Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis—An Update on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Drug Resistance
Abstract
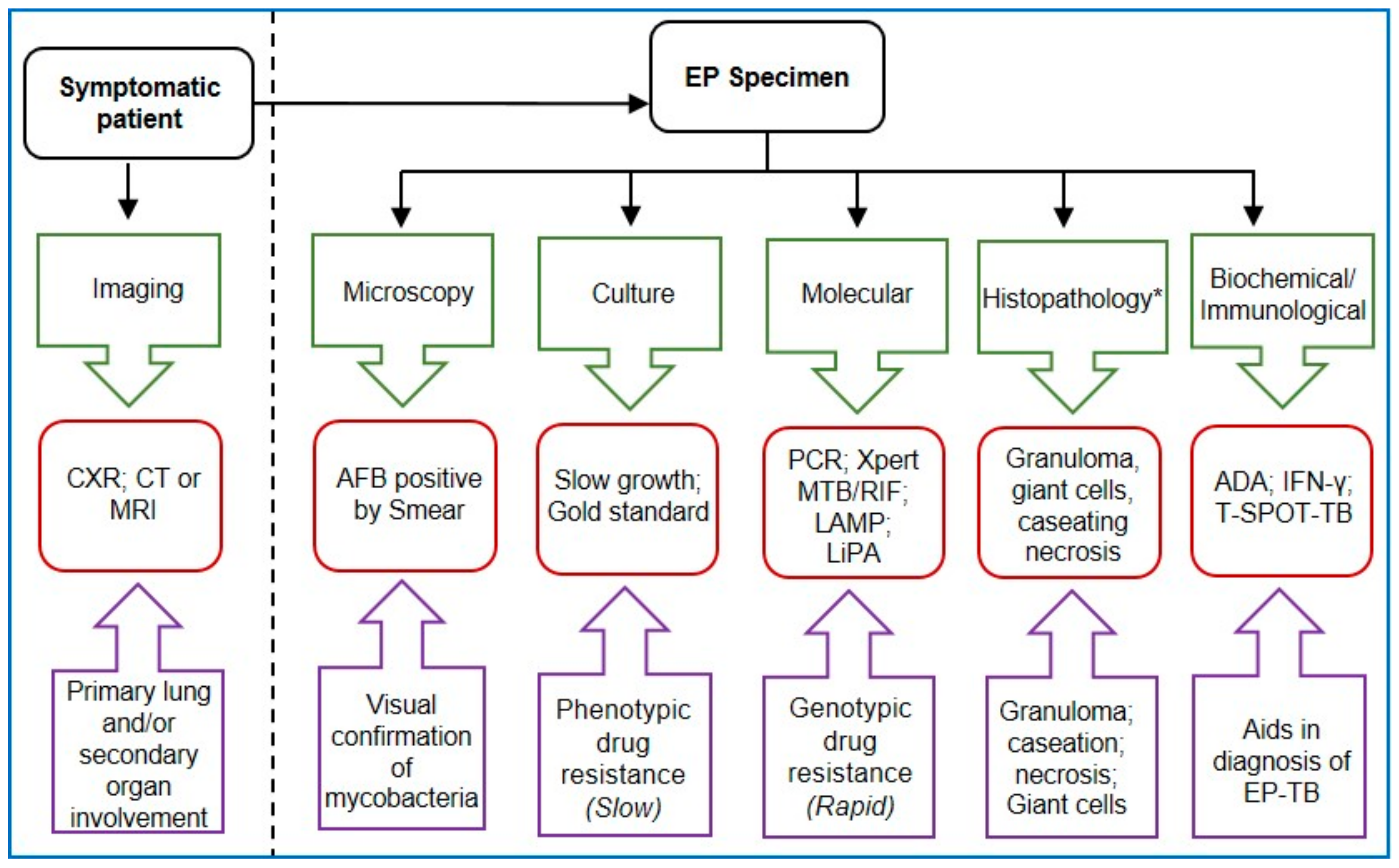
1. Introduction
2. Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis of the Head and Neck
2.1. Tuberculous Meningitis
2.2. Tuberculous Lymphadenitis
2.3. Ocular Tuberculosis
2.4. Oral Tuberculosis
3. Extrapulmonary TB of the Thorax
3.1. Pleural Tuberculosis
3.2. Tuberculous Pericarditis
4. Extrapulmonary TB of Skin, Bone and Muscle
4.1. Cutaneous Tuberculosis
4.2. Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis
5. Tuberculosis of the Abdomen and Genitourinary System
5.1. Abdominal Tuberculosis
5.2. Genitourinary Tuberculosis
6. Miliary Tuberculosis
7. Rising Trend of Drug-Resistant Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
8. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131 (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Golden, M.P.; Vikram, H.R. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis: An overview. Am. Fam. Phys. 2005, 72, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mohan, A.; Kohli, M. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalaswamy, R.; Shanmugam, S.; Mondal, R.; Subbian, S. Of tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections - a comparative analysis of epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechai, F.; Bouchaud, O. Tuberculous meningitis: Challenges in diagnosis and management. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, R.J.; Rohlwink, U.; Misra, U.K.; van Crevel, R.; Mai, N.T.H.; Dooley, K.E.; Caws, M.; Figaji, A.; Savic, R.; Solomons, R.; et al. Tuberculous meningitis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, J.M. Central Nervous System Tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.K. Tuberculosis of the central nervous system. Postgrad. Med. J. 1999, 75, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, R.B.; Olin, M.; Baker, C.A.; Molitor, T.W.; Peterson, P.K. Central nervous system tuberculosis: Pathogenesis and clinical aspects. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.S.; Zhao, M.; Liu, X.J. Risk factors for poor outcome in childhood tuberculous meningitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekermans, P.; Duse, A.; George, J. The dubious value of cerebrospinal fluid adenosine deaminase measurement for the diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pormohammad, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Nasiri, M.J.; Fallah, F.; Aghazadeh, M.; Doustdar, F.; Pouriran, R. Diagnostic test accuracy of adenosine deaminase for tuberculous meningitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2017, 74, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Chen, C.; Yu, S.; Chen, S. Diagnosis of Tuberculous Meningitis Using a Combination of Peripheral Blood T-SPOT.TB and Cerebrospinal Fluid Interferon-gamma Detection Methods. Lab. Med. 2016, 47, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xue, Y.; Guo, X.; Lin, Q.; Mao, L.; Tang, G.; Song, H.; Wang, F.; Sun, Z. Diagnostic Accuracy of T-SPOT.TB Assay for Tuberculous Meningitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, R.K. Microbiological diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis: Phenotype to genotype. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 150, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.K.; Malhotra, H.S.; Jain, A. Neuroimaging in tuberculous meningitis. Neurol. India 2016, 64, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei Taheri, M.; Karimi, M.A.; Haghighatkhah, H.; Pourghorban, R.; Samadian, M.; Delavar Kasmaei, H. Central nervous system tuberculosis: An imaging-focused review of a reemerging disease. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 202806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berwal, A.; Chawla, K.; Vishwanath, S.; Shenoy, V.P. Role of multiplex polymerase chain reaction in diagnosing tubercular meningitis. J. Lab. Phys. 2017, 9, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhong, F.; Ye, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, G. Diagnostic accuracy of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis Module 3: Diagnosis—Rapid Diagnostics for Tuberculosis Detection. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-consolidated-guidelines-on-tuberculosis-module-3-diagnosis---rapid-diagnostics-for-tuberculosis-detection (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Duo, L.; Ying, B.; Song, X.; Lu, X.; Ye, Y.; Fan, H.; Xin, J.; Wang, L. Molecular profile of drug resistance in tuberculous meningitis from southwest china. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Thakur, R.; Gupta, P.; Jalan, N.; Kushwaha, S.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, P.; Aggarwal, A.; Manchanda, V. Evaluation of Geno Type MTBDRplus Line Probe Assay for Early Detection of Drug Resistance in Tuberculous Meningitis Patients in India. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2015, 7, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, S.; Singh, S.; Chalise, S.R. Cytopathological patterns of tuberculous lymphadenitis: An analysis of 126 cases in a tertiary care hospital. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 1898–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, C.; Liang, B.; Tang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Tao, C.; He, J.Q. Performance of interferon-gamma release assay in the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis: A meta-analysis. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.; Abebe, G.; Abdissa, K.; Bekele, A.; Bezabih, M.; Apers, L.; Colebunders, R.; Rigouts, L. Concentration of lymph node aspirate improves the sensitivity of acid fast smear microscopy for the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis in Jimma, southwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derese, Y.; Hailu, E.; Assefa, T.; Bekele, Y.; Mihret, A.; Aseffa, A.; Hussien, J.; Ali, I.; Abebe, M. Comparison of PCR with standard culture of fine needle aspiration samples in the diagnosis of tuberculosis lymphadenitis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2012, 6, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurt, S.; Kucukergin, C.; Yigitbas, B.A.; Seckin, S.; Tigin, H.C.; Kosar, A.F. Diagnostic utility of serum and pleural levels of adenosine deaminase 1-2, and interferon-gamma in the diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2014, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Yan, F.; Xue, Y.; Mao, L.; Lin, Q.; Tang, G.; Song, H.; Wu, S.; Ouyang, R.; Yuan, X.; et al. Diagnostic utility of pleural fluid T-SPOT and interferon-gamma for tuberculous pleurisy: A two-center prospective cohort study in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajman, A.; Kaisermann, C.; Luiz, R.R.; Sperhacke, R.D.; Rossetti, M.L.; Feres Saad, M.H.; Sardella, I.G.; Spector, N.; Kritski, A.L. Pleural fluid ADA, IgA-ELISA and PCR sensitivities for the diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2007, 67, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Singh, N.; Gupta, K.B.; Chaudhary, D.; Yadav, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Agarwal, K.; Varma-Basil, M.; Prasad, R.; Khuller, G.K.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of Several Gene Targets for Designing a Multiplex-PCR for an Early Diagnosis of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, E.; Sarkarati, M.; Spellberg, B. Adenosine Deaminase Diagnostic Testing in Pericardial Fluid. JAMA 2019, 322, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Ock, H.S.; Kang, L.H.; Byun, K.S.; Jeon, D.S.; Kim, S.J. Diagnostic performance of interferon-gamma release assay for diagnosis of tuberculous pericarditis: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegielski, J.P.; Devlin, B.H.; Morris, A.J.; Kitinya, J.N.; Pulipaka, U.P.; Lema, L.E.; Lwakatare, J.; Reller, L.B. Comparison of PCR, culture, and histopathology for diagnosis of tuberculous pericarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3254–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Xing, B.; Wang, W.; Yang, P.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shang, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, N.; Yang, L.; et al. Diagnostic values of Xpert MTB/RIF, T-SPOT.TB and adenosine deaminase for HIV-negative tuberculous pericarditis in a high burden setting: A prospective observational study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.B.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Ferraz, C.E.; Oliveira, M.H.; Silva, P.G.; Medeiros, V.L. Cutaneous tuberculosis: Diagnosis, histopathology and treatment—Part II. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2014, 89, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Singh, E.N.; Agarwal, U.S.; Meena, R.; Purohit, S.; Kumar, S. The role of DNA polymerase chain reaction, culture and histopathology in the diagnosis of cutaneous tuberculosis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2017, 56, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, C.; Rana, T.; Singh, U.B.; Singh, M.; Ramesh, V.; Sharma, V.K.; Ramam, M. mRNA and DNA PCR tests in cutaneous tuberculosis. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2013, 79, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foocharoen, C.; Sarntipipattana, C.; Foocharoen, T.; Mahakkanukrauh, A.; Paupairoj, A.; Teerajetgul, Y.; Nanagara, R. Synovial fluid adenosine deaminase activity to diagnose tuberculous septic arthritis. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2011, 42, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.H.; Bian, S.N.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.F.; Shi, X.C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, F.C.; Liu, X.Q. Diagnostic Value of T-cell Interferon-gamma Release Assays on Synovial Fluid for Articular Tuberculosis: A Pilot Study. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.S.; Lou, S.Q.; Wen, J.M.; Lv, W.X.; Jiao, C.G.; Yang, S.M.; Xu, H.B. Clinical value of polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of joint tuberculosis by detecting the DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Orthop. Surg. 2011, 3, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xue, Y.; Mao, L.; Lin, Q.; Tang, G.; Song, H.; Wang, F.; Sun, Z. Diagnostic Value of T-SPOT.TB Assay for Tuberculous Peritonitis: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 585180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallur, V.; Sharma, M.; Sethi, S.; Sharma, K.; Mewara, A.; Dhatwalia, S.; Yadav, R.; Bhasin, D.; Sinha, S.K.; Rana, S.; et al. Development and evaluation of multiplex PCR in rapid diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, P.; Dorman, S.E.; Alipanah, N.; Barry, P.M.; Brozek, J.L.; Cattamanchi, A.; Chaisson, L.H.; Chaisson, R.E.; Daley, C.L.; Grzemska, M.; et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines: Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e147–e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahid, P.; Mase, S.R.; Migliori, G.B.; Sotgiu, G.; Bothamley, G.H.; Brozek, J.L.; Cattamanchi, A.; Cegielski, J.P.; Chen, L.; Daley, C.L.; et al. Treatment of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. An Official ATS/CDC/ERS/IDSA Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e93–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guidelines for Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis and Patient Care (2017 Update). Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/2017/dstb_guidance_2017/en/ (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- WHO. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240007048 (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Murthy, J.M.K. Tuberculous Meningitis—Adjunctive Therapy: Corticosteroids, Aspirin, or Both. Neurol. India 2019, 67, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Singh, M.B.; Ryan, H. Corticosteroids for managing tuberculous meningitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 4, CD002244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thwaites, G.E. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhare, A.; Mahashur, A. Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes: Many facets, many hues. Astrocytes 2017, 4, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, H.; Agrawal, S.K.; Verma, S.K.; Singh, U.B. Cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis: Clinical profile and diagnostic modalities. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2018, 7, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, Y.A.; Bayazit, N.; Namiduru, M. Mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2004, 66, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, U.; Mundi, I.; Mohan, S. Nodal tuberculosis revisited: A review. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2012, 6, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Shamim, S.H.; Wahab, S.; Javed, A. Yield and Safety Profile of Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) of Lymph Nodes. J. Coll. Phys. Surg. Pak. 2016, 26, 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Sellami, M.; Charfi, S.; Chaabouni, M.A.; Mrabet, S.; Charfeddine, I.; Ayadi, L.; Kallel, S.; Ghorbel, A. Fine needle non-aspiration cytology for the diagnosis of cervical lymph node tuberculosis: A single center experience. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 85, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, B.C.; Dass, A.; Nagarkar, N.M.; Gupta, R.; Singhal, S. Cervical tuberculous lymphadenopathy: Changing clinical pattern and concepts in management. Postgrad. Med. J. 2001, 77, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Som, P.; Curtin, H. Head and Neck Imaging—2 Volume Set, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Y.; Kim, C.; Park, Y.B.; Mo, E.K.; Moon, J.W.; Park, S.; Sim, Y.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Baek, M.S. Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes of Definitive Versus Standard Anti-Tuberculosis Therapy in Patients with Tuberculous Lymphadenitis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, H.; Jeon, J.H.; Oh, K.H.; Choi, H.K.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Seo, H.S.; Kwon, S.Y.; Park, D.W. Characteristics of residual lymph nodes after six months of antituberculous therapy in HIV-negative individuals with cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loenhout-Rooyackers, J.H.; Laheij, R.J.; Richter, C.; Verbeek, A.L. Shortening the duration of treatment for cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, D.M.; Raven, M.L. Ocular Tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzler, B.K.; Gupta, V.; Agrawal, R. Clinics of ocular tuberculosis: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 49, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Shoughy, S.S.; Mahajan, S.; Khairallah, M.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Curi, A.; Tabbara, K.F. Clinics of ocular tuberculosis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2015, 23, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouammoh, M.; Abu El-Asrar, A.M. Imaging in the diagnosis and management of ocular tuberculosis. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2012, 52, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Mahajan, S.; Khairallah, M.; Mahendradas, P.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, V. Multimodal Imaging in Ocular Tuberculosis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2017, 25, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, N.; Onder, F.; Demir, N.; Altuntas Aydin, O. Primary Conjunctival Tuberculosis. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 48, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroblewski, K.J.; Hidayat, A.A.; Neafie, R.C.; Rao, N.A.; Zapor, M. Ocular tuberculosis: A clinicopathologic and molecular study. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Gupta, V.; Bansal, R.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, M.; Gupta, A. Novel multi-targeted polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of presumed tubercular uveitis. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2013, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balne, P.K.; Barik, M.R.; Sharma, S.; Basu, S. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay targeting the mpb64 gene for diagnosis of intraocular tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3839–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, A.; Singh, R.; Aggarwal, K.; Bansal, R.; Thakur, A.; Prakash, S.; Gupta, V. MTBDRplus for the rapid diagnosis of ocular tuberculosis and screening of drug resistance. Eye 2018, 32, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Gupta, V.; Sharma, A.; Singh, R.; Sharma, M.; Aggarwal, K.; Bansal, R.; Fiorella, P.D.; Prakash, S.; Gupta, A. Gene Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of intra-ocular tuberculosis from vitreous fluid samples. Tuberculosis 2017, 102, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anibarro, L.; Cortes, E.; Chouza, A.; Parafita-Fernandez, A.; Garcia, J.C.; Pena, A.; Fernandez-Cid, C.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, A. Early treatment of tuberculous uveitis improves visual outcome: A 10-year cohort study. Infection 2018, 46, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueira, L.; Fonseca, S.; Ladeira, I.; Duarte, R. Ocular tuberculosis: Position paper on diagnosis and treatment management. Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2017, 23, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, J.L.; Jain, P.; Arora, R.; Dokania, P. Ocular manifestations of tuberculosis. Indian J. Tuberc. 2015, 62, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, A.R.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.J.; Al-Hity, A.; Gupta, B.; Lee, C.S.; Gunasekeran, D.V.; Jayabalan, N.; Grant, R.; Kon, O.M.; Gupta, V.; et al. Anti-tubercular therapy for intraocular tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2016, 61, 628–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakarchi, F.I. Ocular tuberculosis: Current perspectives. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 9, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, S.K.; Abraham, S.; Sudharshan, S. Paradoxical reactions in ocular tuberculosis. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, S.R.; Lalitha, P. Paradoxical worsening of ocular tuberculosis in HIV patients after antiretroviral therapy. Eye 2007, 21, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gupta, G.; Khattak, B.P.; Agrawal, V. Primary gingival tuberculosis: A rare clinical entity. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2011, 2, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, H.; Correa, M.F.; Castillo-Castillo, S.; Nikitakis, N.G. Primary oral tuberculosis: A report of a case diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction. Oral Dis. 2003, 9, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, S.; Bhandari, V.; Kaur Lamba, A.; Faraz, F.; Makker, K.; Aggarwal, K. Literature review of oral tuberculosis and report of a case with unique histological presentation. Indian J. Tuberc. 2020, 67, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Mohan, R.P.; Singh, U.; Agarwal, N. Primary oral tuberculosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, H.L.; Lu, S.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Chen, W.J. Oral tuberculosis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1996, 81, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokotronis, A.; Antoniadis, D.; Trigonidis, G.; Papanagiotou, P. Oral tuberculosis. Oral Dis. 1996, 2, 242–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansare, K.; Gupta, A.; Khanna, V.; Karjodkar, F. Oral tuberculosis: Unusual radiographic findings. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2011, 40, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Sun, A.; Chiang, C.P. Oral tuberculosis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2017, 116, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Jain, I. Oral Manifestations of Tuberculosis: Step towards Early Diagnosis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, ZE18–ZE21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawiecka, E.; Szponar, E. Tuberculosis of the oral cavity: An uncommon but still a live issue. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2015, 32, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bajpai, J.; Pathak, P.K.; Pradhan, A.; Singh, P.; Kant, S. Oral tuberculosis—Current concepts. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, S.K.; Pandit, S.; Basuthakur, S. Tonsillar tuberculosis: A forgotten clinical entity. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2015, 4, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Serhani, A.M.; Al-Mazrou, K. Pharyngeal tuberculosis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2001, 22, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokavarapu, S.; Panta, P. Oral lesions in Tuberculosis. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2015, 22, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Sharma, S.; Diwaker, P. Diagnostic role and limitations of FNAC in oral and jaw swellings. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Garg, N.; Gupta, S.; Marwah, N.; Kalra, R.; Singh, V.; Sen, R. Fine needle aspiration cytology in lesions of oral and maxillofacial region: Diagnostic pitfalls. J. Cytol. 2011, 28, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, J.; Ishihara, K.; Watanabe, A.; Fukumoto, Y.; Okuda, K. PCR method is essential for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis in oral cavity samples. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 18, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, B.; Davies, P.D. Pleural tuberculosis. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2006, 65, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Wong, K.S. Clinical spectrum of tuberculous pleural effusion in children. Pediatr. Int. 2007, 49, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.B.; Andrade, C.F.; Lima, J.B. Pleural tuberculosis in children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2011, 12, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.A.; Diacon, A.H.; Koegelenberg, C.F.N. Tuberculous pleural effusion. Respirology 2019, 24, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, M.B.; Loivos, A.C.; Rezende, V.M.; Soares, S.L.; Mello, F.C.; Reingold, A.L.; Daley, C.L.; Kritski, A.L. Yield of sputum induction in the diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorster, M.J.; Allwood, B.W.; Diacon, A.H.; Koegelenberg, C.F. Tuberculous pleural effusions: Advances and controversies. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Rogers, J.T.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Miller, K.D.; Light, R.W. Adenosine deaminase levels in nontuberculous lymphocytic pleural effusions. Chest 2001, 120, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Q.; Pan, L.; Duan, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, C.; Sun, Q.; Jia, H.; et al. Use of T-SPOT.TB for the diagnosis of unconventional pleural tuberculosis is superior to ADA in high prevalence areas: A prospective analysis of 601 cases. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beukes, A.; Shaw, J.A.; Diacon, A.H.; Irusen, E.M.; Koegelenberg, C.F.N. The Utility of Pleural Fluid Lactate Dehydrogenase to Adenosine Deaminase Ratio in Pleural Tuberculosis. Respiration 2021, 100, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, K.; Lu, Y.; Shi, H.Z. Tuberculous pleural effusion. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E486–E494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Idrees, F.; Jabeen, K.; Zubairi, A.B.S.; Butt, S.; Hasan, R. Accuracy of genotype MTBDRplus line probe assay in patients with tuberculous pleural effusion: Comparison with clinical and culture based diagnosis. Infect. Dis. 2020, 52, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.J. The use of adjunctive corticosteroids in the treatment of pericardial, pleural and meningeal tuberculosis: Do they improve outcome? Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, H.; Yoo, J.; Darsini, P. Corticosteroids for tuberculous pleurisy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 3, CD001876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayosi, B.M.; Burgess, L.J.; Doubell, A.F. Tuberculous pericarditis. Circulation 2005, 112, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntsekhe, M.; Mayosi, B.M. Tuberculous pericarditis with and without HIV. Heart Fail. Rev. 2013, 18, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, G.; Ali, A.; Alpendurada, F.; Prasad, S.; Raphael, C.E.; Vassiliou, V. Tuberculous Constrictive Pericarditis. Res. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 4, e29614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiguzo, G.; Du Bruyn, E.; Howlett, P.; Ntsekhe, M. Diagnosis and Management of Tuberculous Pericarditis: What Is New? Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naicker, K.; Ntsekhe, M. Tuberculous pericardial disease: A focused update on diagnosis, therapy and prevention of complications. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, H.; Burgess, L.; van Vuuren, W.; Doubell, A. Diagnosing tuberculous pericarditis. QJM 2006, 99, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetrit, M.; Natalie Szpakowski, N.; Desai, M.Y. Multimodality imaging for the diagnosis and treatment of constrictive pericarditis. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2019, 17, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, E.T.; Shahid, M.; Watkin, R.W. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of pericardial disease. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2016, 6, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Kwon, D.H.; Klein, A.L. Imaging of the Pericardium: A Multimodality Cardiovascular Imaging Update. Cardiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Y.; Lu, P.X.; Assadi, M.; Huang, X.L.; Skrahin, A.; Rosenthal, A.; Gabrielian, A.; Tartakovsky, M.; Wang, Y.X.J. Updates on (18)F-FDG-PET/CT as a clinical tool for tuberculosis evaluation and therapeutic monitoring. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1132–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.O. Pericardial effusion and pericardiocentesis: Role of echocardiography. Korean Circ. J. 2012, 42, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebenberg, J.; van der Bijl, P. A “Vanishing”, Tuberculous, Pericardial Effusion. Korean Circ. J. 2016, 46, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakamudi, S.; Ho, N.; Cremer, P.C. Pericardial Effusions: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 59, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebenberg, J.J.; Dold, C.J.; Olivier, L.R. A prospective investigation into the effect of colchicine on tuberculous pericarditis. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2016, 27, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayosi, B.M.; Ntsekhe, M.; Bosch, J.; Pandie, S.; Jung, H.; Gumedze, F.; Pogue, J.; Thabane, L.; Smieja, M.; Francis, V.; et al. Prednisolone and Mycobacterium indicus pranii in tuberculous pericarditis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiysonge, C.S.; Ntsekhe, M.; Thabane, L.; Volmink, J.; Majombozi, D.; Gumedze, F.; Pandie, S.; Mayosi, B.M. Interventions for treating tuberculous pericarditis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 9, CD000526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, J.; Tager, P.; Ingleton, R.; Hirsch, R.J.; Weinberg, J.M. Cutaneous tuberculosis: Diagnosis and treatment. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charifa, A.; Mangat, R.; Oakley, A.M. Cutaneous Tuberculosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.K.; Sanders, C.V. Cutaneous Tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zyl, L.; du Plessis, J.; Viljoen, J. Cutaneous tuberculosis overview and current treatment regimens. Tuberculosis 2015, 95, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmalapudi, S.; Morey, A.D.; Madke, B.; Singh, A.L.; Jawade, S. A Rare Case of Tuberculosis Cutis Colliquative. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2021, 10, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabr, A.; Aloua, R.; Kerdoud, O.; Slimani, F. Scorfuloderma of cheek (a cutaneous tuberculosis colliquativa cutis): Case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 64, 102257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Singal, A.; Bhattacharya, S.N.; Mishra, K. Comparison of the radiometric BACTEC 460 TB culture system and Lowenstein-Jensen medium for the isolation of mycobacteria in cutaneous tuberculosis and their drug susceptibility pattern. Int. J. Dermatol. 2008, 47, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.W.; Ko, J.Y.; Park, C.K. Histopathological spectrum of cutaneous tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2012, 39, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawan, H.; Achdiat, P.A.; Hindritiani, R.; Essary, E.D.; Ningtias, L.D.; Siregar, E.P.; Sori, P.R.; Febrina, D. Various cutaneous tuberculosis with rare clinical manifestations: A case series. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2018, 7, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.K.; Blumberg, H.M. Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, B.; Lazarus, A.A. Musculoskeletal tuberculosis. Dis. Mon. 2007, 53, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, H.G.; Lifeso, R.M. Tuberculosis of bones and joints. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1996, 78, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Musbahi, O.; White, V.L.C.; Montgomery, A.S. Spinal Tuberculosis: A Literature Review. JBJS Rev. 2019, 7, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.N.; Ben Husien, M. Spinal tuberculosis: Review of current management. Bone Joint J. 2018, 100, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, K.; Sabharwal, S. Spinal tuberculosis: A comprehensive review for the modern spine surgeon. Spine J. 2019, 19, 1858–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K.; Kumar, J. Tuberculosis of spine: Neurological deficit. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S. Kyphotic deformity in spinal tuberculosis and its management. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Banta, A. The spectrum of tuberculosis of the spine in pediatric age group: A review. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayyad, M.J.; Abumunaser, L.A. Tuberculous arthritis revisited as a forgotten cause of monoarticular arthritis. Ann. Saudi Med. 2011, 31, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, W.; Abebe, B.; Molla, K.; Alemayehu, T. Tuberculous Dactylitis: An Uncommon Presentation of Skeletal Tuberculosis. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2016, 26, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, D.G.; Philips, K.B.; Corbett, C.E.; Bronze, M.S. Sternal osteomyelitis caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis: Case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2000, 319, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibaba, B.; Raj Gopinathan, N.; Santhanam, S.S.; Meena, U.K. Tubercular dactylitis in children. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2017, 26, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saifudheen, K.; Anoop, T.M.; Mini, P.N.; Ramachandran, M.; Jabbar, P.K.; Jayaprakash, R. Primary tubercular osteomyelitis of the sternum. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e164–e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, R.; Kang, H.S.; Dogra, S.; Saggar, R.R.; Sharma, R. Tuberculous osteomyelitis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1997, 79, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaovisidha, S.; Chen, C.; Ryu, K.N.; Siriwongpairat, P.; Pekanan, P.; Sartoris, D.J.; Resnick, D. Tuberculous tenosynovitis and bursitis: Imaging findings in 21 cases. Radiology 1996, 201, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.; Sarwar, S.U.; Haq, E.U.; Islam, M.Z.; Rizvi, T.A.; Ahmad, M.; Shah, K. Tuberculous tenosynovitis: A cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2006, 56, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.P.; Mohan, N.; Garg, R.K.; Bajpai, S.K.; Verma, S.K.; Mohindra, Y. Clinicosocial aspect of osteo-articular tuberculosis. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1990, 88, 307–309. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, P.T.; Horowitz, I. Skeletal tuberculosis. A review with patient presentations and discussion. Am. J. Med. 1970, 48, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Phan, K.; Karim, R.; Jonayed, S.A.; Munir, H.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Alam, T. Surgery for spinal tuberculosis: A multi-center experience of 582 cases. J. Spine Surg. 2015, 1, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbyshire, J. Five-year assessment of controlled trials of short-course chemotherapy regimens of 6, 9 or 18 months’ duration for spinal tuberculosis in patients ambulatory from the start or undergoing radical surgery. Fourteenth report of the Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. Int. Orthop. 1999, 23, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandwal, P.; Vijayaraghavan, G.; Jayaswal, A. Management of Tuberculous Infection of the Spine. Asian Spine J. 2016, 10, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Gannamani, V.; Shay, E.; Alcid, D. Spinal Tuberculosis and Cold Abscess without Known Primary Disease: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2016, 2016, 1780153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzunkoy, A.; Harma, M.; Harma, M. Diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis: Experience from 11 cases and review of the literature. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 3647–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.H.; Coyle, W.J. Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debi, U.; Ravisankar, V.; Prasad, K.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Sharma, A.K. Abdominal tuberculosis of the gastrointestinal tract: Revisited. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14831–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanai, F.M.; Bzeizi, K.I. Systematic review: Tuberculous peritonitis—Presenting features, diagnostic strategies and treatment. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, U.; Almusa, O.; Tung, K.W.; Heller, M.T. Tuberculous peritonitis. Radiol. Case Rep. 2014, 9, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladumor, H.; Al-Mohannadi, S.; Ameerudeen, F.S.; Ladumor, S.; Fadl, S. TB or not TB: A comprehensive review of imaging manifestations of abdominal tuberculosis and its mimics. Clin. Imaging 2021, 76, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Sheek-Hussein, M. Diagnosis of abdominal tuberculosis: Lessons learned over 30 years: Pectoral assay. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzosa, M.; Tsukayama, D.T.; Davies, S.F.; Debol, S.M.; Cen, Y.Y.; Li, R.; Mallery, S. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2010, 14, 578–584. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Guleria, S.; Agarwal, S. Role of endoscopic ultrasound guided FNAC in diagnosis of pancreatic TB presenting as mass lesion: A case report and review of literature. Indian J. Tuberc. 2011, 58, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, P.; Vayoth, S.O.; Dhar, P.; Surendran, S.; Ponnambathayil, S. Laparoscopy in suspected abdominal tuberculosis is useful as an early diagnostic method. ANZ J. Surg. 2008, 78, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukewar, S.; Mukewar, S.; Ravi, R.; Prasad, A.; Dua, K.S. Colon tuberculosis: Endoscopic features and prospective endoscopic follow-up after anti-tuberculosis treatment. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2012, 3, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riquelme, A.; Calvo, M.; Salech, F.; Valderrama, S.; Pattillo, A.; Arellano, M.; Arrese, M.; Soza, A.; Viviani, P.; Letelier, L.M. Value of adenosine deaminase (ADA) in ascitic fluid for the diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Intestinal tuberculosis: Clinico-pathological profile and the importance of a high degree of suspicion. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2019, 24, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, S.; Goel, M.M.; Tandon, P.; Natu, S.M.; Nath, P. Correlative study of histopathology and bacteriology in patients of tubercular lymphadenitis. Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 1994, 36, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinez Tirado, P.; Lopez De Hierro Ruiz, M.; Martinez Garcia, R.; Martinez Cara, J.G.; Martin Rodriguez, M.M.; Castilla Castellano, M.M. Intestinal tuberculosis. A diagnostic challenge. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 26, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Desai, D.; Abraham, P.; Rodrigues, C. Making a Positive Diagnosis of Intestinal Tuberculosis with the Aid of New Biologic and Histologic Features: How Far Have We Reached? Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2019, 3, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.C.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Fei, G.J. Clinical and Laboratory Diagnosis of Intestinal Tuberculosis. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Das, S.K.; Bairagya, T.D. Presenting experience of managing abdominal tuberculosis at a tertiary care hospital in India. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2011, 3, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weledji, E.P.; Pokam, B.T. Abdominal tuberculosis: Is there a role for surgery? World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2017, 9, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbara, A.; Davidson, R.N. Etiology and management of genitourinary tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2011, 8, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, A.A.; Lucon, A.M.; Srougi, M. Urogenital Tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.K.; Budh, D.P. Genitourinary Tuberculosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, M.J.; Bacelar, M.T.; Pinto, P.; Ramos, I. Genitourinary tuberculosis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2005, 55, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.B.; Sharma, E.; Sharma, S.; Dharmendra, S. Female genital tuberculosis: Revisited. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, S71–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.R.; Cheema, F.A.; Khan, M.U. Accuracy of Urinary PCR as Compared with Urine Culture for Early Diagnosis of Genitourinary Tuberculosis. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2013, 7, 675–678. [Google Scholar]
- Altez-Fernandez, C.; Ortiz, V.; Mirzazadeh, M.; Zegarra, L.; Seas, C.; Ugarte-Gil, C. Diagnostic accuracy of nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) in urine for genitourinary tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S. Reconstructive bladder surgery in genitourinary tuberculosis. Indian J. Urol. 2008, 24, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhiravan, T.; Sharma, S.K. Medical management of genitourinary tuberculosis. Indian J. Urol. 2008, 24, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wejse, C. Medical treatment for urogenital tuberculosis (UGTB). GMS Infect. Dis. 2018, 6, Doc04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, P.; Hemal, A.; Kumar, R. Genital tuberculosis: Current status of diagnosis and management. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2017, 6, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajaczkowski, T. Genitourinary tuberculosis: Historical and basic science review: Past and present. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2012, 65, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, R.; Biswas, J. Bilateral choroidal tuberculoma in miliary tuberculosis—Report of a case. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2015, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, B.; Tiewsoh, I.; Lynrah, K.G.; Wankhar, B.; Beyong, T.; Issar, N.K. Miliary tuberculosis with pulmonary and extrapulmonary component complicated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2017, 6, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietbroek, R.C.; Dahlmans, R.P.; Smedts, F.; Frantzen, P.J.; Koopman, R.J.; van der Meer, J.W. Tuberculosis cutis miliaris disseminata as a manifestation of miliary tuberculosis: Literature review and report of a case of recurrent skin lesions. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1991, 13, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savic, I.; Trifunovic-Skodric, V.; Mitrovic, D. Clinically unrecognized miliary tuberculosis: An autopsy study. Ann. Saudi Med. 2016, 36, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mohan, A. Miliary Tuberculosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mohan, A.; Sharma, A. Miliary tuberculosis: A new look at an old foe. J. Clin. Tuberc. Other Mycobact. Dis. 2016, 3, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toptas, T.; Ilhan, B.; Bilgin, H.; Dincses, E.; Ozdogan, O.; Kaygusuz-Atagunduz, I.; Odabasi, Z.; Korten, V.; Firatli-Tuglular, T. Miliary Tuberculosis Induced Acute Liver Failure. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2015, 2015, 759341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bos, F.; Terken, M.; Ypma, L.; Kimpen, J.L.; Nel, E.D.; Schaaf, H.S.; Schoeman, J.F.; Donald, P.R. Tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis in young children. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2004, 9, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, L.; Keating, E.; Parke, T. Miliary tuberculosis in an immunocompetent male with a fatal outcome. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo-Jaimes, L.; Cicero-Sabido, R.; Criales-Cortez, J.L.; Ramirez, E.; Romero, M.; Rivero, V.; Islas, F.; Olivera, H.; Gonzalez, S.; Escobar-Gutierrez, A. Evaluation of the polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of miliary tuberculosis in bone marrow smear. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2003, 7, 580–586. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.H.; Im, J.G.; Lee, J.S.; Song, J.W.; Lee, H.J.; Yeon, K.M. High resolution CT findings of miliary tuberculosis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1998, 22, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.Y. Review of literature on disseminated tuberculosis with emphasis on the focused diagnostic workup. J. Fam. Commun. Med. 2019, 26, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Song, J.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Shin, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, Y.M. Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Presenting as Miliary Tuberculosis without Immune Suppression: A Case Diagnosed Rapidly with the Genotypic Line Probe Assay Method. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2014, 76, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, J.S.; Carignan, S.; Kang, E.Y.; Muller, N.L.; FitzGerald, J.M. Miliary tuberculosis. Diagnostic accuracy of chest radiography. Chest 1996, 110, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mert, A.; Arslan, F.; Kuyucu, T.; Koc, E.N.; Ylmaz, M.; Turan, D.; Altn, S.; Pehlivanoglu, F.; Sengoz, G.; Yldz, D.; et al. Miliary tuberculosis: Epidemiologicaland clinical analysis of large-case series from moderate to low tuberculosis endemic Country. Medicine 2017, 96, e5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saukkonen, J.J.; Cohn, D.L.; Jasmer, R.M.; Schenker, S.; Jereb, J.A.; Nolan, C.M.; Peloquin, C.A.; Gordin, F.M.; Nunes, D.; Strader, D.B.; et al. An official ATS statement: Hepatotoxicity of antituberculosis therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonika, U.; Kar, P. Tuberculosis and liver disease: Management issues. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2012, 33, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadir, A.P.; Han, J.Y.; Youssef, F.A. Intestinal Tuberculosis Masquerading as Crohn’s Disease? A Case of Disseminated Tuberculosis after Anti-TNF Therapy for Suspected Crohn’s Disease. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2019, 2019, 6053503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonsarngsuk, V.; Mangkang, K.; Santanirand, P. Prevalence and risk factors of drug-resistant extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diriba, G.; Kebede, A.; Tola, H.H.; Yenew, B.; Moga, S.; Addise, D.; Alemu, A.; Mohammed, Z.; Getahun, M.; Fantahun, M.; et al. Molecular characterization and drug resistance patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in extrapulmonary tuberculosis patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.; Kang, B.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, T.; Lee, H.K.; Cho, Y.J.; Jeon, D. Drug resistance in extra-pulmonary tuberculosis in South Korea: Comparison with pulmonary tuberculosis. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2019, 23, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, R.; Oberoi, J.K.; Wattal, C. Multidrug-resistant pulmonary & extrapulmonary tuberculosis: A 13 years retrospective hospital-based analysis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2015, 142, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahseen, S.; Khanzada, F.M.; Baloch, A.Q.; Abbas, Q.; Bhutto, M.M.; Alizai, A.W.; Zaman, S.; Qasim, Z.; Durrani, M.N.; Farough, M.K.; et al. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis in Pakistan—A nation-wide multicenter retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohiya, S.; Tripathy, J.P.; Sagili, K.; Khanna, V.; Kumar, R.; Ojha, A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Khanna, A. Does Drug-Resistant Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Hinder TB Elimination Plans? A Case from Delhi, India. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, U.; Joshi, J.M. Extrapulmonary drug-resistant tuberculosis at a drug-resistant tuberculosis center, Mumbai: Our experience—Hope in the midst of despair! Lung India 2019, 36, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusthackeer, A.; Sekar, G.; Chidambaram, S.; Kumar, V.; Mehta, P.; Swaminathan, S. Drug resistance among extrapulmonary TB patients: Six years experience from a supranational reference laboratory. Indian J. Med. Res. 2015, 142, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; An, J.; Shu, W.; Huo, F.; Chu, N.; Gao, M.; Qin, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Xu, S. Epidemiology of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis among Inpatients, China, 2008–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoel, I.M.; Syre, H.; Skarstein, I.; Mustafa, T. Xpert MTB/RIF ultra for rapid diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis in a high-income low-tuberculosis prevalence setting. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xue, M.; He, J.Q. Diagnostic accuracy of the new Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for tuberculosis disease: A preliminary systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 90, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, M.; Schiller, I.; Dendukuri, N.; Yao, M.; Dheda, K.; Denkinger, C.M.; Schumacher, S.G.; Steingart, K.R. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF assays for extrapulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 1, CD012768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kon, O.M. Use of Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert Ultra in extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Xpert MTB/RIF Assay for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary TB in Adults and Children. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/112472/9789241506335_eng.pdf;jsessionid=2848686F97E0888564C0B236B708AAA9?sequence=1 (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, Y.M.; Shin, J.H.; Ko, Y. Drug-resistance pattern of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains from patients with pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis during 2006 to 2013 in a Korean tertiary medical center. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2015, 30, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mase, S.; Chorba, T.; Parks, S.; Belanger, A.; Dworkin, F.; Seaworth, B.; Warkentin, J.; Barry, P.; Shah, N. Bedaquiline for the Treatment of Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Gaharwar, U.S.; Meena, R.; Rajamani, P.; Prasad, T. Recent updates on drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease | Organ Affected | Clinical Presentation | Age of Onset | Recommendations for Adjuvant Therapy | Recommendations for Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meningitis | Brain | Initial—headache, low-grade fever, malaise, vomiting, and confusion Severe—seizures, coma, and stupor | Children ≤5 years of age | Prednisone or dexamethasone-intravenous and continued as an oral treatment | None |
| Cervical Lymphadenitis | Neck-Lymph nodes | Unilateral single or multiple painless lumps; fever, night sweats, and weight loss | Adults of age 20 to 40 years | None | Incision and drainage |
| Ocular | Eye | Primary—eyelid, conjunctival, corneal, and scleral lesions Secondary—inflammation of the uveal tract, retina, and optic nerve | None in particular | Oral prednisone or topical steroids or prednisone drops | None |
| Oral | Mouth, tongue | Primary—painless ulcer, single and associated with lymph node enlargement Secondary—single, irregular, superficial, or deep painful ulcer, odynophagia | Primary—children and young adults Secondary—adults | Topical anti-inflammatory drugs or mucosa protecting agents | None |
| Pleural | Pleura covering the lungs | Fever, chest pain, cough, dyspnoea sometimes associated with weight loss, loss of appetite, and malaise | Adolescents and adults | None | Thoracentesis |
| Pericarditis | Pericardium covering the heart | Pericarditis presents as fever, weight loss, night sweats, cough, chest pain, and breathlessness, along with moderate to high pericardial effusion | Adults | Use of corticosteroids | Echocardiographic or fluoroscopic-guided needle pericardiocentesis |
| Cutaneous | Skin | Usually presents as a reddish or purple papule or nodule accompanied by painful ulcers on the skin; occasional draining sinus tracts or cutaneous abscesses seen No fever, weight loss, or night sweats | TB cutis miliaris disseminate occurs in infants and children with less immunity; | None | Surgical excision and debridement |
| Musculoskeletal | Muscle and Bone * | Pain and swelling of the spine, hip, knee, shoulder, ankle, elbow, femur, humerus, hand, feet, or wrist; occasional fever, weight loss, and night sweats | Primary—children Secondary—elders | None | Surgery when neurological deficit, cord compression, spinal instability, or kyphosis to variable extent particular children; for cold abscesses and sinus tract involvement, debridement and/or drainage is conducted |
| Abdominal | GI tract, Peritoneum, Solid viscera | Symptoms are abdominal pain, fever, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea Specific organs show perforations, obliterations, ulceration, hypertrophy, ulcerohypertrophy, fistulae, and strictures | Adults | None | Surgery when irreversible constrictions, strictures, abscesses, and fistula formation cause organ damage |
| Genitourinary | Kidneys, male or female genital tract | Urinary tract involvement with fever, weight loss, and sweating are observed along with urologic symptoms such as flank pain, pyuria, hematuria, and even urinary incontinence Male genital tract infection shows tender scrotal swelling, irregular/nodular prostate, genital ulcer, and perineal sinus or fistula and may lead to male infertility; female genital tract shows menstrual irregularity, abdominal pain, pelvic inflammatory disease and even infertility | Adults | None | Ablative surgery; reconstructive surgery; percutaneous drainage |
| Miliary | Different parts of the body | The symptoms are fever, malaise, anorexia, weight loss, cough with chills, and rigours when septicaemia is involved Specific symptoms are observed depending on the organ involved and usually show cutaneous lesions (Tuberculosis cutis miliaris disseminate), choroidal tubercles, and commonly TB meningitis; atypical manifestations are also seen | Infants and children as well as elders with comorbidities; predominantly males | Prednisone when meningitis, pleuritis, or pericarditis is involved | Surgery when organ damage is irreversible |
| Type of EP-TB | Sample | Diagnostic Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meningitis | CSF | CSF ADA | 86–89% | 78–91% | [11,12] |
| IFN-γ | 83 | 85 | [13] | ||
| T-SPOT-TB | 76 | 88 | [14] | ||
| Smear | <25% | NA | [9] | ||
| PCR-based | 48–100% | 38–100% | [9] | ||
| Multiplex PCR | 71.4 | 89.6 | [18] | ||
| LAMP | 76 | 99 | [19] | ||
| Xpert MTB/RIF | 70 | 97 | [20] | ||
| Xpert Ultra | 87 | 88 | [20] | ||
| Lymphadenitis | Lymph node aspirate | ADA | NA | NA | |
| FNAC | 88–96 | 88–96 | [23] | ||
| T-SPOT-TB | 91 | 74 | [24] | ||
| Smear | 34.6–66.0% | 87.50% | [25] | ||
| PCR-based | 42 | 89.2 | [26] | ||
| LAMP | 80 | NA | [19] | ||
| Xpert MTB/RIF | 89 | 86 | [20] | ||
| Xpert Ultra | 70 | 100 | [20] | ||
| Pleural TB | Pleural fluid | Pleural ADA | 88.37 | 88 | [27] |
| Pleural IFN-γ | 86.61 | 90.2 | [28] | ||
| T-SPOT-TB | 92.86 | 92.16 | [28] | ||
| PCR | 82 | 85 | [29] | ||
| Multiplex PCR | 95.34 | [30] | |||
| LAMP | 25–75.8 | 83.3–100 | [19] | ||
| Xpert MTB/RIF | 50 | 99 | [20] | ||
| Xpert Ultra | 71 | 71 | [20] | ||
| TB Pericarditis | Pericardial fluid | Pericardial ADA | 87–93 | 89–97 | [31] |
| Pericardial IFN-γ | 87–95 | 91–97 | [32] | ||
| PCR | 15 | 100 | [33] | ||
| T-SPOT-TB | 92.3 | 87.9 | [34] | ||
| Xpert MTB/RIF | 60 | 88 | [20] | ||
| Xpert Ultra | NA | NA | |||
| Cutaneous | Skin biopsy | TST | 33–96% | 62.50% | [35] |
| Culture | 74.3 | NA | [36] | ||
| PCR-based | 25 | 73.7 | [37] | ||
| Xpert MTB/RIF | NA | NA | |||
| Xpert Ultra | NA | NA | |||
| Musculoskeletal | Synovial fluid | Synovial ADA | 83.3 | 96.7 | [38] |
| T-SPOT-TB | 83 | 86 | [39] | ||
| PCR | 82.65 | 91 | [40] | ||
| LAMP | 85.3 | NA | [19] | ||
| Xpert MTB/RIF | 97 | 94 | [20] | ||
| Xpert Ultra | 96 | 97 | [20] | ||
| Abdominal | Peritoneal fluid | ADA | 100 | 97 | [31] |
| T-cell IFNγ | 90 | 78 | [41] | ||
| PCR | 35–65 | 100 | [42] | ||
| Multiplex PCR | 75.7 | 100 | [42] | ||
| Xpert MTB/RIF | 59 | 97 | [20] | ||
| Xpert Ultra | NA | NA |
| Resistance | Regimen | Duration | Choice of Drugs | Primary Recommendations | Conditional Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Standard chemotherapy regimen | 6 months | Intensive phase—2 months of rifampicin, isoniazid, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide Continuation phase—4 months of rifampicin and isoniazid | Continuation phase extended up to 7 months of rifampicin and isoniazid for EPTB | |
| Isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis (Hr-TB) | Mono-INH regimen | 6 months | Rifampicin, ethambutol, pyrazinamide, and levofloxacin is recommended for 6 months | Treatment period extended up to 9–12 months for EPTB No inclusion of streptomycin or other injectable agents Drug susceptibility to fluoroquinolone by genotypic or phenotypic DST needs to be established | |
| MDR/RR-TB | Longer MDR regimen | Total of 18–20 months with 15–17 months after culture conversion | Combination of group A, B, C drugs to add to four drugs; if bedaquiline or linezolid is added, drug combination to retain three drugs throughout treatment | Total of 18–20 months for EPTB when culture-negative or conversion cannot be tested; injectables used for 6–7 months Inclusion of levofloxacin A or moxifloxacin A*; Bedaquiline A# for patients aged 18 years or more; Linezolid A. No inclusion of kanamycin, capreomycin and clavulanic acid | The following drugs may be included: Bedaquiline A# may also be included in patients aged 6–17 years; Clofazimine B# and cycloserine; B*/terizidone B* Ethambutol C#; Delamanid C# for patients aged 3 years or more; Pyrazinamide C; Imipenem-cilastatin C or meropenem C*; Amikacin C# or streptomycin C#; The following drugs may be included when bedaquiline, linezolid, clofazimine, or delamanid are not used: Ethionamide C* or prothionamide C*; p-aminosalicylic acid C#. |
| MDR/RR-TB | Shorter all oral MDR regimen | 9–12 months | For fluoroquinolone sensitive cases: 2 months of Linezolid–Bedaquiline–Levofloxacin–Clofazimine–Pyrazinamide, 4 months of Bedaquiline–Levofloxacin–Clofazimine–Pyrazinamide 3 months of Levofloxacin–Clofazimine–Pyrazinamide | For EPTB cases with meningitis and disseminated disease, a shorter regimen should be avoided Susceptibility to fluoroquinolones needs to be established by genotypic or phenotypic DST | |
| 6 months | For fluoroquinolone resistant cases: 6 months of Bedaquiline–Pretomanid–Linezolid (BPaL regimen) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gopalaswamy, R.; Dusthackeer, V.N.A.; Kannayan, S.; Subbian, S. Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis—An Update on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Drug Resistance. J. Respir. 2021, 1, 141-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1020015
Gopalaswamy R, Dusthackeer VNA, Kannayan S, Subbian S. Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis—An Update on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Drug Resistance. Journal of Respiration. 2021; 1(2):141-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGopalaswamy, Radha, V. N. Azger Dusthackeer, Silambuchelvi Kannayan, and Selvakumar Subbian. 2021. "Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis—An Update on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Drug Resistance" Journal of Respiration 1, no. 2: 141-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1020015
APA StyleGopalaswamy, R., Dusthackeer, V. N. A., Kannayan, S., & Subbian, S. (2021). Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis—An Update on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Drug Resistance. Journal of Respiration, 1(2), 141-164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1020015








