1. The Standard Clinical Approach
In this round of analysis, we compared groups based on the standard sleep disorders clinical cut-offs. For the PLMS index groups, we conducted the Mann–Whitney U test. For age, we conducted the Mann–Whitney U test, and for gender, a Chi-square test. Groups based on the PLMS and AHI cut-offs were compared by the Kruskall–Wallis test. The leg movements (LM indices) were compared using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test, assessing their distribution.
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and percentages unless otherwise indicated. The two-tailed p-value was reported. However, due to multiple comparisons, a correction of the p-value is needed. We consider an adjusted p-value ≤ 0.001 as statistically significant.
2.3.2. The Datamining Approach: Cluster Analysis
Because statistical analyses in the standard clinical approach do not incorporate the potential underlying relationships between the psychiatric state, a comorbid somatic issue or medication with the sleep parameters, we conducted a cluster analysis [25].
That is, to characterize subgroups in this sample given their initial complaint that was clinically diagnosed as RLS with concomitant PSG assessment, we applied a k-means cluster analysis with Euclidean distances, and a 10-fold cross validation [25].
The clusters (or subgroups) were interpreted in terms of cluster centroids. Namely, the cluster analysis statistical algorithm finds and then compares centroids by a one-way analysis of variance with p-value < 0.05. That is, in clustering, subjects are maximally similar to one another within the same cluster and maximally dissimilar to the subjects in other clusters. Cluster analysis allows the identification and representation of patterns between data elements, and therefore allows a better description of “clustering” symptomatology.
The software package Statistica (TIBCO, version 13) was used for statistical analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characterization
Of the 55 subjects that consented, the PSG of 12 subjects could not be retained for further statistical analysis. This was due to premature ending of the sleep recording, leaving the bed multiple times for prolonged periods, complaints of extreme pain or reading at nighttime resulting in discontinued recordings, scattered recordings or multiple artifacts.
Our sample of 43 patients contains various psychiatric diagnoses. Eight primary diagnostic classifications are represented: depression (ICD-10 F33; n = 10), anxiety disorder (ICD-10 F41.1; n = 9), bipolar disorder (ICD-10 F31.2; n = 2), symptoms of mood or affective disorders (ICD-10 F41.2; n = 13), personality disorder (ICD-10 F60.9; n = 1), multi-diagnosis disorders with personality disorder (ICD-10 F33 + F60.9 n = 2; F41.1 + F60.9 n = 1; F31.2 + F60.9 n = 1; F31.2 + F41.1 + F60.9 n = 1), mood with neurotic related disorders (ICD-10 F33 + F41.1; n = 2) and schizophrenia with depression (ICD-10 F20 + F33; n = 1). Several somatic conditions were present in seven of the 43 subjects: obesity, diabetes, epilepsy, narcolepsy, cardiopathy, Crohn’s disease, fibromyalgia, hyperplasia prostate, hypertension, Parkinson’s disease, hypothyroidism, orthostatic hypotension and renal insufficiency.
In this convenience sample, the overall average age was 57.3 ± 15.6 years (min. 29 to max. 83) and 62.8% were males. The TST was 377.7 ± 100 min.; more PSG parameters are presented in Table 1. The mean sleep efficiency was 75.4 ± 14.6%.

Table 1.
Standard sleep study parameters of the sample.
Respiratory measures were available for 34 subjects with the mean AHI being 18.1 ± 17.2 on the first night. The mean PLMS index was 17.8 ± 32.5, and based on the PLMS ≥ 15 times/h cut-off, 16 subjects showed clinically relevant periodic leg movements. The AHI was not different between the two PLMS index groups.
3.2. First- and Second-Night PSG
Because more sleep data were available for the first night, we verified for differences with the second night (Supplementary Materials Figure S1). The first-night effects were found, showing improved SEI on the second night [75.4 ± 14.6% versus 82.3 ± 9.7% (n = 43, t-test for dependent samples(42) = −4.1, p-value = 0.0002)], primarily ascribed to the decrease in WASO. Supplementary Materials Table S1 shows that none of the sleep movement parameters changed on the second night when using the adjusted p-value of ≤0.001.
The respiratory data of 34 subjects were available on the first night (Supplementary Materials Figure S1), yet five subjects wore CPAP on the first night, of which two subjects discontinued wearing the CPAP on the second night. First, we compared the sleep parameters of these 34 to those of the total sample (n = 43) and found no differences (not reported). Next, we verified the AHI given that not all patients underwent a respiratory setting on the second night and that some wore CPAP. In addition, no differences were found upon excluding the subjects wearing CPAP (see Table 2), justifying the use of the largest available complete dataset, i.e., the first night (n = 34).

Table 2.
Comparison of first- and second-night AHI.
3.3. Comparison Across Groups Based on Clinical Cut-Offs of AHI ≥ 5 and PLMS Index ≥15
Per clinical practice, Table 3 shows that the sleep macrostructure was similar across groups (n = 34), apart from the AHI and sleep movement parameters on which they were divided. The PLMS index, their number and the PLM series in TST and N1 were significantly higher in subjects with a clinical presence of AHI and/or PLMS. However, the PLMS index is not significantly different between PLMS alone and the SDB with PLMS group, whilst the AHI is not statistically different between the SDB alone and the SDB with PLMS group.

Table 3.
Comparison across groups based on standard cut-offs of SDB and PLMS.
3.4. Cluster Analysis
To allow multiple factors to be taken into account, we performed a cluster analysis. It tries to identify homogenous groups of cases if the grouping is not previously known. That is, in our physician-based cases of RLS with various psychiatric diagnoses the statistical algorithm will seek underlying associations in terms of the polysomnographic features between the psychiatric state and the comorbid non-psychiatric somatic problems in RLS patients.
Cluster analysis was performed on the six significant sleep parameters per clinical standard approach (see Table 3, bold p-values): Total AHI, PLMS index, number of PLMS, PLMS micro-arousal index, PLMS series TST and PLMS series N1. These six sleep parameters combined with the psychiatric diagnosis (and somatic problems) generates clusters, which are, by the statistical algorithm, significantly different from each other. Due to the combination of all clinical information available, the clusters aid in describing potential subgroups.
Because clustering converges quickly to a local optimum, one case presenting a PLMS index beyond 2SD was excluded. Clustering revealed two significantly distinct clusters. Cluster 1 represents predominantly affective disorders, whereas Cluster 2 seems to represent mostly personality and behavior disorders per the ICD-10’s conceptualization. Their clinical interpretation depends on the cluster characteristic centroids (Table 4), the distribution of diagnoses represented within the cluster (Figure 1) and their normalized means (Figure 2). Gender distribution (p-value = 0.22) and mean age (p-value = 0.10) were not different between clusters.

Table 4.
Centroids of the two clusters.
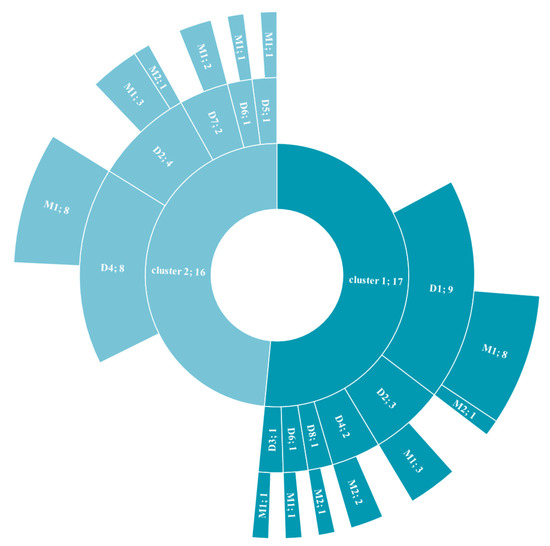
Figure 1.
Distribution of diagnostic criteria across clusters.
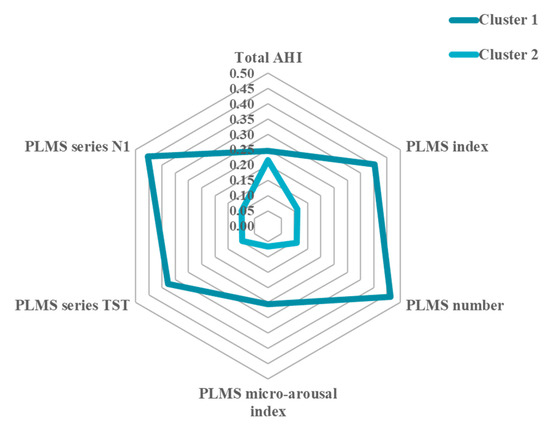
Figure 2.
Normalized means of sleep parameters across clusters.
The centroids that describe the clinical characteristics of each cluster separately are shown in Table 4. Clusters are significantly different from each other in terms of the sleep parameters investigated incorporating psychiatric diagnosis and somatic condition, except regarding the AHI. This suggests that the AHI has a limited contributory value to the formation of the two distinct clusters, in contrast to the PLMS. In Table 4, the power for the statistically significant differences between the centroids is presented indicating that our sample size is adequate for the analysis performed. In Supplementary Materials Figure S2, the distance from their cluster centroid for each case is plotted against the PLMS and AHI.
The distribution of the psychiatric diagnosis within the clusters is shown in Figure 1. From this it can be deduced that Cluster 1 is reflecting primarily depressive issues (n = 17, i.e., the preponderance of depressive disorder) and Cluster 2 is representing present but not predominant mood symptomatology as well as mixed disorders with personality problems (n = 16).
Figure 2 shows the normalized means of the six sleep parameters (allowing for the direct comparison amongst them), demonstrating an indication of severe (Cluster 1) and minor (Cluster 2) PLMS representations of the initial restlessness or restless sleep complaint in physician-based cases of RLS, as measured by the significant PSG parameters. Thus, whilst the AHI is comparable between clusters, Cluster 1 is especially described by higher PLMS values and cluster 2 by lower PLMS values.
This sunburst chart displays the hierarchical data represented by the two clusters. Each ring is broken into its contributing pieces: psychiatric diagnosis and comorbid somatic condition.
D1: depressive disorder (ICD-10 F33); D2: anxiety disorder (ICD-10 F41.1); D3: bipolar disorder (ICD-10 F31.2); D4: symptoms of mood or affective disorders (ICD-10 F41.2); D5: personality disorder (ICD-10 F60.9); D6: multi-disorders with personality disorder (ICD-10 F33 + F60.9, F41.1 + F60.9, F31.2 + F60.9, F31.2 + F41.1 + F60.9); D7: mood with neurotic related disorders (ICD-10 F33 + F41.1); D8: schizophrenia with depression (ICD-10 F20 + F33); M1: no somatic condition; M2: with somatic condition.
Sample size is reported after the semicolon on the diagram.
The normalized means allow for the direct comparison between the sleep parameters of the two clusters. It shows that Cluster 1 is primarily driven by PLMS indices, whereas Cluster 2 by the AHI, which is comparable between clusters.
AHI = apnea–hypopnea index; TST = total sleep time; N1-N3: sleep stage; PLMS = periodic limb movements during sleep; PLMS series: percentage of the different sleep stages associated with PLM. Normalized means allow direct comparison across the sleep parameters.
Expressed in clinical practice cut-offs, a PLMS index ≥ 15 was differentially distributed among the two clusters with Cluster 1 expressing 10 out 17 with a PLMS index ≥ 15 (30.30%) and Cluster 2 expressing 1 out of 16 with a PLMS index ≥ 15 (3.03%) (Chi-square(1) = 10.25, p = 0.0014). This was, however, not true for the AHI ≥ 5: 14 out of 17 for Cluster 1 (42.42%) and 11 out of 16 for Cluster 2 (33.33%) (Chi-square(1) = 0.831, p = 0.362).
Lastly, we generated different LMs indices (Table 5), which showed that Cluster 1 had higher respiratory related movements per the WASM 2016 and AASM criteria.

Table 5.
Leg movement scoring between the two clusters.
Sensitivity Analysis
In this retrospective data analysis, given the convenience sample (Supplementary Materials Table S3), several confounding variables are to be assessed. We therefore performed a sensitivity analysis to assess the robustness of our final results, i.e., in n = 33 with an average AHI = 17.9 ± 17.4 and an average PLMS index = 13.1 ± 14.0. No significant differences were found that could have been ascribed to confounding variables such as CPAP, somatic conditions or medications (Table 6).

Table 6.
Sensitivity analysis (mean ± sd, p-value).
The somatic conditions in the clustered sample (n = 33) were: hypothyroidism, obesity, fibromyalgia, diabetes, cardiopathy, hypotension, prostate hyperplasia, renal insufficiency, and Crohn’s disease. The medications taken by subjects in the clustered sample (n = 33) were: one subject on an antipsychotic, anxiolytic, two subjects on antipsychotics, anxiolytics, antidepressants and a drug for Parkinson’s disease; one subject on antipsychotics, anxiolytics and antidepressants; one subject on antidepressants and a drug for Parkinson’s disease; and one subject on antipsychotic, antidepressants and drug for Parkinson’s disease.
The sensitivity analyses demonstrate that our findings are not due to known confounders.
4. Discussion
The results of the current study indicate that, among patients with psychiatric disorders who have RLS, those with affective disorders have the most significant numbers of PLMS on the PSG. We did not have a measure of RLS severity or duration, but RLS severity and PLMS severity are very closely linked [26,27,28]. It is therefore very likely that more severe RLS would also be linked closely with mood symptoms such as the recurrent nature and diagnostic typology of the major depressive disorder. Further studies, of course, would be needed to bear this additional hypothesis out. Increased awareness of RLS in various psychiatric health issues may assist treatment of complaints reported by patients.
Psychiatry to date has been struggling with the validation of the structure of psychopathology. That is, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) has been predominantly defined by expert opinion and clinical observation, with a recent rapid progressive growth of objective methods such as imaging [29] and genomics [30]. Concomitantly, sleep classifications and the sleep disorders section in the DSM has been advancing. Such prominent changes in the classification of sleep disorders in the DSM has been noted principally for insomnia or difficulties with sleep-onset [31].
Difficulties with sleeping, or the first notions of poor sleep, in fact find their roots in psychiatric observations and as features in their classifications. Polysomnography could therefore serve as an additional objective method to assess the auxiliary crossbreed of sleep disorders with psychopathology in psychiatric patients. Particularly regarding the urge to move the legs (i.e., the clinical screening for restless legs beginning or worsening during rest or inactivity, the partial or total relief of discomfort by moving as well as the occurrence or worsening in the evening or at night of such sensorimotor signs) is needed. That is, they might be uttered as complaints of insomnia or poor sleep quality by the patient.
Our heterogeneous sample consisted chiefly of patients with present, but not predominant, symptoms of mood or affective disorders (30.2%), 23.3% majorly depressed patients, 20.9% patients with anxiety disorders and 11.6% patients exhibiting mixed disorders with personality disorders and other various psychiatric disorders. Associations between anxiety, panic disorder and depression with RLS have been reported in the literature, with their excess morbidity attributed to RLS [32,33]. RLS symptoms alternatively might be masked by more severe psychiatric symptomatology or insomnia (4). Especially in children, but equally relevant for adults, an increased awareness on comorbid diseases/disorders to improve the diagnosis and management of RLS could be advocated for [34]. In addition, somatic conditions were scattered across our patients. In the literature, reports on RLS (co)morbidity in iron deficiency, terminal renal insufficiency, pregnancy, polyneuropathy or psychotropic drug use are progressively discussed [35]. Although incomplete data prevented more in-depth analyses, the role of drugs [36,37,38] cannot be ignored. Perez-Lloret et al. [38] calculated the odds ratios of 15.9 for antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, escitalopram, mianserine, mirtazapine, duloxetine), 17.8 for neuroleptics (e.g., thioridazine, loxapine, risperidone, aripiprazole) and 18.2 for pain relievers (e.g., tramadol) towards RLS. Our convenience sample prevents us from more firm conclusions regarding these aspects, but as shown by the sensitivity analyses, their presence or absence did not affect our outcomes.
Our first approach was, given the customarily used clinical cut-offs, investigating group differences. The results indicated that the clinically significant presence of PLMS or AHI is insufficient to triage. Herein we may question the sensitivity and specificity of the applied clinical cut-offs as well as our scoring method. Prospective data collection in a larger sample may address these questions more appropriately. Nonetheless, 37.2% of our sample showed clinically significant PLMS ≥ 15 and 76.5% exhibited an AHI ≥ 5. Upon comparing the four clinical groups, several findings can be summarized. Firstly, in the absence of clinically significant AHI and PLMS, about 17.6% of the psychiatric patients uttered sleep-related complaints led to a physician-based diagnosis of RLS. Secondly, in our sample, solely the sleep structure of patients with the presence of SDB (per AHI ≥ 5 cut-off) or PLMS was comparable. Similarly, and thirdly, the presence of PLMS alone compared to the co-occurring condition did not alter sleep structure. Yet, and lastly, significantly higher PLMS indices, PLMS numbers, series in TST and N1 and more micro-arousals were found in the co-occurring condition of SDB than in the case of SDB alone. This confirms the finding by Romero-Peralta et al. [39] that the presence of SDB can increase the severity of RLS. Notwithstanding the limitations of our study, our findings highlight the importance of treating SDB or implementing a continued follow-up of CPAP treatment and efficacy.
Next, we performed a cluster analysis on the polysomnographic data collected in these physician-based cases of RLS, incorporating their diagnosis and, when available, their somatic condition. Two distinct clusters were found. In finding the optimal cluster solution, the AHI had no significant contribution. The remaining sleep parameters significantly differ across clinical groups and defining the two clusters were: the PLMS index and number, the PLMS micro-arousal index and the PLMS series in TST and N1. In contrast to Xu et al. [4], in our psychiatric sample, we did not find sleep structure perturbations (e.g., SEI) apart from the PLMS-related parameters.
Cluster 1 predominantly consists of affective disorder (mostly recurrent major depression) patients with RLS (and most somatic conditions, albeit not significantly). Given that more than half of them have clinically significant PLMS and most have SDB, our findings are concurring with others [11,13]. This shared presentation of mood, RLS and SDB will certainly adversely impact the quality of life of the patients. Further studies are needed to elucidate their individual contribution to a poor health-related quality of life [32,40]. Although their association might be complex, their high prevalence rate independently warrants improved clinical awareness and personalized care, particularly in the case of associated psychotic features. Cluster 2 principally represented patients with present, but not predominant, mood symptomatology as well as mixed disorders with personality problems. That is, chiefly representing patients in which neither type of affective symptom is present to the extent that it justifies a diagnosis if considered separately. Fewer patients with clinically significant PLMS (≥ 15; 3.03%) belong to this cluster. The symptomatology of movement may have a diverse etiology such as mitochondrial disease, [41] corticobasal degeneration [42] or underlying RBD [43]. Several of the sleep recordings in our study were excluded due to, for instance, frequent wandering of the patient during nighttime or a request to end the recording, and therefore no usable sleep recording was obtained. Alternatively, drug-induced extrapyramidal signs have been commonly reported as well [44]. Thus, more sleep studies comprising RLS queries are needed in clinical practice to prevent restless movements, such as extrapyramidal motor disturbances, pharmacologically-induced motor disturbances or RLS, from being underestimated or misinterpreted. In general, in our sample, the normalized means of the significant sleep parameters suggest severe (Cluster 1) and minor (Cluster 2) PLMS with associated SDB.
5. Limitations
The study did have some limitations. Patients were a heterogeneous set with unspecified personality disorders and other mixed disorders/symptomatology (see Supplementary Materials Table S3). No clinical score assessing the severity of the depressive or psychotic symptoms with standardized clinical scales were available in the database, leaving aside the question whether the severity of psychiatric symptoms would correlate with the severity of RLS symptoms. However, medication use can be looked upon as a surrogate measure of severity with those on medication having the more severe psychiatric symptoms. As aforementioned, the sensitivity analysis, taking known medication use into account, did not reveal a significant impact upon our major outcomes of interest. Prospective RLS studies may examine in more detail the psychiatric condition, comorbidities and treatments. Ours was a retrospective analysis of an available clinical dataset. The only inclusion criterion applied was the instance of newly diagnosed RLS. Consequently, the psychiatric diagnosis and other aspects were allowed to be heterogeneous because we did not aim for inferential analysis but contrarily had a descriptive purpose. That is, despite the limitations, our study seems to suggest that subgroups exist warranting clinical questioning of RLS symptomatology, particularly in those with affective disorders such as recurrent major depression. This affective disorder supposition is further supported by the fact that in this small sample size, the two clusters described showed significant power.
The strength of this study is that we are the first applying an objective sleep study in a psychiatric sample with newly diagnosed RLS. Subsequently, we investigated clinically defined groups. Next, we applied a datamining approach showing that in the group with patients mostly having a single mood disorder, the PLM were higher. Future studies may consider assessing the severity of anxiety and depression, as well as the impact of antidepressants such as SSRIs [45].
6. Conclusions
This convenience sample concurs that comorbidity in Restless Legs Syndrome might be widespread, and that there is a potential risk of under-recognition if the symptoms of Restless Legs Syndrome are not specifically queried. For example, the sensorimotor discomfort and experienced urge to move might not be clearly reported by the patient. Despite these communicative obstacles, and in the absence of an objective parameter of Restless Legs Syndrome severity, the polysomnography findings show that psychiatric patients with various psychopathological features have a higher number of Periodic Limb Movements in Sleep, especially in association with Sleep Disordered Breathing.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/psychiatryint2030019/s1, Figure S1: Flowchart of patients included in our study, Table S1: Overnight PSG’s compared (n = 43): sleep movement parameters. Figure S2: Distance from the individual cluster centroid, plotted against the PLMS and AHI. Table S1: Overnight PSG’s compared (n = 43): sleep movement parameters. Table S2: Standard sleep study parameters of the clusters. Table S3: Overview of the samples investigated.
Author Contributions
K.S. conceptualized and executed the analyses as well as wrote the first draft and therefore shares first authorship with A.S.W. A.S.W. further edited the final manuscript. The data was discussed and the paper was proofread/edited by J.B., S.C. and M.-F.S.-C. Data pertain to Centre Hospitalier Le Vinatier Sleep Unit (S.C.). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Centre Hospitalier Le Vinatier (IRB-MR004 approved in 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Patients received an individual information document explaining the retrospective analysis of their data and were provided an opposition form to using their data for research purposes. Returning this form precluded using their data per French law (Délibération n° 2018-155 du 3 mai 2018 CNIL.fr). The study was registered on a national public registry database—MR-411-422-019 (www.indsante.fr).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Centre Hospitalier Le Vinatier for providing access to their data and supporting this research endeavor. A special thank you for Reviewer #5.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. A.S.W. has received funding from the USA National Institutes of Health (NIH) as well as funding from Arbor/Xenoport and Mundipharma for studies on Restless Legs Syndrome.
Abbreviations
ADHD: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; AHI: Apnea–Hypopnea Index; CPAP: continuous positive airway pressure; DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; IRLSSG: International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group; OSA: obstructive sleep apnea; PLMD: periodic leg movement disorder; PLMS: Periodic Limb Movements in Sleep; PSG: polysomnography; RBD: rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder; REM: rapid eye movement sleep; RLS: Restless Legs Syndrome; SEI: Sleep Efficiency Index; SDB: sleep disordered breathing disorder; WASO: Wake After Sleep Onset.
References
- Allen, R.P.; Walters, A.S.; Montplaisir, J.; Hening, W.; Myers, A.; Bell, T.J.; Ferini-Strambi, L. Restless legs syndrome prevalence and impact: REST general population study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.P.; Picchietti, D.L.; Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Ondo, W.G.; Walters, A.S.; Winkelman, J.W.; Zucconi, M.; Ferri, R.; Trenkwalder, C.; Lee, H.B. Restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: Updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria—history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.Z.; Jia, C.X. Insomnia and psychopathological features associated with restless legs syndrome in chinese adolescents. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2018, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Deng, Q.; Qin, Q.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Basta, M.; Xie, C.; Li, Y. Sleep disorders in Wilson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montplaisir, J.; Boucher, S.; Poirier, G.; Lavigne, G.; Lapierre, O.; Lesperance, P. Clinical, polysomnographic, and genetic characteristics of restless legs syndrome: A study of 133 patients diagnosed with new standard criteria. Mov. Disord. 1997, 12, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.G.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, S.W.; Cho, S.N.; Han, C.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; Joe, S.H.; Jung, I.K.; et al. Characteristics and clinical correlates of restless legs syndrome in schizophrenia. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, C.H.; Kang, S.G.; Yoon, H.K.; Park, Y.M.; Moon, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Song, H.M.; Kim, L. Association between restless legs syndrome and CLOCK and NPAS2 gene polymorphisms in schizophrenia. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchietti, D.L.; England, S.J.; Walters, A.S.; Willis, K.; Verrico, T. Periodic limb movement disorder and restless legs syndrome in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Child Neurol. 1998, 13, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.J.; Ball, W.A.; Dinges, D.F.; Kribbs, N.B.; Morrison, A.R.; Silver, S.M.; Mulvaney, F.D. Motor dysfunction during sleep in posttraumatic stress disorder. Sleep 1994, 17, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Germain, A.; Nielsen, T.A. Sleep pathophysiology in posttraumatic stress disorder and idiopathic nightmare sufferers. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Yen, T.T.; Chiu, N.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Hsu, W.Y.; Chang, Y.J.; Chang, T.G. Depression is differently associated with sleep measurement in obstructive sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 273, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, R.; Fisher, B.; Couvadelli, B.V.; Moss, N.M.; Walters, A.S. Preliminary study of the prevalence of restless legs syndrome in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2009, 108, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.B.; Hening, W.A.; Allen, R.P.; Kalaydjian, A.E.; Earley, C.J.; Eaton, W.W.; Lyketsos, C.G. Restless legs syndrome is associated with DSM-IV major depressive disorder and panic disorder in the community. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 20, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, S.; Na, M.; Winkelman, J.W.; Ba, D.; Liu, C.F.; Liu, G.; Gao, X. Association of restless legs syndrome with risk of suicide and self-harm. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e199966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubí, G.P. Restless legs syndrome from the perspective of psychiatry. Rev. Med. Chile 2018, 146, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, S.; Winkelman, J.W. Restless legs syndrome and psychiatric disorders. Sleep Med. Clin. 2015, 10, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flick, U. Introducing Research Methodology: A Beginner’s Guide to Doing a Research Project, 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Vecchierini, M.F.; Schröder, C.; Charley Monaca, C. French Consensus: How to diagnose restless legs syndrome. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 174, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, C. American Academy of Sleep. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, R.; Fulda, S.; Allen, R.P.; Zucconi, M.; Bruni, O.; Chokroverty, S.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Frauscher, B.; Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Hirshkowitz, M.; et al. World Association of Sleep Medicine (WASM) 2016 standards for recording and scoring leg movements in polysomnograms developed by a joint task force from the International and the European Restless Legs Syndrome Study Groups (IRLSSG and EURLSSG). Sleep Med. 2016, 26, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. Deliberations of the sleep apnea definitions task force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sateia, M.J. International classification of sleep disorders: Highlights and modifications. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.E.; Harding, S.M.; Marcus, C.L.; Vaughn, B.V. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, R.; Rundo, F.; Zucconi, M.; Manconi, M.; Aricò, D.; Bruni, O.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Fulda, S. Putting the periodicity back into the periodic leg movement index: An alternative data-driven algorithm for the computation of this index during sleep and wakefulness. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, C.; Meila, M.; Murtagh, F.; Rocci, R. Handbook of Cluster Analysis, 1st ed.; Henning, C., Meila, M., Murtagh, F., Rocci, R., Eds.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hornyak, M.; Feige, B.; Voderholzer, U.; Philipsen, A.; Riemann, D. Polysomnography findings in patients with restless legs syndrome and in healthy controls: A comparative observational study. Sleep 2007, 30, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aksu, M.; Demirci, S.; Bara-Jimenez, W. Correlation between putative indicators of primary restless legs syndrome severity. Sleep Med. 2007, 8, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Larrosa, O.; de la Llave, Y.; Granizo, J.J.; Allen, R. Correlation between rating scales and sleep laboratory measurements in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2004, 5, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.A.-O.; Baron, D.; Bartnik-Olson, B.; Caeyenberghs, K.; Esopenko, C.; Hillary, F.G.; Kenney, K.; Koerte, I.A.-O.; Lin, A.P.; Mayer, A.A.-O.; et al. ENIGMA brain injury: Framework, challenges, and opportunities. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoller, J.W.; Andreassen, O.A.; Edenberg, H.J.; Faraone, S.V.; Glatt, S.J.; Kendler, K.S. Psychiatric genetics and the structure of psychopathology. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpy, M.J. Classification of sleep disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2012, 9, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelmann, J.; Prager, M.; Lieb, R.; Pfister, H.; Spiegel, B.; Wittchen, H.U.; Holsboer, F.; Trenkwalder, C.; Ströhle, A. Anxietas tibiarum. Depression and anxiety disorders in patients with restless legs syndrome. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, O.; Şengül, Y.; Şengül, H.S.; Parlakkaya, F.B.; Öztürk, A. Investigation of alexithymia and levels of anxiety and depression among patients with restless legs syndrome. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angriman, M.; Cortese, S.; Bruni, O. Somatic and neuropsychiatric comorbidities in pediatric restless legs syndrome: A systematic review of the literature. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 34, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japaridze, G.; Kasradze, S.; Maisuradze, L.; Popp, R.; Wetter, T. The Restless legs syndrome. Georgian Med. News 2018, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Cuellar, N.G. The psychopharmacological management of RLS in psychiatric conditions: A review of the literature. J. Am. Psychiatr. Nurses Assoc. 2012, 18, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patatanian, E.; Claborn, M.K. Drug-induced restless legs syndrome. Ann. Pharmacother. 2018, 52, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lloret, S.; Rey, M.V.; Bondon-Guitton, E.; Rascol, O.; Montastruc, A.J. Drugs associated with restless legs syndrome: A case/noncase study in the French Pharmacovigilance Database. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 32, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Peralta, S.; Cano-Pumarega, I.; Garcia-Malo, C.; Agudelo Ramos, L.; Garcia-Borreguero, D. Treating restless legs syndrome in the context of sleep disordered breathing comorbidity. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, C.A.; Allen, R.P.; Atkinson, M.J. Modeling the causal relationships between symptoms associated with restless legs syndrome and the patient-reported impact of RLS. Sleep Med. 2004, 5, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martikainen, M.H.; Ng, Y.S.; Gorman, G.S.; Alston, C.L.; Blakely, E.L.; Schaefer, A.M.; Chinnery, P.F.; Burn, D.J.; Taylor, R.W.; McFarland, R.; et al. Clinical, genetic, and radiological features of extrapyramidal movement disorders in mitochondrial disease. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roche, S.; Jacquesson, J.M.; Destee, A.; Defebvre, L.; Derambure, P.; Monaca, C. Sleep and vigilance in corticobasal degeneration: A descriptive study. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2007, 37, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, G.; Belgrado, E.; Marinig, R.; Bergonzi, P. Sleep disorders and extrapyramidal diseases: An historical review. Sleep Med. 2004, 5, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Pérez, J.M.; Marsal-Alonso, C. Drug-induced movement disorders. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 48, S57–S60. [Google Scholar]
- Hutka, P.; Krivosova, M.; Muchova, Z.; Tonhajzerova, I.; Hamrakova, A.; Mlyncekova, Z.; Mokry, J.; Ondrejka, I. Association of sleep architecture and physiology with depressive disorder and antidepressants treatment. Inter. J. Molecular Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).