Potential Application of Soil Probiotics for Sustainable Soil Health and Improved Peanut Yield †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Evaluate the potential of selected microbes under natural field conditions on soil health;
- Identify their beneficial effects on crop productivity.
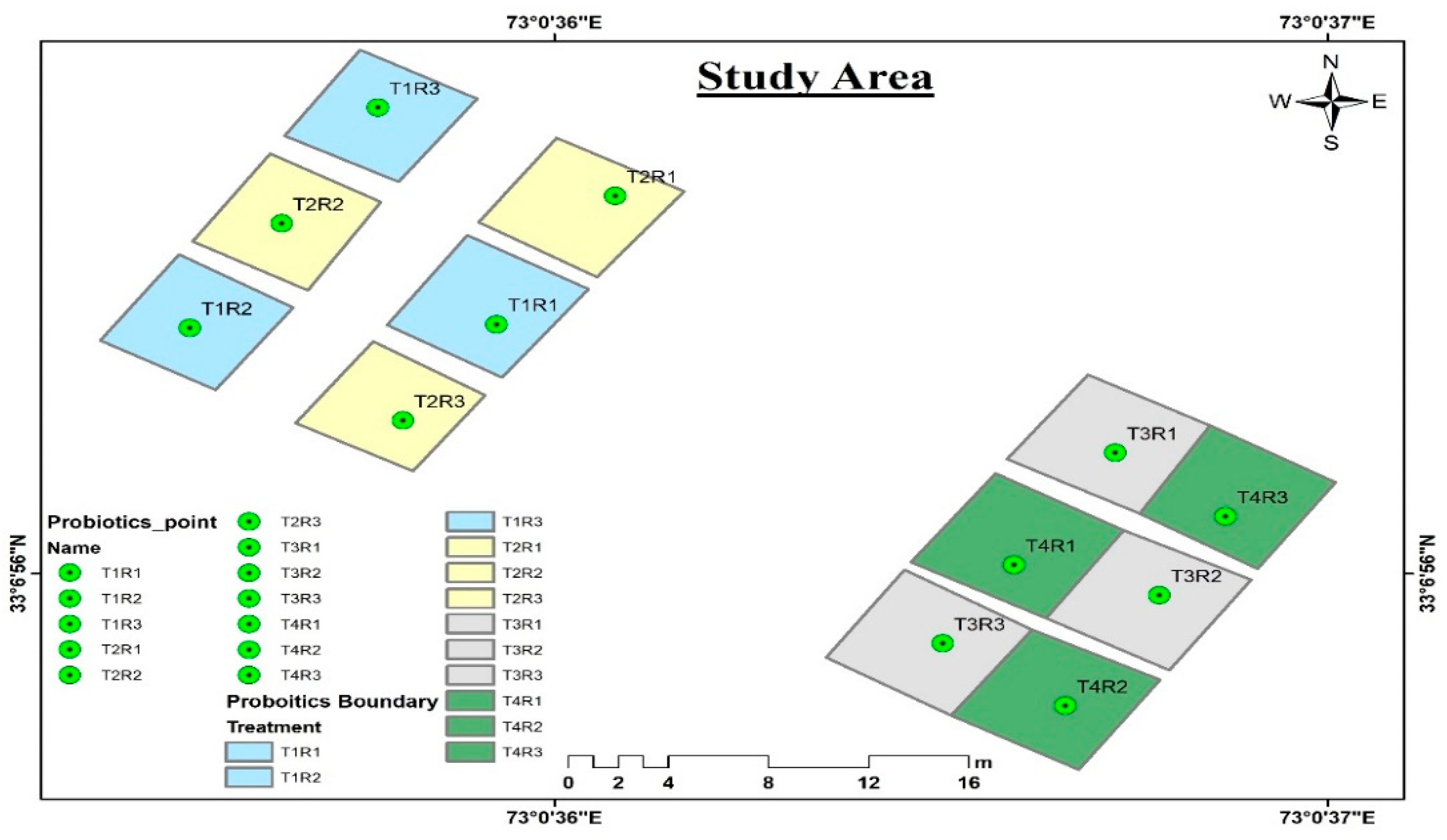
2. Methodology
3. Results
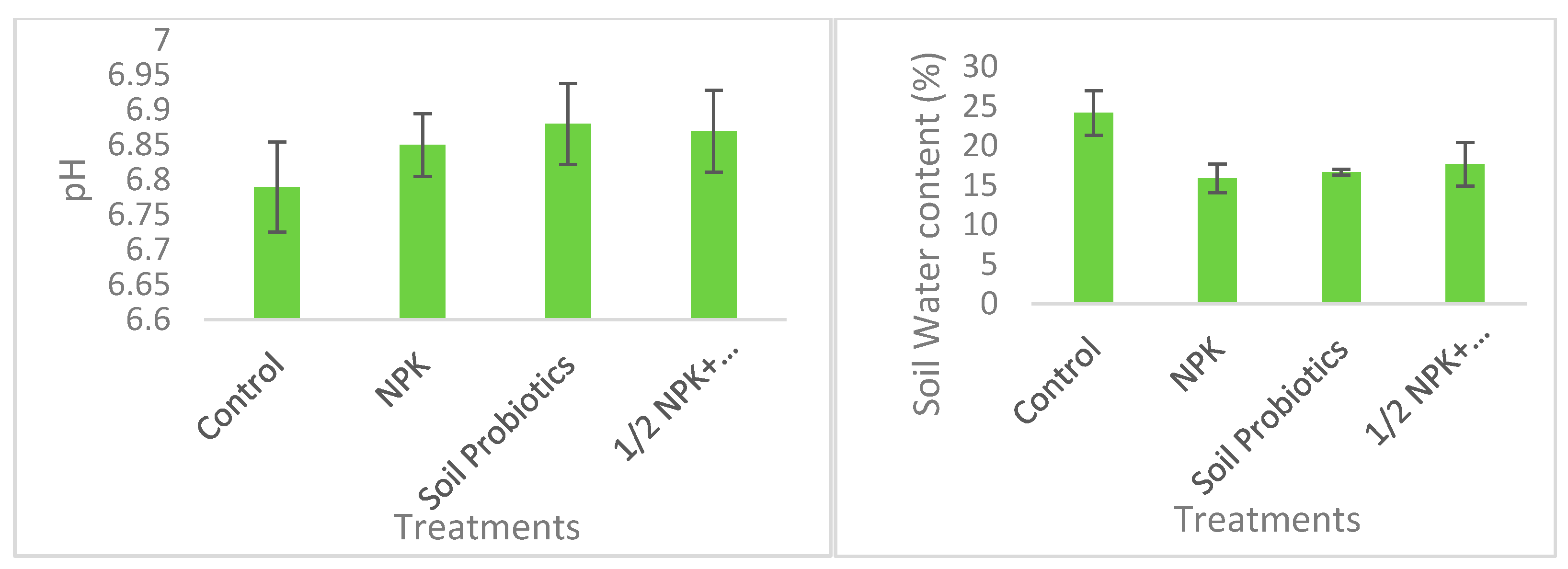
3.1. Experimental Soil Properties
Leaf Area Index of Peanut Crop
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboelill, A.A.; Mehanna, H.M.; Kassab, O.M.; Abdallah, E.F. The Response of Peanut to Foliar Spraying with Potassium Under Water Stress Conditions. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 6, 626–634. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, D.L.; Brandenburg, R.; Brown, B.; Bullen, G.; Roberson, G.; Shew, B. Peanut Information; AG-331; North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service Publications: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2017; p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- Jadon, K.S.; Thirumalaisamy, P.P.; Koradia, V.G.; Padavi, R.D. Management of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) diseases through nutrient supplements. Legume Res. Int. J. 2018, 41, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shi, H.; Du, Z.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. Comparative genomic and functional analysis reveal conservation of plant growth promoting traits in Paenibacillus polymyxa and its closely related species. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.N.; Wei, W.H.; Ren, X.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhou, X.J.; Huang, L.; Tang, X.C.; Jiang, H.F. Construction of a high-quality genomic BAC library for Chinese peanut cultivar Zhonghua 8 with high oil content. Bot. Stud. 2014, 55, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, R.G.; Torrie, J.H. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 401–437. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, N.; Ijaz, S.S.; Hussain, Q.; Khalid, R.; Saleem, S.R.; Kanwal, S.; Tahir, M.N.; Shahzad, B. Potential Application of Soil Probiotics for Sustainable Soil Health and Improved Peanut Yield. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 23, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023027
Javed N, Ijaz SS, Hussain Q, Khalid R, Saleem SR, Kanwal S, Tahir MN, Shahzad B. Potential Application of Soil Probiotics for Sustainable Soil Health and Improved Peanut Yield. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 23(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023027
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Nabeeha, Shahzada Sohail Ijaz, Qaiser Hussain, Rabia Khalid, Shoaib Rashid Saleem, Sehrish Kanwal, Muhammad Naveed Tahir, and Basit Shahzad. 2022. "Potential Application of Soil Probiotics for Sustainable Soil Health and Improved Peanut Yield" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 23, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023027
APA StyleJaved, N., Ijaz, S. S., Hussain, Q., Khalid, R., Saleem, S. R., Kanwal, S., Tahir, M. N., & Shahzad, B. (2022). Potential Application of Soil Probiotics for Sustainable Soil Health and Improved Peanut Yield. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 23(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023027







