Coupling Computational Fluid Dynamics and Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Urban Water Management and Treatment †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
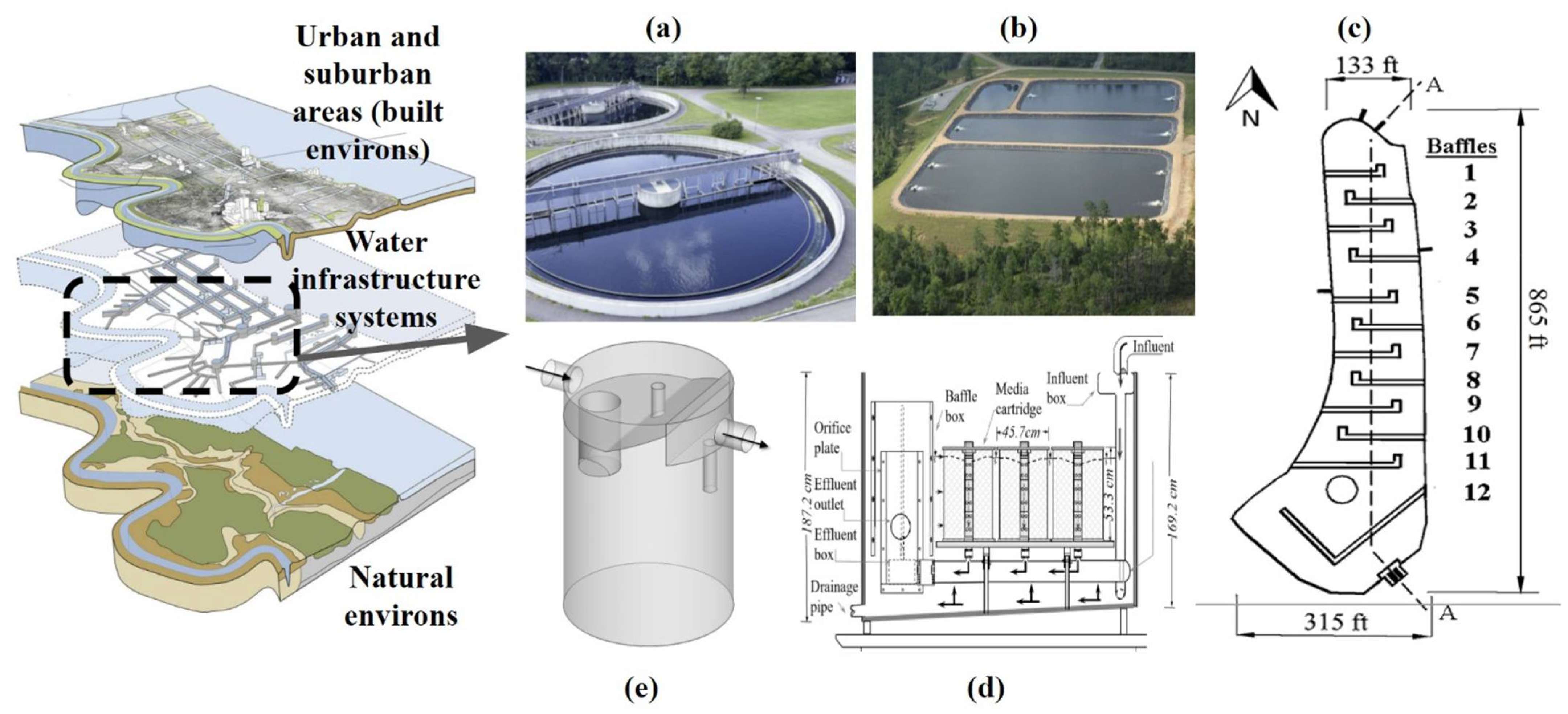
2. Clarification of Particulate Matter (PM) for Urban Drainage Treatment
3. Common Models of Urban Drainage Clarification Units
4. CFD and ML as an Artificial Intelligence (AI) Method
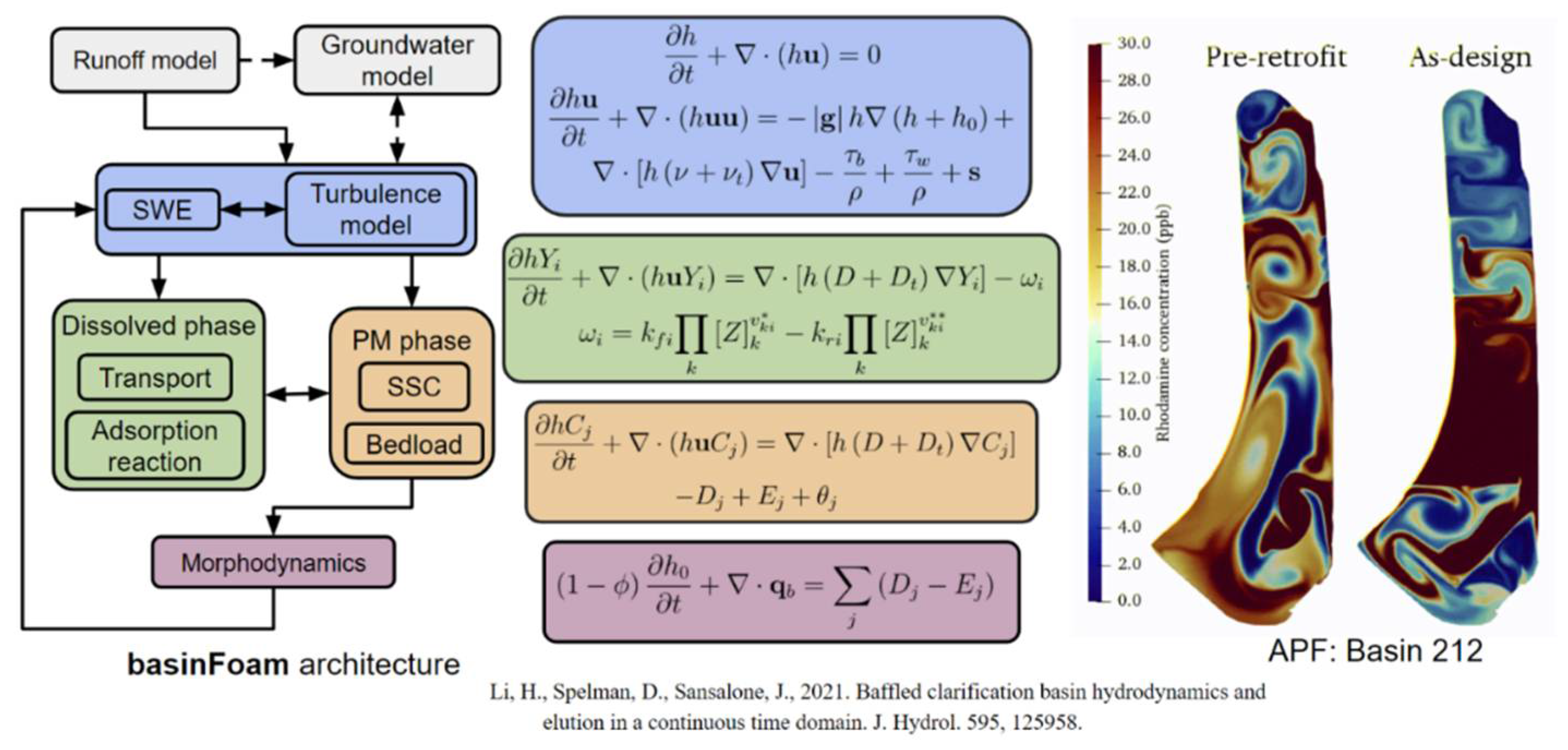
4.1. CFD for Clarification
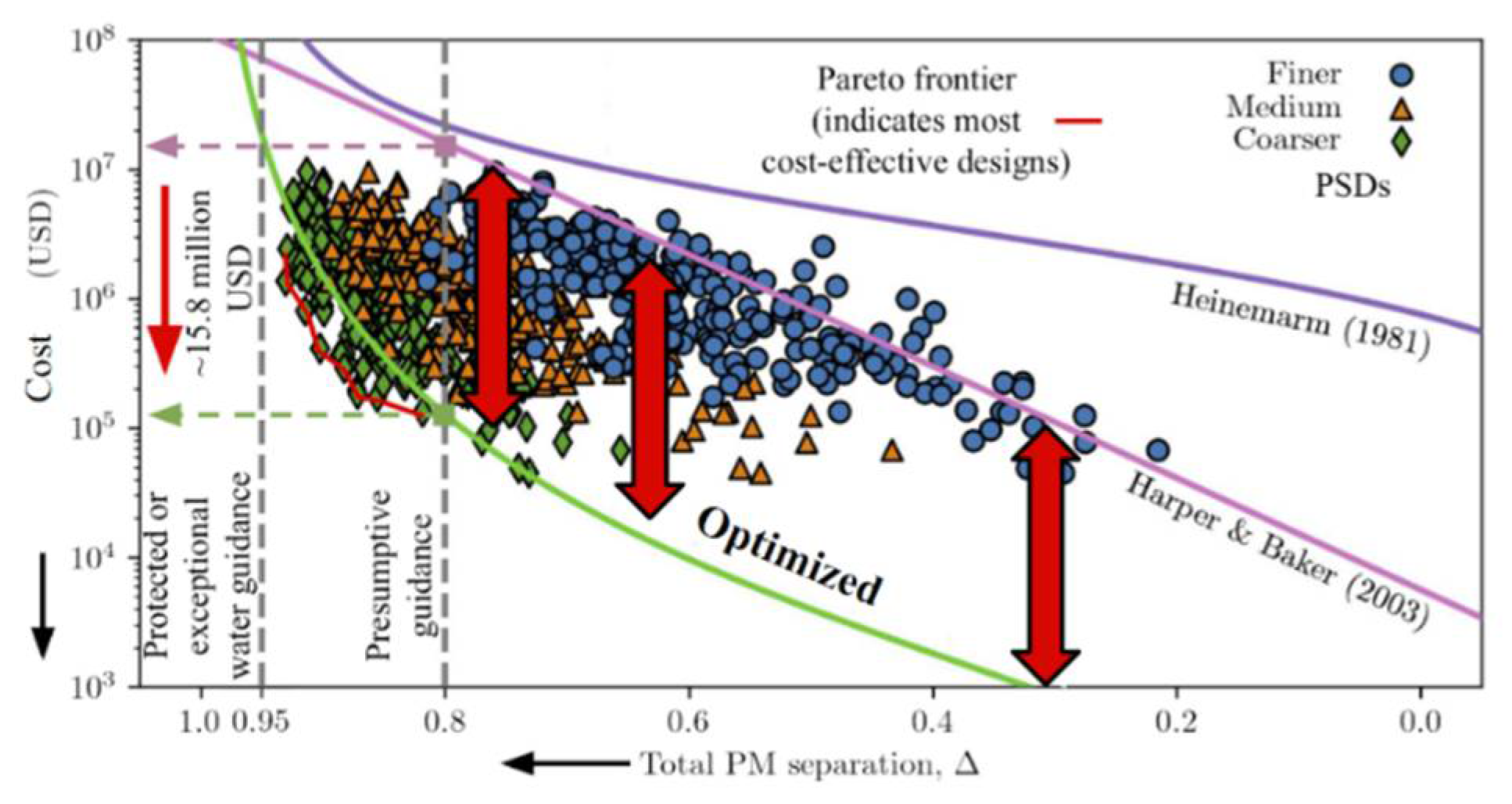
4.2. Machine Learning (ML)
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hazen, A. On sedimentation. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1904, 53, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, G.M. Trap efficiency of reservoirs. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1953, 34, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemarm, H.G. A new sediment trap efficiency curve for small reservoirs. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1981, 17, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. National Engineering Handbook: Sedimentation, 2nd ed.; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
- Harper, H.H.; Baker, D.M. Evaluation of Alternative Stormwater Regulations for Southwest Florida; Technical Report; Water Enhancement and Restoration Coalition, Inc.: Orlando, FL, USA, 2003; Available online: https://chnep.wateratlas.usf.edu/upload/documents/WERCStudyFINAL9-9-03.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Sansalone, J.; Koran, J.; Buchberger, S.; Smithson, J. Physical Characteristics of Solids Transported During Rainfall. J. Environ. Eng. 1998, 124, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sansalone, J. A CFD-ML augmented alternative to residence time for clarification basin scaling and design. Water Res. 2022, 209, 117965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camp, T.R. Study of rational design of settling tanks. Sew. Works J. 1936, 8, 742–758. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Sansalone, J. Interrogating common clarification models for unit operation systems with dynamic similitude. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, W.C.; Cannon, L.; Stouder, M. BMP Modeling Concepts and Simulation; Technical Report; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2006. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-10/documents/bmp_tools_complex.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Li, H.; Sansalone, J. Benchmarking Reynolds-averaged Navier Stokes turbulence models for water clarification systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Balachandar, S.; Sansalone, J. Discordance of tracer transport and particulate matter fate in a baffled clarification system. J. Fluids Eng. 2021, 143, 051202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Balachandar, S.; Sansalone, J. Large-eddy simulation of flow turbulence in clarification systems. Acta Mech. 2021, 232, 1389–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sansalone, J. CFD with evolutionary optimization for stormwater basin retrofits. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Spelman, D.; Sansalone, J. Baffled clarification basin hydrodynamics and elution in a continuous time domain. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spelman, D.; Sansalone, J.J. Methods to model particulate matter clarification of unit operations subject to unsteady loadings. Water Res. 2017, 115, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sansalone, J.J. CFD as a complementary tool to benchmark physical testing of PM separation by unit operations. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sansalone, J.J. CFD Model of PM sedimentation and resuspension in urban water clarification. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04019118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sansalone, J.J. Representation of near-wall particle fate in a Eulerian-Lagrangian approach for clarifier unit operations. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansalone, J.J.; Cristina, C.M. Prediction of Gradation-Based Heavy Metal Mass Using Granulometric Indices of Snowmelt Particles. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Sansalone, J.J. Event-based size distributions of particulate matter transported during urban rainfall-runoff events. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2756–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florida Department of Transportation. Water Management Performance of FAA Pond at Naples Municipal Airport. Tallahassee, FL, 2016. Available online: https://www.florida-aviation-database.com/library/filedownload.aspx?guid=1edf132e-6c5c-4774-9045-faccb850e305 (accessed on 1 May 2022).




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Spelman, D.; Sansalone, J. Coupling Computational Fluid Dynamics and Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Urban Water Management and Treatment. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021087
Li H, Spelman D, Sansalone J. Coupling Computational Fluid Dynamics and Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Urban Water Management and Treatment. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 21(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haochen, David Spelman, and John Sansalone. 2022. "Coupling Computational Fluid Dynamics and Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Urban Water Management and Treatment" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 21, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021087
APA StyleLi, H., Spelman, D., & Sansalone, J. (2022). Coupling Computational Fluid Dynamics and Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Urban Water Management and Treatment. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 21(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021087