Estimating Rainfall Erosivity from Daily Precipitation Using Generalized Additive Models †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.2. Rainfall Erosivity Calculations
2.3. Empirical Equations for the Estimation of Erosivity
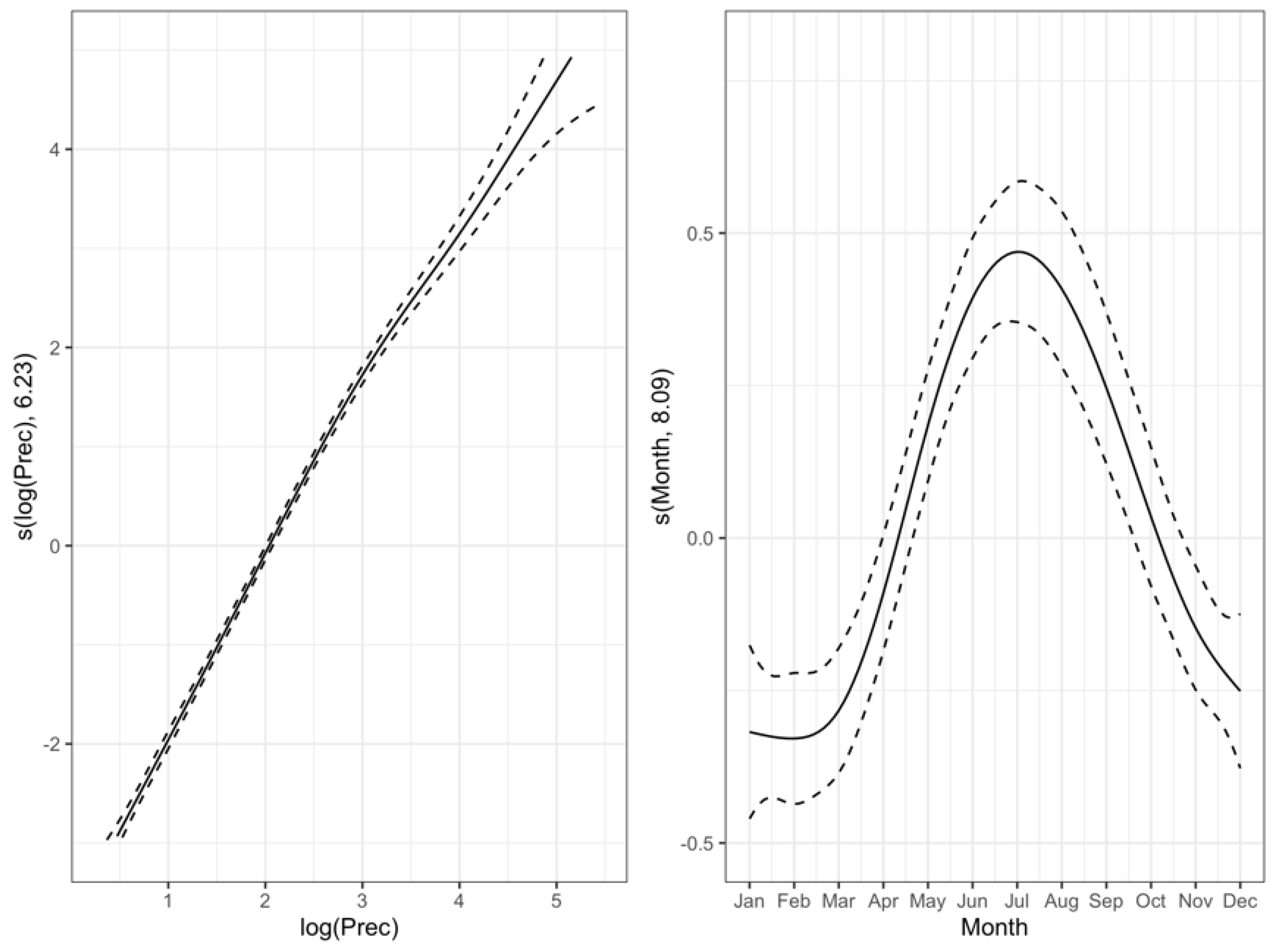
2.4. Generalized Aditive Models
2.5. Validation and Model Performance Criteria
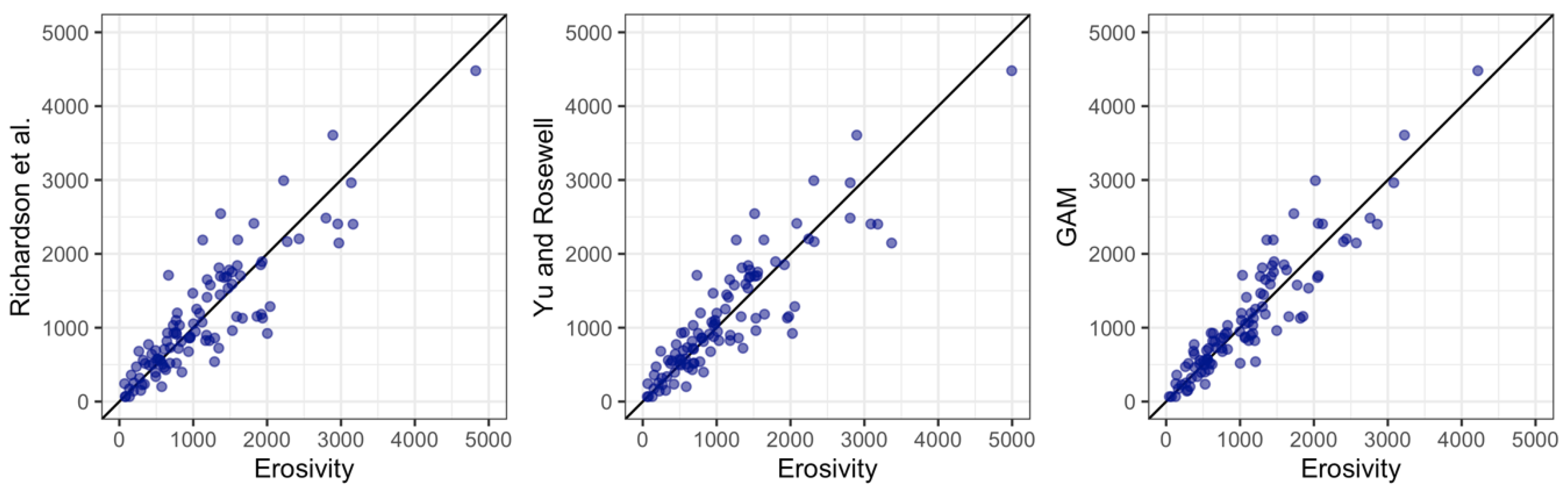
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nearing, M.A.; Yin, S.; Borrelli, P.; Polyakov, V.O. Rainfall erosivity: An historical review. Catena 2017, 157, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, H. Impacts of climate change on water erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantas, K.; Sidiropoulos, E.; Loukas, A. Estimating Current and Future Rainfall Erosivity in Greece Using Regional Climate Models and Spatial Quantile Regression Forests. Water 2020, 12, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeson, N.A.; Brandt, C.J.; Thornes, J.B. Mediterranean Desertification: A Mosaic of Processes and Responses; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Griggs, D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Gaffney, O.; Rockström, J.; Öhman, M.C.; Shyamsundar, P.; Steffen, W.; Glaser, G.; Kanie, N.; Noble, I. Sustainable development goals for people and planet. Nature 2013, 495, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.; Poesen, J. Soil Erosion in Europe: Major Processes, Causes and Consequences. In Soil Erosion in Europe; John Wiley & Sons: Wiltshire, UK, 2006; pp. 477–487. ISBN 10-0-470-85910-5. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Freimund, J.R. Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. J. Hydrol. 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses-a Guide to Conservation Planning; USDA, Agriculture Handbook No. 537; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.P. RUSLE: Revised universal soil loss equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- USDA-ARS. Science Documentation: Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation, Version 2 (RUSLE 2); USDA-Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C.; Alvarez, P.; Anache, J.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Ballabio, C.; Bezak, N.; Biddoccu, M.; Cerdà, A.; Chalise, D.; et al. Soil erosion modelling: A global review and statistical analysis. 2020; Submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Vantas, K.; Sidiropoulos, E.; Evangelides, C. Rainfall Erosivity and Its Estimation: Conventional and Machine Learning Methods. Soil Eros. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantas, K.; Sidiropoulos, E.; Loukas, A. Robustness Spatiotemporal Clustering and Trend Detection of Rainfall Erosivity Density in Greece. Water 2019, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantas, K.; Sidiropoulos, E. Imputation of erosivity values under incomplete rainfall data by machine learning methods. Eur. Water 2017, 57, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. The Elements of statistical Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.J.; Tibshirani, R.J. Generalized Additive Models. Stat. Sci. 1986, 1, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 112. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N.; Pya, N.; S"afken, B. Smoothing parameter and model selection for general smooth models (with discussion). J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 1548–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Charron, C.; Hundecha, Y.; St-Hilaire, A.; Chebana, F. Introduction of the GAM model for regional low-flow frequency analysis at ungauged basins and comparison with commonly used approaches. Environ. Model. Soft. 2018, 109, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Galiano, S.G.; Olmos Gimenez, P.; Giraldo-Osorio, J.D. Assessing Nonstationary Spatial Patterns of Extreme Droughts from Long-Term High-Resolution Observational Dataset on a Semiarid Basin (Spain). Water 2015, 7, 5458–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortridge, J.E.; Guikema, S.D.; Zaitchik, B.F. Machine learning methods for empirical streamflow simulation: a comparison of model accuracy, interpretability, and uncertainty in seasonal watersheds. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 2611–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantas, K.; Sidiropoulos, E.; Vafeiadis, M. Optimal temporal distribution curves for the classification of heavy precipitation using hierarchical clustering on principal components. Glob. NEST J. 2019, 21, 530–538. [Google Scholar]
- Vantas, K. hydroscoper: R interface to the Greek National Data Bank for Hydrological and Meteorological Information. J. Open Source Soft. 2018, 3, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.; Foster, G.; Wright, D. Estimation of erosion index from daily rainfall amount. Trans. ASAE 1983, 26, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Rosewell, C. An assessment of a daily rainfall erosivity model for New South Wales. Soil Res. 1996, 34, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nelder, J.A.; Wedderburn, R.W.M. Generalized Linear Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. Gen. 1972, 135, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T. gam: Generalized Additive Models. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gam (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Hastie, T.J.; Tibshirani, R.J. Generalized Additive Models; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; Volume 43. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 2011, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H. Estimating Optimal Transformations for Multiple Regression and Correlation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1985, 80, 580–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantas, K. Determination of Rainfall Erosivity in the Framework of Data Science Using Machine Learning and Geostatistics Methods; Aristotle University of Thessaloniki: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Beguería, S.; Serrano-Notivoli, R.; Tomas-Burguera, M. Computation of rainfall erosivity from daily precipitation amounts. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvålseth, T.O. Cautionary note about R2. Am. Stat. 1985, 39, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Vantas, K. Hyetor: R Package to Analyze Fixed Interval Precipitation Time Series. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/kvantas/hyetor (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
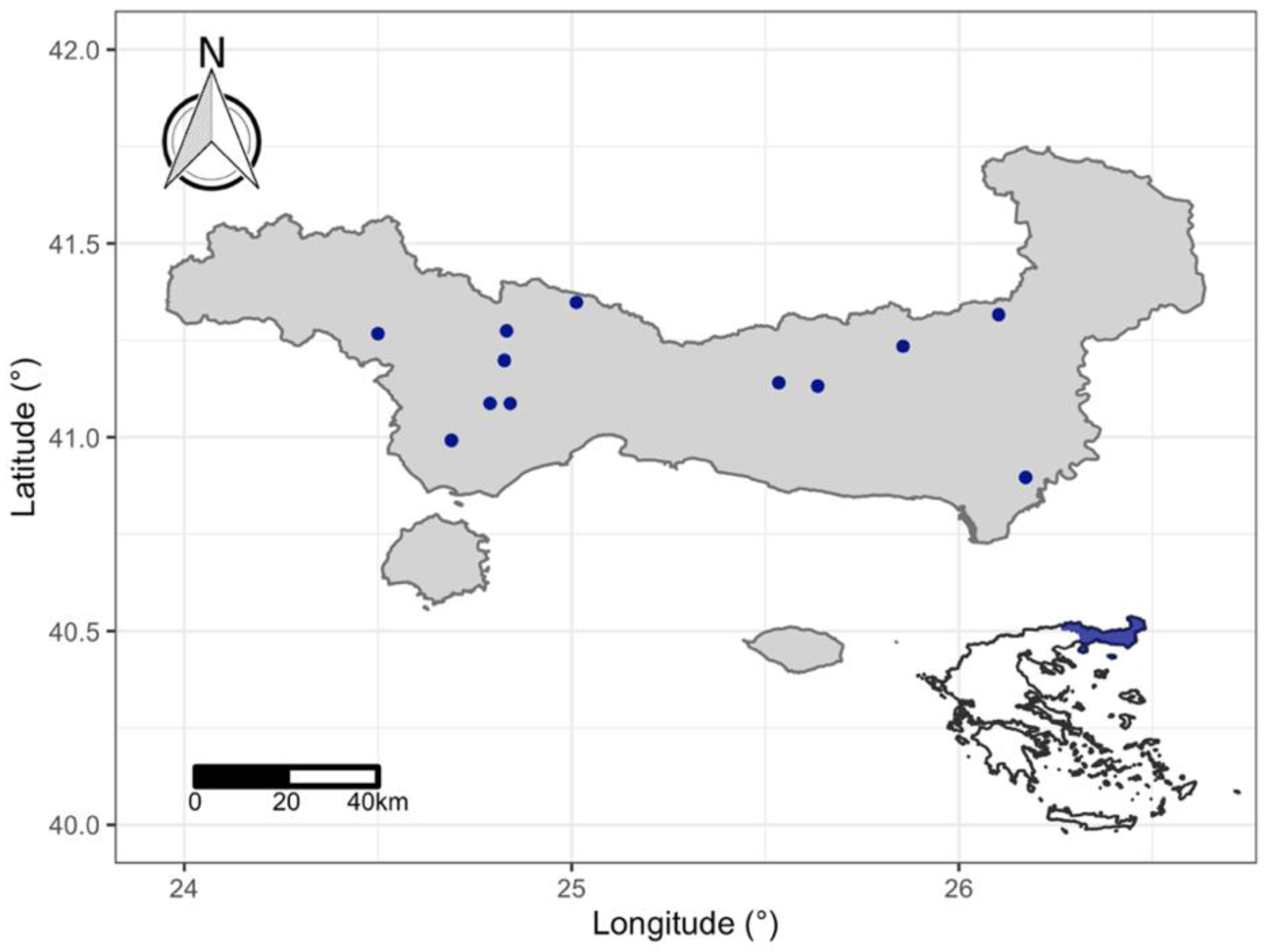
| Name | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Elevation (m) | Duration (y) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TOXOTES | 41.09 | 24.79 | 75 | 27 |
| 2 | M. DEREIO | 41.32 | 26.10 | 116 | 22 |
| 3 | FERRES | 40.90 | 26.17 | 43 | 31 |
| 4 | PARANESTI | 41.27 | 24.50 | 122 | 34 |
| 5 | GRATINI | 41.14 | 25.53 | 120 | 27 |
| 6 | KECHROS | 41.23 | 25.86 | 700 | 24 |
| 7 | M. KSIDIA | 41.13 | 25.64 | 70 | 27 |
| 8 | THERMES | 41.35 | 25.01 | 440 | 26 |
| 9 | GERAKAS | 41.20 | 24.83 | 308 | 24 |
| 10 | ORAIO | 41.27 | 24.83 | 656 | 26 |
| 11 | SEMELH | 41.09 | 24.84 | 65 | 23 |
| 12 | CHRYSOUPOLI | 40.99 | 24.69 | 15 | 14 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAM | 0.88 | 306.43 | 231.20 |
| Richardson et al. | 0.77 | 419.64 | 308.50 |
| Yu and Rosewell | 0.76 | 431.19 | 309.24 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAM | 0.73 | 89.19 | 53.00 |
| Richardson et al. | 0.63 | 104.83 | 61.28 |
| Yu and Rosewell | 0.61 | 107.58 | 59.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vantas, K.; Sidiropoulos, E.; Evangelides, C. Estimating Rainfall Erosivity from Daily Precipitation Using Generalized Additive Models. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2020, 2, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2020002021
Vantas K, Sidiropoulos E, Evangelides C. Estimating Rainfall Erosivity from Daily Precipitation Using Generalized Additive Models. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2020; 2(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2020002021
Chicago/Turabian StyleVantas, Konstantinos, Epaminondas Sidiropoulos, and Chris Evangelides. 2020. "Estimating Rainfall Erosivity from Daily Precipitation Using Generalized Additive Models" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 2, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2020002021
APA StyleVantas, K., Sidiropoulos, E., & Evangelides, C. (2020). Estimating Rainfall Erosivity from Daily Precipitation Using Generalized Additive Models. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 2(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2020002021





