SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Lung Vascular Cells
Abstract
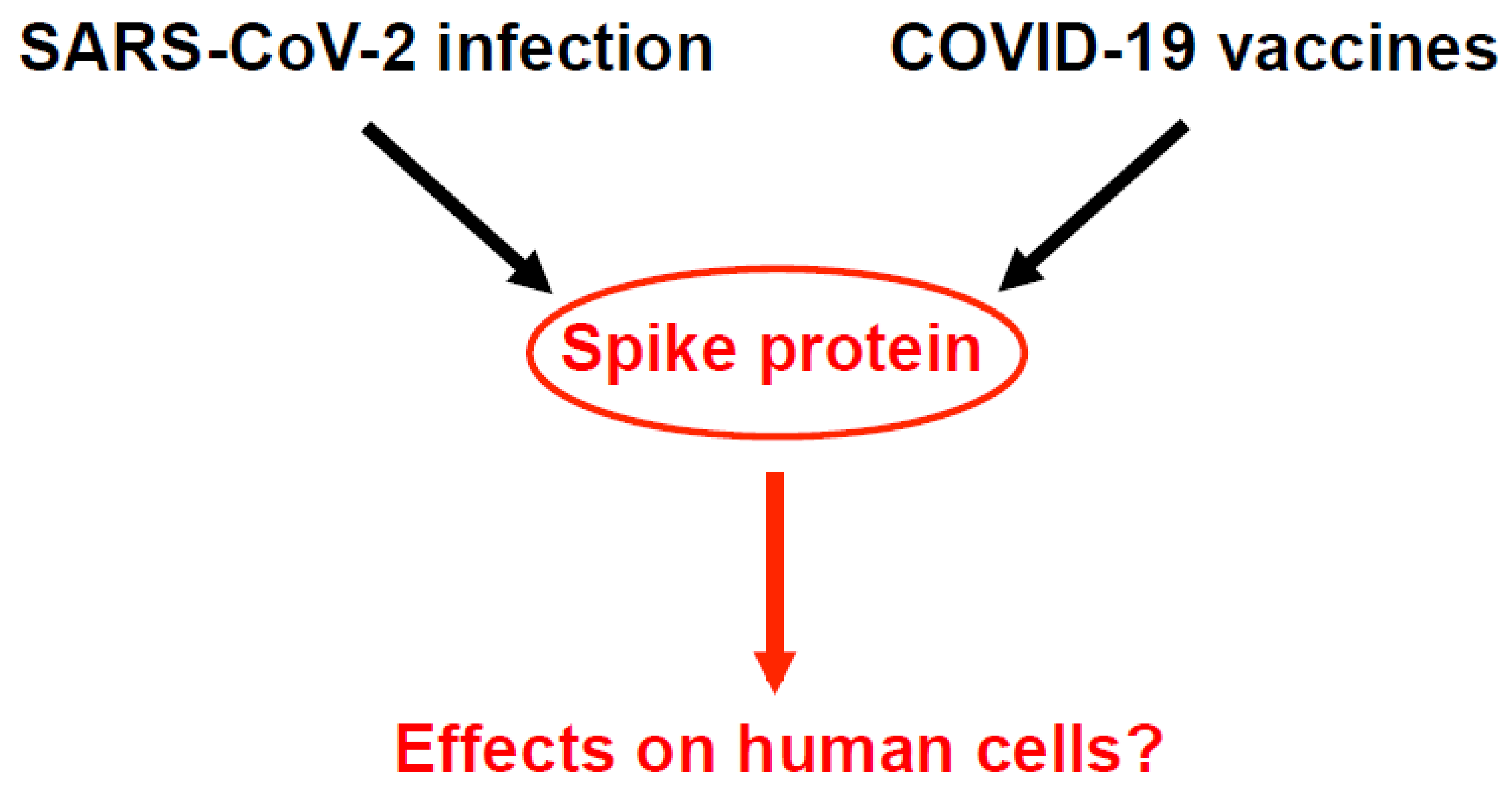
:1. Introduction
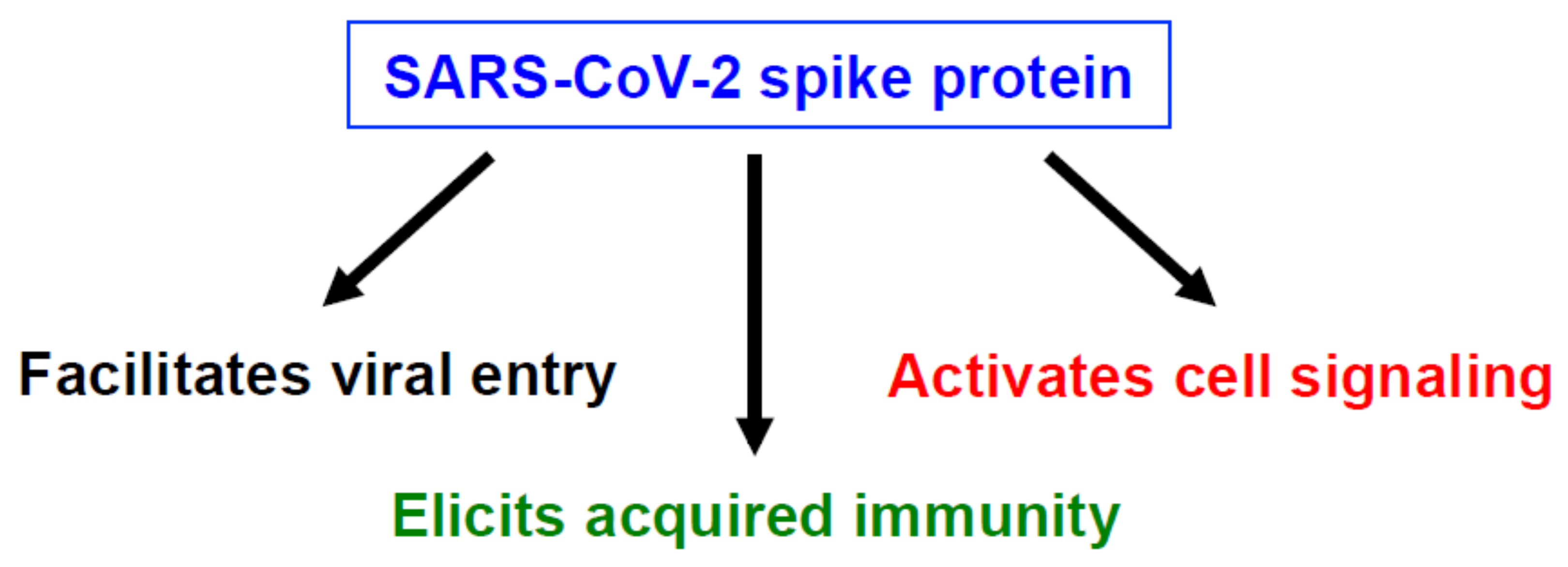
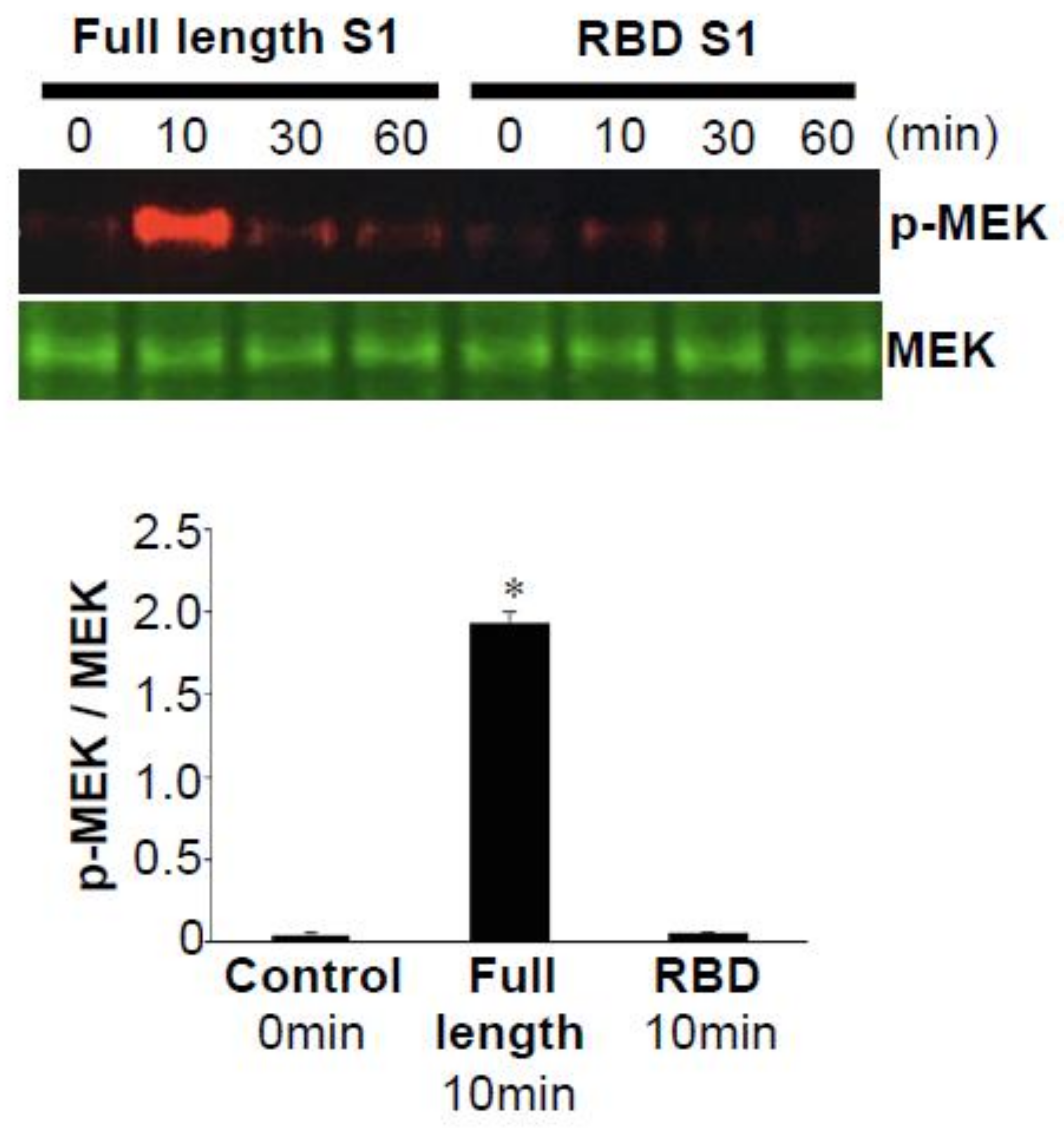
2. The SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Activates Cell Signaling in Lung Vascular Cells
3. Pathology of PAH
4. Do the Membrane Fusion Proteins of Other Viruses Also Activate Cell Signaling in Host Cells without the Rest of the Viral Components?
5. HIV Increases the Incidence of PAH
6. Are Individuals Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Predisposed to Developing PAH?
7. COVID-19 Vaccines and PAH
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Satapathy, A.; Naidu, M.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sharma, S.; Barton, L.M.; Stroberg, E.; Duval, E.J.; Pradhan, D.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19)—Anatomic pathology perspective on current knowledge. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.M.; Delos, S.E.; Brecher, M.; Schornberg, K. Structures and Mechanisms of Viral Membrane Fusion Proteins: Multiple Variations on a Common Theme. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 43, 189–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system: Celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.J.; Van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Nikolaienko, S.I.; Dibrova, V.A.; Dibrova, Y.V.; Vasylyk, V.M.; Novikov, M.Y.; Shults, N.V.; Gychka, S.G. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated cell signaling in lung vascular cells. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcroix, M.; Naeije, R. Optimising the management of pulmonary arterial hypertension patients: Emergency treatments. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2010, 19, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Shah, S.J.; Souza, R.; Humbert, M. Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1976–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Alonzo, G.E.; Barst, R.J.; Ayres, S.M.; Bergofsky, E.H.; Brundage, B.H.; Detre, K.M.; Fishman, A.P.; Goldring, R.M.; Groves, B.M.; Kernis, J.T.; et al. Survival in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 115, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runo, J.R.; Loyd, J.E. Primary pulmonary hypertension. Lancet 2003, 361, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benza, R.L.; Miller, D.P.; Frost, A.; Barst, R.J.; Krichman, A.M.; McGoon, M.D. Analysis of the Lung Allocation Score Estimation of Risk of Death in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Using Data From the REVEAL Registry. Transplantation 2010, 90, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Sitbon, O.; Yaici, A.; Montani, D.; O’Callaghan, D.S.; Jais, X.; Parent, F.; Savale, L.; Natali, D.; Gunther, S.; et al. Survival in incident and prevalent cohorts of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thenappan, T.; Shah, S.J.; Rich, S.S.; Tian, L.; Archer, S.L.; Gombergmaitland, M. Survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A reappraisal of the NIH risk stratification equation. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 35, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsson, K.M.; Delcroix, M.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Tiede, H.; Huscher, D.; Speich, R.; Grünig, E.; Staehler, G.; Rosenkranz, S.; Halank, M.; et al. Anticoagulation and Survival in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Results From the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA). Circulation 2014, 129, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherry, J.D. The chronology of the 2002–2003 SARS mini pandemic. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2004, 5, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Shang, J.; Graham, R.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan: An analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00120–e00127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, I.-Y.; Chang, S.-C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Yu, T.-C.; Wei, W.-C.; Lin, S.; Chien, C.-L.; Chang, M.-F. Upregulation of the Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 2 via a Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike-ACE2 Signaling. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7703–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Itoh, T.; Nagaya, N.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Kyotani, S.; Oya, H.; Sakamaki, F.; Kimura, H.; Nakanishi, N. Increased plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 level in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respirology 2006, 11, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Akhter, S.; Chaudhuri, A.; Kanmogne, G.D. HIV-1 gp120 induces cytokine expression, leukocyte adhesion, and transmigration across the blood–brain barrier: Modulatory effects of STAT1 signaling. Microvasc. Res. 2009, 77, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Cornò, M.; Donninelli, G.; Varano, B.; Da Sacco, L.; Masotti, A.; Gessani, S. HIV-1 gp120 Activates the STAT3/Interleukin-6 Axis in Primary Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11045–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hioe, C.E.; Tuen, M.; Vasiliver-Shamis, G.; Alvarez, Y.; Prins, K.C.; Banerjee, S.; Nadas, A.; Cho, M.W.; Dustin, M.L.; Kachlany, S.C. HIV Envelope gp120 Activates LFA-1 on CD4 T-Lymphocytes and Increases Cell Susceptibility to LFA-1-Targeting Leukotoxin (LtxA). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isasti, G.; Moreno, T.; Pérez, I.; Cabrera, F.; Palacios, R.; Santos, J. High Prevalence of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in a Cohort of Asymptomatic HIV-Infected Patients. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2013, 29, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.J.; Khan, I.A.; Mehta, R.N.; Sepkowitz, D.A. HIV-Related pulmonary hypertension: Analytic review of 131 cases. Chest 2000, 118, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellicelli, A.; Barbaro, G.; Palmieri, F.; Girardi, E.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Rianda, A.; Barbarini, G.; Frigiotti, D.; Borgia, M.C.; Petrosillo, N. Primary Pulmonary Hypertension in HIV Patients: A Systematic Review. Angiology 2001, 52, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O.; Lascoux-Combe, C.; Delfraissy, J.-F.; Yeni, P.G.; Raffi, F.; De Zuttere, D.; Gressin, V.; Clerson, P.; Sereni, D.; Simonneau, G. Prevalence of HIV-related Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the Current Antiretroviral Therapy Era. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schecter, A.D.; Berman, A.B.; Yi, L.; Mosoian, A.; McManus, C.M.; Berman, J.W.; Klotman, M.E.; Taubman, M.B. HIV envelope gp120 activates human arterial smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10142–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, T.A.; Witt, T.A.; Pan, S.; Mueske, C.S.; Kleppe, L.S.; Holroyd, E.W.; Champion, H.C.; Simari, R.D. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Overexpression Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, R.J.; Meoli, D.F.; Swarthout, R.F.; Kallop, D.Y.; Galaria, I.I.; Harvey, J.L.; Miller, C.M.; Blaxall, B.C.; Hall, C.M.; Pierce, R.A.; et al. Plexiform-like lesions and increased tissue factor expression in a rat model of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L583–L590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amsellem, V.; Lipskaia, L.; Abid, S.; Poupel, L.; Houssaini, A.; Quarck, R.; Marcos, E.; Mouraret, N.; Parpaleix, A.; Bobe, R.; et al. CCR5 as a treatment target in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2014, 130, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmogne, G.D.; Primeaux, C.; Grammas, P. Induction of apoptosis and endothelin-1 secretion in primary human lung endothelial cells by HIV-1 gp120 proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine BNT162b2 Selected for a Pivotal Efficacy Study. medRxiv 2020. Available online: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.08.17.20176651v2 (accessed on 28 August 2020). [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA-based Covid-19 vaccine candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Coler, R.N.; McCullough, M.P.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Becker, S.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bellamy, D.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, N.B.; Zahn, R.; Wegmann, F.; Loos, C.; Chandrashekar, A.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Peter, L.; McMahan, K.; Tostanoski, L.H.; et al. Single-shot Ad26 vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Nature 2020, 586, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebre-Xabier, M.; Patel, N.; Tian, J.-H.; Zhou, B.; Maciejewski, S.; Lam, K.; Portnoff, A.D.; Massare, M.J.; Frieman, M.B.; Piedra, P.A.; et al. NVX-CoV2373 vaccine protects cynomolgus macaque upper and lower airways against SARS-CoV-2 challenge. Vaccine 2020, 38, 7892–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, M.J.; Lyke, K.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Raabe, V.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; et al. Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults. Nature 2020, 586, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Vogler, I.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.; Quandt, J.; Maurus, D.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and T H 1 T cell responses. Nature 2020, 586, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suresh, S.J.; Suzuki, Y.J. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Lung Vascular Cells. J. Respir. 2021, 1, 40-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1010004
Suresh SJ, Suzuki YJ. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Lung Vascular Cells. Journal of Respiration. 2021; 1(1):40-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuresh, Sri Jayalakshmi, and Yuichiro Justin Suzuki. 2021. "SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Lung Vascular Cells" Journal of Respiration 1, no. 1: 40-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1010004
APA StyleSuresh, S. J., & Suzuki, Y. J. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Lung Vascular Cells. Journal of Respiration, 1(1), 40-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1010004





