Abstract
In this study, a comprehensive analysis of deadwood was conducted in four macro-areas located in two beech forests of public utility in Enciso (La Rioja, Spain). Dendrometric data, as well as qualitative and quantitative characteristics of deadwood, were collected and analysed with respect to the degree of accessibility to the forest to determine the effect of different levels of forest accessibility on deadwood volume and carbon stocks. All decomposition classes were present except the first, highlighting the development of natural degradation dynamics. Deadwood stored 6.9 t/ha of C in the easy accessibility class, 5.7 t/ha of C in the medium accessibility class and 2.2 t/ha of C in the difficult accessibility class. The average volume of deadwood and carbon stored calculated in this study were higher than the values reported in the Spanish and Italian national forest inventories, including one developed for Riojan beech forests. Deadwood volume was on average 22.5 m3/ha, showing an unequal distribution, with the lowest values found far from the access roads, despite forest accessibility generally being considered a factor that facilitates the human collection of deadwood. The distribution patterns of deadwood in beech forests of La Rioja, apparently counterintuitive, were due to a combination of different factors, including slope, cattle grazing, and weather conditions which might have favoured downward movement of the deadwood.
1. Introduction
In beech forests, where the frequency of fires is very low, wood decomposes within the forest and this implies the existence of an entire trophic network that has evolved in conditions of abundance of this resource [1].
The terms “woody necromass” and “deadwood” define dead woody mass, including standing dead trees (snags), deadwood on the ground (logs), and dead stumps. In October 2002, during the Expert Level Meeting of the Ministerial Conference on the Protection of Forests in Europe, deadwood volume was included among the pan-European quantitative indicators of Sustainable Forest Management, in support of Criterion 4, aimed at the maintenance, conservation and appropriate improvement of biological diversity in forest ecosystems. Deadwood was distinguished into “standing dead tree”—SDT, or snags—and “lying deadwood” or logs, the latter defining deadwood on the ground, which can be further distinguished in “coarse woody debris” or CWD, i.e., coarse woody detritus with a diameter of the smallest section equal to or greater than 10 cm, and “fine woody debris” or FWD, i.e., fine woody detritus with a diameter between 10 and 2.5 cm [2,3,4]. Woody debris with a diameter of less than 2.5 cm is considered part of the litter [4,5]. CWD provides many micro-habitats for several species of micro- and macro-fauna, and the diametric variability of CWD can substantially increase forest biodiversity. For instance, Stokland et al. [6] found that some species prefer small diameters <20 cm, others colonise only dry woods with diameters greater than 20 cm or even 40 cm, while only ~20% of the species examined were found to be generalist [6]. However, these diametric thresholds cannot be generalised because the size and abundance of deadwood is highly variable and depends on forest type, successional phase, climate, and forest management practices [7,8,9,10]. Furthermore, the potential benefits for biodiversity depend on the level of decay of deadwood, either snags, logs, or stumps, and on the presence of all decay classes in the forest (from recently dead stems to highly decomposed debris) [11].
The objective of this research was to quantify and qualify deadwood in two beech forests of the Spanish autonomous community La Rioja, in order to determine the effect of different levels of forest accessibility on deadwood. Moreover, using values established by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2006 [12], we contributed to define estimates of the amount of carbon (C) stored both in living trees and in the deadwood within beech forests of La Rioja.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
La Rioja is the second-smallest Spanish autonomous community (5045 km2), and it has the lowest number of inhabitants (315,675, for a density of 62.57 inhabitants/km2) [13]. La Rioja has a wide variety of landscapes, flora, and fauna, due to the different geographical characteristics of its areas: it is possible to distinguish a valley area in the north, called “Valle del Ebro”, and a mountainous area in the south, called “Sistema Ibérico”. The proximity with the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea greatly influences climatic variability in a region characterised by complex topography. Hence, climatic conditions in La Rioja are remarkably heterogeneous, but in general are characterised by a cold and humid winter season, with frequent snowfall both on the mountain ranges and in some valleys, while the summer season is dry and hot, with minimal rainfall. Spring and autumn are characterised by mild temperatures and abundant rains, especially in spring. Yearly temperature generally varies from −2 °C (January) to 26 °C (August) and rarely drops below −3 °C or rises above 35 °C. The average annual rainfall is 400 mm. La Rioja has a total extension of over half a million hectares, of which almost 62% is devoted to forest use, higher (7%) than the national average. More than half (66%) of La Rioja’s forest area is publicly owned, and the remaining 34% is privately owned [14].
The study area is about 10 km away from the historic centre of Enciso, a municipality of La Rioja with a population of about 170 inhabitants. This study was conducted in two pure beech forests, although in the surrounding areas beech stands are often located near or intermixed with reforested stands of Pinus sylvestris. Stands located in areas characterised by difficult accessibility are generally left to natural evolution, given their relevance from conservation, soil protection, and aesthetical points of view. On the other hand, more accessible stands undergo phytosanitary thinning or cuts, following the approval of a Project or Technical Plan for the Management of Forest Resources of Public Utility Forests, as established by Law 2/1995, concerning the protection and development of the forest heritage of La Rioja [14]. The studied beech forests, located on slopes of 10–20%, were evenly aged high forests, with small coppice areas. They had not been subjected to any management plan, but there may have been legal concessions in past years.
2.2. Data Collection
The field surveys were carried out for gathering: (1) dendrometric information of the stan; (2) quantitative; and (3) qualitative descriptions of deadwood. The surveys were conducted in four macro-areas of study (MAS1, MAS2, MAS3, MAS4), located within beech forests served by forest roads. In each MAS, three circular plots with a radius of 20 m and a surface area of 1256 m2 each were established, for a total of twelve sampling plots. The presence of a quantitative gradient of deadwood from the access roads to the inner forest was investigated by placing the three plots in each MAS at increasing distance from the access road to define three accessibility classes: the easy accessibility class from 20 to 60 m (E); the medium accessibility class from 60 to 100 m (M); and the difficult accessibility class from 100 to 140 m (D). Being located on slopes, increasing distance from the road always corresponded to an increase in altitude: as a result, MAS1 ranged between 1400 and 1430 m a.s.l., MAS2 between 1340 and 1365 m a.s.l., MAS3 between 1295 and 1310 m a.s.l., and MAS4 between 1490 and 1515 m a.s.l. For each plot, elevation, slope, aspect, and coordinates were recorded. Once the centre of the plot was identified, for each living tree, diameter at breast height (DBH) was recorded using a calliper to the nearest millimetre; for each snag, height using a Vertex hypsometer with metric precision, decay class, and DBH and diameter at half height (for snags with total height equal to or less than 4 m) were recorded; for each dead stump, diameter, height, and decay class were recorded. Furthermore, the height of at least 8 live trees/plot were measured, generally at least two per diameter class. To obtain the quantitative and qualitative information of the logs, two linear transects 50 m long and 1 m wide were performed in each plot, perpendicular to each other and with the centre falling in the same centre of the plot. The parameters of the logs with a diameter ≥2.5 cm, snags, and dead stumps were measured along the transect. The degree of decay of deadwood was defined using the visual classification system of Hunter [15] and Morelli et al. [16]. According to the classification system, each snag, log, and dead stump was assigned to a specific decay class.
2.3. Data Analysis
Tree density (trees/ha), basal area (m2/ha), average diameter (cm), and average height (m) were calculated for each MAS. The woody volume per hectare (m3/ha) of each sampling area was calculated using double-entry volume tables [17]. In order to convert living trees and deadwood volumes in carbon stocks, the carbon concentration and the basal density typical of the species are needed. These values were not available for the Riojan beech trees; therefore, reference values for carbon concentration were obtained from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [12] (49% of the dry mass of living trees). The basic density of deadwood varies according to the decay class. In this study, values obtained experimentally for central Italian beech [18] were used, according to which the five decay classes had a basic density of 0.61 t/m3, 0.51 t/m3, 0.45 t/m3, 0.42 t/m3, and 0.24 t/m3, respectively. Differences in volumes found in each plot and decay class were investigated for categories of deadwood (snags, logs, and dead stumps) and forest accessibility class using Tukey’s test and ANOVA after homogeneity of variances between sampling plots had been assessed using Levene’s test.
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Dendrometric Analysis
The results of the dendrometric analysis are shown in Table 1. For each MAS, density, basal area, average diameter, average height, and average volume were reported. The p-value shows the results of the ANOVA.

Table 1.
Results of the dendrometric analysis for each macro-areas of study (MAS).
3.2. Results of the Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of the Deadwood
The quantitative analysis of volumes in snags, dead stumps, and logs, by MAS and accessibility class, showed that in most cases the D plots had on average the lowest deadwood volume (9.9 m3/ha) (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The largest deadwood volume was found in the E plots (31.6 m3/ha), followed by the M plots (25.7 m3/ha) (Figure 2). Hence, the average volumes of snags, logs, and dead stumps decreased with decreasing accessibility (Figure 1).
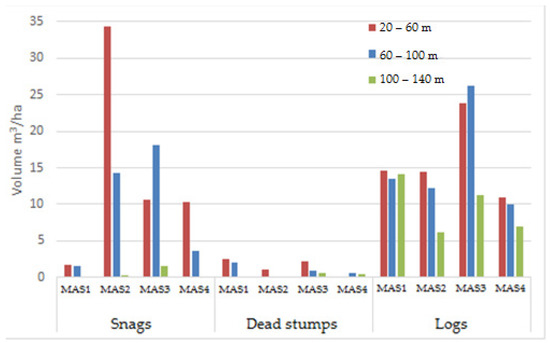
Figure 1.
Volumes of snags, dead stumps, and logs divided by MAS and accessibility classes.
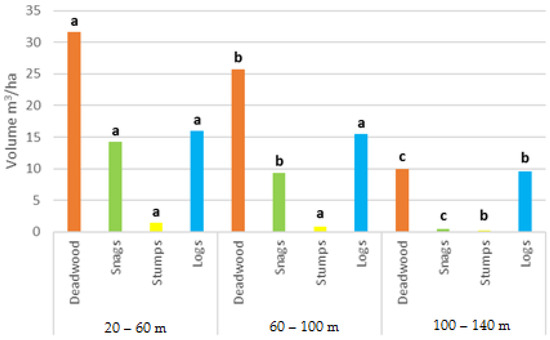
Figure 2.
Volumes of deadwood categories for each accessibility class. Different letters indicate significant statistical differences by Tukey’s test in total deadwood and each deadwood category.
Deadwood volume decreased from the easy accessibility class to the forest to the difficult one (Figure 2). In relative terms, deadwood represented 5.9% of the total volume (biomass + necromass) in the easy accessibility class, 5.1% in the medium accessibility class, and only 2% in the difficult accessibility class.
The Tukey test was applied to check if there were statistically significant differences within the same deadwood category as the accessibility class changed. The same letters within each category indicate no statistical difference based on the accessibility class (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Deadwood in general and snags indicated that, as the accessibility class increased, the average volumes decreased in a statistically significant way. The average volumes of dead stumps and logs decreased more gradually; no significant difference was detected in the E and M plots (Figure 2). It is interesting to note that the differences in deadwood total volume were driven by the snag volume in E and M; dead stump and log volume showed no statistical difference.
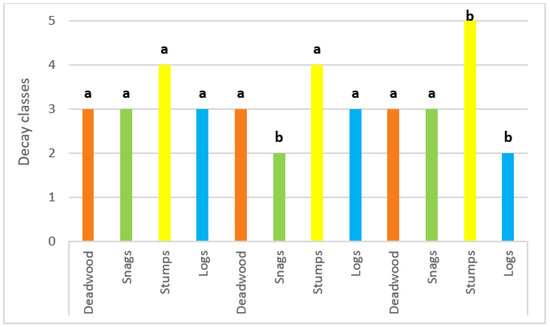
Figure 3.
Decay classes of the categories of deadwood for each accessibility class. Different letters indicate significant statistical differences by Tukey’s test in total deadwood and each deadwood category.
Deadwood in general had an average decay value of 3 in each accessibility class, hence no statistical differences were detected by the Tukey test (Figure 3). Snags had an average decay value of 3 in the E and D plots, and of 2 in the M plot; in fact, the Tukey test revealed this difference. Dead stumps had an average decay value of 4 in the E and M plots, statistically different from those in the D plot. Logs had an average decay value of 3 in the E and M plots and of 2 in the D plot, statistically different from those in the D plot. The Tukey test detected the statistical difference between the E and M plots, and the D plot (Figure 3). Hence, all the decay classes were present, except the first (Figure 3).
3.3. Carbon Storage
Live trees had an average biomass of 289.2 t/ha in the easy accessibility classes, 273.8 t/ha in the medium accessibility classes, 282.3 t/ha in the difficult accessibility classes, and stored 141.7 t/ha, 134.2 t/ha, and 138.3 t/ha of C, respectively.
Total deadwood was on average 14.2 t/ha in the easy accessibility class, 11.6 t/ha in the medium accessibility class, and 4.5 t/ha in the difficult accessibility class, stocking 6.9 t/ha, 5.7 t/ha, and 2.2 t/ha of C, respectively. Specifically, snags showed an average mass of 6.4 t/ha in the easy accessibility class, 4.8 t/ha in the medium accessibility class, and 0.2 t/ha in the difficult accessibility class, stocking 3.2 t/ha, 2.4 t/ha, and 0.1 t/ha of C, respectively. Dead stumps had an average mass of 0.6 t/ha in the easy accessibility class, 0.4 t/ha in the medium accessibility class, and 0.1 t/ha in the difficult accessibility class, stocking 0.3 t/ha, 0.2 t/ha, and 0.032 t/ha of C, respectively. The logs had an average mass of 7.2 t/ha in the easy accessibility class, 6.9 t/ha in the medium accessibility class, and 4.9 t/ha in the difficult accessibility class, stocking 3.5 t/ha, 3.4 t/ha and 2.4 t/ha of C, respectively.
4. Discussions
The volume of the deadwood decreased with the lower accessibility. This trend is opposite to the knowledge in literature; in fact, the accessibility to the forest is considered a factor that facilitates the collection of deadwood by man, and generally, a decrease in the amount of deadwood is expected approaching the access roads [19]. Other factors may affect accessibility, such as ground slope and its direction relative to the road. The size and decay class of deadwood can also influence the propensity to collect. The human use of deadwood as fuel is normally more related to fallen trees than to snags or dead stumps, as well as to the lower decay class [19].
The volume of deadwood found was compared with the data of the National Forest Inventory of La Rioja [20]. The inventory showed that, in the beech forests of La Rioja, there were 3.74 m3/ha of standing dead trees with DBH > 7.5 cm, 0.49 m3/ha of standing dead trees with DBH < 7.5 cm, 3.86 m3/ha of logs with DBH > 7.5 cm, 0.39 m3/ha of logs with DBH < 7.5 cm, 0.10 m3/ha of dead stumps, 2.62 m3/ha of dead branches, and 1.07 m3/ha of stumps. Adding together the volumes of these categories, we obtained 5.3 m3/ha for snags, 6.87 m3/ha for logs, and 0.10 m3/ha for dead stumps, for a total of 12.27 m3/ha of deadwood. As reported by Crecente-Campo et al. [21], the average volume of wood necromass in the Spanish forests was 8 and 10.5 m3/ha according to the third and fourth Spanish National Forest Inventories (SNFI3, 1997–2007; SFNI4, 2008–2013), respectively. Therefore, the volumes recorded in this research far exceeded the national average volume estimated from the inventories; in fact, almost 22.5 m3/ha of deadwood have been estimated, but it was distributed differently according to the class of accessibility. This situation could be due to several causes, among these, the combination of slope, cattle grazing, and frequent rain and snow phenomena may have favoured the rolling and the accumulation of deadwood from mountain to valley, then towards the roads; and the deadwood might have been collected by man in the access classes furthest from the road, because they are less visible.
The values of carbon stored in deadwood within the sampling areas far exceed those estimated by Gasparini and Di Cosmo [22] and by Vallauri et al. [23] for the Italian beech forests, i.e., 3.1 t/ha and 5 t/ha, respectively. The stored carbon values depend on the volume of deadwood, therefore these also decrease as the distance from the access road to the forest increases. These high carbon accumulations are one of the positive consequences resulting from the presence of high quantities of deadwood in the forests.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, both the quantity and the quality of the deadwood in the investigated areas were determined. The deadwood, and therefore the amount of stored carbon, were higher than those reported in the Spanish and Italian national forest inventories. Specifically, they were also higher than the average reported for Riojan beech forests, and also compared to the averages reported in other Italian and European studies in the literature. All decomposition classes except the first were found, and this suggests minimal anthropogenic pressure on the deadwood within the studied beech forests. The lack of anthropic disturbance, in fact, leads to the natural decomposition of this important ecosystem component. In any case, it is a desirable compliance with the regulations in force, so that, in the absence of specific authorisation, the deadwood is not removed but left to decompose naturally.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L.M., C.P.-C. and I.C.; methodology, A.L.M., C.P.-C. and I.C.; software, A.L.M.; validation, A.L.M. and E.Z.; formal analysis, A.L.M., C.P.-C. and E.Z; investigation, I.C.; resources, C.P.-C. and A.L.M.; data curation, I.C., E.Z. and A.L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, I.C.; writing—review and editing, E.Z., A.L.M. and I.C.; supervision, I.C. and A.L.M.; funding acquisition, C.P.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, AGL2016-76769-C2-2-R.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Olano, J.M.; Peralta de Andrés, J. 9150 Hayedos calcícolas medioeuropeas del Cephalanthero-Fagion; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente; y Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2008; pp. 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, M.E.; Sexton, J. Guidelines for Measurements of Woody Detritus in Forest Ecosystems; Publication No. 20; LTER Network Office, University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1996; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Densmore, N.; Parminter, J.; Stevens, V. Corse debris: Inventory, decay modeling, and management implications in three biogeoclimatic zones. BC J. Ecosyst. Manag. 2004, 5, 14–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini, P.; Di Cosmo, L.; Pompei, E. Inventario Nazionale delle Foreste e dei serbatoi forestali di Carbonio INFC 2005. In Secondo Inventario Forestale Nazionale Italiano. Metodi e Risultati Dell’indagine Integrativa; Ministero delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari e Forestali, Corpo Forestale dello Stato: Trento, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Woldendorp, G.; Keenan, R.J.; Ryan, M.F. Coarse woody debris in Australian forest ecosystems. In A Report for the National Greenhouse Strategy; Module 6.6 (Criteria and Indicators of Sustainable Forest Management); Bureau of Rural Sciences: Canberra, Australian, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Stokland, J.N.; Tomter, S.M.; Söderberg, U. Development of Dead Wood Indicators for Biodiversity Monitoring: Experiences from Scandinavia. In Proceedings of the EFI Proceedings, Epinal, France, 27 June–2 July 2004; p. 211. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Larsen, D.R.; Shilley, S.R.; Thompson, F.R. Estimating cavity tree abundance by stand age and basal area, Missouri, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 179, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Shifley, S.R.; Thompson, F.R.; Larsen, D.R. Simulated cavity tree dynamics under alternative timber harvest regimes. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 193, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhl, J.; Brändli, U.B. Deadwood volume assessment in the third swiss national forest inventory: Methods and first results. Eur. J. For. Res. 2007, 126, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaike, T. Snag abundance and species composition in a managed forest landscape in central Japan composed of Larix kaempferi plantation and secondary broadleaf forests. Silva Fenn. 2009, 43, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Long, S.C.; Sutherland, G.D.; Daniels, L.D.; Heemskerk, B.H.; Storaunet, K.O. Temporal dynamics of snags and development of snag habitats in wet spruce-fir stands in east-central British Columbia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 3613–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Institute for global environmental strategies: Hayama, Japan, 2006; pp. 4–83.
- INE—Insituto Nacional de Estadística. Available online: https://www.ine.es/ (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Gobierno de La Rioja. Available online: https://web.larioja.org/ (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Hunter, M.L. Wildlife, Forests, and Forestry: Principles of Managing Forests for Biological Diversity; Prentice Hall: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Morelli, S.; Paletto, A.; Tosi, V. Il legno morto dei boschi: Indagine sulla densità basale del legno di alcune specie del Trentino. Forest 2007, 4, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, C. Tavole Stereometriche ed Alsometriche Costruite per i Boschi Italiani; Istituto Sperimentale per l’Assestamento Forestale e per l’Alpicoltura: Trento, Italy, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Sipala, B. L’importanza della Necromassa Legnosa: Caratterizzazione Quali-Quantitativa e Variabilità del Legno Morto in Relazione All’accessibilità delle Faggete Gestite del Parco Nazionale d’Abruzzo, Lazio e Molise. Master’s Thesis, Università degli Studi della Tuscia, Viterbo, Italy, September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Behjou, F.K.; Lo Monaco, A.; Tavankar, F.; Venanzi, R.; Nikooy, M.; Mederski, P.S.; Picchio, R. Coarse Woody Debris variability due to human accessibility to forest. Forests 2018, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuarto Inventario Forestal Nacional—La Rioja; Gobierno de España; Ministerio de Agricultura: Alimentación y Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2013.
- Crecente-Campo, F.; Pasalodos-Tato, M.; Alberdi, I.; Hernández, L.; Ibañez, J.J.; Cañellas, I. Assessing and modelling the status and dynamics of deadwood through national forest inventory data in Spain. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 360, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, P.; Di Cosmo, L. Forest carbon in Italian forests: Stocks, inherent variability and predictability using NFI data. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 337, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallauri, D.; André, J.; Blondel, J. Le Bois Mort, un Attribut Vital de la Biodiversité de la Forêt Naturelle, une Lacune de la Forêt Gérée; Rapport WWF: France, Paris, 2003. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).