Mapping Flash Floods in Iraq by Using GIS †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
The Nearest Neighbor Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
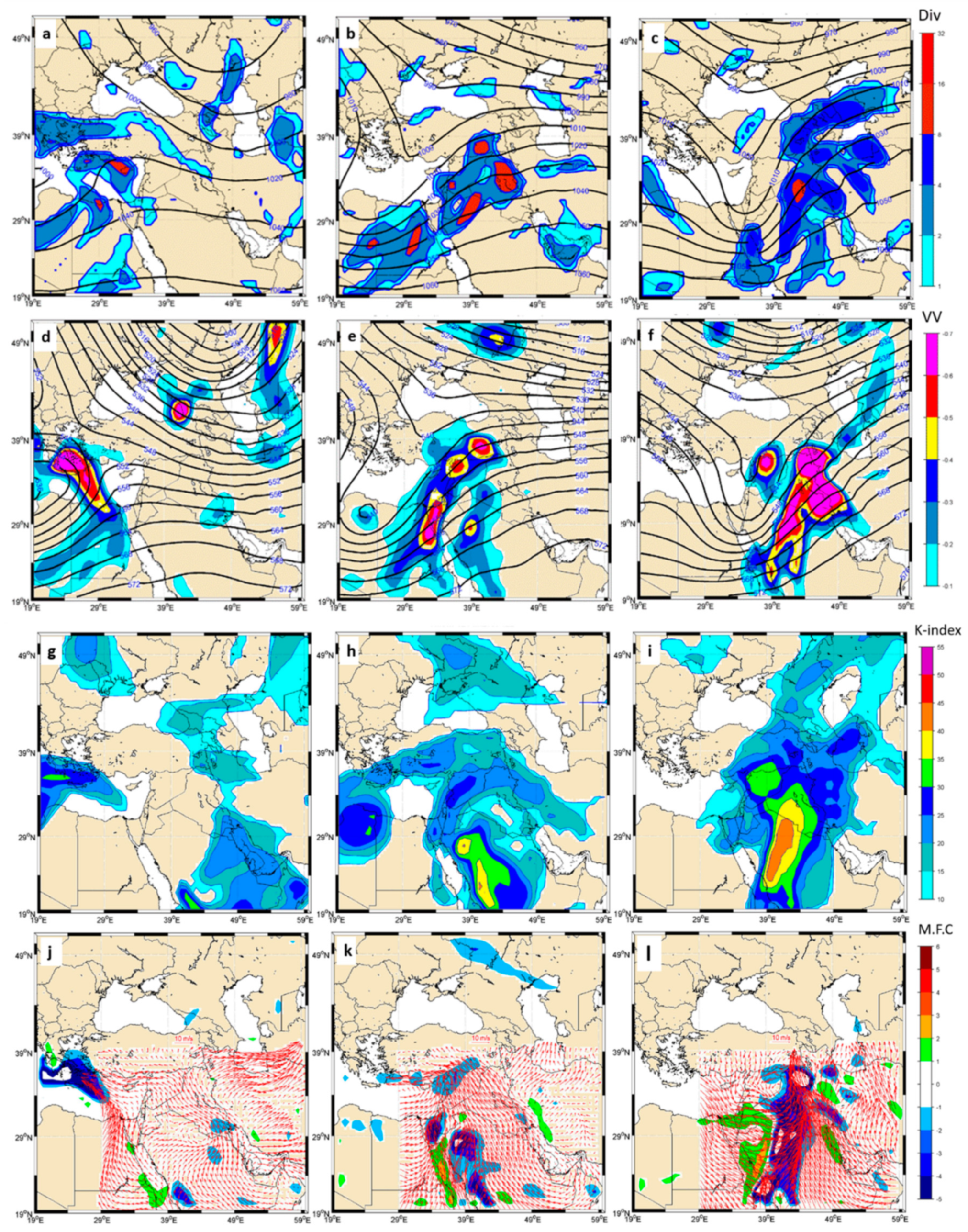
3.1. Synoptic and Dynamic Analysis of the Heavy Rain That Fell in Basra Station on 24 January 2017
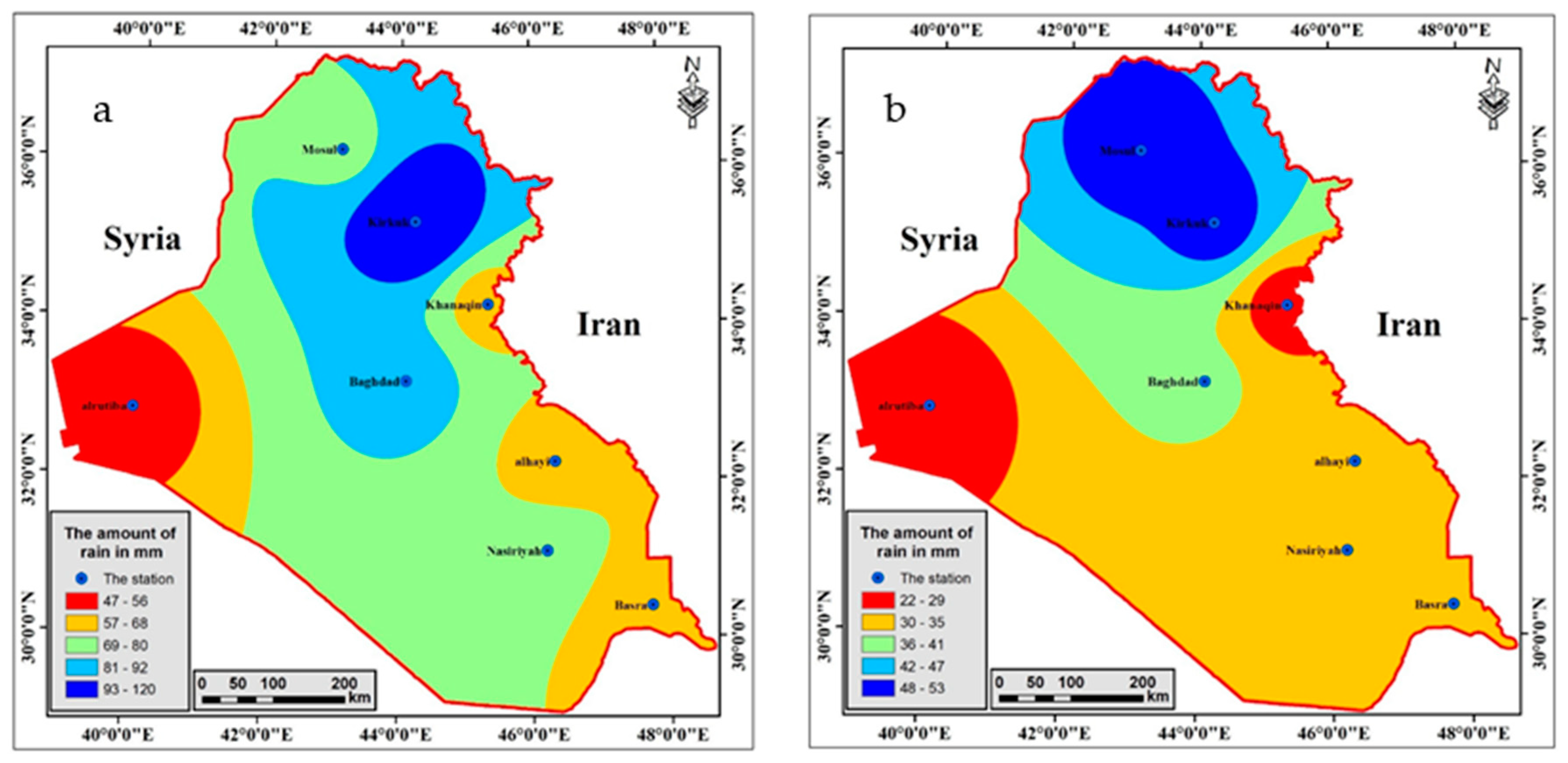
3.2. Flash Flood Modelling
3.2.1. The First Model
3.2.2. The Second Model
3.2.3. The Third Model
3.2.4. The Fourth Model
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Buchwaldt, R. Encyclopedia of Natural Hazards; Bobrowsky, P.T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany; Simon Fraser University Canada: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2013; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA. National Weather Service, Flood and Flash Flood Definitions, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/mrx/flood_and_flash (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Al-Nassar, A.R.; Pelegrí, J.L.; Sangrà, P.; Alarcon, M.; Jansa, A. Cut-off low systems over Iraq: Contribution to annual precipitation and synoptic analysis of extreme events. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 908–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboud Al-Kinani, M.N.; Al-shamry, M.K. Synoptic analysis of floodwaters affecting East Wasit Governorate and its impacts on infrastructure and agricultural land. J. Coll. Educ. 2019, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul-Jabbar, A.M.; Khtan, A. Predicted the Cumulative Annual Rainfall in Iraq using SDSM Moda. Al-Mustansiriyah J. Sci. 2021, 32, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nassar, A.R.T. Dynamics of Cyclones and Precipitation over the Middle East. Ph.D. Thesis, Departament de Física, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vahidnia, M.H.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Alimohammadi, A.; Hosseinali, F. A GIS-based neurofuzzy procedure for integrating knowledge and data in landslide susceptibility mapping. Comput. Geosci. 2010, 36, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghmand, S.; Bin-Abdullah, R.; Abustan, I.; Vosoogh, B. GIS-based River Flood Hazard Mapping in Urban Area: A Case Study in Kayu Ara River Basin, Malaysia. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2010, 2, 488–500. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zeng, G. A GIS-based spatial multi-criteria approach for flood risk assessment in the Dongting Lake Region, Hunan, Central China. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 3465–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.P.; Srivastava, P.K. Flood hazards mitigation analysis using remote sensing and GIS: Correspondence with town planning scheme. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2353–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, A.; Najafi, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Rezaeian, J.; Sattarian, A. A GIS-based frequency ratio and index of entropy models for landslide susceptibility assessment in the Caspian forest, northern Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldescu, G.C. The Necessity of Flood Risk Maps on Timis River; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bled, Slovenia, 2008; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Koehler, K.A.; Volckens, J. Prospects and pitfalls of occupational hazard mapping: ‘between these lines there be dragons’. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2011, 55, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernández, D.S.; Lutz, M.A. Urban flood hazard zoning in Tucumán Province, Argentina, using GIS and Multi Criteria Decision Analysis. Eng. Geol. 2010, 111, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, K.; John, C.M.; Shrivasthava, N.K. Urban flood vulnerability zoning of Cochin City, southwest coast of India, using Remote Sensing and GIS. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerl, T.; Bochow, M.; Kreibich, H. Flood Damage Modeling on the basis of Urban Structure Mapping Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data. Water 2014, 6, 2367–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emmanouloudis, D.; Myronidis, D.; Ioannou, K. Assessment of flood risk in Thasos Island with the combined use of multicriteria analysis AHP and geographical information system. Innov. Appl. Inf. Agric. Environ. 2008, 2, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, R.; Bapalu, G.; Singh, L.; Rath, B. Flood risk analysis in the Kosi river basin, north Bihar using multi-parametric approach of analytical hierarchy process (AHP). J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2008, 36, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, V.; Scheuer, S.; Haase, D. A multicriteria approach for flood risk mapping exemplified at the Mulde river, Germany. Nat. Hazards 2009, 48, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Yeh, C.-H.; Yu, B. Integrated application of the analytic hierarchy process and the geographic information system for flood risk assessment and flood plain management in Taiwan. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tehrany, M.S.; Pradhan, B.; Jebur, M.N.; Neamah, M. Flood susceptibility mapping using a novel ensemble weights-of-evidence and support vector machine models in GIS. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
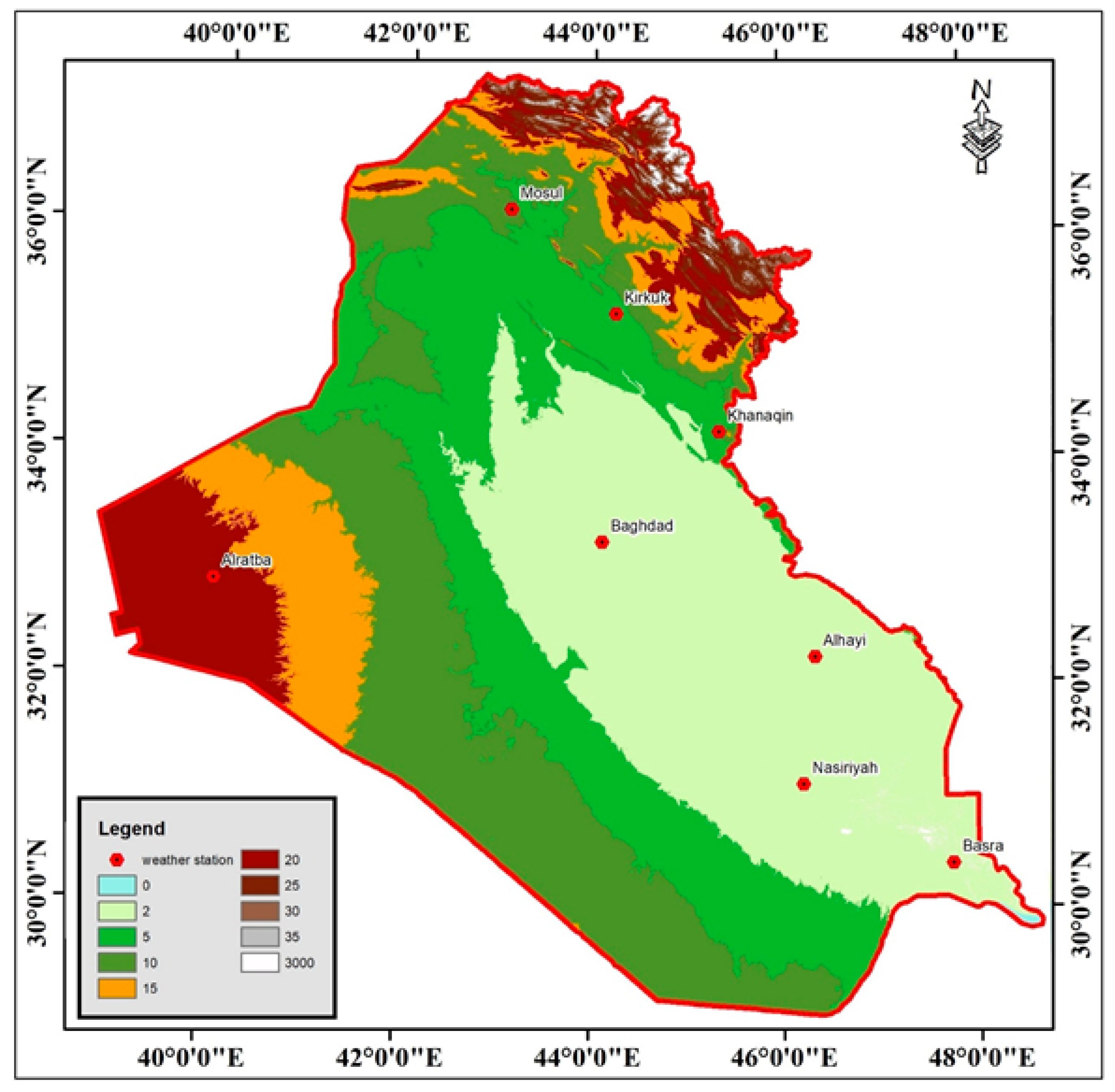



| Stations | longitude | Latitude | Elevation (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mosul | 43.09° | 36.19° | 223 |
| 2 | Kirkuk | 44.24° | 35.28° | 331 |
| 3 | Khanaqin | 45.39° | 34.35° | 185 |
| 4 | Baghdad | 44.24° | 33.18° | 34 |
| 5 | Rutba | 40.17° | 33.02° | 615 |
| 6 | Hai | 46.14° | 32.08° | 15 |
| 7 | Nasiriya | 46.14° | 31.01° | 3 |
| 8 | Basrah | 47.47° | 30.31° | 2.40 |
| Stations | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mosul | 48.3 | 52.7 | 27.3 | 46.6 | 52.1 | 62.4 | 75.3 | 66.3 | 64.7 | 44.7 | 27.1 | 51.59 |
| Kirkuk | 60.6 | 24.7 | 41.2 | 52.3 | 44.7 | 44.4 | 117.2 | 45.3 | 58.9 | 72.4 | 25.2 | 53.35 |
| Khanaqin | ــــــــــــــــــــ | ــــــــــــــــــــ | ــــــــــــــــــــ | ــــــــــــــــــــ | ــــــــــــــــــــ | 29.5 | 58.7 | 37.5 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 4.4 | 22.48 |
| Baghdad | 24.6 | 14.5 | 15.1 | 17.4 | 29.1 | 67.5 | 89.9 | 17.8 | 84.9 | 29.6 | 23.9 | 36.25 |
| Rutba | 19.9 | 17.3 | 7 | 41 | 47.2 | 22.5 | 40.6 | 24.1 | 13 | 8 | 8 | 22.6 |
| Hai | 13.701 | 21.8 | 23.101 | 20.2 | 30.80 | 23.7 | 32 | 33.802 | 60.3 | 43.602 | 18 | 29.18 |
| Nasiriya | 75.8 | 20.4 | 18.5 | 14.7 | 11.6 | 40.3 | 68.4 | 60.7 | 22.8 | 20.5 | 4.8 | 32.59 |
| Basrah | 40.3 | 18 | 27.8 | 7.7 | 12.2 | 26.2 | 29.6 | 58.5 | 41.6 | 25.6 | 54.3 | 31.07 |
| Stations | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | Avg. | r * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mosul | Days | 5 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5.91 | 0.37 |
| rain(mm) | 48.3 | 32.9 | 48 | 35.302 | 52.101 | 10 | 33.1 | 66.3 | 38 | 44.7 | 27.1 | 39.62 | ||
| Kirkuk | Days | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5.91 | 0.27 |
| rain(mm) | 60.6 | 24.3 | 14.6 | 47 | 32.9 | 24.6 | 117.2 | 38.6 | 40.8 | 10.1 | 25.2 | 39.63 | ||
| Khanaqin | Days | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | 6 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4.67 | 0.15 |
| rain(mm) | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | ــــــــ | 4.3 | 58.7 | 7.2 | 1 | 1.5 | 4.4 | 12.85 | ||
| Baghdad | Days | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4.64 | 0.07 |
| rain(mm) | 6.7 | 3 | 11 | 13.6 | 6.1 | 35 | 16.1 | 16.7 | 84.9 | 10.9 | 9.7 | 19.43 | ||
| Rutba | Days | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3.36 | 0.41 |
| rain(mm) | 19.9 | 15.8 | 0.01 | 11.8 | 6.3 | 22.5 | 21 | 7 | 6.2 | 8 | 0.6 | 10.83 | ||
| Hai | Days | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 4.18 | 0.46 |
| rain(mm) | 13.7 | 20 | 23.1 | 10.4 | 1.4 | 8.8 | 17.8 | 33.8 | 22.9 | 43.6 | 1.9 | 17.95 | ||
| Nasiriya | Days | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 3.82 | 0.34 |
| rain(mm) | 75.8 | 20.4 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 9.5 | 40.3 | 45.9 | 60.7 | 4.5 | 2.6 | 4.8 | 24.4 | ||
| Basrah | Days | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 0.46 |
| rain(mm) | 40.3 | 15.7 | 27.8 | 6.4 | 4.3 | 13.8 | 6.1 | 58.5 | 16.8 | 25.6 | 21.4 | 21.52 |
| Station | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | Avg. | r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mosul | Frequency | 9 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6.73 | −0.12 |
| Rain(mm) | 26.2 | 0.804 | 28.104 | 56.003 | 118.803 | 50.8 | 35.9 | 53.9 | 22.804 | 42.201 | 50.1 | 44.15 | ||
| Kirkuk | Frequency | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 6.09 | 0.51 |
| Rain(mm) | 34.3 | 49.001 | 54.501 | 29.203 | 71.801 | 52.4 | 40.301 | 80.201 | 37.4 | 88.7 | 95.1 | 57.54 | ||
| Khanaqin | Frequency | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | 4 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 4.83 | 0.24 |
| Rain(mm) | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | 35.1 | 21 | 15.5 | 6.4 | 3.4 | 2.3 | 13.95 | ||
| Baghdad | Frequency | 4 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 5.36 | 0.02 |
| Rain(mm) | 32.2 | 23.703 | 11.404 | 5.504 | 25.103 | 83.203 | 70.806 | 35.802 | 28.203 | 30.303 | 42.005 | 35.29 | ||
| Rutba | Frequency | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4.91 | 0.12 |
| Rain(mm) | 16.3 | 10.5 | 0.703 | 24.501 | 20.805 | 0.206 | 13.91 | 36.502 | 13.603 | 0.001 | 11.002 | 13.46 | ||
| Hai | Frequency | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5.36 | 0.01 |
| Rain(mm) | 3.304 | 45.304 | 6.405 | 26.204 | 50.104 | 32.1 | 51.505 | 46.901 | 56.901 | 35.201 | 31.2 | 35.01 | ||
| Nasiriya | Frequency | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 5.27 | 0.15 |
| Rain(mm) | 9.202 | 1.401 | 7.102 | 29.202 | 19.905 | 19.303 | 7.803 | 83.005 | 36.101 | 11.6 | 19 | 22.15 | ||
| Basra | Frequency | 5 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 4.64 | −0.06 |
| Rain(mm) | 46.703 | 31.6 | 39.601 | 17.502 | 22.4 | 28.902 | 40.201 | 60 | 43.802 | 26.1 | 64.104 | 38.27 |
| Scheme 2007. | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | Avg. | r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mosul | Rainstorms | 40 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 41 | 39 | 33 | 36 | 36 | 35 | 28 | 35 | 0.23 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 193.8 | 216.318 | 223.815 | 240.616 | 294.718 | 278.61 | 455.513 | 340.811 | 288.809 | 216.007 | 145.103 | 263.1 | ||
| Kirkuk | Rainstorms | 27 | 27 | 32 | 27 | 35 | 34 | 29 | 37 | 40 | 26 | 31 | 31.36 | 0.28 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 173.106 | 134.916 | 225.814 | 267.212 | 221.81 | 292.105 | 394.305 | 319.008 | 315.505 | 321.504 | 204.504 | 260.89 | ||
| Khanaqin | Rainstorms | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | 26 | 23 | 28 | 20 | 15 | 8 | 20 | 0.81 |
| Rainfall (mm) | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | ـــــــ | 116.4 | 169.35 | 170.3 | 14.9 | 4.9 | 10.1 | 80.99 | ||
| Baghdad | Rainstorms | 20 | 22 | 33 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 27 | 32 | 29 | 27 | 30 | 27.27 | −0.002 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 99.214 | 59.119 | 67.524 | 92.519 | 96.021 | 184.422 | 296.725 | 107.524 | 190.923 | 104.522 | 71.829 | 124.58 | ||
| Rutba | Rainstorms | 12 | 15 | 24 | 26 | 29 | 29 | 33 | 30 | 17 | 3 | 21 | 21.73 | 0.7 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 58.401 | 72.901 | 23.312 | 109.017 | 87.92 | 73.018 | 135.219 | 157.61 | 41.908 | 10.301 | 21.814 | 71.95 | ||
| Hai | Rainstorms | 21 | 26 | 27 | 22 | 24 | 28 | 27 | 30 | 28 | 21 | 21 | 25 | 0.64 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 64.51 | 87.621 | 85.32 | 80.309 | 120.313 | 81.207 | 156.814 | 188.615 | 194.612 | 123.513 | 43.105 | 111.45 | ||
| Nasiriya | Rainstorms | 22 | 17 | 29 | 20 | 28 | 24 | 28 | 31 | 28 | 24 | 28 | 25.36 | 0.4 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 112.515 | 65.505 | 56.917 | 57.616 | 85.119 | 116.22 | 174.22 | 219.723 | 93.22 | 68.3 | 29.7 | 98.1 | ||
| Basrah | Rainstorms | 23 | 13 | 29 | 16 | 21 | 22 | 14 | 5 | 19 | 19 | 17 | 18 | 0.5 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 139.21 | 67.103 | 89.811 | 57.007 | 65.307 | 115.309 | 48.31 | 60.5 | 131.508 | 86.908 | 128.209 | 89.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Nassar, A.R.; Kadhim, H. Mapping Flash Floods in Iraq by Using GIS. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 8, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10696
Al-Nassar AR, Kadhim H. Mapping Flash Floods in Iraq by Using GIS. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2021; 8(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10696
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Nassar, Ali Raheem, and Hussein Kadhim. 2021. "Mapping Flash Floods in Iraq by Using GIS" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 8, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10696
APA StyleAl-Nassar, A. R., & Kadhim, H. (2021). Mapping Flash Floods in Iraq by Using GIS. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 8(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2021-10696






