Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products for Hydroclimatic Applications over Potohar Region, Pakistan †
Abstract
1. Introduction
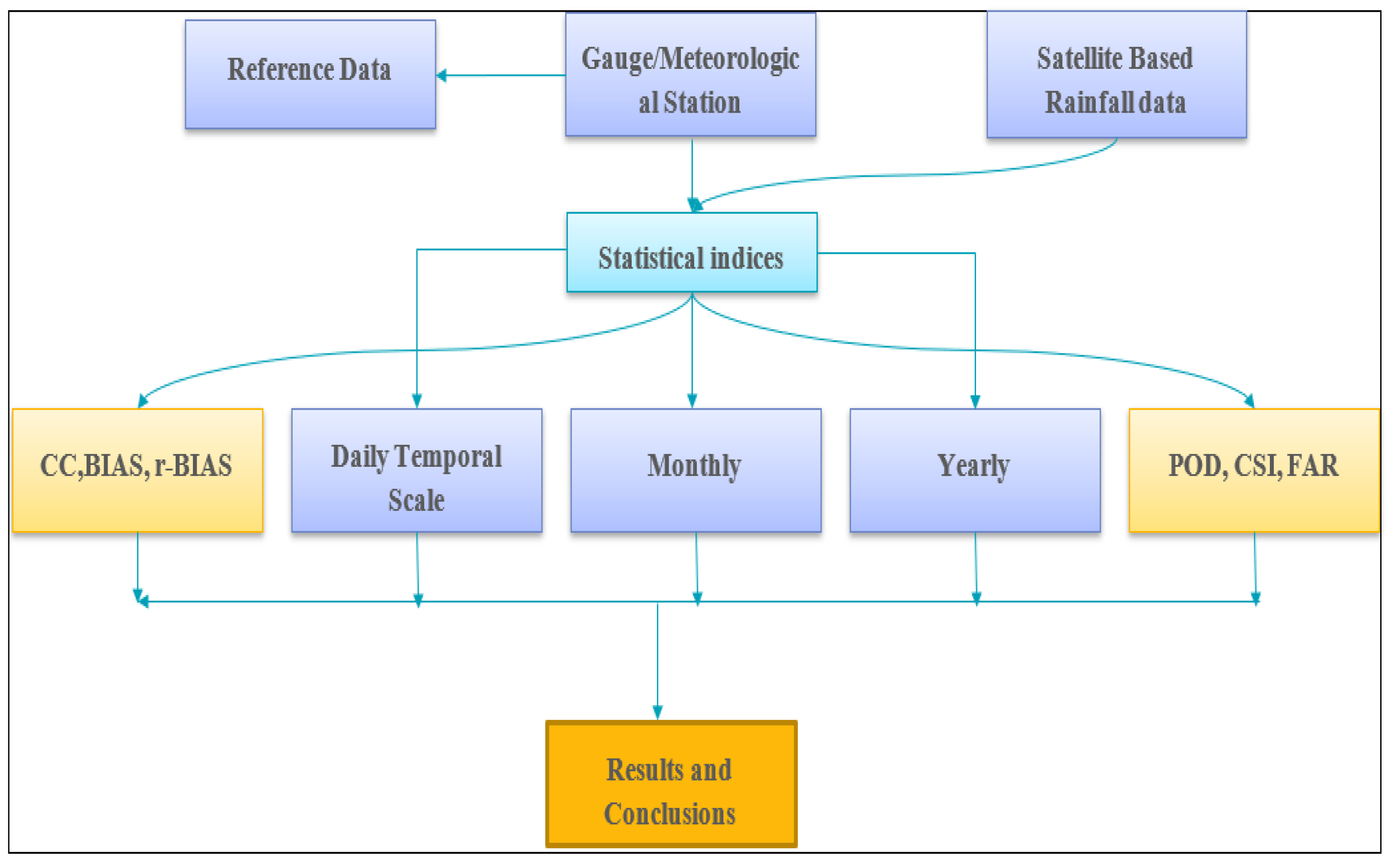
2. Materials and Methods
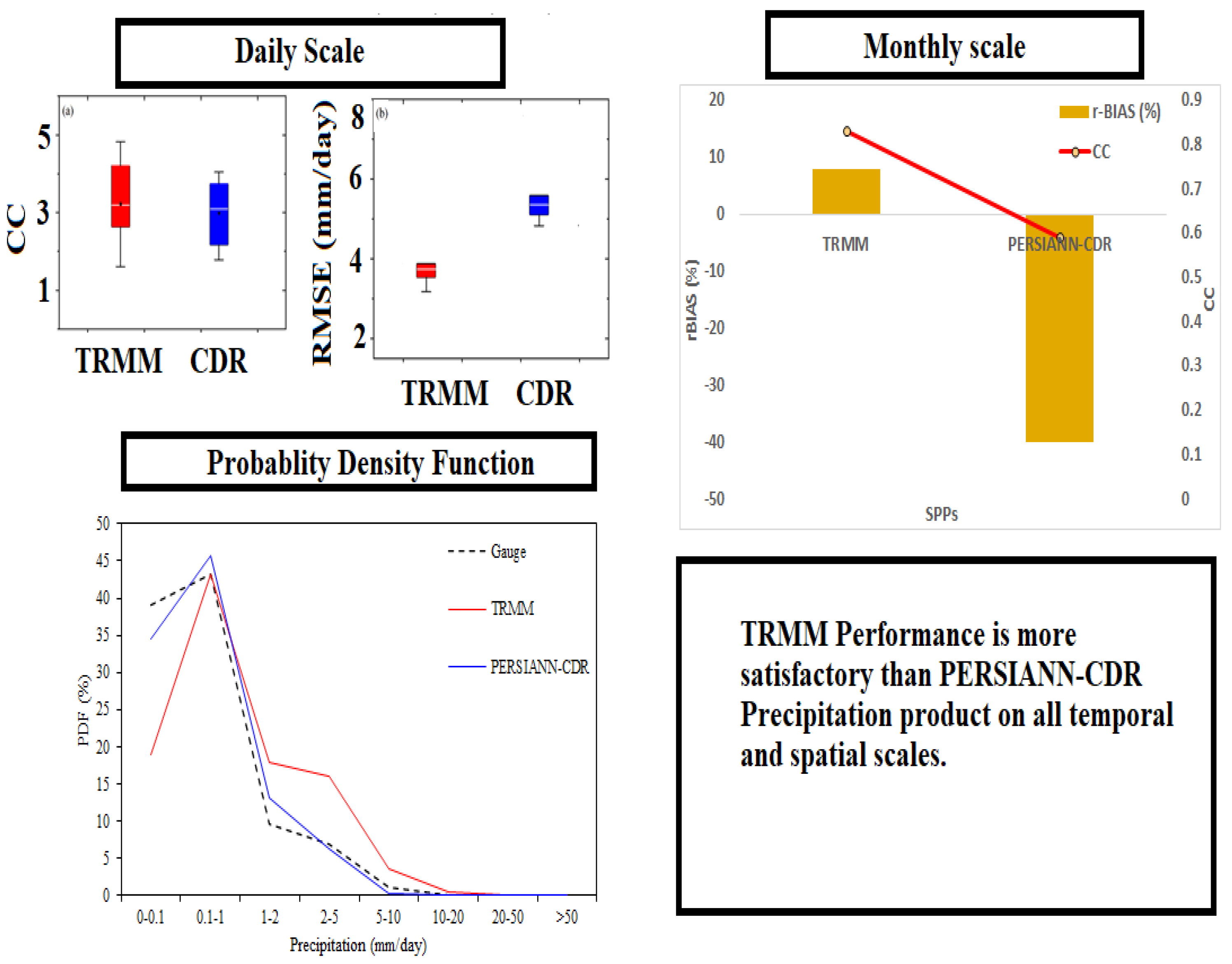
3. Results and Conclusions
- On a daily scale, the performance of TRMM is more satisfactory than PERSIANN-CDR.
- On a monthly scale, the precipitation estimates of both SPPs (TRMM and PERSIANN-CDR) are in good contact with gauge data.
- The daily PERSIANN-CDR performance is unsatisfactory (CC < 0.7). However, its monthly CC value (CC = 0.83) is acceptable.
- The error value RMSE is also the maximum for PERSIANN-CDR compared to TRMM.
- The TRMM outperforms the PERSIANN product based on a yearly scale.
- The POD and FAR are close to 1 for TRMM, but the PERSIANN-CDR values are not in acceptable ranges.
- PERSIANN-CDR has a higher false alarm ratio (FAR) than TRMM.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anjum, M.N.; Irfan, M.; Waseem, M.; Leta, M.K.; Niazi, U.M.; Rahman, S.; Ghanim, A.; Mukhtar, M.A.; Nadeem, M.U. Assessment of PERSIANN-CCS, PERSIANN-CDR, SM2RAIN-ASCAT, and CHIRPS-2.0 Rainfall Products over a Semi-Arid Subtropical Climatic Region. Water 2022, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations). AQUASTAT. 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/aquastat (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Ashraf, M. Water Scarcity in Pakistan: Issues and Options. 2018. Available online: http://pcrwr.gov.pk/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Water-Scarcity-in-Pakistan-Issues-and-Options-May-18.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Nadeem, M.U.; Waheed, Z.; Ghaffar, A.M.; Javaid, M.M.; Hamza, A.; Ayub, Z.; Nawaz, M.A.; Waseem, W.; Hameed, M.F.; Zeeshan, A.; et al. Application of HEC-HMS for flood forecasting in Hazara catchment Pakistan, south Asia. Int. J. Hydrol. 2022, 6, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.U.; Anjum, M.N.; Afzal, A.; Azam, M.; Hussain, F.; Usman, M.; Javaid, M.M.; Mukhtar, M.A.; Majeed, F. Assessment of Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products over the Himalayan Mountains of Pakistan, South Asia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.U.; Ghanim, A.A.J.; Anjum, M.N.; Shangguan, D.; Rasool, G.; Irfan, M.; Niazi, U.M.; Hassan, S. Multiscale Ground Validation of Satellite and Reanalysis Precipitation Products over Diverse Climatic and Topographic Conditions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.F.; Xiao, C.; Anjum, M.N.; Adnan, M.; Nawaz, Z.; Ijaz, M.W.; Sajid, M.; Farid, H.U. Evaluation and comparison of TRMM multi-satellite precipitation products with reference to rain gauge observations in Hunza River basin, Karakoram Range, northern Pakistan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.U.; Rasool, G.; Nawaz, M.A. Runoff Estimations by Using Satellite-Based Rainfall Products (Srps) and Then, Identifying Its Relation with Other Gauge Data Over Potohar Plateau, Pakistan. Int. J. Water Res. 2022, 4, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, J.d.S.; Viola, M.R.; Junqueira, R.; de Oliveira, V.A.; de Mello, C.R. Evaluation of satellite precipitation products for hydrological modeling in the Brazilian cerrado biome. Water 2020, 12, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, A.A.; Chevallier, P.; Arnaud, Y.; Ahmad, B. Snow cover dynamics and hydrological regime of the Hunza River basin, Karakoram Range, Northern Pakistan. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2275–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Anjum, M.N.; Gao, Y. Performance evaluation of version 5 (V05) of Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (IMERG) over the Tianshan Mountains of China. Water 2019, 11, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nadeem, M.U.; Anjum, M.N.; Asif, M.; Iqbal, T.; Hussain, S.; Sarwar, H.R.A.; Abbas, A. Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products for Hydroclimatic Applications over Potohar Region, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 23, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023018
Nadeem MU, Anjum MN, Asif M, Iqbal T, Hussain S, Sarwar HRA, Abbas A. Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products for Hydroclimatic Applications over Potohar Region, Pakistan. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 23(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023018
Chicago/Turabian StyleNadeem, Muhammad Umer, Muhammad Naveed Anjum, Muhammad Asif, Tahir Iqbal, Saddam Hussain, Hafiz Rana Azeem Sarwar, and Akhtar Abbas. 2022. "Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products for Hydroclimatic Applications over Potohar Region, Pakistan" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 23, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023018
APA StyleNadeem, M. U., Anjum, M. N., Asif, M., Iqbal, T., Hussain, S., Sarwar, H. R. A., & Abbas, A. (2022). Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products for Hydroclimatic Applications over Potohar Region, Pakistan. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 23(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022023018








