Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning-Based Decentralized Controller for Battery Modular Multilevel Inverter Systems
Abstract
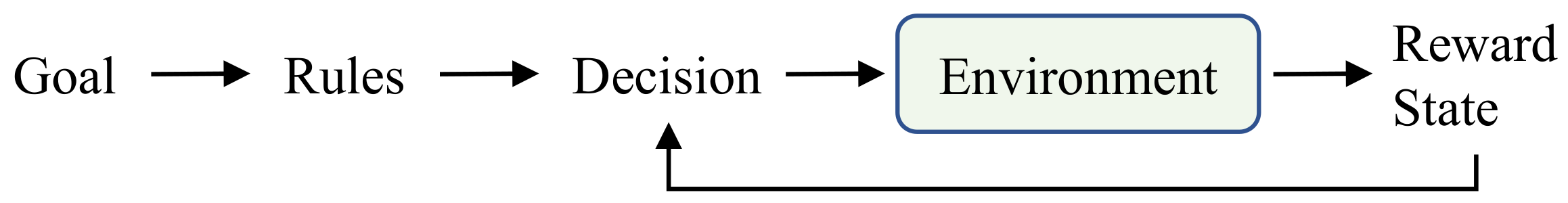
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
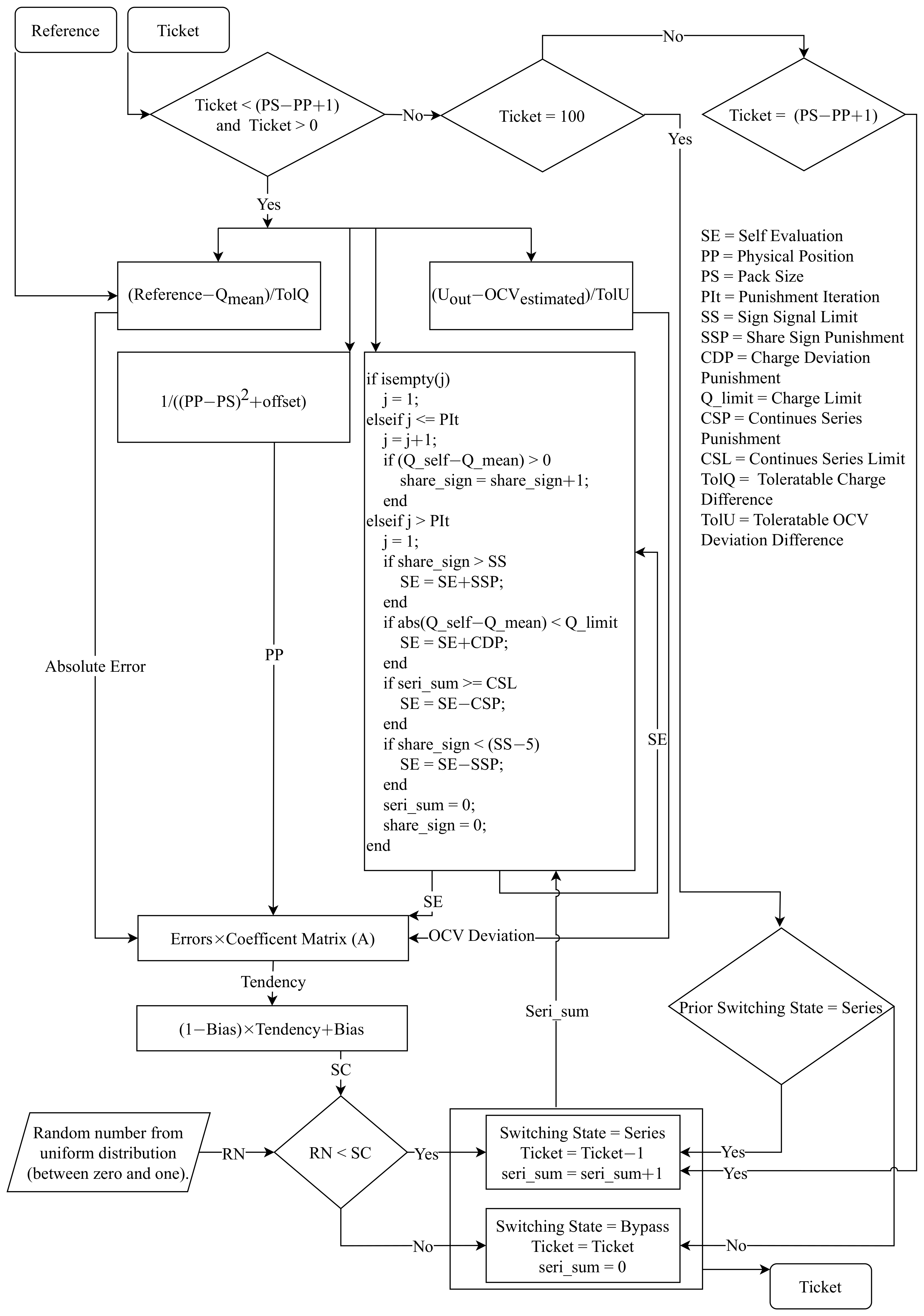
2.1. Intelligent Switching System
2.2. Self-Evaluation
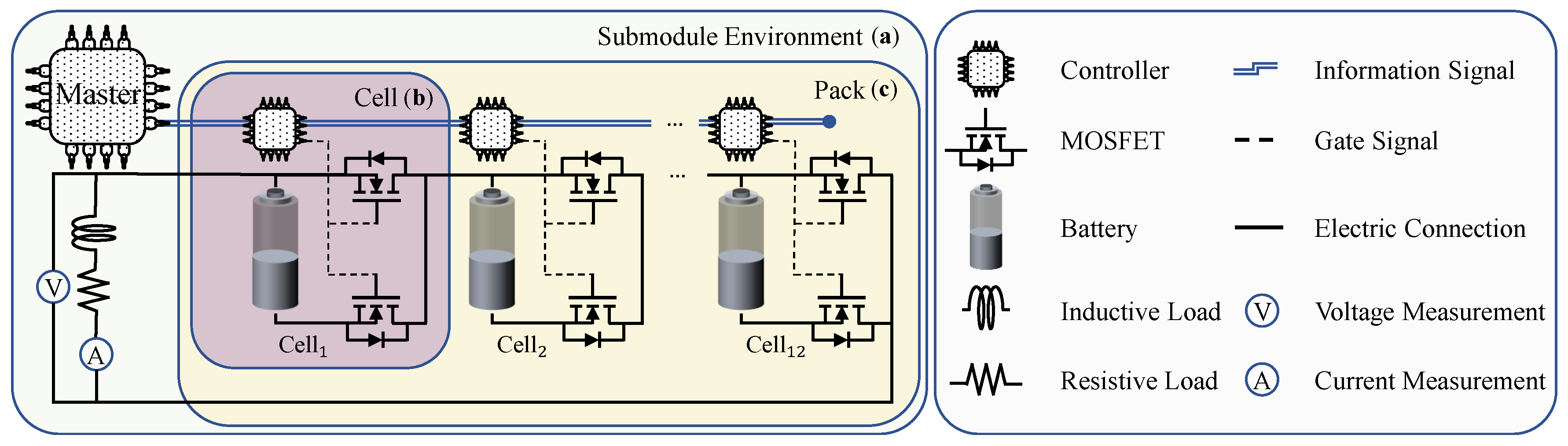
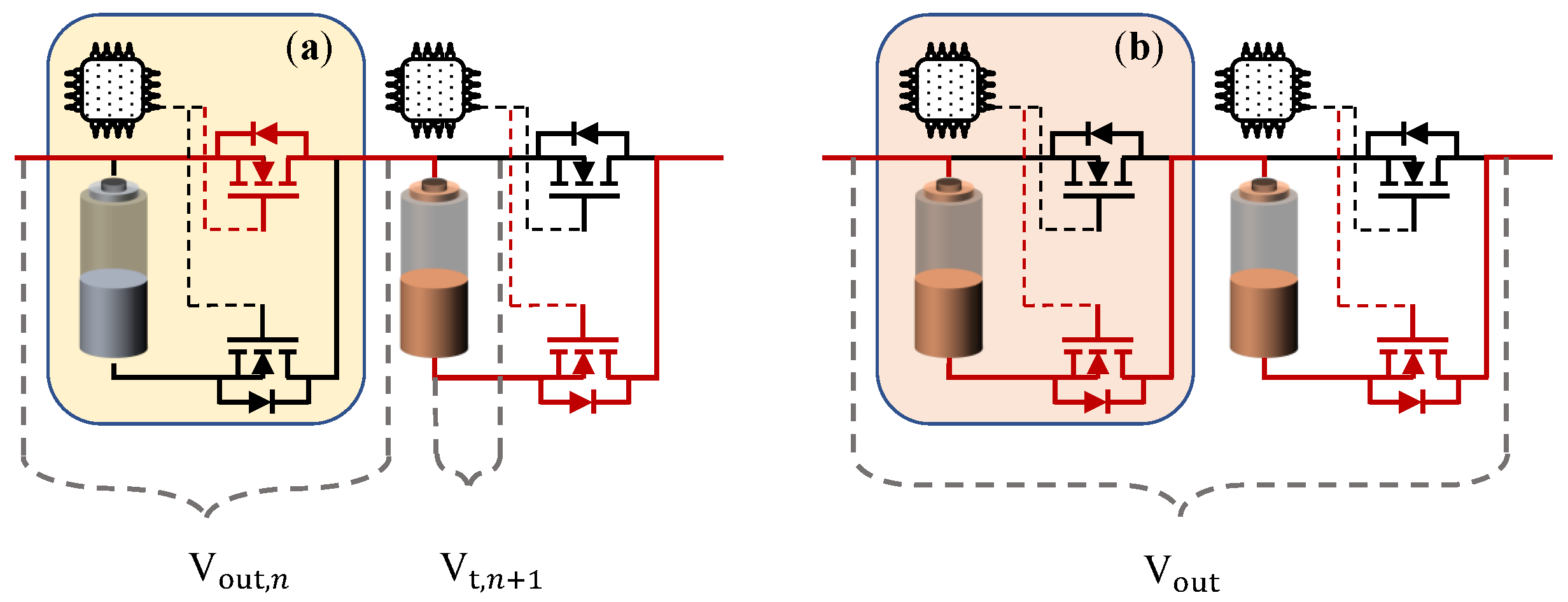
3. Simulation Structure and Results
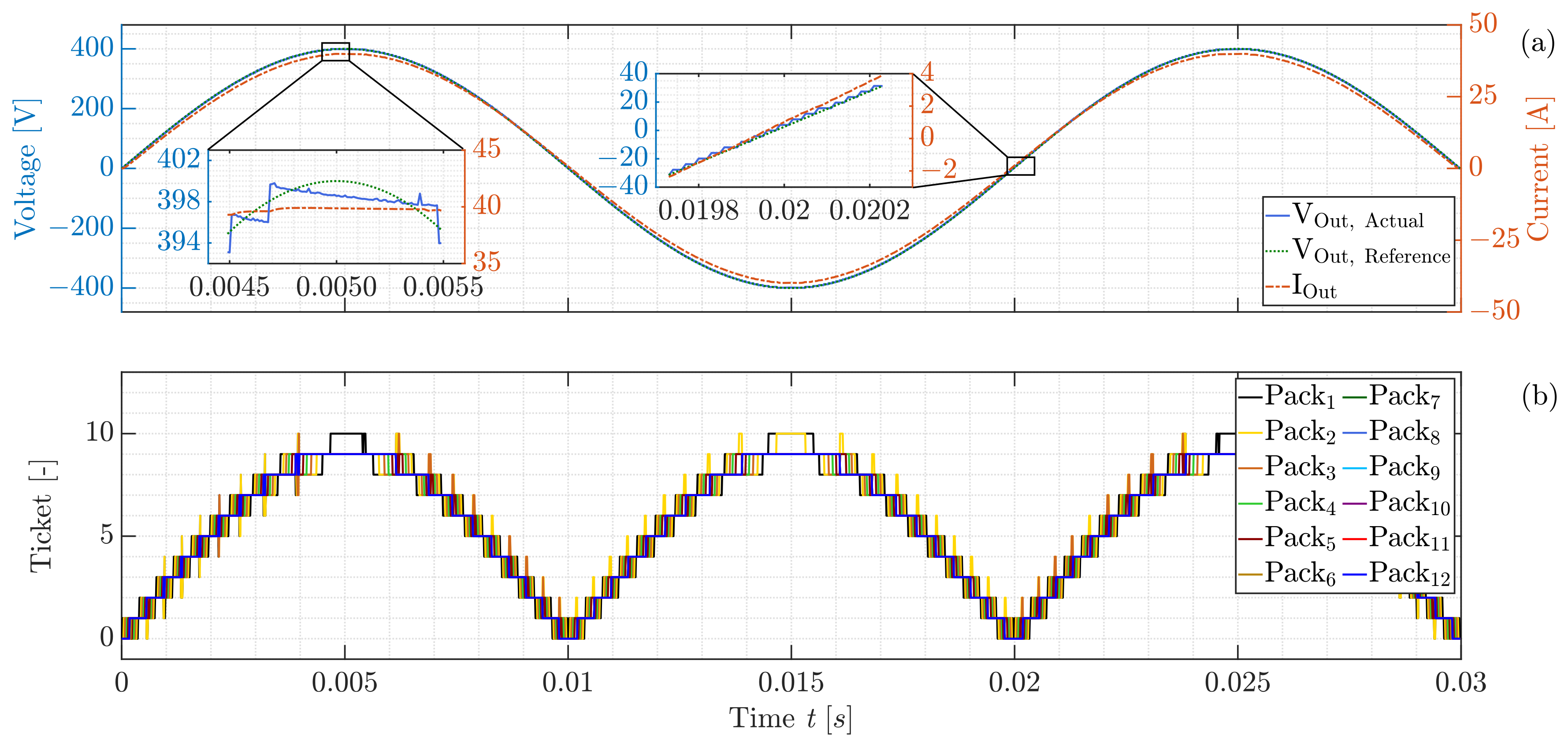
3.1. Submodule Environment
3.2. Module Environment
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ISS | Intelligent Switching System |
| EVs | Electric Vehicles |
| BMS | Battery Management System |
| LIBs | Lithium-ion Batteries |
| MLI | Multilevel Inverter |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| MARL | Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning |
| Modular Multi Level Converter | |
| ADC | Average Depleted Charge |
| PS | Pack Size |
| MILO | Mixed Integer Linear Optimization |
| SC | Switching Chance |
| MDP | Markov Decision Process |
| SoC | State of Charge |
| SoH | State of Health |
| OCV | Open Circuit Voltage |
| GT | Game Theory |
| Ref | Reference |
| PP | Physical Position |
| PIt | Punishment Iteration |
| SSL | Sign Signal Limit |
| SSP | Share Sign Punishment |
| CDP | Charge Deviation Punishment |
| CSP | Continues Series Punishment |
| CSL | Continues Series Limit |
| RN | Random Number |
References
- Zhou, W.; Cleaver, C.J.; Dunant, C.F.; Allwood, J.M.; Lin, J. Cost, range anxiety and future electricity supply: A review of how today’s technology trends may influence the future uptake of BEVs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 173, 113074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.; Tate, J.E.; Wadud, Z.; Nellthorp, J. Total cost of ownership and market share for hybrid and electric vehicles in the UK, US and Japan. Appl. Energy 2018, 209, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.; Bakhshoodeh, R. Climate change/global warming/climate emergency versus general climate research: Comparative bibliometric trends of publications. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmuch, R.; Wagner, R.; Hörpel, G.; Placke, T.; Winter, M. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Pohlmann, S.; Guenter, F.J.; Hille, L.; Hagemeister, J.; Reinhart, G. Early Quality Classification and Prediction of Battery Cycle Life in Production Using Machine Learning. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuder, M.; Schneider, J.; Kersten, A.; Thiringer, T.; Eckerle, R.; Weyh, T. Battery Modular Multilevel Management (BM3) Converter applied at Battery Cell Level for Electric Vehicles and Energy Storages. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe Digital Days 2020, International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nuremberg, Germany, 7–8 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kersten, A.; Kuder, M.; Thiringer, T. Hybrid Output Voltage Modulation (PWM-FSHE) for a Modular Battery System Based on a Cascaded H-Bridge Inverter for Electric Vehicles Reducing Drivetrain Losses and Current Ripple. Energies 2021, 14, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buberger, J.; Kersten, A.; Kuder, M.; Singer, A.; Mashayekh, A.; Estaller, J.; Thiringer, T.; Eckerle, R.; Weyh, T. Charging Strategy for Battery Electric Vehicles with a Battery Modular Multilevel Management (BM3) Converter System using a PR controller. In Proceedings of the 2021 23rd European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’21 ECCE Europe), Ghent, Belgium, 6–10 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorfakhraei, A.; Narimani, M.; Emadi, A. A Review of Multilevel Inverter Topologies in Electric Vehicles: Current Status and Future Trends. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2021, 2, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraan, M.; Tricoli, P.; D’Arco, S.; Piegari, L. Efficiency Assessment of Modular Multilevel Converters for Battery Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnicar, A.; Marquardt, R. An Innovative Modular Multilevel Converter Topology Suitable for a Wide Power Range. Power Tech. Conf. Proc. 2003, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.; Liebhart, B.; Endisch, C. Active state and parameter estimation as part of intelligent battery systems. J. Energy Storage 2021, 39, 102638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitzgebel, F.; Buberger, J.; Kuder, M.; Karnehm, D.; Sorokina, N.; Wiedenmann, A.; Mashayekh, A.; Eckerle, R.; Weyh, T. Multilevel Inverter based Battery System Operation using a Decentralized Controller. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 5–7 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekh, A.; Kersten, A.; Kuder, M.; Estaller, J.; Khorasani, M.; Buberger, J.; Eckerle, R.; Weyh, T. Proactive SoC Balancing Strategy for Battery Modular Multilevel Management (BM3) Converter Systems and Reconfigurable Batteries. In Proceedings of the 2021 23rd European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’21 ECCE Europe), Ghent, Belgium, 6–10 September 2021; pp. P.1–P.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.; Asim, M.; Tawfik, H.; Aldawsari, B.; Buyya, R. An energy-aware service composition algorithm for multiple cloud-based IoT applications. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 89, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, O.H.; Motamedi, S.A.; Sharifian, S.; Nazari-Heris, M. Intelligent Service Selection in a Multi-Dimensional Environment of Cloud Providers for Internet of Things Stream Data through Cloudlets. Energies 2021, 14, 8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Nayyar, A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A. Fog computing: From architecture to edge computing and big data processing. J. Supercomput. 2019, 75, 2070–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhorst, S.; Shao, Z.; Chakraborty, S.; Kauer, M.; Li, S.; Lukasiewycz, M.; Narayanaswamy, S.; Rafique, M.; Wang, Q. Distributed reconfigurable battery system management architectures. In Proceedings of the Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, ASP-DAC, Macao, China, 25–28 January 2016; pp. 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Mcgrath, B.; Holmes, G.; Kong, W. A Decentralized Controller Architecture for a Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Converter. Ind. Electron. IEEE Trans. 2014, 61, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlacu, P.D.; Mathe, L.; Teodorescu, R. Synchronization of the distributed PWM carrier waves for modular multilevel converters. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Bran, Romania, 22–24 May 2014; pp. 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, R.; Sebaaly, F.; Kanaan, H.Y. A Review on Modular Multilevel Converters in Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the IECON 2020 the 46th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Singapore, 18–21 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Hosseini, E.; Liserre, M.; Fernández-Ramírez, L.M. Reinforcement Learning Based Modulation for Balancing Capacitor Voltage and Thermal Stress to Enhance Current Capability of MMCs. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Kiel, Germany, 26–29 June 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; Blaabjerg, F. Supervised imitation learning of FS-MPC algorithm for multilevel converters. In Proceedings of the 2021 23rd European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’21 ECCE Europe), Ghent, Belgium, 6–10 September 2021; pp. P.1–P.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorennec, P.Y. Reinforcement learning: An overview. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Intelligent Techniques (ESIT-00), Aachen, Germany, 8–11 September 1997; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- François-Lavet, V.; Henderson, P.; Islam, R.; Bellemare, M.G.; Pineau, J. An Introduction to Deep Reinforcement Learning. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2018, 11, 219–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littman, M.L. Markov games as a framework for multi-agent reinforcement learning. In Machine Learning Proceedings; Cohen, W.W., Hirsh, H., Eds.; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buşoniu, L.; Babuška, R.; De Schutter, B. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning: An Overview. In Innovations in Multi-Agent Systems and Applications-1; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 183–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, Z.; Başar, T. Multi-agent reinforcement learning: A selective overview of theories and algorithms. In Handbook of Reinforcement Learning and Control; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 321–384. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Lei, X.; Du, J. Evolutionary Game Theory in Multi-Objective Optimization Problem. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2010, 3, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Ye, Y.; Xie, N.-g. Multi-objective optimization design methods based on game theory. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Jinan, China, 7–9 July 2010; pp. 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J.; Morgenstern, O. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moranchel, M.; Bueno, E.J.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Sanz, I. Implementation of nearest level modulation for Modular Multilevel Converter. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 6th International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Aachen, Germany, 22–25 June 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, W. Improved Nearest-Level Modulation for a Modular Multilevel Converter With a Lower Submodule Number. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5369–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralphs, T.; Shinano, Y.; Berthold, T.; Koch, T. Parallel solvers for mixed integer linear optimization. In Handbook of Parallel Constraint Reasoning; Hamadi, Y., Sais, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 283–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdrilić, M.; Pandžić, H.; Kuzle, I. The mixed-integer linear optimization model of virtual power plant operation. In Proceedings of the 2011 8th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Zagreb, Croatia, 25–27 May 2011; pp. 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Boundary Condition | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| TolQ | 0.006 | Ah |
| TolU | 0.01 | V |
| CSL | 10 | - |
| SSL | 25 | - |
| Matrix A Index | Value | Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | ||
| 0.5 | ||
| 0.4 | ||
| 1.0 |
| Boundary Condition | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Module count | 1 | - |
| Cells per module | 12 | - |
| Update frequency | 50 | kHz |
| Resistive load | 5 | |
| Inductive load | 0.5 | mH |
| Hyperparameter | Value | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Punishment iteration | 50 | PIt |
| Share sign punishment | 0.1 | SSP |
| Charge deviation punishment | 0.2 | CDP |
| Continues series punishment | 0.7 | CSP |
| Boundary Condition | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Module count | 12 | - |
| Cells per module | 12 | - |
| Update frequency | 50 | kHz |
| Resistive load | 10 | |
| Inductive load | 0.5 | mH |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mashayekh, A.; Pohlmann, S.; Estaller, J.; Kuder, M.; Lesnicar, A.; Eckerle, R.; Weyh, T. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning-Based Decentralized Controller for Battery Modular Multilevel Inverter Systems. Electricity 2023, 4, 235-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity4030014
Mashayekh A, Pohlmann S, Estaller J, Kuder M, Lesnicar A, Eckerle R, Weyh T. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning-Based Decentralized Controller for Battery Modular Multilevel Inverter Systems. Electricity. 2023; 4(3):235-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity4030014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMashayekh, Ali, Sebastian Pohlmann, Julian Estaller, Manuel Kuder, Anton Lesnicar, Richard Eckerle, and Thomas Weyh. 2023. "Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning-Based Decentralized Controller for Battery Modular Multilevel Inverter Systems" Electricity 4, no. 3: 235-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity4030014
APA StyleMashayekh, A., Pohlmann, S., Estaller, J., Kuder, M., Lesnicar, A., Eckerle, R., & Weyh, T. (2023). Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning-Based Decentralized Controller for Battery Modular Multilevel Inverter Systems. Electricity, 4(3), 235-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/electricity4030014










