Consumer Trust in AI–Human News Collaborative Continuum: Preferences and Influencing Factors by News Production Phases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
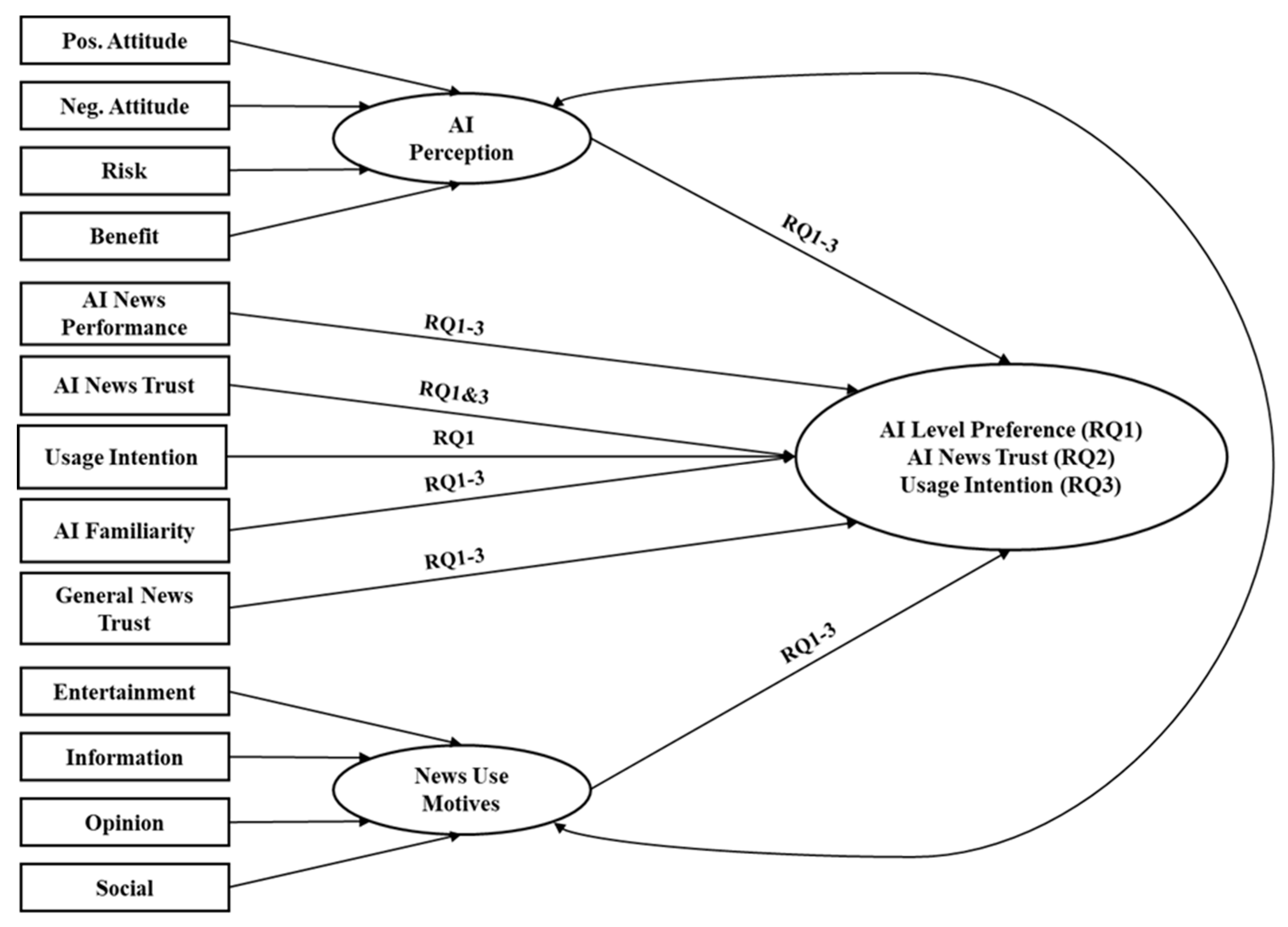
2. Conceptual Background and Research Questions
- RQ1: What are the consumer perceptions of and preferences for AI applications during the main news production phases of discovery/information gathering and writing/editing, and what factors within the news production process play a role in shaping these perceptions and preferences?
- RQ2: What factors affect consumer trust in news when AI is used in the news production process?
- RQ3: Which factors influence consumer intention to use the news as AI is used in the various phases of the production process?
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Measures
3.2.1. Production Phase and Level of Integration
3.2.2. AI Perception
3.2.3. AI Familiarity
3.2.4. AI News Performance
3.2.5. News Use Motives
3.2.6. General News Trust
3.2.7. AI News Trust
3.2.8. Usage Intention
3.3. Modeling Approach
4. Results
4.1. Consumers’ Preferred Level of AI Integration
4.2. AI Integration Level Impact on Consumers’ Trust in the News
4.3. AI Integration Level Impact on Consumers’ News Usage Intentions
5. Discussion and Conclusions
6. Limitations and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Item | Statement | Composite | Cronbach α | Construct | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Familiarity | How familiar would you say you are with AI use in news? | Familiarity with AI | AI Perception | (Chan-Olmsted and Luo 2022) | |
| Perception | In your opinion, when a news outlet creates news […] it should: [1–5] | AI Usage Perception | |||
| PosAtt1 | AI is useful for people’s daily lives | Positive Attitude towards AI | αPos = 0.83 | (Schepman and Rodway 2020) | |
| PosAtt2 | There are many beneficial applications of AI | ||||
| PosAtt3 | AI is exciting | ||||
| NegAtt1 | Organizations often use AI unethically | Negative Attitude towards AI | αneg = 0.83 | ||
| NegAtt2 | AI is threatening | ||||
| NegAtt3 | AI is dangerous | ||||
| Benefit1 | AI will be beneficial for democratic society | AI Benefit | αBenefit = 0.87 | (Bao et al. 2022) | |
| Benefit2 | AI will be beneficial for me personally | ||||
| Benefit3 | AI will be beneficial for most Americans | ||||
| Risk1 | AI will be risky for a democratic society | AI Risk | αRisk = 0.84 | ||
| Risk2 | AI will be risky for me personally | ||||
| Risk3 | AI will be risky for most Americans | ||||
| Entertainment1 | I consume news because it’s enjoyable | Entertainment Needs | α = 0.83 | News Use Motives | (Chan-Olmsted and Wang 2020; Lee 2013; Lin et al. 2004; Siakalli et al. 2015) |
| Entertainment2 | I consume news because it’s amusing | ||||
| Entertainment3 | I consume news because it’s entertaining | ||||
| Information1 | I consume news to keep up with what’s going on | Information Needs | α = 0.87 | ||
| Information2 | I consume news to learn about what’s happening around me | ||||
| Information3 | I consume news to get timely information | ||||
| Opinion1 | I consume news to know about others’ opinions | Opinion Needs | α = 0.78 | ||
| Opinion2 | I consume news to learn about other people’s viewpoints | ||||
| Opinion3 | I consume news to help form opinions on issues | ||||
| Social1 | I consume news to learn about things to converse with others | Social Needs | α = 0.77 | ||
| Social2 | I consume news to appear informed to those around me | ||||
| Social3 | I consume news to feel part of a community | ||||
| NewsTrust1 | News aims to inform the public | General News Trust | α = 0.85 | General News Trust | (Mourão et al. 2018) |
| NewsTrust2 | News is generally truthful | ||||
| NewsTrust3 | News is a reliable source of information | ||||
| NewsTrust4 | In general, news presents a true depiction of the world | ||||
| Performance1 | In the scenario [1–5] what would you expect the news content to be?—Errors | AI News Performance | Discovery: αNoAI = 0.79 αAISup = 0.82 αEqual = 0.84 αHumanSup = 0.86 αAIOnly = 0.87 Writing: αNoAI = 0.8 αAISup = 0.84 αEqual = 0.86 αHumanSup = 0.86 αAIOnly = 0.87 | AI News Performance | (Gursoy et al. 2019) |
| Performance2 | In the scenario [1–5] what would you expect the news content to be?—Consistency | ||||
| Performance3 | In the scenario [1–5] what would you expect the news content to be?—Accuracy | ||||
| Intention1 | I would consume the news without hesitation | News Usage Intention | Discovery: αNoAI = 0.87 αAISup = 0.89 αEqual = 0.9 αHumanSup = 0.91 αAIOnly = 0.93 Writing: αNoAI = 0.89 αAISup = 0.9 αEqual = 0.9 αHumanSup = 0.92 αAIOnly = 0.93 | News Usage Intention | (Venkatesh et al. 2012) |
| Intention2 | I think consuming the news would lead to positive outcomes | ||||
| Intention3 | I would feel comfortable relying on the news | ||||
| Intention4 | I would plan to consume the news regularly | ||||
| Trust Ranking | Please rank-order the level of trust you would have on the news content in the following scenarios concerning the use of AI in the “discovery and information gathering” news phase. | AI News Trust | AI News Trust | (Chan-Olmsted 2019; Domingo et al. 2008; Marconi 2020) |
| No AI | AI Support | Equal | Human Support | AI Only | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor Loadings | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | |
| Model Fit Indices | χ2 | 968.97 | 977.15 | 1027.92 | 983.76 | 1071.92 | 1029.64 | 1036.6 | 1039.62 | 1078.2 | 1129.58 |
| RMSEA | 0.141 | 0.141 | 0.145 | 0.142 | 0.149 | 0.145 | 0.146 | 0.146 | 0.149 | 0.153 | |
| CFI | 0.602 | 0.601 | 0.58 | 0.598 | 0.57 | 0.587 | 0.59 | 0.595 | 0.583 | 0.578 | |
| p | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| No AI | AI Support | Equal | Human Support | AI Only | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor Loadings | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | |
| Model Fit Indices | χ2 | 755.76 | 790.26 | 827.91 | 834.28 | 841.64 | 849.99 | 840.13 | 861.8 | 886.46 | 905.75 |
| RMSEA | 0.143 | 0.147 | 0.15 | 0.151 | 0.152 | 0.153 | 0.152 | 0.154 | 0.156 | 0.158 | |
| CFI | 0.636 | 0.634 | 0.61 | 0.606 | 0.607 | 0.601 | 0.607 | 0.604 | 0.595 | 0.592 | |
| p | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| No AI | AI Support | Equal | Human Support | AI Only | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor Loadings | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | |
| Model Fit Indices | χ2 | 835.2 | 858.08 | 887.04 | 853.14 | 889.15 | 896.53 | 882.05 | 897.86 | 945.19 | 957.32 |
| RMSEA | 0.139 | 0.141 | 0.144 | 0.141 | 0.144 | 0.145 | 0.144 | 0.145 | 0.149 | 0.15 | |
| CFI | 0.681 | 0.674 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.663 | 0.661 | 0.668 | 0.662 | 0.654 | 0.655 | |
| p | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
References
- Andriole, Steve. 2018. AI: The Good, the Disruptive, and the Scary. Cutter Business Technology Journal 31: 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ariely, Gal. 2015. Trusting the press and political trust: A conditional relationship. Journal of Elections, Public Opinion and Parties 25: 351–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Luye, Nicole M. Krause, Mikhaila N. Calice, Dietram A. Scheufele, Christopher D. Wirz, Dominique Brossard, Todd P. Newman, and Michael A. Xenos. 2022. Whose AI? How different publics think about AI and its social impacts. Computers in Human Behavior 130: 107182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benes, Ross. 2018. How Flipboard Sorts through Hundreds of Thousands of Articles Each Day. Insider Intelligence. March 22. Available online: https://www.insiderintelligence.com/content/publishers-use-ai-for-content-recommendations-and-ad-targeting (accessed on 24 November 2022).
- Bitkina, Olga V., Heejin Jeong, Byung Cheol Lee, Jangwoon Park, Jaehyun Park, and Hyun K. Kim. 2020. Perceived trust in artificial intelligence technologies: A preliminary study. Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing & Service Industries 30: 282–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, Meredith, Nicholas Diakopoulos, Andrea L. Guzman, Rediet Abebe, Michel Dupagne, and Ching-Hua Chuan. 2019. Artificial intelligence and journalism. Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly 96: 673–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, Tathagata, Subbarao Kambhampati, Matthias Scheutz, and Yu Zhang. 2017. AI challenges in human-robot cognitive teaming. arXiv arXiv:1707.04775. [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Olmsted, Sylvia M. 2019. A review of artificial intelligence adoptions in the media industry. International Journal on Media Management 21: 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Olmsted, Sylvia M., and Anran Luo. 2022. Application of AI in Media Content Production: Perception, Decision, and Intention to Use. Paper presented at 2022 AEJMC, Detroit, MI, USA, August 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Olmsted, Sylvia M., and Rang Wang. 2020. Understanding podcast users: Consumption motives and behaviors. New Media & Society 24: 684–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Keliang, Yunxiao Zu, and Danzhi Wang. 2021. Design and implementation of intelligent creation platform based on artificial intelligence technology. Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering 20: 1109–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, Jose. M. 1993. What is coefficient alpha? An examination of theory and applications. Journal of Applied Psychology 78: 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ballester, Elena, and José Luis Munuera-Alemán. 2005. Does brand trust matter to brand equity? Journal of Product & Brand Management 14: 187–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-Lima-Santos, Mathias-Felipe, and Wilson Ceron. 2021. Artificial intelligence in news media: Current perceptions and future outlook. Journalism and Media 3: 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, David, Thorsten Quandt, Ari Heinonen, Steve Paulussen, Jane B. Singer, and Marina Vujnovic. 2008. Participatory Journalism Practices in the Media and Beyond. Journalism Practice 2: 326–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Liang, Reid G. Smithm, and Bruce G. Buchanan. 2011. Automating the selection of storiesfor AI in the news. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 176–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillath, Omri, Ting Ai, Michael S. Branicky, Shawn Keshmiri, Robert B. Davison, and Ryan Spaulding. 2021. Attachment and trust in artificial intelligence. Computers in Human Behavior 115: 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glikson, Ella, and Anita Williams Woolley. 2020. Human Trust in Artificial Intelligence: Review of empirical research. Academy of Management Annals 14: 627–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy, Dogan, Oscar Hengxuan Chi, Lu Lu, and Robin Nunkoo. 2019. Consumers acceptance of artificially intelligent (AI) device use in service delivery. International Journal of Information Management 49: 157–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurviez, Patricia, and Michaël Korchia. 2003. Proposal for a Multidimensional Brand Trust Scale. Paper presented at 32nd EMAC Conference Proceedings, Glasgow, UK, May 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, Steffen, Sylvia Chan-Olmsted, Claudia Fantapié Altobelli, Michael Fretschner, and Lisa-Charlotte Wolter. 2022. Exploring Trust in Media Brands today: Definition, Dimensions and cross-national Differences. Discussion Paper of the Institute for Marketing at Helmut Schmidt University Hamburg 11: 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hofeditz, Lennart, Milad Mirbabaie, Jasmin Holstein, and Stefan Stieglitz. 2021. Do you trust the AI-journalist? A credibility analysis of news content with AI-authorship. Paper presented at ECIS 2021 Proceedings, Marrakech, Morocco, June 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Daewon, and Seongcheol Kim. 2017. Newspaper companies’ determinants in adopting robot journalism. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 117: 184–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Soyoung, and Boyoung Kim. 2020. A decision-making model for adopting al-generated news articles: Preliminary results. Sustainability 12: 7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohring, Matthias, and Jörg Matthes. 2007. Trust in news media. Communication Research 34: 231–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolo, Castulus, Joschka Mütterlein, and Sarah Anna Schmid. 2022. Believing journalists, AI, or fake news: The role of trust in media. Paper presented at the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, January 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, Roderick M., and Tom R. Tyler. 1996. Trust in Organizations: Frontiers of Theory and Research. Thousand Oaks: SAGE. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, Markus, and Richard N. Landers. 2021. The future of artificial intelligence at work: A review on effects of decision automation and augmentation on workers targeted by algorithms and third-party observers. Computers in Human Behavior 123: 106878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Angela M. 2013. News audiences revisited: Theorizing the link between audience motivations and news consumption. Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media 57: 300–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Sangwon, Seungahn Nah, Deborah S. Chung, and Junghwan Kim. 2020. Predicting AI news credibility: Communicative or social capital or both? Communication Studies 71: 428–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Joon Soo, and Jun Zhang. 2022. Adoption of AI-driven personalization in digital news platforms: An integrative model of technology acceptance and perceived contingency. Technology in Society 69: 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Joon Soo, Donghee Shin, Jun Zhang, Stephen Masiclat, Regina Luttrell, and Dennis Kinsey. 2022. News audiences in the age of artificial intelligence: Perceptions and behaviors of optimizers, mainstreamers, and skeptics. Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media 67: 353–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Carolyn, Michael B. Salwen, and Rasha A. Abdulla. 2004. Uses and gratifications of online and offline news: New wine in an old bottle? In Online News and the Public. London: Routledge, pp. 241–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, Francesco. 2020. Newsmakers: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Journalism. New York: Columbia University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Mourão, Rachel R., Esther Thorson, Weiyue Chen, and Samuel M. Tham. 2018. Media repertoires and news trust during the early Trump administration. Journalism Studies 19: 1945–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoriyarwa, Allen, Sarah Chiumbu, and Gilbert Motsaathebe. 2021. Artificial intelligence practices in everyday news production: The case of South Africa’s mainstream newsrooms. Journalism Practice 17: 1374–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munuera-Aleman, Jose Luis, Elena Delgado-Ballester, and Maria Jesus Yague-Guillen. 2003. Development and validation of a brand trust scale. International Journal of Market Research 45: 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigall, Christoph, Ulf Kroehne, Friedrich Funke, and Rolf Steyer. 2003. (Why) Should We Use SEM? Pros and Cons of Structural Equation Modeling. Methods of Psychological Research Online 8: 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Owsley, Chad S., and Keith Greenwood. 2022. Awareness and perception of artificial intelligence operationalized integration in news media industry and society. AI & Society, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, Sebastian, and Sebastian Krakowski. 2021. Artificial intelligence and management: The automation–augmentation paradox. Academy of Management Review 46: 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuters. 2023. Google Explores AI Tools for Journalists, in Talks with Publishers. Reuters. July 20. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/technology/google-explores-ai-tools-journalists-talks-with-publishers-spokesperson-2023-07-20/ (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Samek, Wojciech, and Klaus-Robert Müller. 2019. Towards explainable artificial intelligence. In Explainable AI: Interpreting, Explaining and Visualizing Deep Learning. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer International Publishing, pp. 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepman, Astrid, and Paul Rodway. 2020. Initial validation of the general attitudes towards Artificial Intelligence Scale. Computers in Human Behavior Reports 1: 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schranz, Mario, Jörg Schneider, and Mark Eisenegger. 2018. Media trust and media use. In Trust in Media and Journalism. Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, pp. 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, Ivor. 2010. Evaluating journalism. Journalism Practice 4: 143–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siakalli, Michailina, Andreas Masouras, and Christos Papademetriou. 2015. Understanding online news: Uses and gratifications of mainstream news sites and social media. International Journal of Strategic Innovative Marketing 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovsgaard, Morten, Erik Albæk, Peter Bro, and Claes de Vreese. 2012. Media professionals or organizational marionettes? Professional values and constraints of Danish journalists. In The Global Journalist in the 21st Century. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Mi-Kyung, Feng-Chang Lin, Sandra E. Ward, and Jason P. Fine. 2013. Composite variables. Nursing Research 62: 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridou, Lia-Paschalia, and Andreas Veglis. 2016. Convergence and the changing labor of journalism: Towards the ‘super journalist’ paradigm. In Media Convergence Handbook. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, vol. 1, pp. 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, Viswanath, James Y. L. Thong, and Xin Xu. 2012. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Quarterly 36: 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xuya, and Feng Zhu. 2021. The application of artificial intelligence in AI news anchor. Paper presented at 2021 International Conference on Big Data Analytics for Cyber-Physical System in Smart City, Bangkok, Thailand, December 16–17; Singapore: Springer, pp. 1093–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Shangyuan, Edson C. Tandoc Jr., and Charles T. Salmon. 2018. Journalism reconfigured. Journalism Studies 20: 1440–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Xuelin. 2021. Psychological Factors in Consumer Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence in Leisure Economy: A Structural Equation Model. Journal of Internet Technology 22: 697–705. [Google Scholar]
| No AI | AI Support | Equal | Human Support | AI Only | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor Loadings | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri |
| PosAtt → AI Perception | 0.649 *** | 0.664 | 0.662 *** | 0.672 *** | 0.650 *** | 0.669 *** | 0.654 *** | 0.661 *** | 0.662 *** | 0.668 *** |
| NegAtt → AI Perception | −0.291 *** | −0.295 *** | −0.294 *** | −0.296 *** | −0.292 *** | −0.296 *** | −0.292 *** | −0.294 *** | −0.293 *** | −0.294 *** |
| Risk → AI Perception | −0.213 *** | −0.219 *** | −0.220 *** | −0.223 *** | −0.214 *** | −0.222 *** | −0.216 *** | −0.218 *** | −0.218 *** | −0.221 *** |
| Benefit → AI Perception | 0.928 *** | 0.908 *** | 0.910 *** | 0.898 *** | 0.927 *** | 0.901 *** | 0.921 *** | 0.912 *** | 0.912 *** | 0.903 *** |
| Entertainment → News Use Motivation | 0.654 *** | 0.652 *** | 0.653 *** | 0.650 *** | 0.653 *** | 0.650 *** | 0.653 *** | 0.651 *** | 0.652 *** | 0.650 *** |
| Information → News Use Motivation | 0.506 *** | 0.509 *** | 0.507 *** | 0.512 *** | 0.508 *** | 0.513 *** | 0.508 *** | 0.513 *** | 0.508 *** | 0.512 *** |
| Opinion → News Use Motivation | 0.801 *** | 0.803 *** | 0.801 *** | 0.804 *** | 0.802 *** | 0.805 *** | 0.802 *** | 0.804 *** | 0.802 *** | 0.804 *** |
| Social → News Use Motivation | 0.823 *** | 0.821 *** | 0.822 *** | 0.820 *** | 0.822 *** | 0.819 *** | 0.822 *** | 0.819 *** | 0.822 *** | 0.820 *** |
| Path Coefficients | ||||||||||
| AI Perception → AI Level Preference | 0.257 *** | 0.273 *** | 0.293 *** | 0.331 *** | 0.294 *** | 0.332 *** | 0.235 *** | 0.213 *** | 0.210 *** | 0.199 *** |
| AI Use Motivation → AI Level Preference | 0.023 | −0.046 | 0.000 | −0.130 ** | −0.025 | −0.146 ** | −0.021 | −0.130 ** | −0.012 | −0.137 ** |
| AI Performance → AI Level Preference | −0.013 | −0.052 | 0.036 | 0.055 | 0.079 * | −0.011 | 0.066 | 0.095 * | 0.080 | 0.119 ** |
| AI News Trust → AI Level Preference | −0.190 *** | −0.060 | −0.152 *** | −0.157 *** | 0.025 | −0.020 | 0.137 *** | 0.109** | 0.140 *** | 0.097 * |
| AI Familiarity → AI Level Preference | −0.099** | 0.164 *** | 0.111 ** | 0.168 *** | 0.134 *** | 0.173 *** | 0.105 | 0.152 *** | 0.080 | 0.134 ** |
| Usage Intention → AI Level Preference | −0.045 | −0.166 *** | −0.039 | −0.058 | −0.005 | 0.041 | 0.080 | 0.117 ** | 0.123 ** | 0.133 ** |
| General News Trust → AI Level Preference | 0.009 | 0.002 | −0.033 | −0.076 | −0.052 | −0.109 ** | −0.061 | −0.107 ** | −0.044 | −0.099 ** |
| Covariances | ||||||||||
| AI Perception ↔ News Use Motives | 0.482 *** | 0.486 *** | 0.486 *** | 0.487 *** | 0.482 *** | 0.487 *** | 0.483 *** | 0.485 *** | 0.486 *** | 0.487 *** |
| No AI | AI Support | Equal | Human Support | AI Only | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor Loadings | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri |
| PosAtt → AI Perception | 0.678 *** | 0.651 *** | 0.595 *** | 0.633 *** | 0.663 *** | 0.661 *** | 0.643 *** | 0.645 *** | 0.621 *** | 0.623 *** |
| NegAtt → AI Perception | −0.302 *** | −0.299 *** | −0.275 *** | −0.288 *** | −0.295 *** | −0.293 *** | −0.290 *** | −0.291 *** | −0.285 *** | −0.285 *** |
| Risk → AI Perception | −0.236 *** | −0.219 *** | −0.186 *** | −0.205 *** | −0.221 *** | −0.217 *** | −0.210 *** | −0.212 *** | −0.200 *** | −0.201 *** |
| Benefit → AI Perception | 0.886 *** | 0.923 *** | 10.007 *** | 0.950 *** | 0.909 *** | 0.913 *** | 0.937 *** | 0.933 *** | 0.967 *** | 0.965 *** |
| Entertainment → News Use Motivation | 0.652 *** | 0.652 *** | 0.654 *** | 0.654 *** | 0.652 *** | 0.649 *** | 0.653 *** | 0.651 *** | 0.648 *** | 0.652 *** |
| Information → News Use Motivation | 0.510 *** | 0.508 *** | 0.510 *** | 0.507 *** | 0.509 *** | 0.511 *** | 0.508 *** | 0.511 *** | 0.518 *** | 0.512 *** |
| Opinion → News Use Motivation | 0.804 *** | 0.803 *** | 0.802 *** | 0.800 *** | 0.802 *** | 0.803 *** | 0.801 *** | 0.805 *** | 0.806 *** | 0.803 *** |
| Social → News Use Motivation | 0.820 *** | 0.821 *** | 0.820 *** | 0.823 *** | 0.822 *** | 0.822 *** | 0.822 *** | 0.819 *** | 0.816 *** | 0.819 *** |
| Path Coefficients | ||||||||||
| AI Perception → AI News Trust | −0.321 *** | −0.374 *** | −0.277 *** | −0.109 * | 0.204 *** | 0.185 *** | 0.109 * | 0.133 ** | 0.148 *** | 0.105 * |
| News Use Motivation → AI News Trust | 0.112 * | 0.084 | 0.077 | −0.015 | −0.004 | 0.088 | −0.053 | −0.148 ** | −0.173 *** | −0.085 |
| AI Performance → AI News Trust | 0.155 *** | 0.213 *** | 0.109 ** | 0.162 *** | 0.127 *** | 0.067 | 0.122 *** | 0.153 *** | 0.170 *** | 0.122 *** |
| AI Familiarity → AI News Trust | −0.106 ** | −0.096 ** | −0.083 * | −0.080 * | 0.015 | −0.095 * | 0.079 | 0.092 * | 0.142 *** | 0.206 *** |
| General News Trust → AI News Trust | 0.169 *** | 0.085 * | 0.057 | 0.036 | −0.130 *** | −0.106 ** | −0.057 | −0.069 | −0.119 *** | −0.069 |
| Covariances | ||||||||||
| AI Perception ↔ News Use Motives | 0.489 *** | 0.482 *** | 0.453 *** | 0.475 *** | 0.486 *** | 0.485 *** | 0.479 *** | 0.479 *** | 0.467 *** | 0.469 *** |
| No AI | AI Support | Equal | Human Support | AI Only | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor Loadings | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri | Dis | Wri |
| PosAtt → AI Perception | 0.653 *** | 0.651 *** | 0.635 *** | 0.636 *** | 0.641 *** | 0.642 *** | 0.617 *** | 0.619 *** | 0.614 *** | 0.618 *** |
| NegAtt → AI Perception | −0.293 *** | −0.292 *** | −0.290 *** | −0.289 *** | −0.290 *** | −0.288 *** | −0.285 *** | −0.284 *** | −0.283 *** | −0.285 *** |
| Risk → AI Perception | −0.215 *** | −0.213 *** | −0.207 *** | −0.205 *** | −0.213 *** | −0.209 *** | −0.199 *** | −0.198 *** | −0.197 *** | −0.197 *** |
| Benefit → AI Perception | 0.922 *** | 0.926 *** | 0.946 *** | 0.947 *** | 0.939 *** | 0.939 *** | 0.972 *** | 0.971 *** | 0.977 *** | 0.972 *** |
| Entertainment → News Use Motivation | 0.651 *** | 0.654 *** | 0.657 *** | 0.653 *** | 0.654 *** | 0.658 *** | 0.660 *** | 0.658 *** | 0.659 *** | 0.660 *** |
| Information → News Use Motivation | 0.527 *** | 0.517 *** | 0.517 *** | 0.512 *** | 0.515 *** | 0.509 *** | 0.499 *** | 0.502 *** | 0.499 *** | 0.499 *** |
| Opinion → News Use Motivation | 0.806 *** | 0.806 *** | 0.795 *** | 0.801 *** | 0.799 *** | 0.796 *** | 0.791 *** | 0.794 *** | 0.793 *** | 0.791 *** |
| Social → News Use Motivation | 0.810 *** | 0.813 *** | 0.821 *** | 0.821 *** | 0.820 *** | 0.823 *** | 0.830 *** | 0.827 *** | 0.829 *** | 0.830 *** |
| Path Coefficients | ||||||||||
| AI Perception → Usage Intention | −0.098 * | −0.076 | 0.218 *** | 0.227 *** | 0.347 *** | 0.337 *** | 0.379 *** | 0.367 *** | 0.344 *** | 0.390 *** |
| News Use Motivation → Usage Intention | 0.447 *** | 0.417 *** | 0.337 *** | 0.301 *** | 0.291 *** | 0.196 *** | 0.177 *** | 0.166 *** | 0.167 *** | 0.200 *** |
| AI Performance → Usage Intention | 0.153 *** | 0.122 *** | 0.141 *** | 0.095 ** | 0.158 *** | 0.180 *** | 0.226 *** | 0.211 *** | 0.208 *** | 0.175 *** |
| AI News Trust → Usage Intention | 0.157 *** | 0.151 *** | 0.033 | 0.073 * | 0.037 | 0.025 | 0.092 *** | 0.097 ** | 0.218 *** | 0.246 *** |
| AI Familiarity → Usage Intention | −0.016 | −0.012 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.055 | 0.037 | 0.100 ** | 0.121 *** | 0.171 *** | 0.113 *** |
| General News Trust → Usage Intention | 0.438 *** | 0.422 *** | 0.341 *** | 0.351 *** | 0.224 *** | 0.291 *** | 0.165 *** | 0.155 *** | 0.110 *** | 0.074 * |
| Covariances | ||||||||||
| AI Perception ↔ News Use Motives | 0.482 *** | 0.481 *** | 0.478 *** | 0.476 *** | 0.479 *** | 0.480 *** | 0.470 *** | 0.470 *** | 0.468 *** | 0.470 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heim, S.; Chan-Olmsted, S. Consumer Trust in AI–Human News Collaborative Continuum: Preferences and Influencing Factors by News Production Phases. Journal. Media 2023, 4, 946-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia4030061
Heim S, Chan-Olmsted S. Consumer Trust in AI–Human News Collaborative Continuum: Preferences and Influencing Factors by News Production Phases. Journalism and Media. 2023; 4(3):946-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia4030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeim, Steffen, and Sylvia Chan-Olmsted. 2023. "Consumer Trust in AI–Human News Collaborative Continuum: Preferences and Influencing Factors by News Production Phases" Journalism and Media 4, no. 3: 946-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia4030061
APA StyleHeim, S., & Chan-Olmsted, S. (2023). Consumer Trust in AI–Human News Collaborative Continuum: Preferences and Influencing Factors by News Production Phases. Journalism and Media, 4(3), 946-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia4030061







