How Does Organic Amendment and NPK Fertilization Improve Forage Yield of Cereals under Salinity and Arid Conditions?: Case of Moroccan Sahara †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Characteristics
2.2. Experimental Design, Crop Management and Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
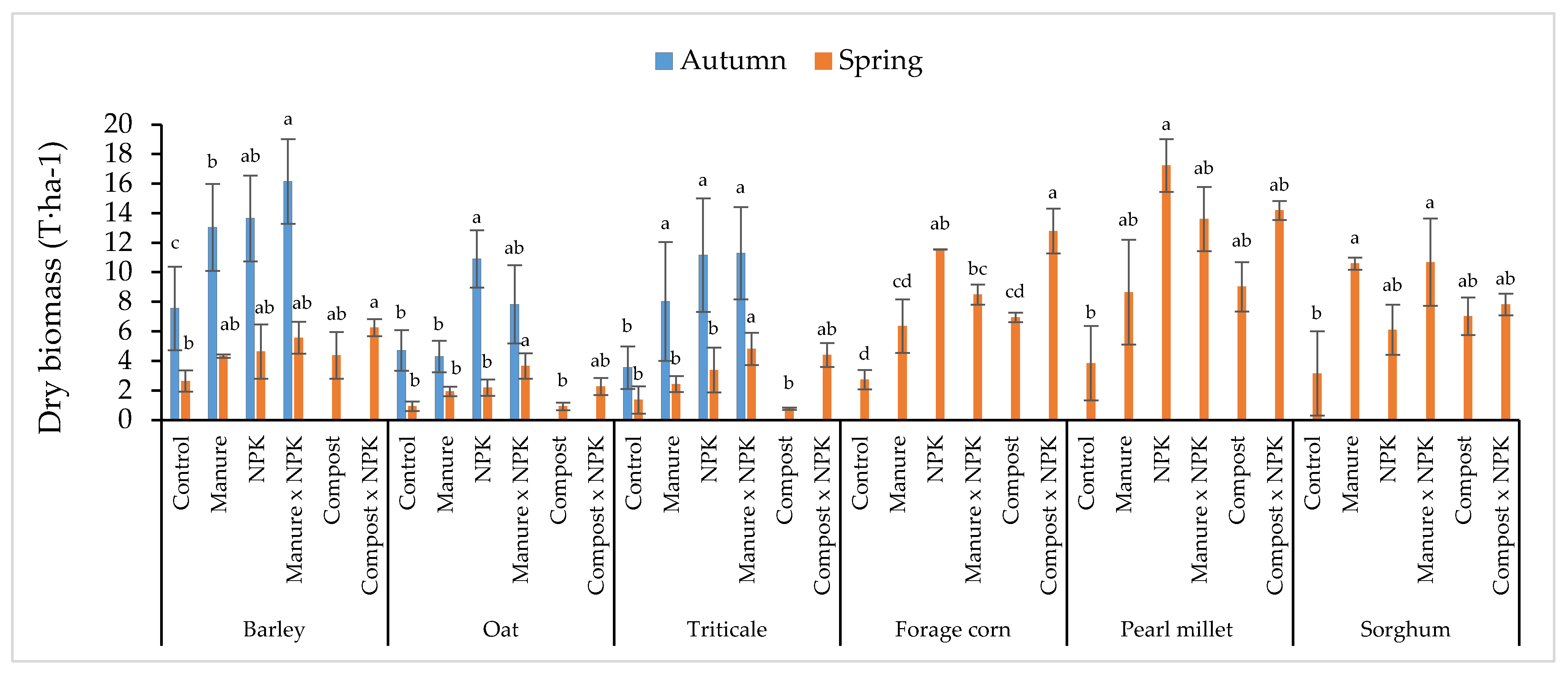
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daoud, S.; Lyagoubi, A.; Harrouni, M. Moroccan Agriculture Facing Climate Change: Adaptation and Local Distribution of the Value Added. In Science, Policy and Politics of Modern Agricultural System; Behnassi, M., Shahid, S., Mintz-Habib, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hssaisoune, M.; Bouchaou, L.; Sifeddine, A.; Bouimetarhan, I.; Chehbouni, A. Moroccan Groundwater Resources and Evolution with Global Climate Changes. Geosciences 2020, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. In Agronomy for Sustainable Development; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 30, pp. 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saudi, A.R.; Mahrous, Y.M.A.; Sabry, A.H.; Mamdouh, A.E. Effect of some organic amendments on barley plants under saline condition. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1840–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.; Abd El-Maaboud, M.; Draz, M.; El Shaer, H. Performance of sorghum and pearl millet forage crops productivity by using different agricultural managements under salinity conditions. J. Plant Prod. 2016, 7, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Autumn | Spring | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traits | Treatment | Barley | Oat | Triticale | Barley | Oat | Triticale | Maize | Pearl Millet | Sorghum |
| Plant height (cm) | Control | 49.4 ± 11.5 c | 24.5 ± 0.5 b | 62.8 ± 14 b | 39.25 ± 8.17 b | 20.5 ± 0.9 c | 54.5 ± 10.64 a | 88.3 ± 4.9 b | 48.5 ± 5.5 b | 81 ± 0.8 a |
| Manure | 70.5 ± 12.9 a | 54 ± 9 a | 83.9 ± 9.3 a | 45.25 ± 3.9 ab | 51 ± 4 ab | 59.5 ± 5.02 a | 107.7 ± 6.2 a | 114 ± 9 a | 89 ± 5.7 a | |
| NPK | 63.6 ± 11 b | 52.3 ± 5.7 a | 79.3 ± 13.8 a | 49.25 ± 6.76 a | 50.33 ± 6.7 ab | 58.5 ± 9.71 a | 99.5 ± 1.5 ab | 111 ± 10 a | 95 ± 5.7 a | |
| Manure × NPK | 71.2 ± 8.3 a | 57 ± 2.2 a | 86.3 ± 14.1 a | 50 ± 3.54 a | 51 ± 2.6 a | 60 ± 4.64 a | 107 ± 5.7 a | 106 ± 11 a | 92.3 ± 12.7 a | |
| Compost | - | - | - | 41.5 ± 4.09 ab | 38.33 ± 2.3 bc | 53.75 ± 7.98 a | 105.7 ± 5.3 a | 102 ± 6.5 a | 84.3 ± 9.7 a | |
| Compost × NPK | - | - | - | 45.25 ± 1.92 ab | 49.33 ± 1.7 ab | 65.5 ± 9.21 a | 104.7 ± 3.9 ab | 122.7 ± 3.4 a | 85 ± 7.9 a | |
| Root length (cm) | Control | 9.9 ± 2.5 ab | 4 ± 0 c | 8.2 ± 1.8 b | 7.25 ± 3.27 a | 4.2 ± 0.18 a | 5.75 ± 1.64 a | 31.3 ± 1.7 ab | 12.0 ± 1.0 b | 23.7 ± 1.3 a |
| Manure | 11 ± 3 a | 6.5 ± 0.5 b | 10.2 ± 2.7 ab | 6.5 ± 1.5 a | 5.3 ± 0.4 a | 5 ± 1.87 a | 26.3 ± 1.9 ab | 25.0 ± 3.0 a | 25.3 ± 4.1 a | |
| NPK | 8.3 ± 1.9 c | 7.3 ± 0.5 ab | 10.8 ± 4 a | 6 ± 1.22 a | 6.81 ± 0.53 a | 6.25 ± 1.79 a | 19.5 ± 4.5 b | 27.0 ± 3.0 a | 29 ± 8 a | |
| Manure × NPK | 9.7 ± 2.7 bc | 8.7 ± 0.5 a | 10.4 ± 2.1 ab | 7.25 ± 2.49 a | 7.5 ± 0.71 a | 6.75 ± 2.86 a | 34 ± 3.7 a | 23.0 ± 1.0 a | 24 ± 12.1 a | |
| Compost | - | - | - | 7 ± 2.12 a | 7 ± 2.45 a | 7 ± 1.58 a | 35.3 ± 2.1 a | 22.0 ± 1.6 a | 20 ± 2.9 a | |
| Compost × NPK | - | - | - | 6.25 ± 3.11 a | 7.33 ± 1.25 a | 5.25 ± 1.79 a | 25.7 ± 4.5 ab | 26.0 ± 2.5 a | 19.7 ± 2.4 a | |
| IWP (Kg/m3) | Control | 0.9 ± 0.33 c | 0.56 ± 0.1 ab | 0.42 ± 0.16 b | 0.67 ± 0.18 b | 0.24 ± 0.08 b | 0.35 ± 0.24 b | 0.7 ± 0.17 d | 0.99 ± 0.65 b | 0.81 ± 0.73 b |
| Manure | 1.55 ± 0.34 b | 0.51 ± 0.15 b | 0.95 ± 0.45 a | 1.11 ± 0.03 ab | 0.5 ± 0.09 b | 0.62 ± 0.14 b | 1.62 ± 0.46 cd | 2.22 ± 0.9 ab | 2.71 ± 0.1 a | |
| NPK | 1.63 ± 0.33 ab | 1.3 ± 0.29 a | 1.33 ± 0.43 a | 1.19 ± 0.47 ab | 0.56 ± 0.14 b | 0.87 ± 0.39 b | 2.96 ± 0.01 ab | 4.41 ± 0.46 a | 1.57 ± 0.44 ab | |
| Manure × NPK | 1.92 ± 0.33 a | 0.93 ± 0.3 ab | 1.35 ± 0.35 a | 1.43 ± 0.27 ab | 0.94 ± 0.22 a | 1.23 ± 0.28 a | 2.17 ± 0.17 bc | 3.48 ± 0.5 ab | 2.73 ± 0.76 a | |
| Compost | - | - | - | 1.12 ± 0.4 ab | 0.24 ± 0.07 b | 0.2 ± 0.02 b | 1.78 ± 0.09 cd | 2.31 ± 0.4 ab | 1.8 ± 0.33 ab | |
| Compost × NPK | - | - | - | 1.6 ± 0.15 a | 0.58 ± 0.1 ab | 1.13 ± 0.2 ab | 3.27 ± 0.39 a | 3.63 ± 0.1 ab | 2 ± 0.19 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Mouttaqi, A.; Mnaouer, I.; Nilahyane, A.; Belcaid, M.; Ibourki, M.; Lazaar, K.; Diatta, L.; Devkota, K.P.; Kouisni, L.; Hirich, A. How Does Organic Amendment and NPK Fertilization Improve Forage Yield of Cereals under Salinity and Arid Conditions?: Case of Moroccan Sahara. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 16, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016051
El Mouttaqi A, Mnaouer I, Nilahyane A, Belcaid M, Ibourki M, Lazaar K, Diatta L, Devkota KP, Kouisni L, Hirich A. How Does Organic Amendment and NPK Fertilization Improve Forage Yield of Cereals under Salinity and Arid Conditions?: Case of Moroccan Sahara. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 16(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016051
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Mouttaqi, Ayoub, Ihssane Mnaouer, Abdelaziz Nilahyane, Mohamed Belcaid, Mohamed Ibourki, Karima Lazaar, Lamine Diatta, Krishna Prasad Devkota, Lamfeddal Kouisni, and Abdelaziz Hirich. 2022. "How Does Organic Amendment and NPK Fertilization Improve Forage Yield of Cereals under Salinity and Arid Conditions?: Case of Moroccan Sahara" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 16, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016051
APA StyleEl Mouttaqi, A., Mnaouer, I., Nilahyane, A., Belcaid, M., Ibourki, M., Lazaar, K., Diatta, L., Devkota, K. P., Kouisni, L., & Hirich, A. (2022). How Does Organic Amendment and NPK Fertilization Improve Forage Yield of Cereals under Salinity and Arid Conditions?: Case of Moroccan Sahara. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 16(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016051







