Designing the Path for Soil Salinity Management: Lessons Learned and Future Perspectives in Morocco †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and methods
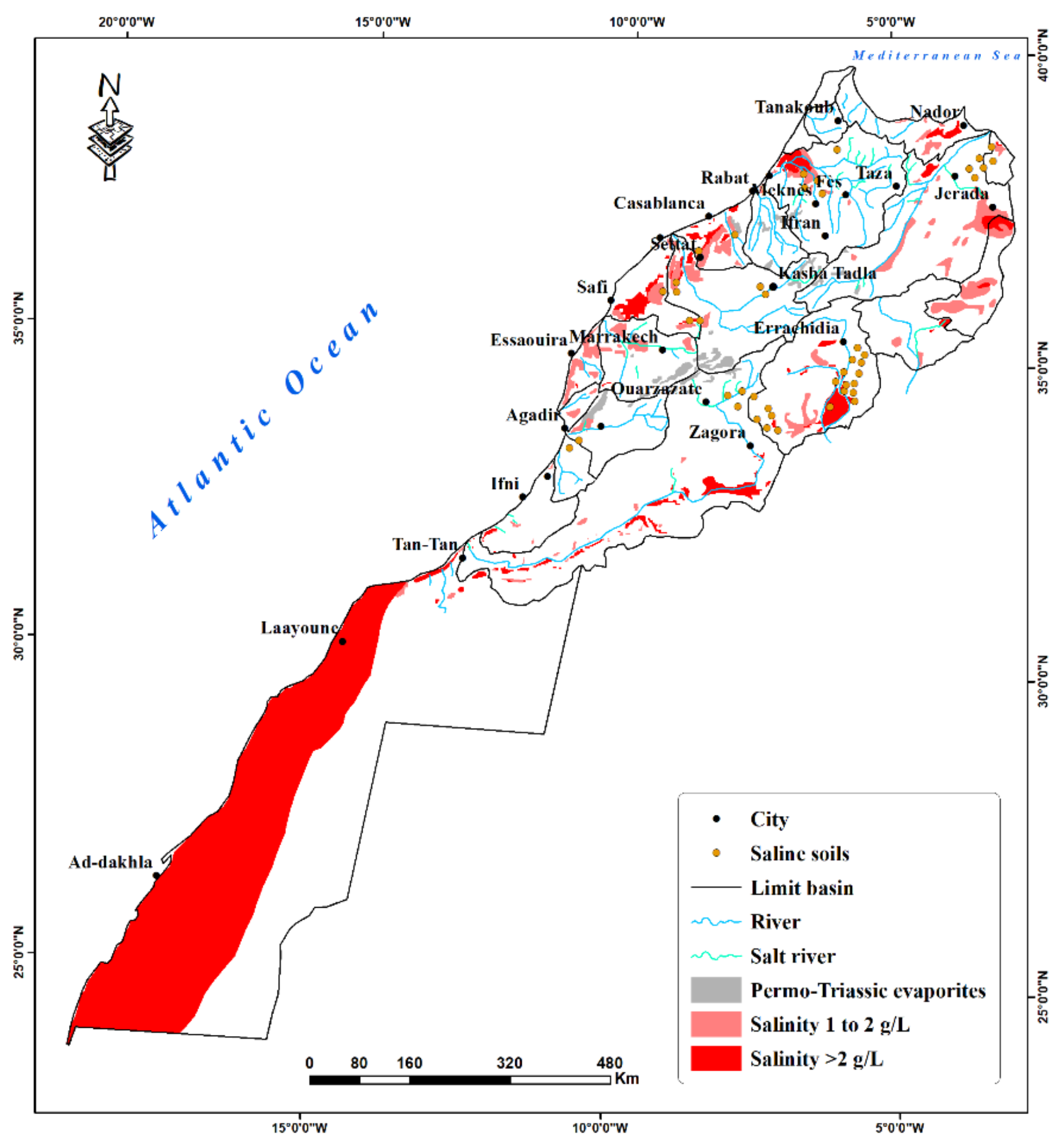
2.1. Soil Salinity Situation in Morocco
2.2. Study Approach
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Findings on Soil Salinity Rehabilitation in Morocco
3.2. How to Go Forward
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abiala, M.A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Burritt, D.J.; Tran, L.-S.P. Salt Stress Tolerance Mechanisms and Potential Applications of Legumes for Sustainable Reclamation of Salt-Degraded Soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3812–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, H.; Pan, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Zheng, M. Analysis of Saline Groundwater Infiltration into Two Loam Soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3795–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, S.; Elbrik, K.; Tachbibi, N.; Bouqbis, L.; Brakez, M.; Harrouni, M.C. 9-The Potential Use of Halophytes for the Development of Marginal Dry Areas in Morocco. In Halophytes for Food Security in Dry Lands; Khan, M.A., Ozturk, M., Gul, B., Ahmed, M.Z., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hssaisoune, M.; Bouchaou, L.; Sifeddine, A.; Bouimetarhan, I.; Chehbouni, A. Moroccan Groundwater Resources and Evolution with Global Climate Changes. Geosci. J. 2020, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, N.; Grové, B.; Barnard, J.H.; van Rensburg, L.D. Modelling the Economic Tradeoffs between Allocating Water for Crop Production or Leaching for Salinity Management. Water SA 2010, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hasini, S.; De Nobili, M.; El Azzouzi, M.; Azim, K.; Douaik, A.; Laghrour, M.; El Idrissi, Y.; El Alaoui El Belghiti, M.; Zouahri, A. The Influence of Compost Humic Acid Quality and Its Ability to Alleviate Soil Salinity Stress. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2020, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strategies or Management Practice | Target 1 | Type 2 | Resolution 3 | Level 4 | Type of Coast 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic amendment (gypsum, phosphogypsum) | S | C | R | F | D |
| Organic amendment (Compost, humic acids, etc.) | S | B | R | F | I |
| Development and use of salt-tolerant cultivar | C | B | A | C | D |
| Introduction of alternative crops (e.g., Quinoa, Blue panicum, etc.) | CSW | B | A | F | I |
| Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) (e.g., Robinia pseudoacacia, Phaseolus vulgaris L., etc.) | S | B | A | F | D |
| Remote sensing and GIS in salinity mapping | S | P | R | C | D |
| Electromagnetic and tomographic technique in soil salinity | S | P | A | C | I |
| Genetic engineering (e.g., Exogenous application of compatible solutes such as proline) | C | B | A | C | I |
| Leaching, implementation of subsurface drainage Systems | W | P | PAR | F | D |
| Use of brackish water | W | P | A | C | D |
| Mixing saline and freshwater | W | C | A | C | D |
| Alternative water sources, e.g., Seawater desalination, Desalination of Irrigation water | W | C | A | C | D |
| Plant halophytes in high salinity areas | C | B | R | C | D |
| Inoculation with mycorrhizal associations | C | B | A | F | I |
| Incorporate agroforestry into management | S | B | A | C | D |
| Apply biological agents to increase crop resistance to salinity or plant growth under saline conditions (Example: Ulva lactuca extract) | C | B | A | F | I |
| Use halophilic green algaeto counter salinisation effects on the crop (e.g., Dunaliella salina) | C | B | A | F | I |
| Intervention in the nutrition of plants (e.g., Phosphorus fertilization) | S | C | A | F | I |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seif-Ennasr, M.; Chikhaoui, M.; Naimi, M.; Chaaou, A.; Choukr-Allah, R. Designing the Path for Soil Salinity Management: Lessons Learned and Future Perspectives in Morocco. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 16, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016040
Seif-Ennasr M, Chikhaoui M, Naimi M, Chaaou A, Choukr-Allah R. Designing the Path for Soil Salinity Management: Lessons Learned and Future Perspectives in Morocco. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 16(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016040
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeif-Ennasr, Marieme, Mohamed Chikhaoui, Mustapha Naimi, Abdelwahed Chaaou, and Redouane Choukr-Allah. 2022. "Designing the Path for Soil Salinity Management: Lessons Learned and Future Perspectives in Morocco" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 16, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016040
APA StyleSeif-Ennasr, M., Chikhaoui, M., Naimi, M., Chaaou, A., & Choukr-Allah, R. (2022). Designing the Path for Soil Salinity Management: Lessons Learned and Future Perspectives in Morocco. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 16(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016040






