Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the functional response of Panicum antidotale Retz, Chenopodium quinoa, and Zea mays L. to different levels of saline irrigation water. Nutrient uptake, biochemical content, and growth response were evaluated to select potential crops best suited for biosaline agriculture. The results suggest that blue panicum is highly tolerant to saline water irrigation, followed by quinoa up to 10 dS m−1, and then silage maize which is sensitive to saline conditions. The introduction of blue panicum as an alternative crop on salt-effected soils, such as the irrigated perimeter of Foum El Oued in Laâyoune in Morocco, would exhibit high performance better than traditional crops such as silage maize and therefore would improve the local farmers’ income.
1. Introduction
As part of the development of a sustainable solution to manage and mitigate the impact of salinity on the soils of irrigated areas in marginal lands, a larger Agroecological megaproject of INRA-Morocco’s medium-term program was established. This study is part of that program and aims to select potential crops best suited for biosaline agriculture. Blue panicum and quinoa are classified as halophyte species, and silage maize is moderately sensitive to salt stress, but they differ in adaptation under salinity conditions. Testing their functional response to different levels of saline irrigation would contribute to the use of cultivated land suffering from salinity, which represents 20% of cultivated land in the world, and salt irrigated land [1].
2. Materials and Methods
The study was conducted on three plants: blue panicum (public type from Kuwait), quinoa (ICBA Q5), and silage maize (Dragma variety). The seeds were gathered from previous field trials at the INRA experimental station of Foum El Oued in Laâyoune. The experiment had a factorial design, with four levels of irrigation-water-salinity treatments (0.9 “tap water”; 3; 6 and 10 dS m−1), and four replicates. The substrate used in the experiment was peat.
At the end of the experiment, the leaves, stems, and roots were harvested, and the roots were washed without substrate. The fresh plant material was weighed and then oven-dried at 80 °C until a constant weight. The physiological, biochemical, and mineral parameters studied during the experiment were the chlorophyll content, proline content, ionic content of leaves, and the amount of potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), and sodium (Na+) in the shoots and roots. The methodology adopted to measure these parameters is detailed in Oumasst et al. [2]. The normal distribution and homogeneity of variance between the plants were firstly tested by Shapiro–Wilk test and Barlett’s test. The analysis of variance for different irrigation water treatments was performed using the SPSS program (IBM Corp. Released in 2011, Version 20, Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Physiological and Biochemical Properties
Table 1 shows the mean of the stem height, aboveground and root dry biomass, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoid, and proline content of the blue panicum, quinoa, and silage maize of the tested treatments. The physiological and biochemical properties of blue panicum were not affected by the applied salinity treatments, except for the root dry matter biomass, which decreased by 39 % at 10 dS m−1 compared to the control. For quinoa, increasing irrigation-water-salinity only decreased plant growth and root dry matter biomass without significant effect on the other parameters compared to control. The increasing irrigation-water-salinity resulted in a significant decrease in silage maize growth in the aboveground and root dry matter biomass, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoid compared to the control (T0). No effect of the applied salt concentrations on the proline content for all of the crop species was observed.

Table 1.
Mean of stem height, aboveground and root dry biomass, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoid, and proline content of blue panicum, quinoa and silage maize by tested treatments. The symbols T0 (0.9 dS m−1), T1 (3 dS m−1), T2 (6 dS m−1), and T3 (10 dS m−1) refer to the four saline irrigation water treatments. Lower-case (a, b, c, d) show differences between treatments within each measured parameter for each plant species; Data with different lowercase are significantly different (p < 0.05). (Mean ± standard deviation; n = 4 for blue panic and silage maize, and n = 3 for quinoa).
3.2. Plant Mineral Content
The means of the calcium Ca2+ (%), potassium K+ (%) and sodium Na+ (%) content in the leaves, stems, and roots of blue panicum, quinoa, and silage Maize for each treatment are shown in Figure 1. Except for the increasing calcium content in blue panicum, no significant differences were observed for potassium uptake in blue panicum and for calcium and potassium uptake in quinoa between treatments. At different parts of silage maize, Ca2+ and K+ uptake decreased with increasing salinity levels to be significant for irrigation water with an electrical conductivity ≥ 6 dS m−1 relative to control. In contrast, the sodium content of leaves, stems and roots increased significantly with increasing water salinity for all three species.
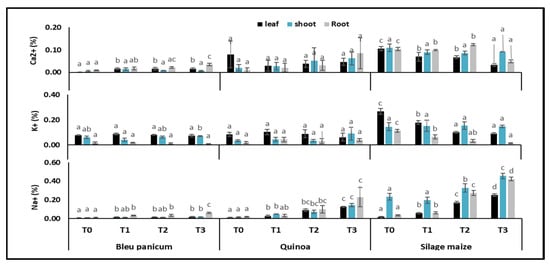
Figure 1.
Mean content of calcium Ca2+ (%), potassium K+ (%) and sodium Na+ (%) in the leaves, stems, and roots of blue panicum, quinoa and silage maize for each treatment. The symbols T0 (0.9 dS m−1), T1 (3 dS m−1), T2 (6 dS m−1), and T3 (10 dS m−1) refer to the four saline irrigation water treatments. Lower-case (a, b, c, d) show differences between treatments for leaf, shoot and root within each tested plant species. Columns with the same letter over them are not significantly different (p < 0.05) (Mean ± standard deviation; n = 3).
4. Discussion
4.1. Physiological and Biochemical Properties
Blue panicum showed high tolerance to irrigation water salinity in terms of growth and production, as has been observed in many studies [3,4]. Furthermore, in terms of the biochemical properties, which did not affect the chlorophyll a, b, and proline leaf content and increased the carotenoid content only in the T2 (6 dS m−1) treatment. Saline water irrigation in quinoa decreased the steam height and root dry biomass significantly to 10 dS m−1. Similar results were obtained by Hirich et al. [5], who reported that quinoa is considered a facultative halophyte with a salt-tolerance threshold equal to 9 dS m−1. The biochemical properties of quinoa were not affected by saline water irrigation. For silage maize, the physiological and biochemical properties decreased in all of the treatments at salt concentrations of > 6 dS m−1, where the plants show stress symptoms. The decrease in chlorophyll levels in silage maize is due to the high enzymatic activity of chlorophyllase under high salinity conditions [6].
4.2. Plant Mineral Content
Our results indicate that if the cropped species are sensitive to high salinity conditions, the Na+ content competes with the ions in the cell, which will lead to a decrease in their accumulation as the salinity increases. However, if the plant is tolerant to high or moderate saline conditions, the plant excludes the toxic ions Na+ and Cl− in order to maintain the uptake of K+ and Ca2+. The findings also show that the uptake of K+ and Ca2+ in maize silage with a high sensitivity to saline conditions decreased with increasing salinity, compared to panicum blue and quinoa, where these ions remained stable due to their salt tolerance. This finding is consistent with the results reported by Roman et al. [7], which show that quinoa plants are able to maintain the uptake of potassium despite high Na+ concentrations in the soil after extended salt stress. This is also consistent with the results of Shabala et al. [8], which indicated that the capacity of plants to exclude toxic ions such as Na+ and Cl− from transport systems is correlated to their salt tolerance. Silage maize showed a significantly higher Na+ content than blue panicum and quinoa. This would be attributed to the ability differences of both crops to involve both mechanisms (expulsion and compartmentalization) of adaptation to salt stress [9].
Author Contributions
A.O., writing—original draft preparation; A.O. and S.A., methodology; J.H., supervision, review and editing; A.M., review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Institute for Agronomic Research Morocco (CRRA-INRA) for supporting and providing research facilities and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L. Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 3-319-96190-X. [Google Scholar]
- Oumasst, A.; Azougay, S.; Taqarort, N.; Mimouni, A.; Hallam, J. Effets de La Salinité Sur l’absorption Des Nutriments, Les Paramètres Biochimiques et La Croissance Du Bleu Panicum (Panicum Antidotale Retz) et Du Maïs d’ensilage (Zea Mays L). Afr. Mediterr. Agric. J.—Al Awamia 2021, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyro, H.-W.; Hussain, T.; Huchzermeyer, B.; Khan, M.A. Photosynthetic and Growth Responses of a Perennial Halophytic Grass Panicum Turgidum to Increasing NaCl Concentrations. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 91, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, A.; Debez, A.; Rabhi, M.; Barhoumi, Z.; Haouari, C.C.; Gouia, H.; Abdelly, C.; Smaoui, A. Salt Tolerance and Potential Uses for Saline Agriculture of Halophytes from the Poaceae. In Sabkha Ecosystems; Gul, B., Böer, B., Khan, M.A., Clüsener-Godt, M., Hameed, A., Eds.; Tasks for Vegetation Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 49, pp. 223–237. ISBN 978-3-030-04416-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hirich, A.; Choukr-Allah, R.; Jacobsen, S.-E. Deficit Irrigation and Organic Compost Improve Growth and Yield of Quinoa and Pea. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2014, 200, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.V. Regulation of Chlorophyll Biosynthesis and Degradation by Salt Stress in Sunflower Leaves. Sci. Hortic. 2004, 103, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, V.J. Salt Tolerance Strategies of the Ancient Andean Crop Quinoa; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S. Learning from Halophytes: Physiological Basis and Strategies to Improve Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crops. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).