Time-Series-Based Air Temperature Forecasting Based on the Outlier Robust Extreme Learning Machine †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Improved Outlier Robust Extreme Learning Machine (IORELM)
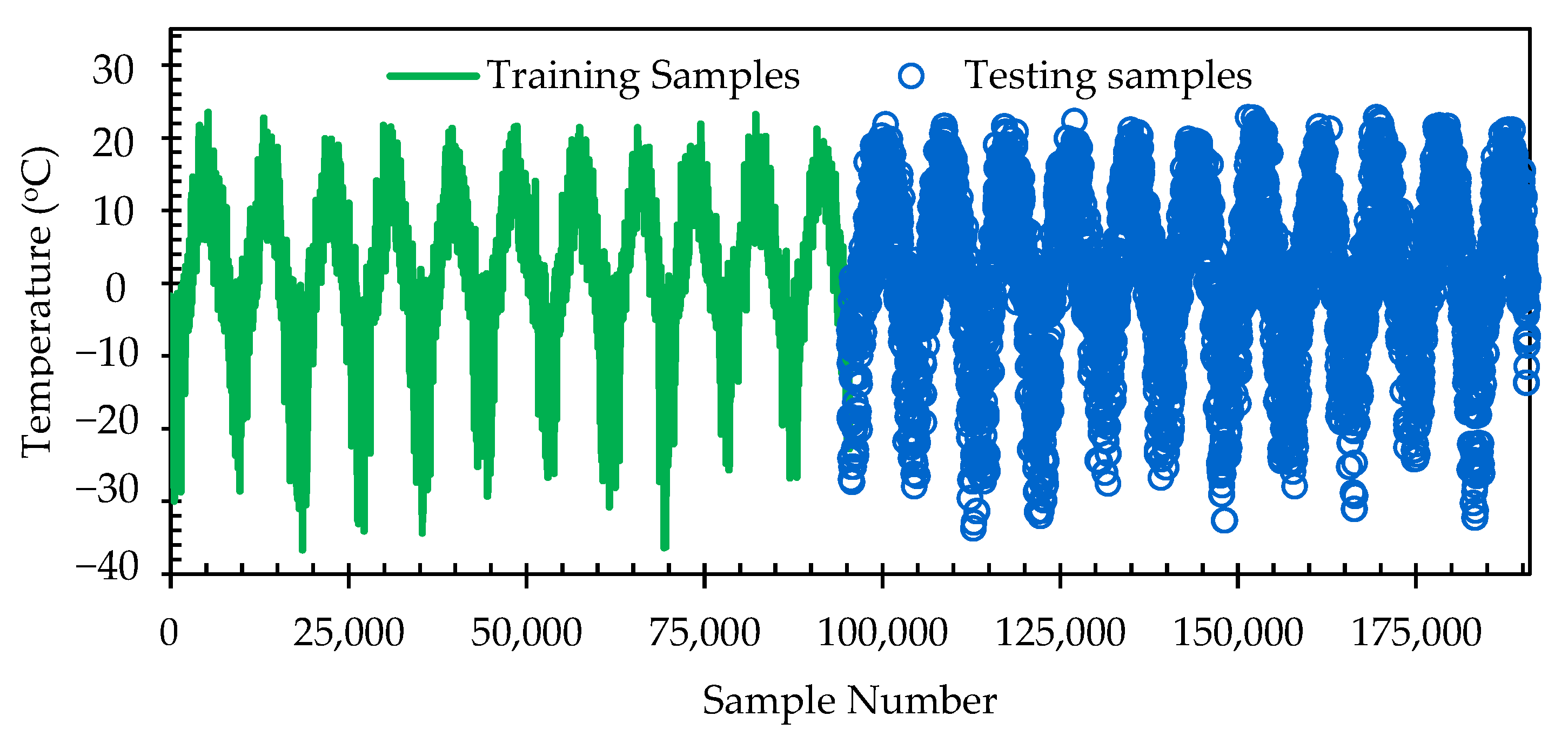
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tol, R.S. Estimates of the damage costs of climate change. Part 1: Benchmark estimates. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2002, 21, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Hua, J.; Shi, Y.; Ren, C. Constructing air temperature and relative humidity-based hourly thermal comfort dataset for a high-density city using machine learning. Urban Clim. 2023, 47, 101400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombaycı, Ö.A.; Gölcü, M. Daily means ambient temperature prediction using artificial neural network method: A case study of Turkey. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, K.; Chen, X. Machine-Learning Estimation of Snow Depth in 2021 Texas Statewide Winter Storm Using SAR Imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL099119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonakdari, H.; Ebtehaj, I. A comparative study of extreme learning machines and support vector machines in prediction of sediment transport in open channels. Int. J. Eng. 2016, 29, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Bonakdari, H.; Ebtehaj, I.; Samui, P.; Gharabaghi, B. Lake Water-Level fluctuations forecasting using Minimax Probability Machine Regression, Relevance Vector Machine, Gaussian Process Regression, and Extreme Learning Machine. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 3965–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonakdari, H.; Qasem, S.N.; Ebtehaj, I.; Zaji, A.H.; Gharabaghi, B.; Moazamnia, M. An expert system for predicting the velocity field in narrow open channel flows using self-adaptive extreme learning machines. Measurement 2020, 151, 107202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H.; Moradi, F.; Gharabaghi, B.; Khozani, Z.S. An Integrated Framework of Extreme Learning Machines for Predicting Scour at Pile Groups in Clear Water Condition. Coastal Eng. 2018, 135, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H. A reliable hybrid outlier robust non-tuned rapid machine learning model for multi-step ahead flood forecasting in Quebec, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, M. Outlier-robust extreme learning machine for regression problems. Neurocomputing 2015, 151, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebtehaj, I.; Soltani, K.; Amiri, A.; Faramarzi, M.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Bonakdari, H. Prognostication of shortwave radiation using an improved No-Tuned fast machine learning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministère de l’Environnement et de la Lutte Contre les Changements Climatiques, de la Faune et des Parcs. Données du Réseau de Surveillance du Climat du Québec, Direction de la Qualité de l’air et du Climat, Québec. 2022. Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/ (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H. Discussion of “Comparative Study of Time Series Models, Support Vector Machines, and GMDH in Forecasting Long-Term Evapotranspiration Rates in Northern Iran” by Afshin Ashrafzadeh, Ozgur Kişi, Pouya Aghelpour, Seyed Mostafa Biazar, and Mohammadreza Askarizad Masouleh. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2021, 147, 07021005. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, R.; Binns, A.; Bonakdari, H.; Ebtehaj, I.; Gharabaghi, B. Estimating 2-year flood flows using the generalized structure of the Group Method of Data Handling. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeynoddin, M.; Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H. Development of a linear based stochastic model for daily soil temperature prediction: One step forward to sustainable agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 176, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H.; Gharabaghi, B.; Khelifi, M. Time-Series-Based Air Temperature Forecasting Based on the Outlier Robust Extreme Learning Machine. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14236
Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H, Gharabaghi B, Khelifi M. Time-Series-Based Air Temperature Forecasting Based on the Outlier Robust Extreme Learning Machine. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2023; 25(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14236
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbtehaj, Isa, Hossein Bonakdari, Bahram Gharabaghi, and Mohamed Khelifi. 2023. "Time-Series-Based Air Temperature Forecasting Based on the Outlier Robust Extreme Learning Machine" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 25, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14236
APA StyleEbtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H., Gharabaghi, B., & Khelifi, M. (2023). Time-Series-Based Air Temperature Forecasting Based on the Outlier Robust Extreme Learning Machine. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 25(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14236








