STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Review Focusing on Pathophysiology and Treatment Options
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Approach
2.1. Cutaneous Manifestations
2.2. Musculoskeletal Manifestations
2.3. Pulmonary Manifestations
2.4. Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
2.5. High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT)
2.6. Laboratory Findings
2.7. Diagnostic Approach
3. Differential Diagnosis
3.1. Childhood Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA)
3.2. Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
3.3. Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases (PIDDs)
3.4. Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome (AGS)
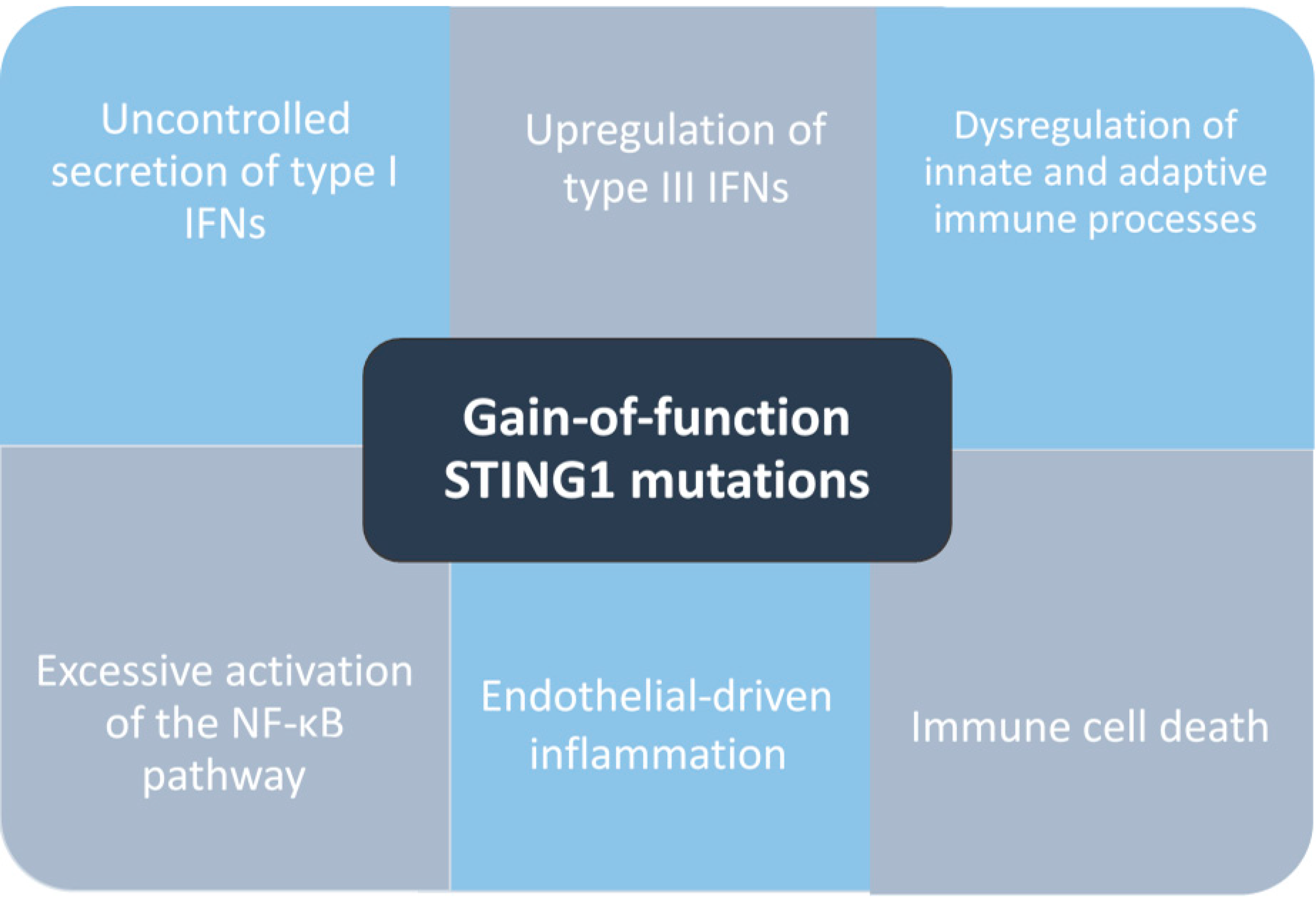
4. Pathogenesis
5. Therapeutic Strategy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Jesus, A.A.; Marrero, B.; Yang, D.; Ramsey, S.E.; Montealegre Sanchez, G.A.; Tenbrock, K.; Wittkowski, H.; Jones, O.Y.; Kuehn, H.S.; et al. Activated STING in a Vascular and Pulmonary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frémond, M.-L.; Crow, Y.J. STING-Mediated Lung Inflammation and Beyond. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, J.; Eroglu, F.K.; Özen, S.; Orhan, D.; Montealegre-Sanchez, G.; De Jesus, A.A.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Cowen, E.W. Failure to Thrive, Interstitial Lung Disease, and Progressive Digital Necrosis with Onset in Infancy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frémond, M.-L.; Hadchouel, A.; Berteloot, L.; Melki, I.; Bresson, V.; Barnabei, L.; Jeremiah, N.; Belot, A.; Bondet, V.; Brocq, O.; et al. Overview of STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI) Among 21 Patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 803–818.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.L.N.; Robertson, L.; Rice, G.I.; Seabra, L.; Hilliard, T.N.; Crow, Y.J.; Ramanan, A.V. Type 1 Interferonopathy Presenting as Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis with Interstitial Lung Disease: Report of a New Phenotype. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2020, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X. STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Familial Case Series Report and Literature Review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, C.; Frémond, M.-L. Lung Inflammation in STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI). Cells 2022, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, F.; Betrains, A.; Doubel, P.; Willemsen, M.; Cleemput, V.; Vanderschueren, S.; Corveleyn, A.; Meyts, I.; Sprangers, B.; Crow, Y.J.; et al. Adult-Onset ANCA-Associated Vasculitis in SAVI: Extension of the Phenotypic Spectrum, Case Report and Review of the Literature. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin Gedik, K.; Lamot, L.; Romano, M.; Demirkaya, E.; Piskin, D.; Torreggiani, S.; Adang, L.A.; Armangue, T.; Barchus, K.; Cordova, D.R.; et al. The 2021 European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology/American College of Rheumatology Points to Consider for Diagnosis and Management of Autoinflammatory Type I Interferonopathies: CANDLE/PRAAS, SAVI and AGS. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, S.; Picco, P.; Caorsi, R.; Candotti, F.; Gattorno, M. Type I Interferonopathies in Pediatric Rheumatology. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2016, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, G.I.; Melki, I.; Frémond, M.-L.; Briggs, T.A.; Rodero, M.P.; Kitabayashi, N.; Oojageer, A.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Belot, A.; Bodemer, C.; et al. Assessment of Type I Interferon Signaling in Pediatric Inflammatory Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; De Jesus, A.A.; Brooks, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; VanTries, R.; Montealegre Sanchez, G.A.; Rotman, Y.; Gadina, M.; Goldbach-Mansky, R. Development of a Validated Interferon Score Using NanoString Technology. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama, M.; Mura, T.; Kone-Paut, I.; Boursier, G.; Aouinti, S.; Touitou, I.; Sarrabay, G. Is Gene Panel Sequencing More Efficient than Clinical-Based Gene Sequencing to Diagnose Autoinflammatory Diseases? A Randomized Study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 203, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoyinmi, E.; Standing, A.; Keylock, A.; Price-Kuehne, F.; Melo Gomes, S.; Rowczenio, D.; Nanthapisal, S.; Cullup, T.; Nyanhete, R.; Ashton, E.; et al. Clinical Impact of a Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Gene Panel for Autoinflammation and Vasculitis. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0181874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.C.; Gibson, L.E.; Davis, D.M.R. Cutaneous Manifestations of Pediatric Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Clinicopathologic and Immunopathologic Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shteinberg, M.; Haq, I.J.; Polineni, D.; Davies, J.C. Cystic Fibrosis. Lancet 2021, 397, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, L. The Challenge of Diagnosing SAVI: Case Studies. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2019, 32, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesenak, M.; Banovcin, P.; Jesenakova, B.; Babusikova, E. Pulmonary Manifestations of Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, Y.J. Type I Interferonopathies: A Novel Set of Inborn Errors of Immunity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1238, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, S.; Caseley, E.A.; McDermott, M.F. Moving towards a Systems-Based Classification of Innate Immune-Mediated Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarlis, C.; Mavragani, C.P. Immune Dysfunction and Drug Targets in Autoinflammatory Syndromes. In Comprehensive Pharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 479–491. ISBN 978-0-12-820876-2. [Google Scholar]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of Type-I- and Type-II-Interferon-Mediated Signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, V.E.; Skarlis, C.; Evangelopoulos, M.-E.; Mavragani, C.P. Type I Interferon Detection in Autoimmune Diseases: Challenges and Clinical Applications. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.; Steiner, A.; Harapas, C.R.; Masters, S.L. An Update on Autoinflammatory Diseases: Interferonopathies. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, Y.J.; Manel, N. Aicardi–Goutières Syndrome and the Type I Interferonopathies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Fayand, A.; Rodrigues, F.; Bachmeyer, C.; Savey, L.; Grateau, G. Autoinflammatory Diseases: State of the Art. Presse Médicale 2019, 48, e25–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablasser, A.; Chen, Z.J. CGAS in Action: Expanding Roles in Immunity and Inflammation. Science 2019, 363, eaat8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.J.; Bai, X.; Zhang, X. Cryo-EM Structures of STING Reveal Its Mechanism of Activation by Cyclic GMP–AMP. Nature 2019, 567, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; He, J.; Yin, Q. Stimulator of Interferon Genes-Associated Vasculopathy With Onset in Infancy: A Systematic Review of Case Reports. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 577918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Torreggiani, S.; Kahle, D.; Rumsey, D.G.; Wright, B.L.; Montes-Cano, M.A.; Silveira, L.F.; Alehashemi, S.; Mitchell, J.; Aue, A.G.; et al. Case Report: Novel SAVI-Causing Variants in STING1 Expand the Clinical Disease Spectrum and Suggest a Refined Model of STING Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 636225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, Q.; Best Rocha, A.; Larsen, C.P.; Schulert, G.; Marsh, R.; Yasin, S.; Patty-Resk, C.; Valentini, R.P.; Adams, M.; Baracco, R. APOL1-Associated Collapsing Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in a Patient with Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING)-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.; Rodière, M.; Jeremiah, N.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Oojageer, A.; Rice, G.I.; Rozenberg, F.; Crow, Y.J.; Bessis, D. Stimulator of Interferon Genes–Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Mimic of Childhood Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, S.; Insalaco, A.; Caorsi, R.; Santori, E.; Messia, V.; Sacco, O.; Terheggen-Lagro, S.; Cardinale, F.; Scarselli, A.; Pastorino, C.; et al. Efficacy and Adverse Events During Janus Kinase Inhibitor Treatment of SAVI Syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balci, S.; Ekinci, R.M.K.; De Jesus, A.A.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Yilmaz, M. Baricitinib Experience on STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Representative Case from Turkey. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 212, 108273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoman, W.; El Chazli, Y.; ElSawy, I.; Aróstegui, J. First Egyptian Patient with STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 48, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frémond, M.-L.; Rodero, M.P.; Jeremiah, N.; Belot, A.; Jeziorski, E.; Duffy, D.; Bessis, D.; Cros, G.; Rice, G.I.; Charbit, B.; et al. Efficacy of the Janus Kinase 1/2 Inhibitor Ruxolitinib in the Treatment of Vasculopathy Associated with TMEM173 -Activating Mutations in 3 Children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1752–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, S. STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy in Three Children with New Clinical Aspect and Unsatisfactory Therapeutic Responses to Tofacitinib. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremiah, N.; Neven, B.; Gentili, M.; Callebaut, I.; Maschalidi, S.; Stolzenberg, M.-C.; Goudin, N.; Frémond, M.-L.; Nitschke, P.; Molina, T.J.; et al. Inherited STING-Activating Mutation Underlies a Familial Inflammatory Syndrome with Lupus-like Manifestations. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5516–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caorsi, R.; Rice, G.; Cardinale, F.; Volpi, S.; Buoncompagni, A.; Crow, Y.; Martini, A.; Gattorno, M.; Picco, P. AB1014 Enlarging the Clinical Spectrum of Sting-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.L.N.; Pellowe, E.J.; De Jesus, A.A.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Hilliard, T.N.; Ramanan, A.V. Interstitial Lung Disease Caused by STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, C.; Thouvenin, G.; Kannengiesser, C.; Dubus, J.-C.; Jeremiah, N.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Crestani, B.; Belot, A.; Thivolet-Béjui, F.; Secq, V.; et al. Severe Pulmonary Fibrosis as the First Manifestation of Interferonopathy (TMEM173 Mutation). Chest 2016, 150, e65–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagher, R.; Ghiye, R.; Nicolas, G.; Feghali, H.; Khalife, M.F.; Seabra, L.; Crow, Y. THU0528 Sting-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI): A Differential Diagnosis of Inflammatory Interstitial Lung Disease. In Proceedings of the Poster Presentations; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and European League Against Rheumatism: London, UK, 2017; p. 406. [Google Scholar]
- Raffaele, C.G.L.; Messia, V.; Moneta, G.; Caiello, I.; Federici, S.; Pardeo, M.; Bracaglia, C.; De Benedetti, F.; Insalaco, A. A Patient with Stimulator of Interferon Genes–Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy without Skin Vasculopathy. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 905–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, N.; Fiehn, C.; Wolf, C.; Schuster, M.; Cura Costa, E.; Tüngler, V.; Alvarez, H.A.; Chara, O.; Engel, K.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; et al. Familial Chilblain Lupus Due to a Gain-of-Function Mutation in STING. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoussakis, M.N.; Mavragani, C.P.; Nezos, A.; Zampeli, E.; Germenis, A.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Type I Interferonopathy in a Young Adult. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 2241–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melki, I.; Rose, Y.; Uggenti, C.; Van Eyck, L.; Frémond, M.-L.; Kitabayashi, N.; Rice, G.I.; Jenkinson, E.M.; Boulai, A.; Jeremiah, N.; et al. Disease-Associated Mutations Identify a Novel Region in Human STING Necessary for the Control of Type I Interferon Signaling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 543–552.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, K.; Brogan, P.; Burrows, N.; Gass, J.; Bale, P.; Armon, K. P04 STING: Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI). Rheumatology 2018, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskitalo, S.; Haapaniemi, E.; Einarsdottir, E.; Rajamäki, K.; Heikkilä, H.; Ilander, M.; Pöyhönen, M.; Morgunova, E.; Hokynar, K.; Lagström, S.; et al. Novel TMEM173 Mutation and the Role of Disease Modifying Alleles. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Kang, J.-A.; Suh, D.I.; Park, E.-B.; Lee, C.-R.; Choi, S.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.-H.; Ye, M.; et al. Tofacitinib Relieves Symptoms of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING)–Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy Caused by 2 de Novo Variants in TMEM173. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1396–1399.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Berard, R.; Al Rasheed, A.; Aladba, B.; Kranzusch, P.J.; Henderlight, M.; Grom, A.; Kahle, D.; Torreggiani, S.; Aue, A.G.; et al. A Novel STING1 Variant Causes a Recessive Form of STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1204–1208.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, R.G.; Balka, K.R.; Davidson, S.; Wainstein, B.K.; Wong, M.; Macintosh, R.; Loo, C.K.C.; Weber, M.A.; Kamath, V.; CIRCA; et al. A Mutation Outside the Dimerization Domain Causing Atypical STING-Associated Vasculopathy With Onset in Infancy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Zhou, M.; Imamichi, H.; Jiao, X.; Sherman, B.T.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T. STING Is an Essential Mediator of the Ku70-Mediated Production of IFN-Λ1 in Response to Exogenous DNA. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaah5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlakõiv, T.; Hernandez, P.; Gronke, K.; Diefenbach, A.; Staeheli, P. Leukocyte-Derived IFN-α/β and Epithelial IFN-λ Constitute a Compartmentalized Mucosal Defense System That Restricts Enteric Virus Infections. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Dobbs, N.; Sakai, T.; Liou, J.; Miner, J.J.; Yan, N. STING-Mediated Disruption of Calcium Homeostasis Chronically Activates ER Stress and Primes T Cell Death. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 867–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennion, B.G.; Croft, C.A.; Ai, T.L.; Qian, W.; Menos, A.M.; Miner, C.A.; Frémond, M.-L.; Doisne, J.-M.; Andhey, P.S.; Platt, D.J.; et al. STING Gain-of-Function Disrupts Lymph Node Organogenesis and Innate Lymphoid Cell Development in Mice. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.M.; Marshak-Rothstein, A.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Type-1 Interferon-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms in Cyclic GMP–AMP Synthase–Stimulator of Interferon Genes-Driven Auto-Inflammation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2023, 80, 102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Tabula Muris Consortium; Overall coordination; Logistical coordination; Organ collection and processing; Library preparation and sequencing; Computational data analysis; Cell type annotation; Writing group; Supplemental text writing group; Principal investigators. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of 20 Mouse Organs Creates a Tabula Muris. Nature 2018, 562, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digre, A.; Lindskog, C. The Human Protein Atlas—Spatial Localization of the Human Proteome in Health and Disease. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.M.; Motwani, M.; Tedder, T.; Marshak-Rothstein, A.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Radioresistant Cells Initiate Lymphocyte-Dependent Lung Inflammation and IFNγ-Dependent Mortality in STING Gain-of-Function Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2202327119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechman, K.; Yates, M.; Galloway, J.B. The New Entries in the Therapeutic Armamentarium: The Small Molecule JAK Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, X.; Lu, M. Use of Tofacitinib for Infant-Onset STING-Associated Vasculopathy: A Case Report from China. Medicine 2022, 101, e31832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhong, L.; Gou, L.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Quan, M.; Jian, S.; Tang, X.; et al. Janus Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Type I Interferonopathies: A Case Series From a Single Center in China. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 825367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Flanagan, M.E.; Telliez, J.-B. Discovery and Development of Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors for Inflammatory Diseases: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5023–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjadj, J.; Frémond, M.-L.; Neven, B. Emerging Place of JAK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Inborn Errors of Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 717388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Brooks, K.M.; Tang, C.C.; Wakim, P.; Blake, M.; Brooks, S.R.; Montealegre Sanchez, G.A.; De Jesus, A.A.; Huang, Y.; Tsai, W.L.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Proposed Dosing of the Oral JAK1 and JAK2 Inhibitor Baricitinib in Pediatric and Young Adult CANDLE and SAVI Patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 104, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, G.A.M.; Reinhardt, A.; Ramsey, S.; Wittkowski, H.; Hashkes, P.J.; Berkun, Y.; Schalm, S.; Murias, S.; Dare, J.A.; Brown, D.; et al. JAK1/2 Inhibition with Baricitinib in the Treatment of Autoinflammatory Interferonopathies. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, N.; Ishii, T.; Takita, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Nishikomori, R. Efficacy and Safety of Baricitinib in Japanese Patients with Autoinflammatory Type I Interferonopathies (NNS/CANDLE, SAVI, And AGS). Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2023, 21, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
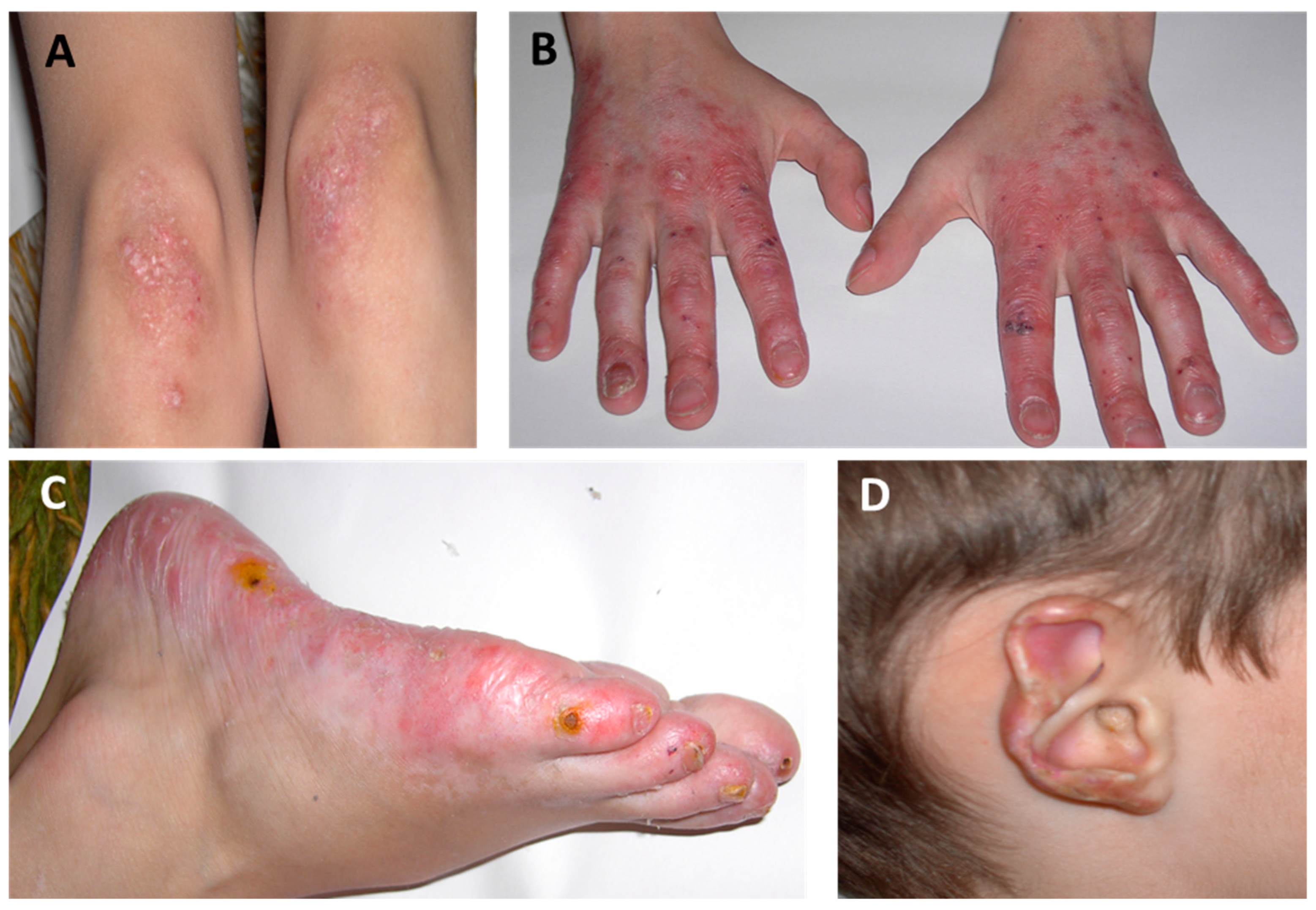
| Systemic Manifestations | Cutaneous Manifestations | Musculoskeletal Manifestations | Pulmonary Manifestations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal-onset systemic inflammation Growth retardation (failure to thrive) Recurrent febrile episodes |
Acral violaceous patches and plaques (cold-sensitive areas) Violaceous/erythematous rash Telangiectasia Chilblains Ulcerations Tissue loss/skin necrosis
| Polyarthralgia/Polyarthritis Myositis/Muscle atrophy Acro-osteolysis of distal phalanges Bone demineralization | Interstitial lung disease Pulmonary fibrosis Pulmonary hypertension Paratracheal adenopathy Emphysema Obliterative bronchiolitis Recurrent lung infections |
| Childhood GPA | CF | PIDDs | AGS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlapping Characteristics | Differentiating Factors | Overlapping Characteristics | Differentiating Factors | Overlapping Characteristics | Differentiating Factors | Overlapping Characteristics | Differentiating Factors |
| Interstitial lung disease Cutaneous manifestations
| Childhood GPA-specific skin lesions
Positive serum c-ANCA titers | Interstitial lung disease End-stage respiratory failure in adolescence | CF-specific multiorgan manifestations
CF screening tests
| Early-onset pulmonary manifestations | PIDDs respiratory findings
| Cutaneous manifestations
Musculoskeletal manifestations
Elevated peripheral blood IFN signature | AGS neurological manifestations
|
| STING1-Activating Mutations | Location | References |
|---|---|---|
| H72N | exon 3 | [30] |
| V147L | exon 5 | [1,31] |
| V147M | exon 5 | [32] |
| F153V | exon 5 | [30] |
| N154S | exon 5 | [1,3,17,33,34,35] |
| V155M | exon 5 | [1,33,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] |
| G158A | exon 5 | [30] |
| G166E | exon 5 | [44] |
| C206G | exon 6 | [45] |
| C206Y | exon 6 | [46,47] |
| G207E | exon 6 | [48] |
| F279L | exon 7 | [49] |
| R281W | exon 7 | [50] |
| R281Q | exon 7 | [33,46] |
| R284G | exon 7 | [46] |
| R284S | exon 7 | [51] |
| Therapeutic Agent | Mechanism of Action | Common Adverse Reactions | Therapeutic Use in Autoinflammatory Diseases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tofacitinib | JAK1/2/3 inhibition | Upper respiratory tract infections Diarrhea Headache | SAVI, AGS, CANDLE, COPA, FCL |
| Baricitinib | JAK1/2 inhibition | Upper respiratory tract infections | |
| Ruxolitinib | JAK1/2 inhibition |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drougkas, K.; Smerla, R.; Skarlis, C.; Mavragani, C.P. STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Review Focusing on Pathophysiology and Treatment Options. J. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 4, 294-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4040024
Drougkas K, Smerla R, Skarlis C, Mavragani CP. STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Review Focusing on Pathophysiology and Treatment Options. Journal of Molecular Pathology. 2023; 4(4):294-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrougkas, Konstantinos, Roubini Smerla, Charalampos Skarlis, and Clio P. Mavragani. 2023. "STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Review Focusing on Pathophysiology and Treatment Options" Journal of Molecular Pathology 4, no. 4: 294-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4040024
APA StyleDrougkas, K., Smerla, R., Skarlis, C., & Mavragani, C. P. (2023). STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy: A Review Focusing on Pathophysiology and Treatment Options. Journal of Molecular Pathology, 4(4), 294-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4040024






