Flood Disaster Mapping Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study of the 2022 Pakistan Floods †
Abstract
1. Introduction
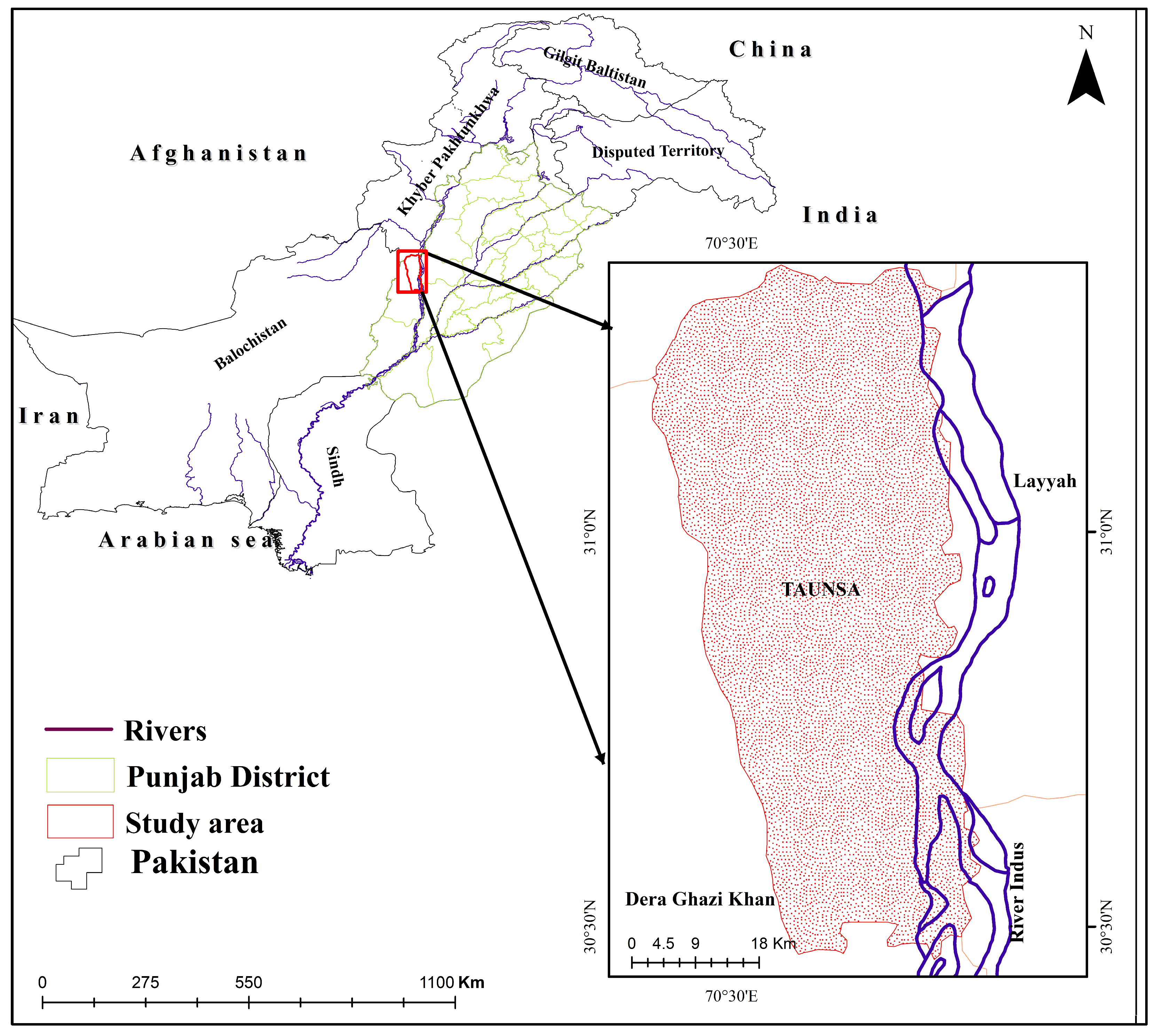
Study Area
2. Data and Methodology
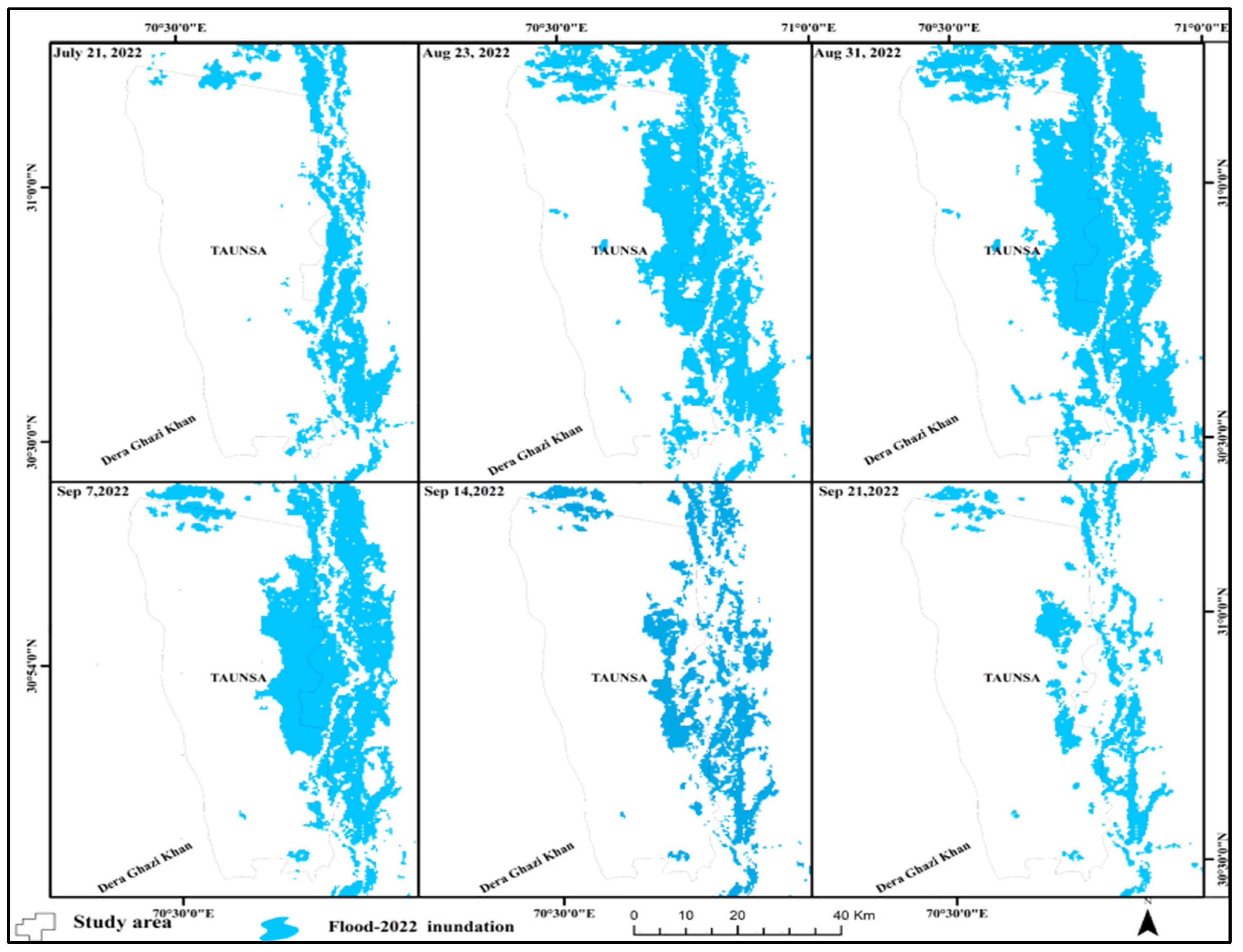
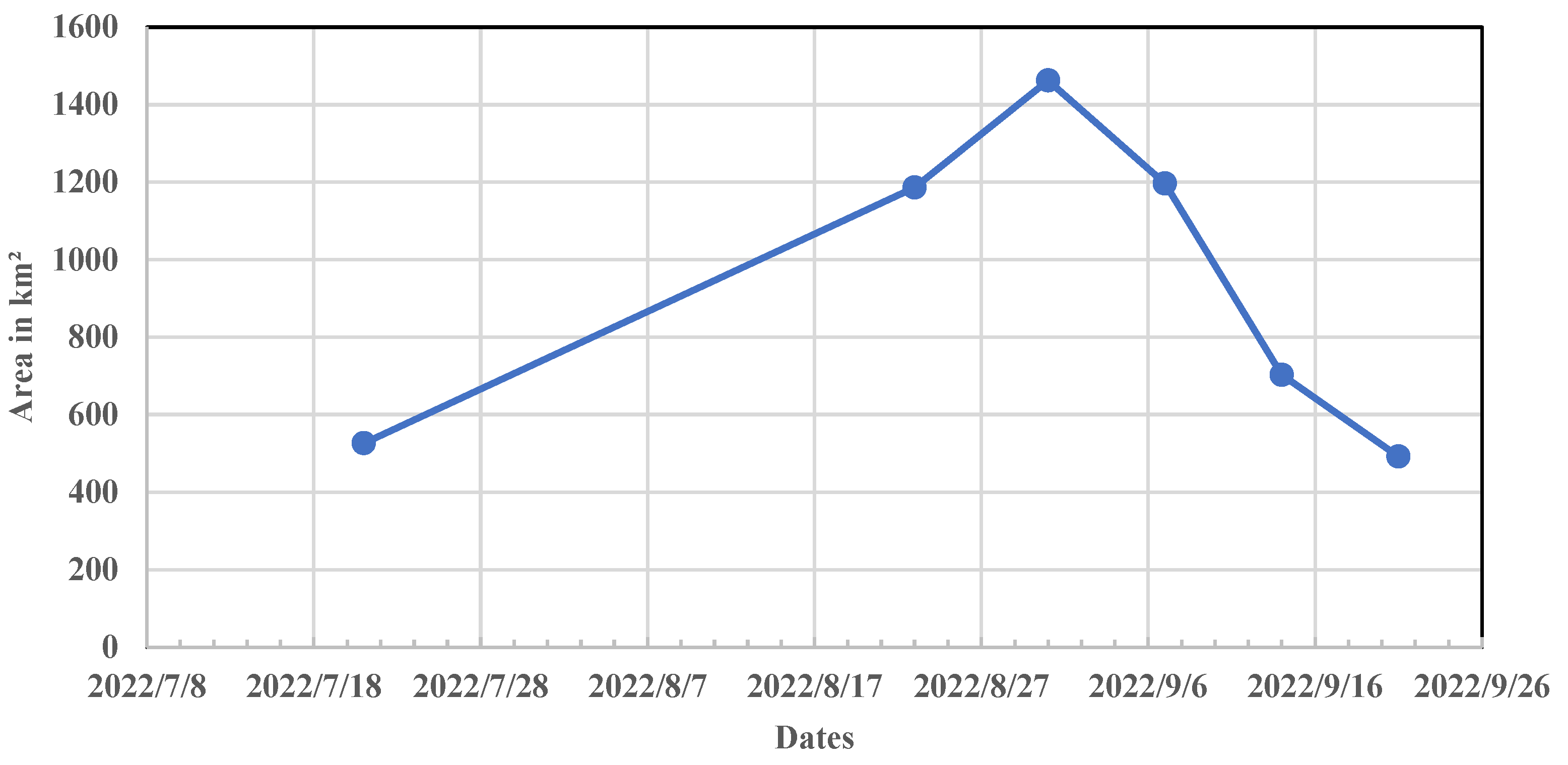
3. Results and Discussion
Spatio-Temporal Flooded Area Mapping
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Syvitski, J.P.; Brakenridge, G.R. Causation and avoidance of catastrophic flooding along the Indus River, Pakistan. GSA Today 2013, 23, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, C.M.; Rao, G.S.; Farooq, M.; Manjusree, P.; Shukla, A.; Sharma, S.V.S.P.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Begum, A.; Bhanumurthy, V.; Diwakar, P.G.; et al. Satellite-based assessment of the catastrophic Jhelum floods of September 2014, Jammu & Kashmir, India. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 8, 309–327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X.; Liu, H. Hydrodynamic and Inundation Modeling of China’s Largest Freshwater Lake Aided by Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4858–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Bates, P.D.; Apel, H.; Aronica, G.T. Global Flood Hazard Mapping, Modeling, and Forecasting: Challenges and Perspectives. In Global Flood Hazard: Applications in Modeling, Mapping, and Forecasting; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, S.; Sajjad, A.; Rahman, A. Cause and damage analysis of 2010 food disaster in district Muzaffar Garh, Pakistan. Nat. Hazards 2021, 107, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, B.; Cholaw, B.; Alvim, D.S.; Javeed, S.; Khan, J.A.; Javed, M.A.; Khan, A.H. Riverine flood assessment in Jhang district in connection with ENSO and summer monsoon rainfall over Upper Indus Basin for 2010. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 971–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgamuge, M.N.; Nirmalathas, A. Analysis of large flood events: Based on flood data during 1985–2016 in Australia and India. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Wetherald, R.T.; Dunne, K.A.; Delworth, T.L. Increasing risk of great floods in a changing climate. Nature 2002, 415, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Akhtar, M.; Muhammad, S.; Paras, S.; Rahmatullah, J. Techniques of Remote Sensing and GIS for flood monitoring and damage assessment: A case study of Sindh province, Pakistan. Egypt J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2012, 15, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.S.; Bala, S.K.; Haque, M. Flood inundation map of Bangladesh using MODIS time-series images. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2010, 3, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, K.; Sindha, R.; Panda, P.K. The Indus flood of 2010 in Pakistan: A perspective analysis using remote sensing data. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, H.N.; Siddiqui, Q.T.M.; Ghuman, A.R.; Kamal, M.A.; Mughal, H. A critical analysis of 2010 floods in Pakistan. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, S.; Rahman, A.; Sajjad, A. Assessment of 2010 flood disaster causes and damages in district Muzaffargarh, Central Indus Basin, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Chisenga, C.; Mahmood, S. The riverine flood catastrophe in August 2010 in South Punjab, Pakistan: Potential causes, extent and damage assessment. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 14121–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Chisenga, C.; Saleem, N.; Hassan, H. Operational Monitoring and Damage Assessment of Riverine Flood-2014 in the Lower Chenab Plain, Punjab, Pakistan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, B.; Azmat, M.; Tao, H.; Ahmad, S.; Khattak, M.U.; Haider, S.; Ahmad, S.; Khero, Z.; Goodell, C.R. Flood Hazard Assessment for the Tori Levee Breach of the Indus River Basin, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Chisenga, C.; Mazhar, N.; Nadeem, B. Riverine flood mapping and impact assessment using remote sensing technique: A case study of Chenab flood-2014 in Multan district, Punjab, Pakistan. Nat Hazards 2022, 110, 2207–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Disaster Management Authority((NDMA). Annual Flood Report; Regional Office: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2021.
- Punjab Provincial Disaster Management Authority (PPDMA). Annual Flood Report; Regional Office: Lahore, Pakistan, 2021.
- Siddiqui, M.; Haider, S.; Gabriel, H.F.; Shahzad, A. Rainfall–run off, flood inundation and sensitivity analysis of the 2014 Pakistan flood in the Jhelum and Chenab River basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Flood Commission Islamabad (FFCI). Annual Flood Report; Ministry of Water and Power, Government of Pakistan: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2021.
- Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD). Annual Report; Regional Meteorological Observatory: Lahore, Pakistan, 2022.
- Munasinghe, D.; Cohen, S.; Huang, Y.F.; Tsang, Y.P.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Z.F. Intercomparison of Satellite Remote Sensing-Based Flood Inundation Mapping Techniques. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 54, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Romero, B.; Hirpa, F.A.; Pozo, J.T.; Salamon, P.; Brakenridge, R.; Pappenberger, F.; De Groeve, T. On the use of global flood forecasts and satellite-derived inundation maps for flood monitoring in data-sparse regions. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15702–15728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Li, C. Water body extraction from Landsat ETM+ imagery using adaboost algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Alphan, H.; Doygun, H.; Unlukaplan, Y.I. Post-classification comparison of land cover using multitemporal Landsat and ASTER imagery: The case of Kahramanmaras, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 151, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokni, K.; Ahmad, A.; Selamat, A.; Hazini, S. Water feature extraction and change detection using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4173–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalized difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A.; Meyer, F.J. Operational Flood Mapping Using Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 SAR Images: A Case Study from Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Giordan, D.; Caló, F.; Pepe, A.; Zucca, F.; Pedro Galve, J. Potential and Limitations of Open Satellite Data for Flood Mapping. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, C.; Gioia, A.; Iacobellis, V.; Manfreda, S. Detection of Surface Water and Floods with Multispectral Satellites. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güvel, Ş.P.; Akgül, M.A.; Aksu, H. Flood inundation maps using Sentinel-2: A case study in Berdan Plain. Water Supply 2022, 22, 4098–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajjad, A.; Lu, J.; Aslam, R.W.; Ahmad, M. Flood Disaster Mapping Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study of the 2022 Pakistan Floods. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14312
Sajjad A, Lu J, Aslam RW, Ahmad M. Flood Disaster Mapping Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study of the 2022 Pakistan Floods. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2023; 25(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14312
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajjad, Asif, Jianzhong Lu, Rana Waqar Aslam, and Muhammad Ahmad. 2023. "Flood Disaster Mapping Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study of the 2022 Pakistan Floods" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 25, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14312
APA StyleSajjad, A., Lu, J., Aslam, R. W., & Ahmad, M. (2023). Flood Disaster Mapping Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study of the 2022 Pakistan Floods. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 25(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14312








