Impact of COVID-19 Restrictions on Air Quality Levels in Samsun, Turkey †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
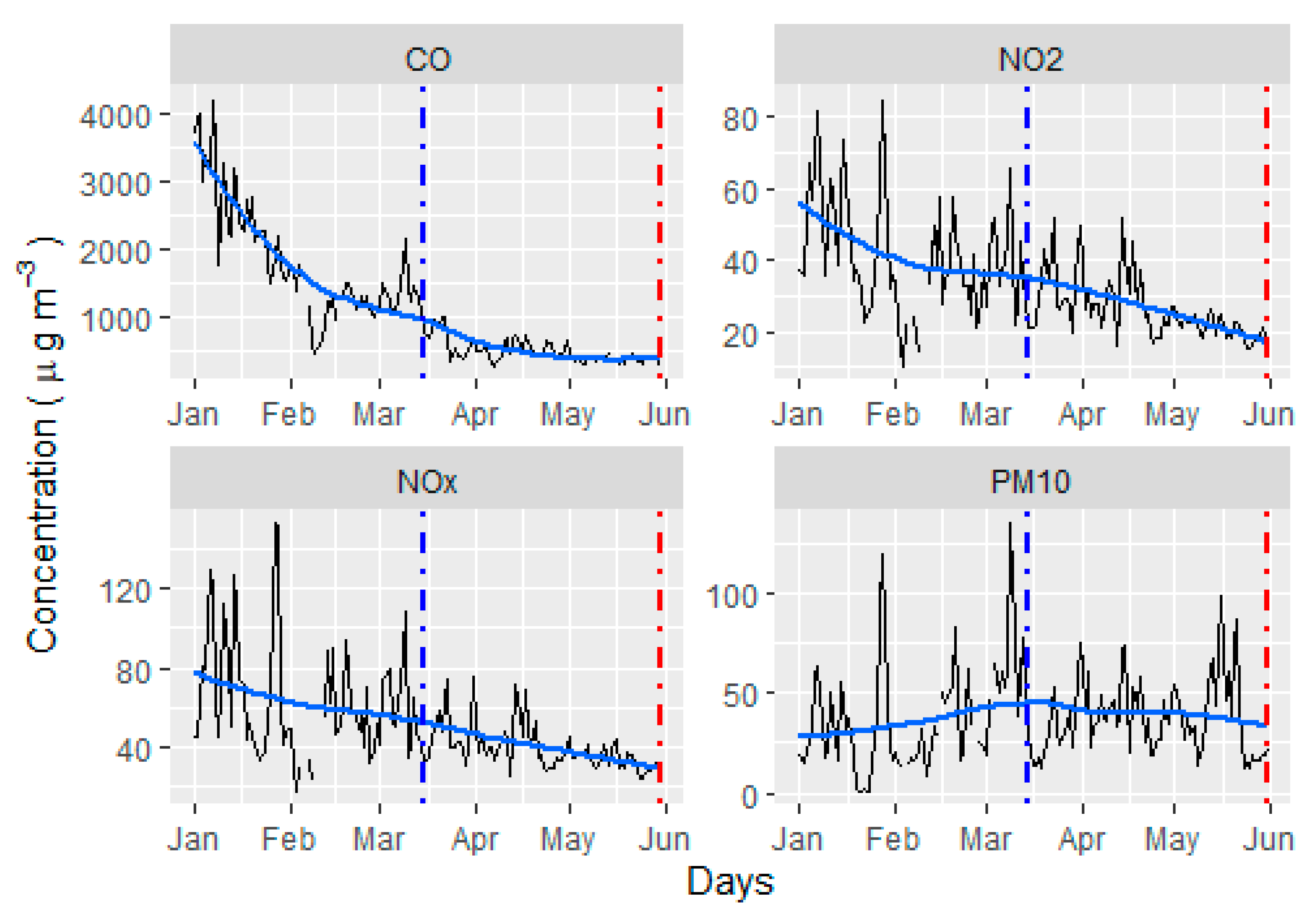
3.1. Comparison of Lockdown and Pre-Lockdown Periods
3.2. Comparison of Sub-Periods in Lockdown Period
3.3. Comparison of the Lockdown Concentrations with the Same Period of 2019
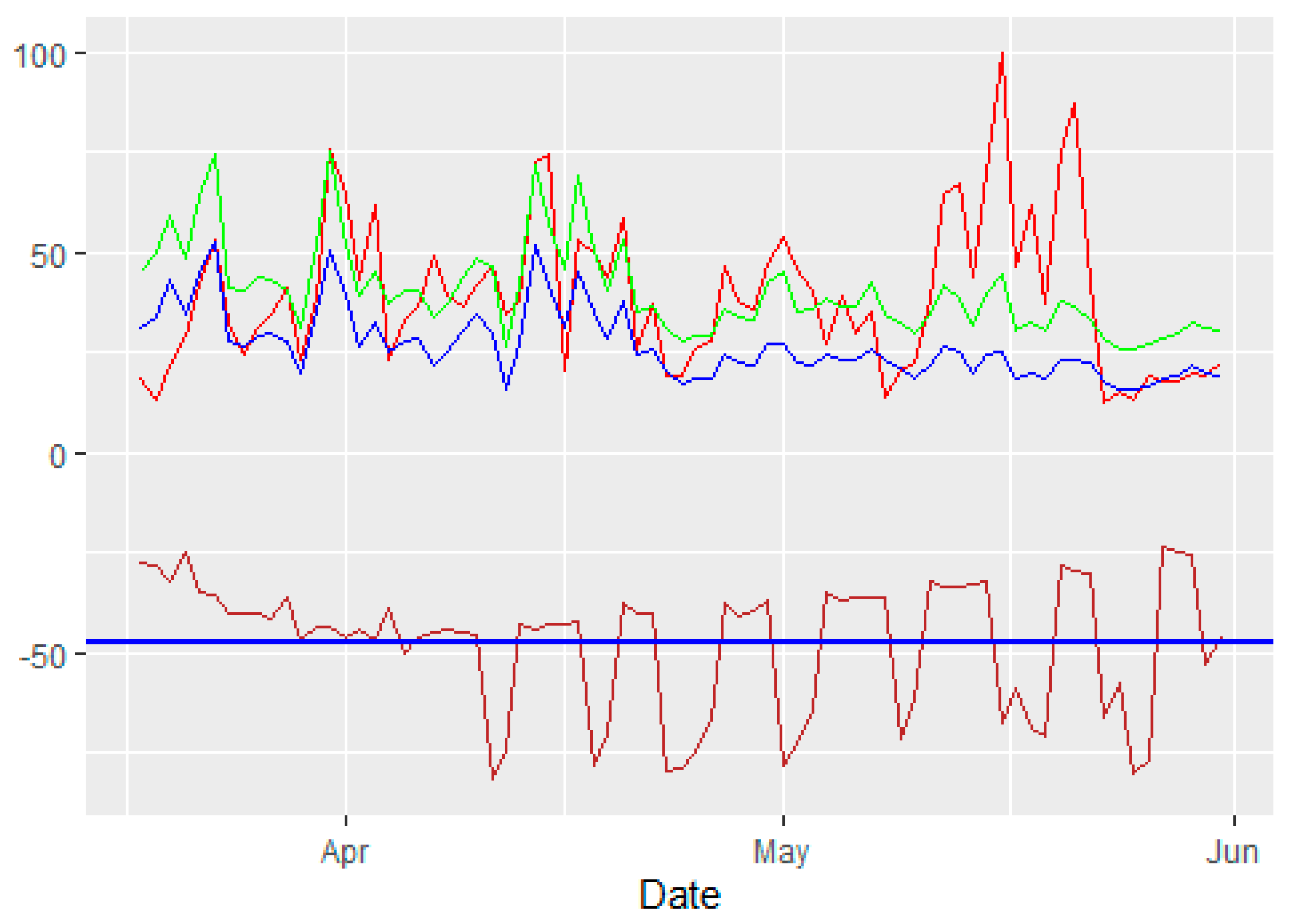
3.4. Relationship between Mobility and Air Pollution
4. Conclusions
- The mean concentrations of CO, NO2 and NOx declined by 72, 37 and 35%, while the mean concentration of PM10 increased by 3% during the lockdown according to the pre-lockdown period. The PM10 concentrations exceeded the WHO limits 19 times before the lockdown and 16 times during the lockdown, although the mean concentrations of PM10 increased during the lockdown according to the pre-lockdown period.
- The mean concentration of all the pollutants decreased during the period of the full lockdown measures compared to the remaining lockdown days at different levels. The CO concentration decreased just 1% during the period of the full lockdown measures with respect to the remaining days of the lockdown. NO2, NOx and PM10 decreased by 25, 20 and 18%, respectively.
- NO2 concentrations did not change during the lockdown with respect to 2019. CO and NOx increased by 4 and 2.5%, respectively, whilst PM10 decreased by 21%.
- The correlation between mobility change and pollutant concentrations was calculated and tested via Pearson’s test. Only the correlation coefficient between mobility and NO2 was statistically significant at the 99% confidence level, with a value of 0.30.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
References
- Baldasano, J.M. COVID-19 lockdown effects on air quality by NO2 in the cities of Barcelona and Madrid (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Bertanza, G.; Pedrazzani, R.; Ricciardi, P.; Miino, M.C. Lockdown for CoViD-2019 in Milan: What are the effects on air quality? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, L.Y.K.; Urban, R.C. COVID-19 Pandemic: Impacts on the Air Quality during the Partial Lockdown in São Paulo State, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobías, A.; Carnerero, C.; Reche, C.; Massagué, J.; Via, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Changes in air quality during the lockdown in Barcelona (Spain) one month into the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, Ü.A. The Effects of COVID-19 Measures on Air Pollutant Concentrations at Urban and Traffic Sites in Istanbul. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1874–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, B.; Dantas, G.; Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. Increased ozone levels during the COVID-19 lockdown: Analysis for the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Cui, K.; Young, L.H.; Hsieh, Y.K.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Wan, S. Impact of the COVID-19 Event on Air Quality in Central China. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Tartarini, F. Changes in air quality during the COVID-19 lockdown in Singapore and associations with human mobility trends. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, S.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Yan, J.; et al. Airborne particulate matter, population mobility and COVID-19: A multi-city study in China. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TUIK. Turkish Statistical Institute, Population and Housing Census 2020. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/DownloadIstatistikselTablo?p=D/iyuDY0YaNRJp8DX69ESortYsYRQss36XKkV5ynlsLTp4WYhvc8Woz6qEb2bTRj (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, O3, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide: Global Update 2005, Summ. Risk Assess. 2006. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/69477/1/WHO_SDE_PHE_OEH_06.02_eng.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Google. COVID–19 Community Mobility Reports. 2020. Available online: https://www.google.com/covid19/mobility/?hl=en-GB (accessed on 20 December 2020).
| Station | PM10 | CO | NOx | NO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tekkekoy | 2019–2020 | 2019–2020 | 2019–2020 | 2019–2020 |
| Pollutant | Before Lockdown (µg/m3) | Lockdown (µg/m3) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO | 1807 | 496 | −73 |
| NO2 | 41 | 26 | −37 |
| NOx | 62 | 40 | −35 |
| PM10 | 37 | 38 | +3 |
| Pollutant | Before Lockdown | Lockdown | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO2 | 0 | 0 | - |
| PM10 | 19 | 16 | −16 |
| Pollutant | Full Lockdown Days (µg/m3) | Remaining Days (µg/m3) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO | 497 | 491 | −1 |
| NO2 | 28 | 21 | −25 |
| NOx | 41 | 33 | −20 |
| PM10 | 40 | 31 | −18 |
| Pollutant | 2019 (µg/m3) | 2020 (µg/m3) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO | 474 | 496 | +4 |
| NO2 | 26 | 26 | 0 |
| NOx | 39 | 40 | +2.5 |
| PM10 | 48 | 38 | −21 |
| CO | NOx | NO2 | PM10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.30 * | 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Efe, B. Impact of COVID-19 Restrictions on Air Quality Levels in Samsun, Turkey. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 8, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10692
Efe B. Impact of COVID-19 Restrictions on Air Quality Levels in Samsun, Turkey. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2021; 8(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10692
Chicago/Turabian StyleEfe, Bahtiyar. 2021. "Impact of COVID-19 Restrictions on Air Quality Levels in Samsun, Turkey" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 8, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10692
APA StyleEfe, B. (2021). Impact of COVID-19 Restrictions on Air Quality Levels in Samsun, Turkey. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 8(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10692






