‘All Fishing Is Wildlife Poaching:’ Nonhuman Animal Imagery and Mutual Avowal in Racing Extinction and Seaspiracy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Racing Extinction and Seaspiracy—Context and Synopsis
4. Methodology
5. Results
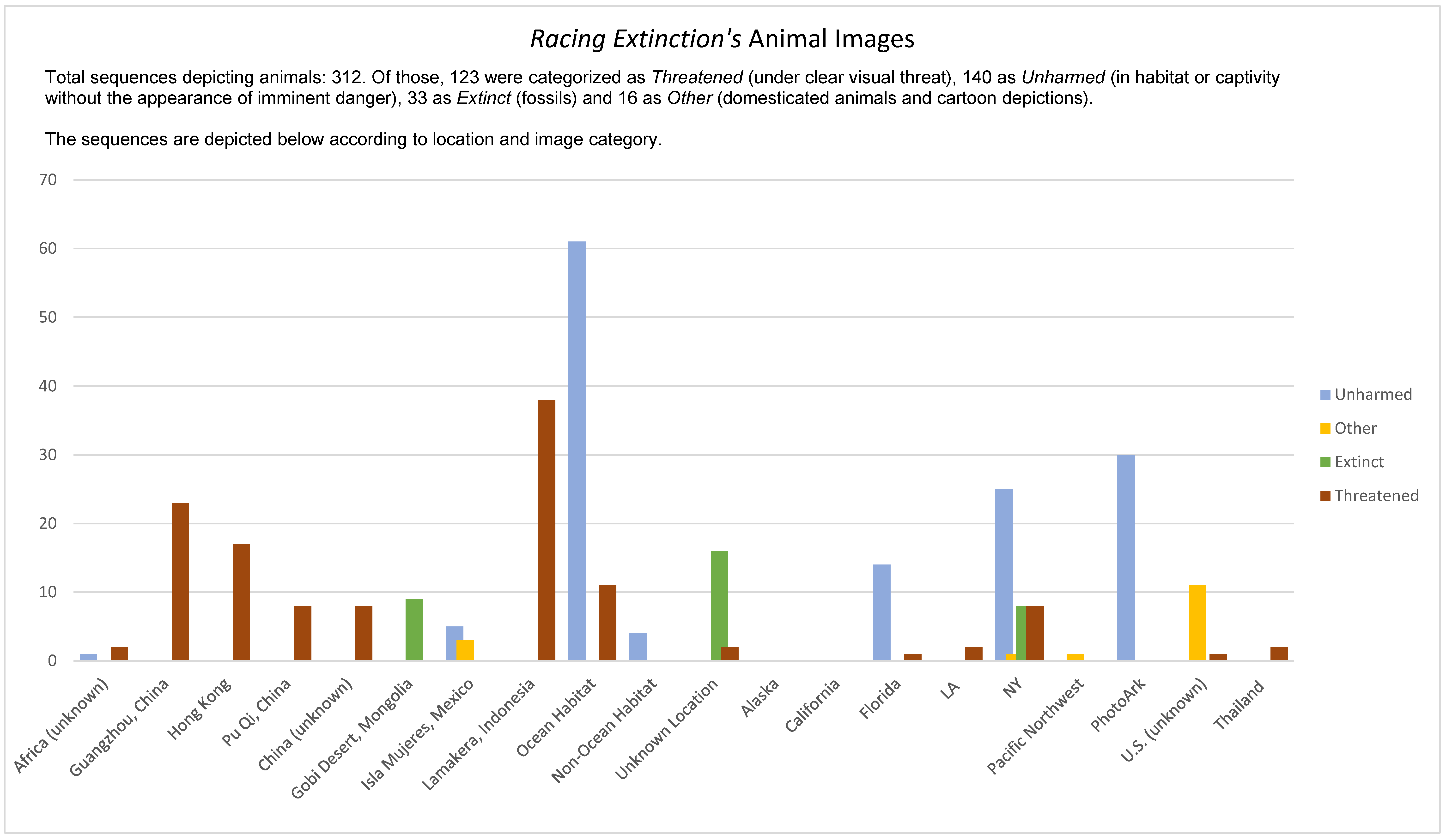
5.1. Racing Extinction’s Visuals
5.1.1. Unharmed Wildlife
5.1.2. Extinct Animals
5.1.3. Threatened Animals
5.1.4. Threatening Actors
5.1.5. Other
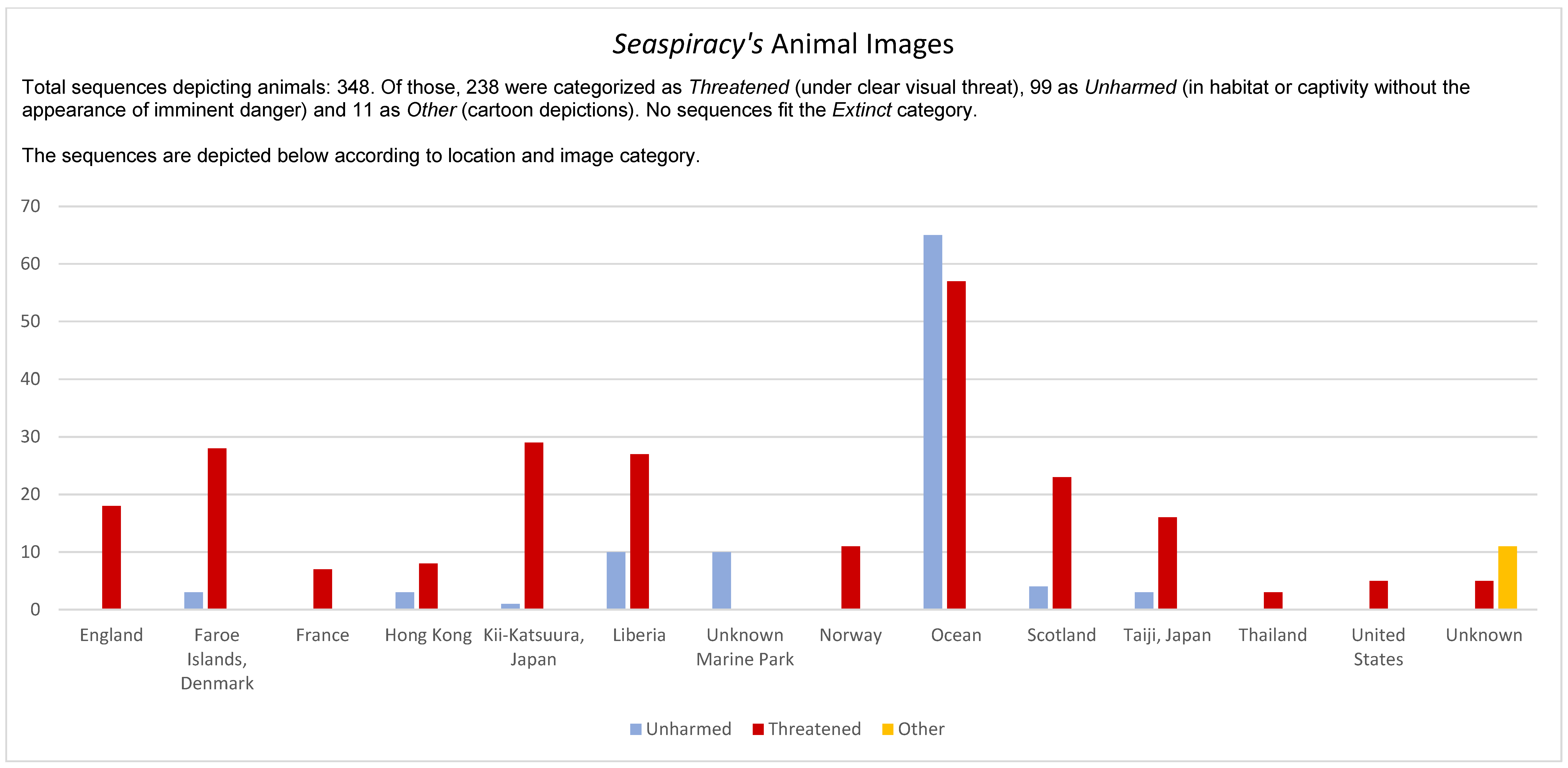
5.2. Seaspiracy’s Visuals
5.2.1. Unharmed Wildlife
5.2.2. Threatened Animals
5.2.3. Threatening Actors
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The use of the term “wildlife” is intended to represent nonhuman animals who are free-living (non-domesticated) and not meaning “wild” in a derogatory sense. |
References
- Aaltola, Elisa. 2014. Animal suffering: Representations and the act of looking. Anthrozoos 27: 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, Carol. 2015a. The Sexual Politics of Meat: A Feminist-Vegetarian Critical Theory. London: Bloomsbury Publishing USA. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, Carol. 2015b. Consumer Vision: Speciesism, Misogyny, and Media. In Critical Animal and Media Studies. New York: Routledge, pp. 70–87. [Google Scholar]
- Almiron, Núria. 2019. Greening animal defense? Examining whether appealing to climate change and the environment is an effective advocacy strategy to reduce oppression of nonhumans. American Behavioral Scientist 63: 1101–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almiron, Núria, and Catia Faria. 2019. Climate Change Impacts on Free-Living Nonhuman Animals. Challenges for Media and Communication Ethics. Studies in Media and Communication 7: 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Almiron, Núria, Matthew Cole, and Carrie Packwood Freeman. 2016. Critical Animal and Media Studies. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Recarte, Claudia. 2022. Tiger King and the Exegesis of COVID-19 Media Coverage of Nonhuman Animals. Journalism and Media 3: 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiot, Catherine, and Brock Bastian. 2017. Solidarity with animals: Assessing a relevant dimension of social identification with animals. PLoS ONE 12: e0168184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekoff, Marc. 2010. Vegans Shouldn’t Eat Oysters, and If You Do You’re Not Vegan, So... Huffington Post. June 10. Available online: https://www.huffpost.com/entry/vegans-shouldnt-eat-oyste_b_605786 (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Belhabib, Dyhia. 2021. Ocean science and advocacy work better when decolonized. Nature Ecology & Evolution 5: 709–10. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, John. 1980. Why Look at Animals? In About Looking. New York: Pantheon Books. [Google Scholar]
- Bergin, Daniel, Derek Wu, and Wander Meijer. 2020. Response to “The imaginary ‘Asian Super Consumer’: A critique of demand reduction campaigns for the illegal wildlife trade”. Geoforum 117: 285–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, Hollie, Ulfah Mardhiah, Hanifah Siregar, Jonathan Hunter, Giyanto, Mochamad Iqbal Herwata Putra, Jo Marlow, Andi Cahyana, Boysandi, Apolinardus Yosef Lia Demoor, and et al. 2021. An integrated approach to tackling wildlife crime: Impact and lessons learned from the world’s largest targeted manta ray fishery. Conservation Science and Practice 3: e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgi, Marta, and Francesca Cirulli. 2016. Pet face: Mechanisms underlying human-animal relationships. Frontiers in Psychology 7: 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, Dorothea. 2019. Bearing witness? Polar bears as icons for climate change communication in National Geographic. Environmental Communication 13: 649–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, Dorothea. 2021. Polar bears as cultural symbols. In Communicating Endangered Species: Extinction, News and Public Policy. Edited by Eeric Freedman, Sara Shipley Hiles and David Sachsman. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Bousé, Derek. 2011. Wildlife Films. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. [Google Scholar]
- Brereton, Pat. 2015. Environmental Ethics and Film. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Broad, Garrett. 2016. Animal production, Ag-gag laws, and the social production of ignorance: Exploring the role of storytelling. Environmental Communication 10: 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, Matthew. 2011. Developing Animals: Wildlife and Early American Photography. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, Jonathan. 2002. Animals in Film. London: Reaktion Books. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, Vincent. 2014. Framing environmental risks and natural disasters in factual entertainment television. Environmental Communication 8: 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, Iri. 2021. Jumping the Shark: White Shark Representations in Great White Serial Killer Lives—The Fear and the (Pseudo-) Science. Journalism and Media 2: 584–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Darren, and Lauren Corman. 2021. Multispecies disposability: Taxonomies of power in a global pandemic. Animal Studies Journal 10: 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chris, Cynthia. 2006. Watching Wildlife. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, Matthew. 2015. Getting (green) beef: Anti-vegan rhetoric and the legitimizing of eco-friendly oppression. In Critical Animal and Media Studies. New York: Routledge, pp. 121–37. [Google Scholar]
- Collard, Rosemary-Claire. 2020. Animal Traffic: Lively Capital in the Global Exotic Pet Trade. Durham: Duke University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, Christopher. 2010. Consider the Oyster. Slate. April 7. Available online: https://slate.com/human-interest/2010/04/it-s-ok-for-vegans-to-eat-oysters.html (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Crenshaw, Kimberlé. 1989. Demarginalizing the intersection of race and sex: A black feminist critique of antidiscrimination doctrine, feminist theory and antiracist politics. In Feminist Legal Theory. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Deckha, Maneesha. 2008. Intersectionality and posthumanist visions of equality. Wisconsin Journal of Law, Gender & Society 23: 249. [Google Scholar]
- Derrida, Jacques. 2008. The Animal That therefore I Am. New York: Fordham University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Domke, David, David Perlmutter, and Meg Spratt. 2002. The primes of our times? An examination of the ‘power’ of visual images. Journalism 3: 131–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Ran, Katherine Hepworth, Kerri Jean Ormerod, and Chelsea Canon. 2021. Promoting Concern for Climate Change: A Study of Wildfire Photographs Using Q Methodology. Science Communication 43: 624–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulvy, Nicholas K., Nathan Pacoureau, Cassandra L. Rigby, Riley A. Pollom, Rima W. Jabado, David A. Ebert, Brittany Finucci, Caroline M. Pollock, Jessica Cheok, Danielle H. Derrick, and et al. 2021. Overfishing drives over one-third of all sharks and rays toward a global extinction crisis. Current Biology 31: 4773–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliz, Julia. 2017. The Case for Vegans Eating Oysters, Mussels, & Other Invertebrates? Medium. March 18. Available online: https://medium.com/@jd.feliz/the-case-for-vegans-eating-oysters-mussels-other-invertebrates-961747367305 (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Fernández, Laura. 2019. Using images of farmed animals in environmental advocacy: An antispeciesist, strategic visual communication proposal. American Behavioral Scientist 63: 1137–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, Laura. 2021. Images That Liberate: Moral Shock and Strategic Visual Communication in Animal Liberation Activism. Journal of Communication Inquiry 45: 138–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francione, Gary. 2020. Veganism as a Moral Imperative. In Why Veganism Matters. New York: Columbia University Press, pp. 124–65. [Google Scholar]
- Francione, Gary, and Anna Charlton. 2017. Advocate for Animals!: An Abolitionist Vegan Handbook. Providence: Exempla Press. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, Robert, Jr., Anthony Nelson, Michelle Baker, Joseph Beeney, Theresa Vescio, Aurora Lenz-Watson, and Reginald Adams, Jr. 2013. Neural responses to perceiving suffering in humans and animals. Social Neuroscience 8: 217–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, Carrie Packwood. 2009. This little piggy went to press: The American news media’s construction of animals in agriculture. The Communication Review 12: 78–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, Carrie Packwood. 2012. Fishing for animal rights in The Cove: A holistic approach to animal advocacy documentaries. Journal for Critical Animal Studies 10: 104–18. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, Carrie Packwood. 2014. Framing Farming: Communication Strategies for Animal Rights. New York: Rodopi. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, Carrie Packwood, and Debra Merskin. 2015. Respectful representation: An animal issues style guide for all media practitioners. In Critical Animal and Media Studies. New York: Routledge, pp. 219–34. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, Carrie Packwood, and Scott Tulloch. 2013. Was blind but now I see: Animal liberation documentaries’ deconstruction of barriers to witnessing injustice. In Screening Nature: Cinema Beyond the Human. Oxford: Berghahn Books. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnthorsdottir, Anna. 2001. Physical attractiveness of an animal species as a decision factor for its preservation. Anthrozoös 14: 204–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, Anders, and David Machin. 2008. Visually branding the environment: Climate change as a marketing opportunity. Discourse Studies 10: 777–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, Melissa. 2013. Regulating abjection: Disgust, tolerance, and the politics of The Cove. ESC: English Studies in Canada 39: 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, Claire. 2014. A cow’s eye view? Cattle empathy and ethics in screen representations of Temple Grandin. Animal Studies Journal 3: 6–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, Martin. 2001. Empathy and Moral Development: Implications for Caring and Justice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Huggan, Graham. 2016. Never-ending stories, ending narratives: Polar bears, climate change populism, and the recent history of British nature documentary film. In Affect, Space and Animals. Edited by Jopi Nyman and Nora Schuurman. Abingdon: Taylor and Francis, pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. 2021. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Edited by Valérie Masson-Delmotte, Panmao Zhai, Anna Pirani, Sarah Connors, Clotilde Péan, Sophie Berger, Nada Caud, Yang Chen, Leah Goldfarb, Melissa Gomis and et al. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Kakoudaki, Despina. 2002. Spectacles of history: Race relations, melodrama, and the science fiction/disaster film. Camera Obscura 17: 1–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalof, Linda, Joe Zammit-Lucia, and Jennifer Rebecca Kelly. 2011. The meaning of animal portraiture in a museum setting: Implications for conservation. Organization & Environment 24: 150–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kalof, Linda, Joe Zammit-Lucia, Jessica Bell, and Gina Granter. 2016. Fostering kinship with animals: Animal portraiture in humane education. Environmental Education Research 22: 203–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Claire Jean. 2015. Dangerous Crossings. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Aph. 2019. Racism as Zoological Witchcraft: A Guide to Getting Out. New York: Lantern Books. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Aph, and Syl Ko. 2017. Aphro-Ism: Essays on Pop Culture, Feminism, and Black Veganism from Two Sisters. Brooklyn: Lantern Publishing & Media. [Google Scholar]
- Korban, Demi. 2021. ‘Seaspiracy’ leaps into Netflix top 10 as social media frenzy hits seafood industry. IntraFish. March 29. Available online: https://www.intrafish.com/analysis/seaspiracy-leaps-into-netflix-top-10-as-social-media-frenzy-hits-seafood-industry/2-1-989318 (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- Le Busque, Brianna, and Carla Litchfield. 2021. Sharks on film: An analysis of how shark-human interactions are portrayed in films. Human Dimensions of Wildlife 27: 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerberg, Matthew. 2016. Jabbering Jaws: Reimagining Representations of Sharks Post-Jaws. In Screening the Nonhuman: Representations of Animal Others in the Media. Edited by Amber George and Joseph Leeson-Schatz. Lanham: Lexington Books, pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lousley, Cheryl. 2016. Charismatic life: Spectacular biodiversity and biophilic life writing. Environmental Communication 10: 704–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, Loredana. 2016. Media Activism and Animal Advocacy: What’s Film Got to Do with It? In Critical Animal and Media Studies. New York: Routledge, pp. 235–47. [Google Scholar]
- Manzo, Kate. 2010. Beyond polar bears? Re-envisioning climate change. Meteorological Applications 17: 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulies, Jared, Rebecca Wong, and Rosaleen Duffy. 2019. The imaginary ‘Asian Super Consumer’: A critique of demand reduction campaigns for the illegal wildlife trade. Geoforum 107: 216–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoldi, Carlotta, Giovanni Bearzi, Cristina Brito, Inês Carvalho, Elena Desiderà, Lara Endrizzi, Luis Freitas, Eva Giacomello, Ioannis Giovos, Paolo Guidetti, and et al. 2019. From sea monsters to charismatic megafauna: Changes in perception and use of large marine animals. PLoS ONE 14: e0226810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClanahan, Timothy, Alan Friedlander, Laurent Wantiez, Nicholas Graham, Heinrich Bruggemann, Pascale Chabanet, and Remy Oddenyo. 2021. Best-practice fisheries management associated with reduced stocks and changes in life histories. Fish and Fisheries 23: 422–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVeigh, Karen. 2021. Seaspiracy: Netflix documentary accused of misrepresentation by participants. The Guardian. March 31. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/mar/31/seaspiracy-netflix-documentary-accused-of-misrepresentation-by-participants (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Mikos, Lothar. 2014. Analysis of film. In The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis. London: Sage, pp. 409–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mikos, Lothar. 2017. Collecting media data: TV and film studies. In The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Collection. London: Sage, pp. 412–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mitman, Gregg. 2012. Reel Nature: America’s Romance with Wildlife on Film. Seattle: University of Washington Press. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, S. Marek. 2020. Impersonating Animals: Rhetoric, Ecofeminism, and Animal Rights Law. East Lansing: Michigan State University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, S. Marek. 2021. Carnistic Colonialism: A Rhetorical Dissection of “Bushmeat” in the 2014 Ebola Outbreak. Frontiers in Communication 6: 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, Svarti Kirsten. 2021. 3 Documentaries to Watch Instead of ‘Seaspiracy’. Outside. April 20. Available online: https://www.outsideonline.com/culture/books-media/seaspiracy-what-to-watch-instead/ (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- Nibert, David. 2002. Animal Rights/Human Rights: Entanglements of Oppression and Liberation. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Nocella, Anthony, II, Richard White, and Erika Cudworth, eds. 2015. Anarchism and Animal Liberation: Essays on Complementary Elements of Total Liberation. Jefferson: McFarland. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, Saffron. 2020. More than meets the eye: A longitudinal analysis of climate change imagery in the print media. Climatic Change 163: 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, Saffron, and Sophie Nicholson-Cole. 2009. “Fear won’t do it” promoting positive engagement with climate change through visual and iconic representations. Science Communication 30: 355–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, Maria Therese Bager, Jonas Geldmann, Mike Harfoot, Derek P. Tittensor, Becky Price, Pablo Sinovas, Katarzyna Nowak, Nathan J. Sanders, and Neil D. Burgess. 2021. Thirty-six years of legal and illegal wildlife trade entering the USA. Oryx 55: 432–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumwood, Val. 1993. Feminism and the Mastery of Nature. New York: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Psihoyos, Louie, dir. 2015. Racing Extinction. Nicasio: Ocean Preservation Society [Prod.]. [Google Scholar]
- Salt, Barry. 1974. Statistical style analysis of motion pictures. Film Quarterly 28: 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, Barry. 2001. Practical film theory and its application to TV series dramas. Journal of Media Practice 2: 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, Barry. 2009. Film style and technology: History and analysis, 3rd ed. London: Starwood. [Google Scholar]
- Shiffman, David, Catherine Macdonald, Julia Wester, Matthew Walsh, Audrey Chevalier, Daniel Kachelriess, and Kim Friedman. 2021. Marine species conservation at CITES: How does media coverage inform or misinform? Marine Policy 134: 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaill, Belinda. 2016. Regarding Life: Animals and the Documentary Moving Image. New York: SUNY Press. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, Uptal, Jennifer Churchill Cihlar, and Bruce Budowle. 2021. International Wildlife Trafficking: A perspective on the challenges and potential forensic genetics solutions. Forensic Science International: Genetics 54: 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steadman, Daniel. 2021. Seaspiracy—Let’s Not Lose Sight of the Urgent Message behind the Flawed Arguments. Fauna & Flora. April 6. Available online: https://www.fauna-flora.org/news/seaspiracy-lets-not-lose-sight-of-the-urgent-message-behind-the-flawed-arguments/ (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- Swim, Janet, and Brittany Bloodhart. 2015. Portraying the perils to polar bears: The role of empathic and objective perspective-taking toward animals in climate change communication. Environmental Communication 9: 446–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, Ali, dir. 2021. Seaspiracy. Santa Rosa: A.U.M. Films, Disrupt Studios [Prod.]. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, Chui-Ling, Suzanne Chew, Anabela Carvalho, and Julie Doyle. 2021. Climate Change Totems and Discursive Hegemony Over the Arctic. Frontiers in Communication 6: 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, Nik. 2015. Suffering is not enough: Media depictions of violence to other animals and social change. In Critical Animal and Media Studies. New York: Routledge, pp. 56–69. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas-Walters, Laura, Claire McNulty, and Diogo Veríssimo. 2020. A scoping review into the impact of animal imagery on pro-environmental outcomes. Ambio 49: 1135–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdell, Clement Allan, and Clevo Wilson. 2006. Information, wildlife valuation, conservation: Experiments and policy. Contemporary Economic Policy 24: 144–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdell, Clement Allan, Hemanath Swarna Nantha, and Clevo Wilson. 2004. Endangerment and Likeability of Wildlife Species: How Important Are They for Proposed Payments for Conservation. No. 1741–2016-140526. Brisbane: University of Queensland. [Google Scholar]
- Truscello, Michael. 2018. Catastrophism and Its Critics: On the New Genre of Environmentalist Documentary Film. In Interrogating the Anthropocene. Edited by Jan Jagodzinski. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 257–75. [Google Scholar]
- von Mossner, Alexa Weik. 2012. Facing The Day After Tomorrow: Filmed disaster, emotional engagement, and climate risk perception. In American Environments: Climate-Cultures-Catastrophe. Edited by Christof Mauch and Sylvia Mayer. Heidelberg: Universitätsverlag, pp. 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- von Mossner, Alexa Weik. 2018. Engaging Animals in Wildlife Documentaries: From Anthropomorphism to Trans-Species Empathy. In Cognitive Theory and Documentary Film. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 163–79. [Google Scholar]
- von Mossner, Alexa Weik. 2020. Larger than Life: Endangered Species across Media in Louis Psihoyo’s Racing Extinction. Ekphrasis. Images, Cinema, Theory, Media 24: 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, Cameron Thomas, and Linda Kalof. 2014. Animal imagery in the discourse of climate change. International Journal of Sociology 44: 10–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, Cameron Thomas, Linda Kalof, and Tim Flach. 2021. Using animal portraiture to activate emotional affect. Environment and Behavior 53: 837–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, Christie. 2015. Shark fin ban masks growing appetite for its meat. The Guardian. September 12. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2015/sep/12/shark-fin-ban-not-saving-species (accessed on 15 January 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rooney, D. ‘All Fishing Is Wildlife Poaching:’ Nonhuman Animal Imagery and Mutual Avowal in Racing Extinction and Seaspiracy. Journal. Media 2022, 3, 257-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia3020020
Rooney D. ‘All Fishing Is Wildlife Poaching:’ Nonhuman Animal Imagery and Mutual Avowal in Racing Extinction and Seaspiracy. Journalism and Media. 2022; 3(2):257-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia3020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleRooney, David. 2022. "‘All Fishing Is Wildlife Poaching:’ Nonhuman Animal Imagery and Mutual Avowal in Racing Extinction and Seaspiracy" Journalism and Media 3, no. 2: 257-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia3020020
APA StyleRooney, D. (2022). ‘All Fishing Is Wildlife Poaching:’ Nonhuman Animal Imagery and Mutual Avowal in Racing Extinction and Seaspiracy. Journalism and Media, 3(2), 257-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia3020020





