Experimental Study of the Effects of Heating or Cooling on the Water Surface in an Open Channel †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- In a basin for water supply of an area, where it is very useful to know where the water intake should be placed so that high temperature water is not drained.
- Knowledge of any height change in water temperature of a heated basin by solar radiation.
- The study of dispersion of liquid waste pollutants in water recipients (lakes, seas, etc).
2. Materials and Methods
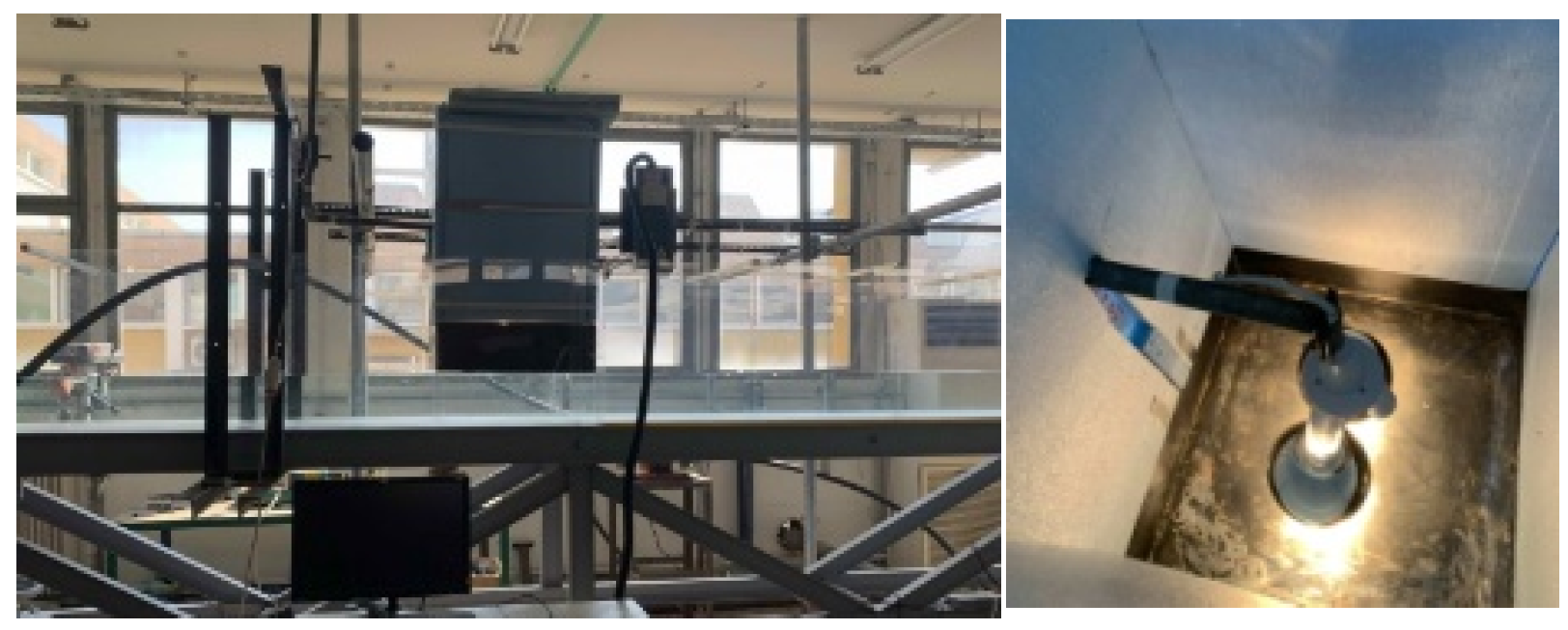
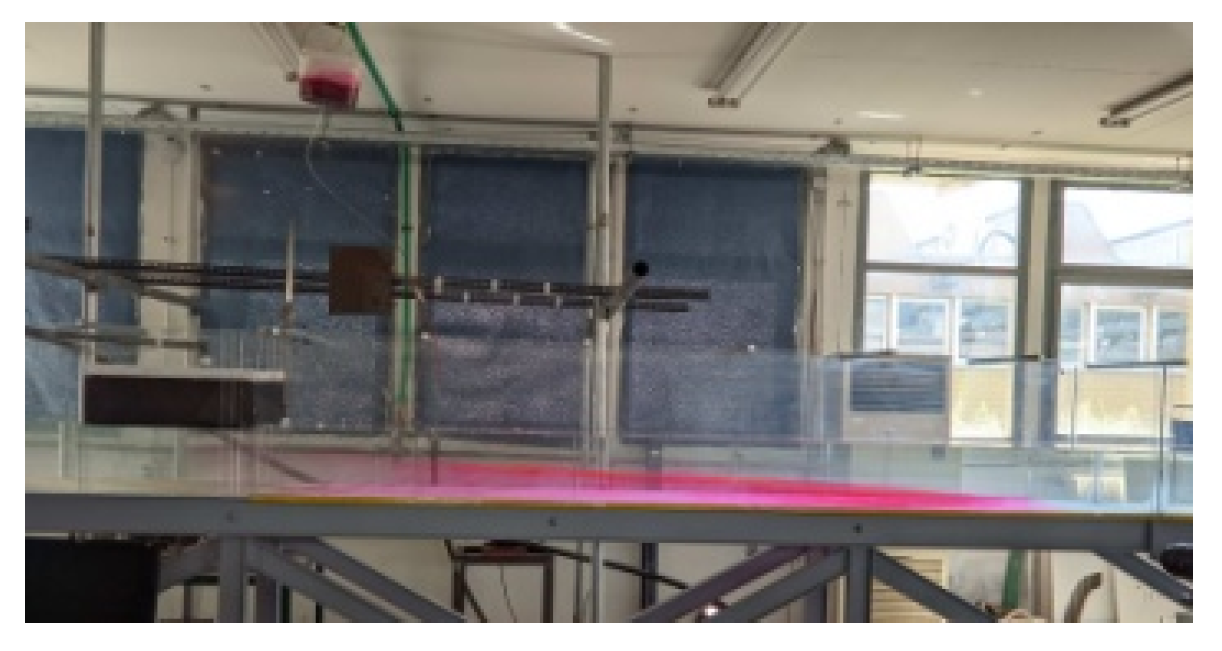
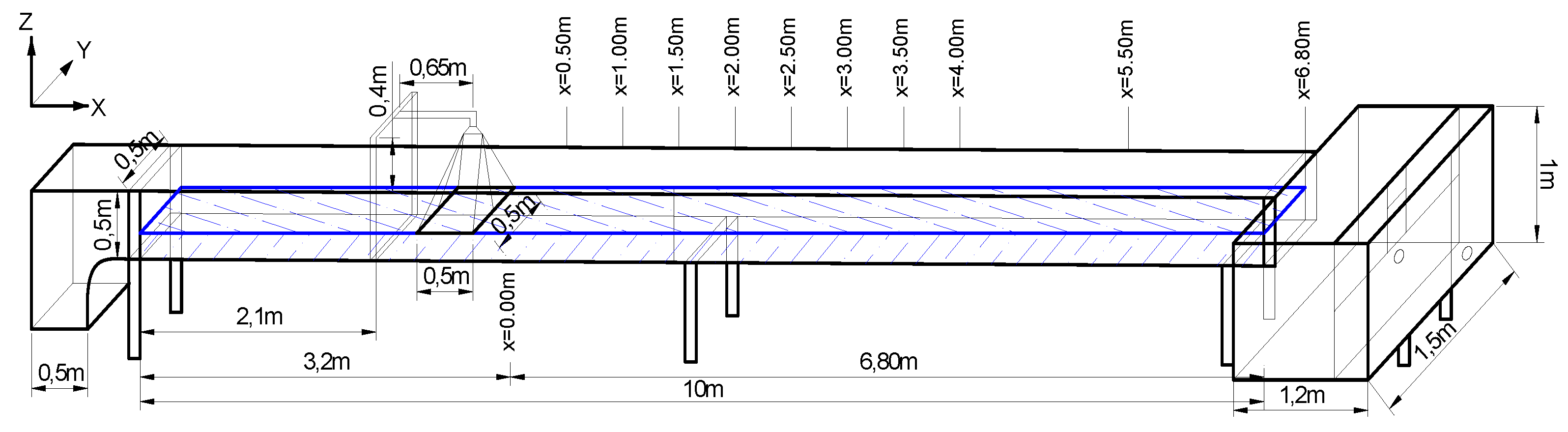
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experiments
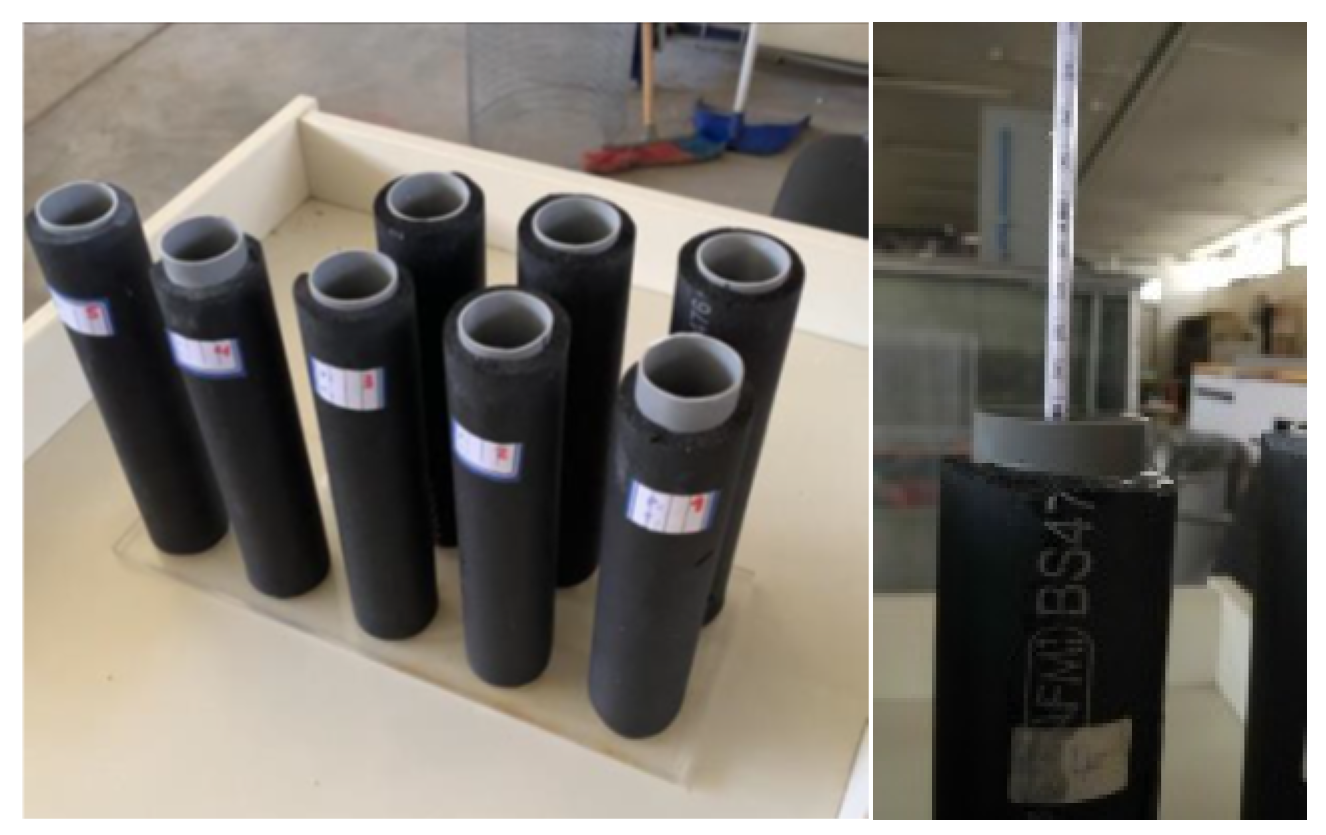
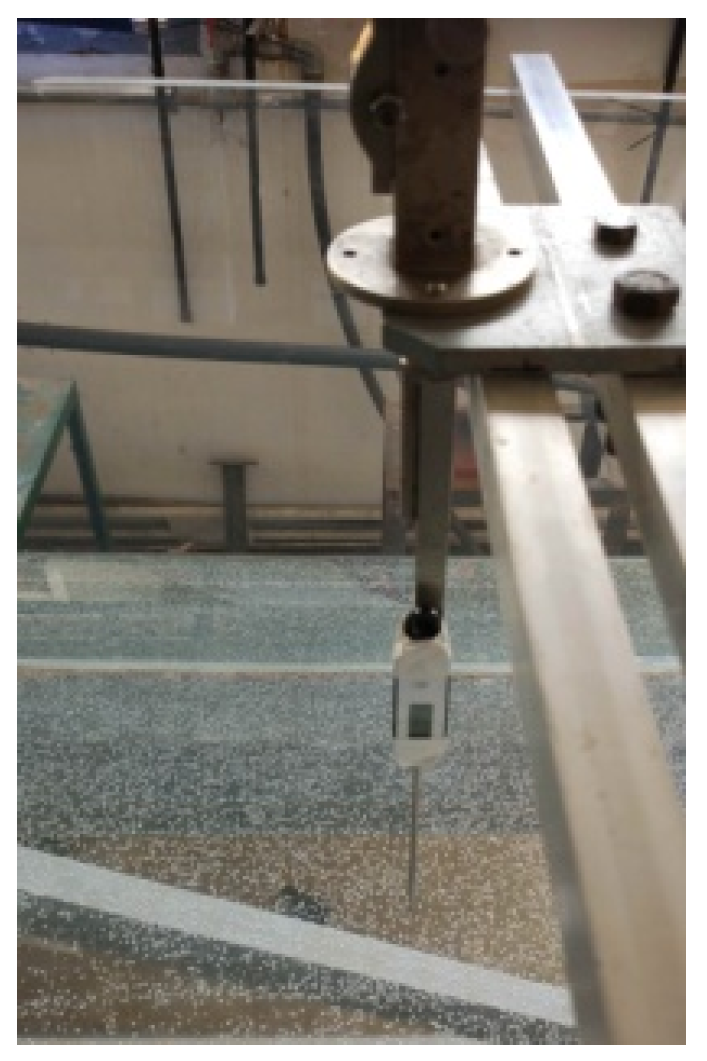
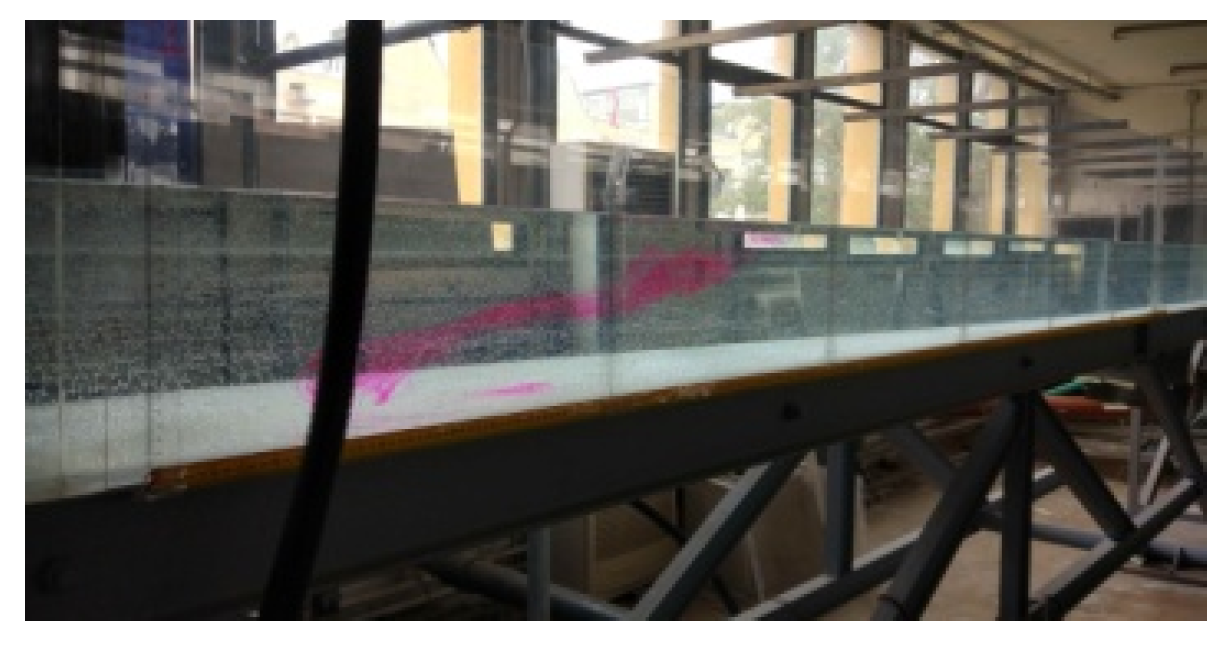
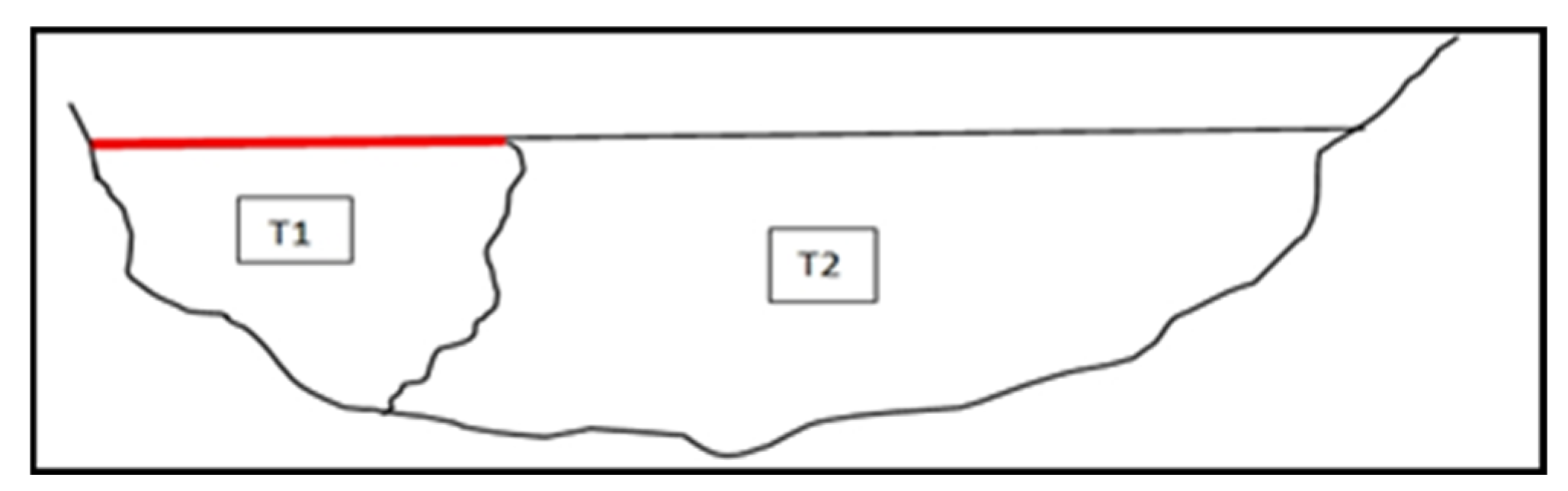
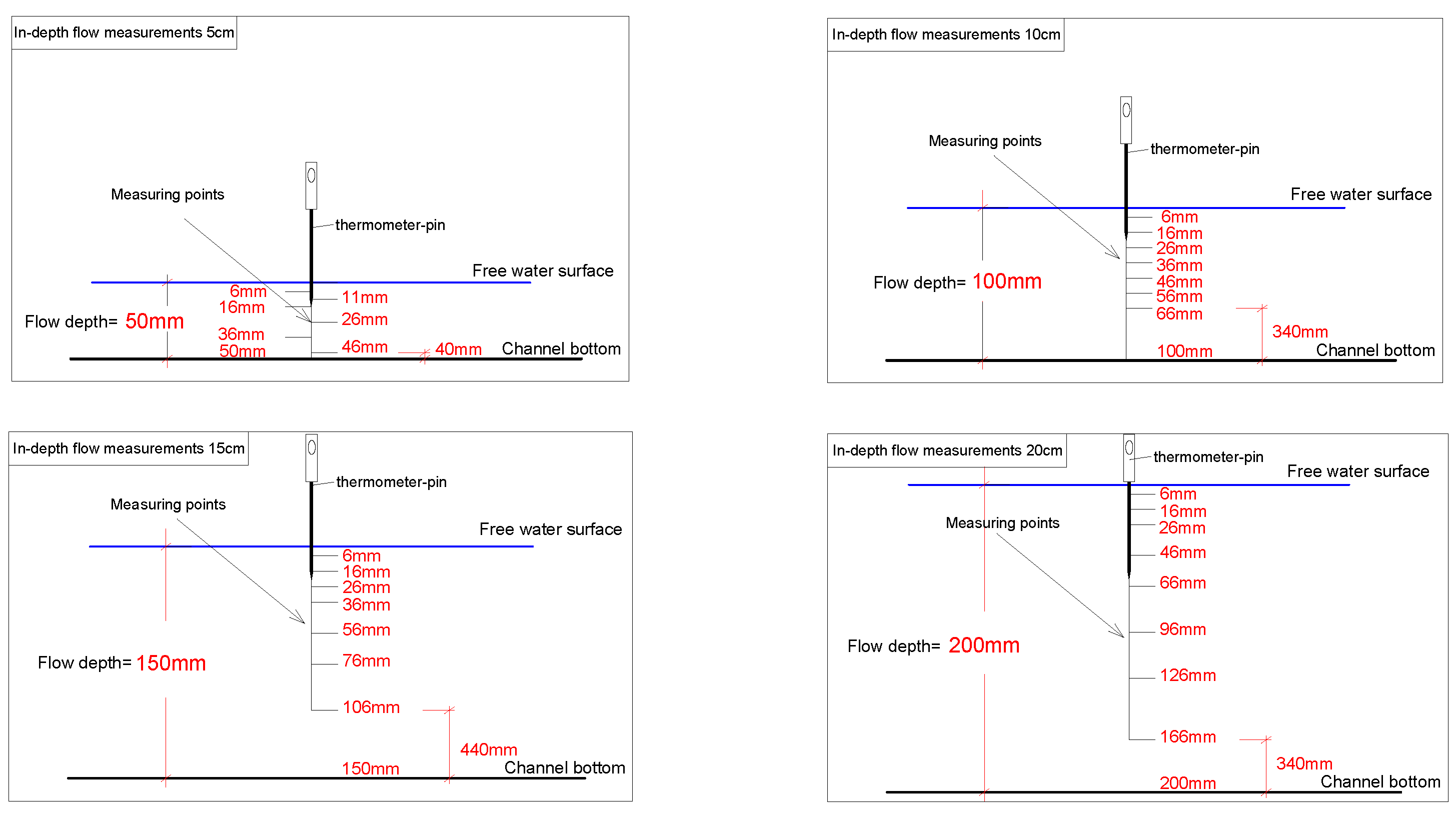
3. Measurements
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajibade, A.O.; Ojeagbase, P.O. Steady natural convection heat and mass transfer flowt hrough a vertical porous channel with variable viscosityand thermal conductivity. Eng. Rep. 2020, 2, e12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, K.S.M. Employing the Concept of Fractal Shape to Enhance Heat Transfer. Ph.D. Thesis, Cleveland State University, Cleveland, OH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, A.H.; Cardenas, M.B.; Buttles, J. Hyporheic temperature dynamics and heat exchange near channel-spanning logs. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W01529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinokrot, B.A.; Stefan, H.G. Stream Water-Temperature Sensitivity to Weather and Bed Parameters. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1994, 120, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, E.T.; Doyle, M.W.; Poole, G.C. The influence of in-stream structures on summer water temperatures via induced hyporheic exchange. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, W.; Jasperse, J.; Seymour, D.; Constantz, J. Estimation of Hydraulic Conductivity in an Alluvial System Using Temperatures. Ground Wat. 2004, 42, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.A. Experimental and Numerical Study on Evaporation of Water at Low Pressures. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Le Person, S.; Favre-Marinet, M. Scale effects on hydrodynamics and heat transfer in two-dimensional mini and microchannels. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2002, 41, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythman, R. Hydrodynamics and Heat Transfer of Laminar Pulsating Flow in a Rectangular Channel. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lyubimova, T.; Lepikhin, A.; Konovalov, V.; Parshakova, Y.; Tiunov, A. Formation of the density currents in the zone of confluence of two rivers. J. Hydr. 2014, 508, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






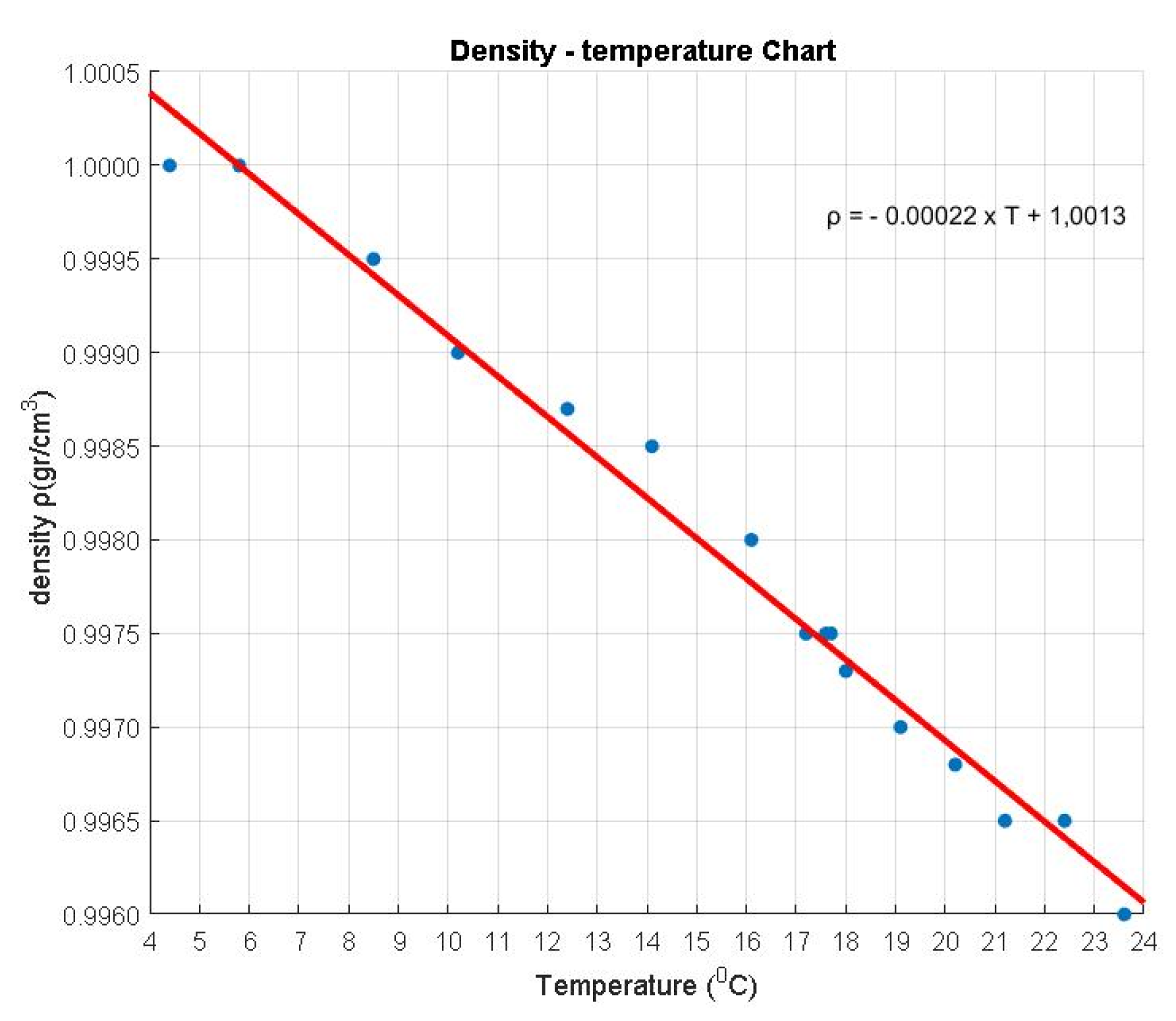

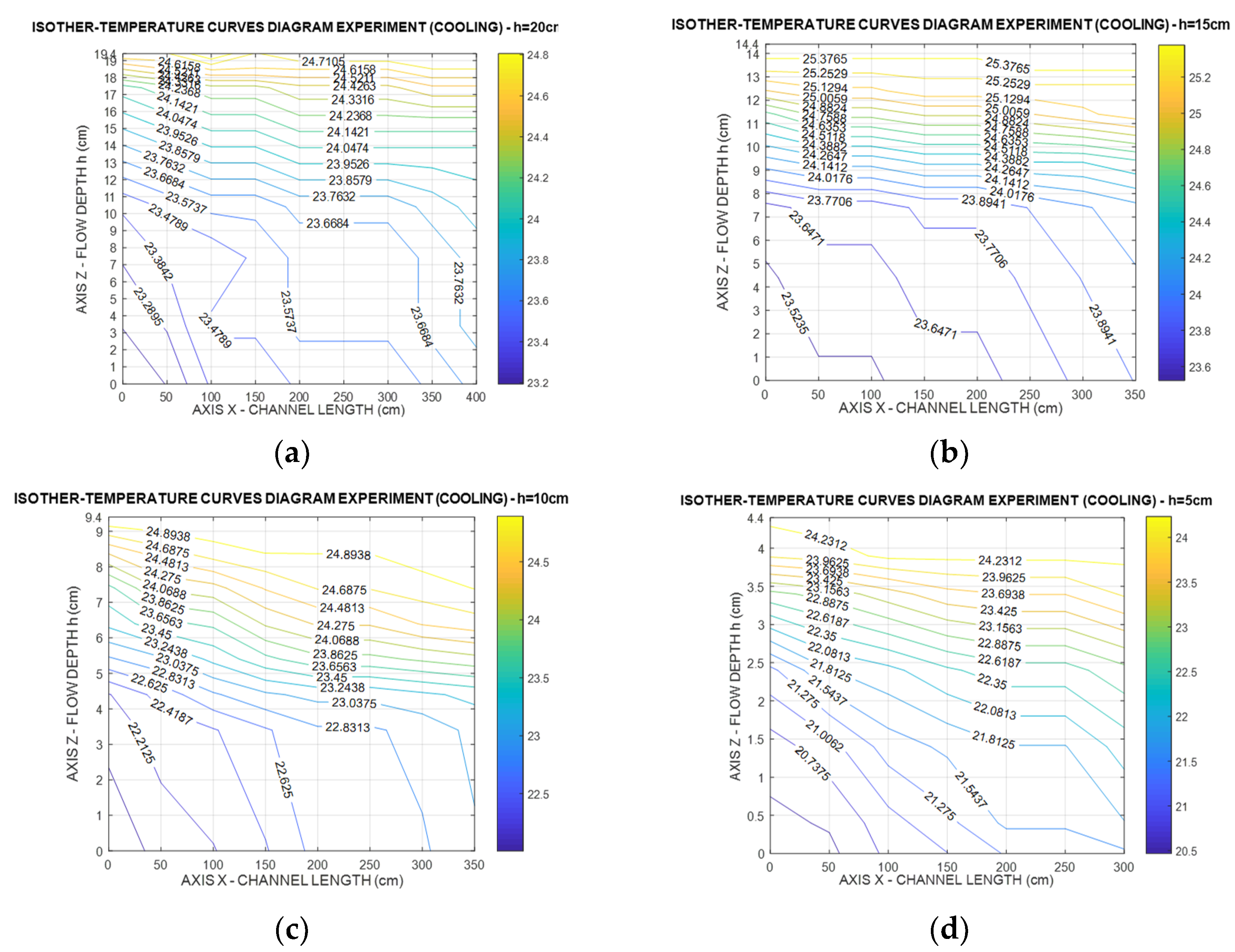
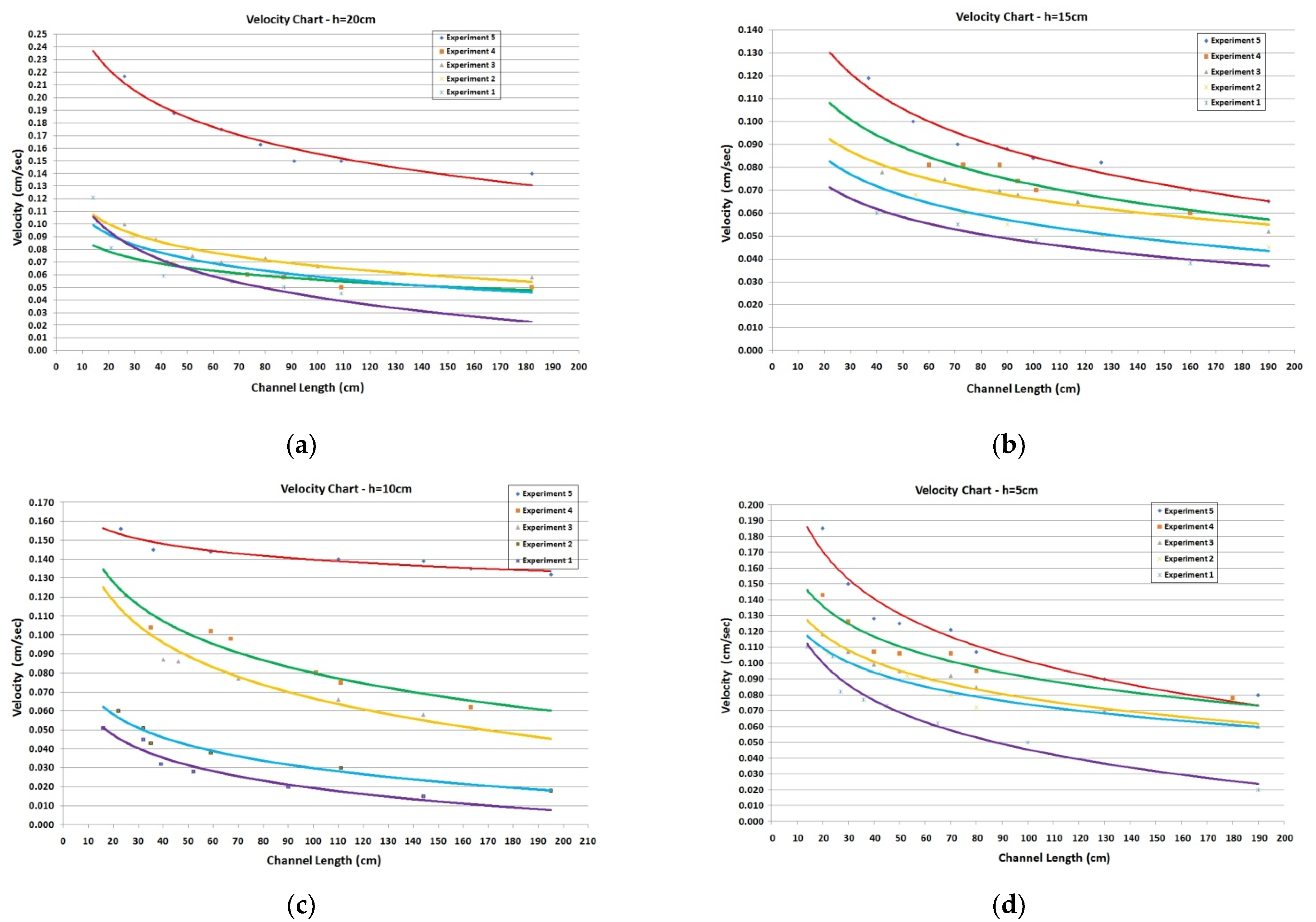
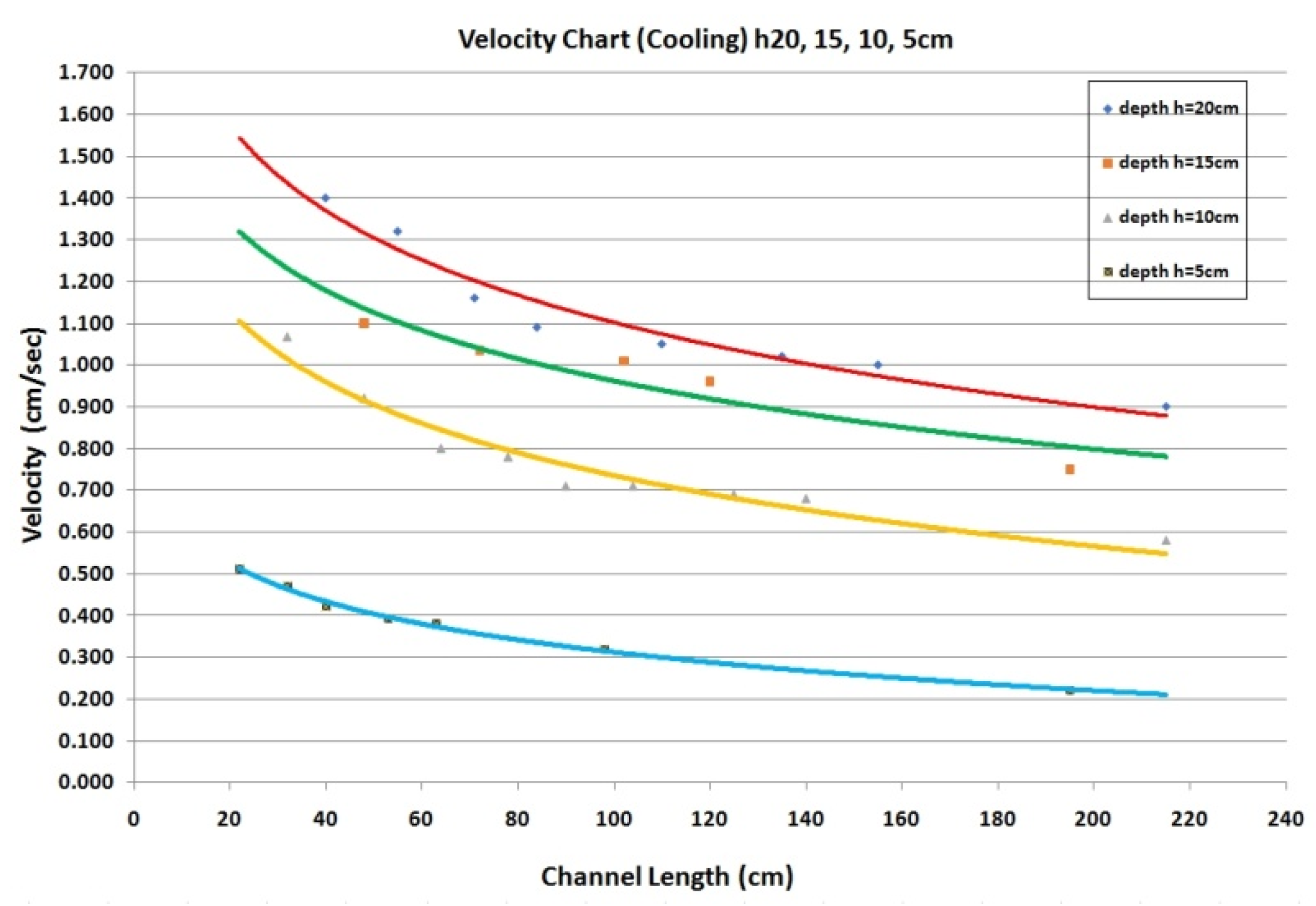

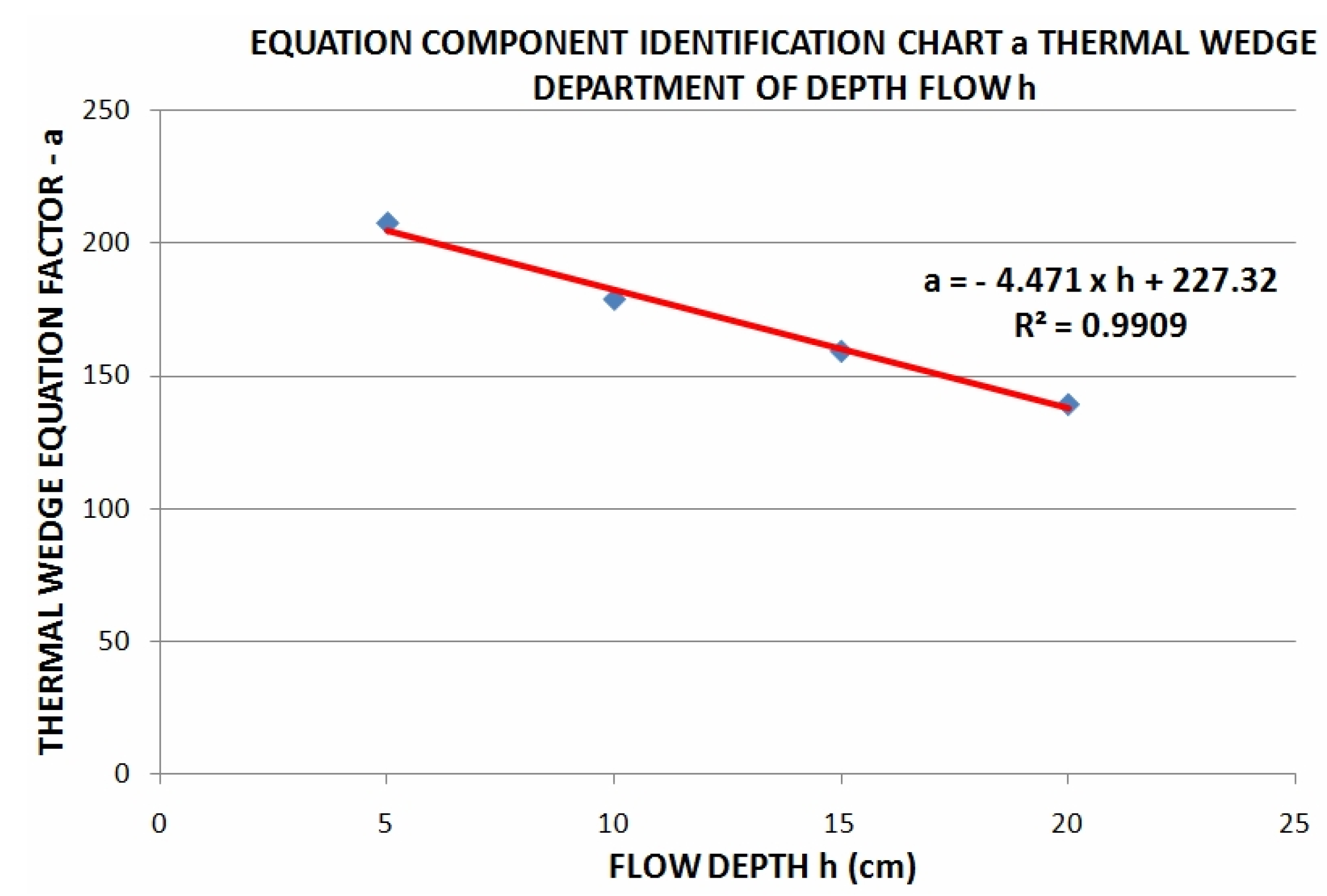
| Tank | Temperature °C | Density ρ (gr/cm3) | Tank | Temperature | Density ρ (gr/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| measurement 1 | 17.2 | 0.9975 | measurement 9 | 17.7 | 0.9975 |
| measurement 2 | 17.6 | 0.9975 | measurement 10 | 16.1 | 0.9985 |
| measurement 3 | 18.0 | 0.9975 | measurement 11 | 14.1 | 0.9985 |
| measurement 4 | 19.1 | 0.9970 | measurement 12 | 12.4 | 0.9990 |
| measurement 5 | 20.2 | 0.9970 | measurement 13 | 10.2 | 0.9990 |
| measurement 6 | 21.2 | 0.9965 | measurement 14 | 8.5 | 0.9995 |
| measurement 7 | 22.4 | 0.9965 | measurement 15 | 5.8 | 1.0000 |
| measurement 8 | 23.6 | 0.9960 | measurement 16 | 4.4 | 1.0000 |
| Depth | Equation | Depth | Equation | Depth | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 cm | u = −0.033 × ln(L) + 0.1920 | 15 cm | u = −0.017 × ln(L) + 0.1457 | 10 cm | u = −0.017 × ln(L) + 0.0996 |
| 20 cm | u = −0.021 × ln(L) + 0.1143 | 15 cm | u = −0.018 × ln(L) + 0.1385 | 5 cm | u = −0.043 × ln(L) + 0.3000 |
| 20 cm | u = −0.021 × ln(L) + 0.1621 | 15 cm | u = −0.016 × ln(L) + 0.1205 | 5 cm | u = −0.028 × n(L) + 0.2198 |
| 20 cm | u = −0.017 × ln(L) + 0.1331 | 10 cm | u = −0.009 × ln(L) + 0.1817 | 5 cm | y = −0.025 × ln(L) + 0.1934 |
| 20 cm | u = −0.042 × ln(L) + 0.3467 | 10 cm | u = −0.030 × ln(L) + 0.2171 | 5 cm | u = −0.022 × ln(L) + 0.1755 |
| 15 cm | u = −0.030 × ln(L) + 0.2237 | 10 cm | u = −0.032 × ln(L) + 0.2134 | 5 cm | u = −0.034 × ln(L) + 0.2018 |
| 15 cm | u = −0.024 × ln(L) + 0.1812 | 10 cm | u = −0.018 × ln(L) + 0.1111 |
| Depth | Equation | Depth | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 cm | u = −0.293 × ln(x) + 2.4493 | 10 cm | u = −0.245 × ln(x) + 1.8618 |
| 15 cm | u = −0.236 × ln(x) + 2.0507 | 5 cm | u = −0.133 × ln(x) + 0.9225 |
| Heat Transfer | Flow Depth (cm) | Initial Water Temperature Τν (°C) | Thermal Equilibrium Temperature Τo the Position Χ = 0.0 cm (°C) | Experiment Thermal Wedge Length L (cm) | b–Thermal Mass Thickness in Place X = 0.0 (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| experiment 1 | 20 | 15.5 | 16.3 | 170 | 2.6 |
| experiment 2 | 20 | 15.7 | 17.5 | 260 | 4.0 |
| experiment 3 | 20 | 15.4 | 17.9 | 320 | 5.0 |
| experiment 4 | 20 | 15.5 | 18.3 | 380 | 6.2 |
| experiment 5 | 20 | 15.3 | 18.8 | 500 | 10.5 |
| experiment 1 | 15 | 18.9 | 20.2 | 200 | 2.2 |
| experiment 2 | 15 | 16.0 | 18.2 | 280 | 2.5 |
| experiment 3 | 15 | 15.6 | 18.5 | 400 | 2.8 |
| experiment 4 | 15 | 15.4 | 18.6 | 500 | 3.0 |
| experiment 5 | 15 | 15.4 | 19.0 | 680 | 3.5 |
| experiment 1 | 10 | 19.4 | 20.4 | 300 | 1.3 |
| experiment 2 | 10 | 18.1 | 20.4 | 400 | 1.6 |
| experiment 3 | 10 | 19.4 | 22.4 | 600 | 2.2 |
| experiment 4 | 10 | 18.8 | 22.4 | 650 | 2.6 |
| experiment 5 | 10 | 19.4 | 23.6 | 680 | 3.0 |
| experiment 1 | 5 | 21.0 | 21.5 | 150 | 1.7 |
| experiment 2 | 5 | 19.9 | 21.9 | 320 | 2.4 |
| experiment 3 | 5 | 20.2 | 22.5 | 430 | 3.0 |
| experiment 4 | 5 | 20.3 | 22.9 | 580 | 3.4 |
| experiment 5 | 5 | 20.4 | 23.4 | 680 | 3.8 |
| Flow Depth (cm) | Coefficient a |
|---|---|
| 5 | 207.59 |
| 10 | 179.04 |
| 15 | 159.52 |
| 20 | 139.58 |
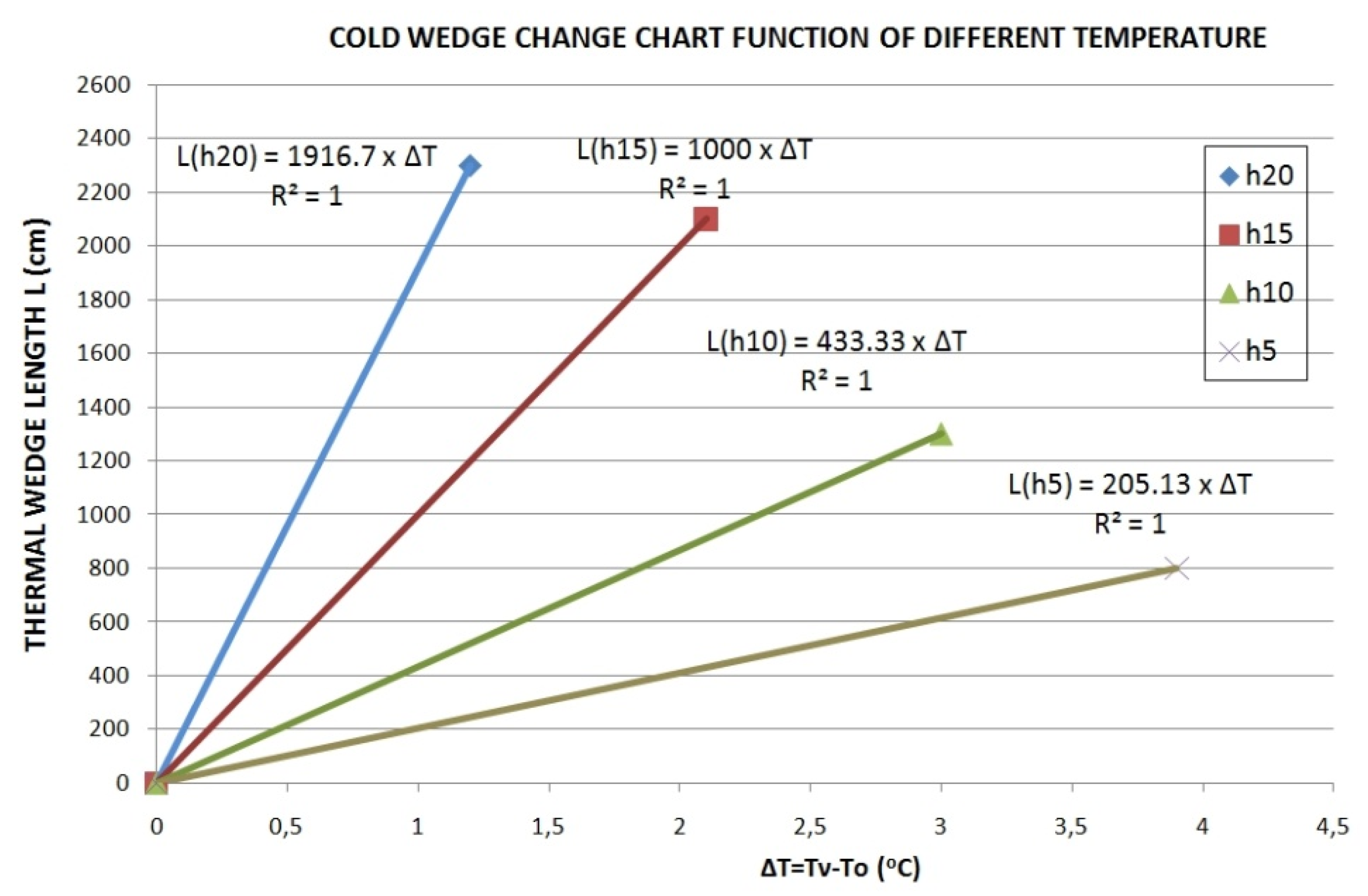
| Cooling | Flow Depth (cm) | Initial Water Temperature Τν (°C) | Thermal (°C) Equilibrium Temperature Τo the Position Χ = 0.0 cm | Experiment Cooling Coil Length L (cm) | * Length Estimation from Gear Chart *L (cm) | b–Coolant Thickness in Place X = 0.0 (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| experiment 1 | 20 | 24.4 | 23.2 | 680 | 2300 | 14.0 |
| experiment 2 | 15 | 25.5 | 23.4 | 680 | 2100 | 9.0 |
| experiment 3 | 10 | 23.6 | 21.8 | 680 | 1300 | 6.5 |
| experiment 4 | 5 | 24.1 | 20.2 | 680 | 800 | 3.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leousidis, A.; Pechlivanidis, G.; Keramaris, E.; Savvidis, Y. Experimental Study of the Effects of Heating or Cooling on the Water Surface in an Open Channel. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021060
Leousidis A, Pechlivanidis G, Keramaris E, Savvidis Y. Experimental Study of the Effects of Heating or Cooling on the Water Surface in an Open Channel. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 21(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021060
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeousidis, Alexandros, George Pechlivanidis, Evangelos Keramaris, and Yiannis Savvidis. 2022. "Experimental Study of the Effects of Heating or Cooling on the Water Surface in an Open Channel" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 21, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021060
APA StyleLeousidis, A., Pechlivanidis, G., Keramaris, E., & Savvidis, Y. (2022). Experimental Study of the Effects of Heating or Cooling on the Water Surface in an Open Channel. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 21(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021060







