Groundwater Resources in Moroccan Coastal Aquifers: Insights of Salinization Impact on Agriculture †
Abstract
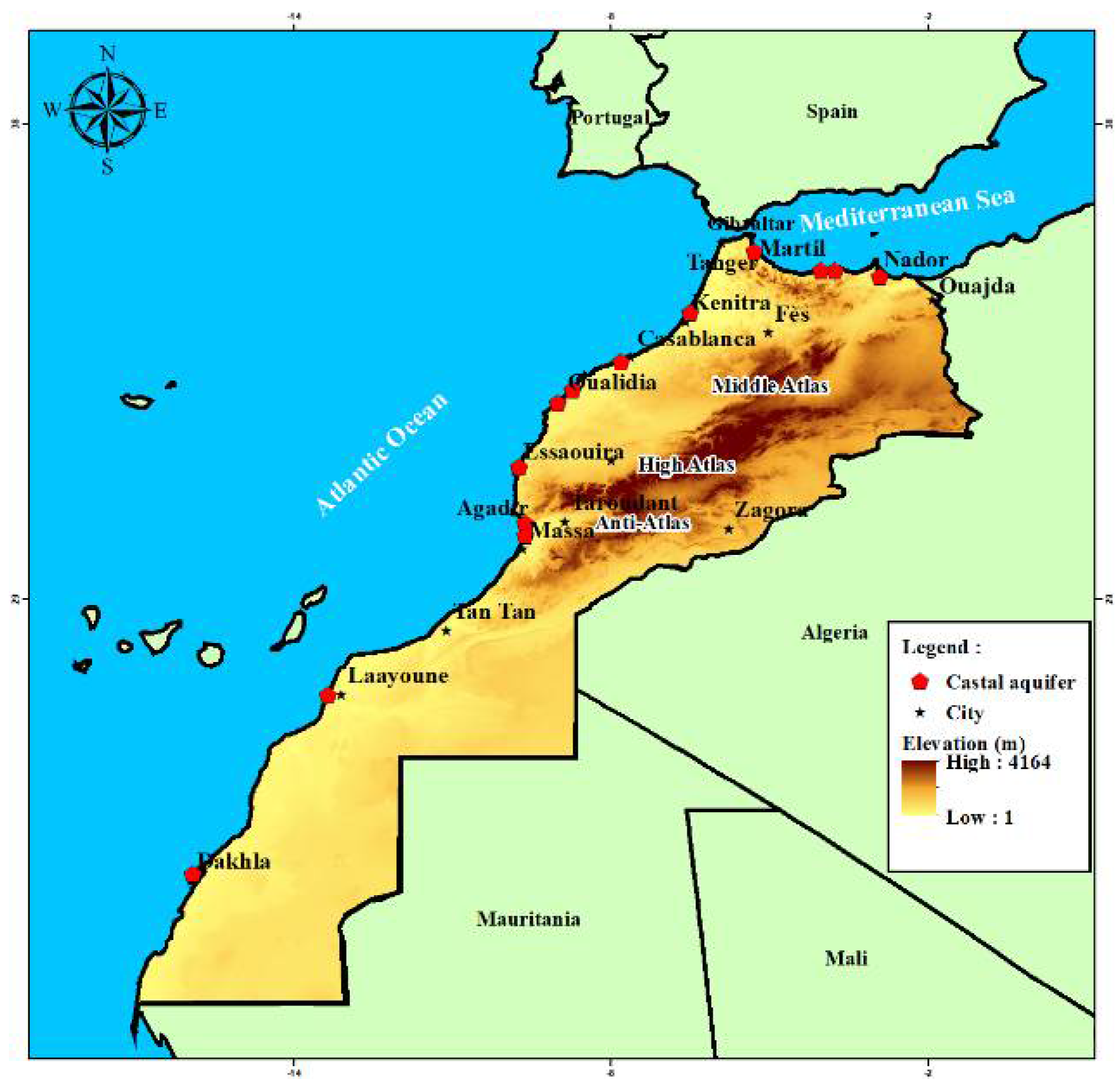
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hssaisoune, M.; Bouchaou, L.; Sifeddine, A.; Bouimetarhan, I.; Chehbouni, A. Moroccan groundwater resources and evolution with global climate changes. Geosciences 2020, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ez-zaouy, Y.; Bouchaou, L.; Saad, A.; Hssaisoune, M.; Brouziyne, Y.; Dhiba, D.; Chehbouni, A. Morocco’s coastal aquifers: Recent observations, evolution and perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziane, N.; Khaddari, A.; Ebn Touhami, M.; Zouahri, A.; Nassali, H.; Elyoubi, M. Evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation in the coastal aquifer of Mnasra (Gharb, Morocco). Mediterr. J. Chem. 2020, 10, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkaline Soils; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; pp. 1–159.
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Szaboles, I.; Darab, C. The Influence of Irrigation Water of High Sodium Carbonate Content on Soils. 8th International Congress Soil Science Sodics Soils; Research Institute for Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences: Budapest, Hungaria, 1964; pp. 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, C.N.; Mccarty, P.L. Chemistry for Sanitary Engineers, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967; p. 518. [Google Scholar]
- Doneen, L.D. Notes on Water Quality in Agriculture. Published as a Water Science and Engineering; Paper 4001; Department of Water Sciences and Engineering, University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.K.; Gupta, I.C. Management of Saline Soils and Water; Oxford and IBH Publication Co.: New Delhi, India, 1987; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.P. Permissible composition and concentration of irrigation water. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1940, 66, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakir, Y.; Zerouali, A.; Aboufirassi, M.; Bouabdelli, M. Potential exploitation and salinity of aquifers, Chaouia coast, Atlantic shoreline. Morocco. J. African Earth Sci. 2001, 32, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, V.; Sacchi, E. Tackling the salinity-pollution nexus in coastal aquifers from arid regions using nitrate and boron isotopes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13247–13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | EC | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | HCO3− | Cl− | SO42− | NO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µS/cm) | (mg/L) | ||||||||
| Max | 21,000 | 37.1 | 65.6 | 200.0 | 6.4 | 21.0 | 220.0 | 46.3 | 521.1 |
| Min | 190 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Mean | 3243 | 7.7 | 8.4 | 17.8 | 0.3 | 5.0 | 21.3 | 7.4 | 64.8 |
| SD | 2600 | 5.8 | 7.6 | 20.9 | 0.6 | 2.6 | 26.1 | 7.6 | 66.2 |
| Index | Index Formula | Equation Number | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Absorption Ratio | (1) | [4] | |
| Sodium Percentage | Na+% = ((Na+ + K+) ∗ 100/(Ca2+ + Mg2+ + Na+ + K+)) | (2) | [5] |
| Magnesium Ratio | MR = (Mg2+ ∗ 100/(Ca2+ + Mg2+)) | (3) | [6] |
| Total Hardness | TH = (2.497 Ca2+ + 4.11 Mg2+) | (4) | [7] |
| Permeability Index | PI = (Na+ + √HCO3−) ∗ 100/Ca2+ + Mg2+ + Na+ | (5) | [8] |
| Residual Sodium Bicarbonate | RSBC = (HCO3− − Ca2+) | (6) | [9] |
| Kelly’s Ratio | KR = (Na+/(Ca2+ + Mg2+)) | (7) | [10] |
| Index | Min | Max | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAR | 0.2 | 45.2 | 6.1 | 6.3 |
| Na% | 5.5 | 94.9 | 45.8 | 17.9 |
| MR | 4.2 | 93.3 | 49.3 | 13.7 |
| TH | 74.1 | 4316.4 | 808.2 | 637.6 |
| RSBC | −33.2 | 15.9 | −2.7 | 6.1 |
| KR | 0.1 | 18.1 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| PI | 10.8 | 101.8 | 57.0 | 15.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ez-zaouy, Y.; Bouchaou, L.; Saad, A.; Hssaisoune, M.; Brouziyne, Y.; Dhiba, D.; Chehbouni, A. Groundwater Resources in Moroccan Coastal Aquifers: Insights of Salinization Impact on Agriculture. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 16, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016048
Ez-zaouy Y, Bouchaou L, Saad A, Hssaisoune M, Brouziyne Y, Dhiba D, Chehbouni A. Groundwater Resources in Moroccan Coastal Aquifers: Insights of Salinization Impact on Agriculture. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 16(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016048
Chicago/Turabian StyleEz-zaouy, Yassine, Lhoussaine Bouchaou, Aicha Saad, Mohammed Hssaisoune, Youssef Brouziyne, Driss Dhiba, and Abdelghani Chehbouni. 2022. "Groundwater Resources in Moroccan Coastal Aquifers: Insights of Salinization Impact on Agriculture" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 16, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016048
APA StyleEz-zaouy, Y., Bouchaou, L., Saad, A., Hssaisoune, M., Brouziyne, Y., Dhiba, D., & Chehbouni, A. (2022). Groundwater Resources in Moroccan Coastal Aquifers: Insights of Salinization Impact on Agriculture. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 16(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016048








