Prediction of Tropospheric Ozone Levels from Land Surface Temperature in the Urban Area of Durango, Dgo., Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Tropospheric Ozone Monitoring: Remote Sensing Techniques and Estimation Algorithms
1.2. Passive and Active Sensors
1.3. Tropospheric Ozone Recovery: Methods and Algorithms
- (a)
- Direct Recovery
- (b)
- Residue Minimization: Model Adjustment
1.4. Neural Networks
1.5. Extreme Value Approach (Extreme Value Approach)
Satellite Instruments
1.6. Radiometric Calibration and Recovery of Ozone Profiles
1.7. Use of Remote Sensors for Tropospheric Ozone Determination
- (a)
- Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
- (b)
- TROPOMI SENTINEL5
2. Materials and Methods
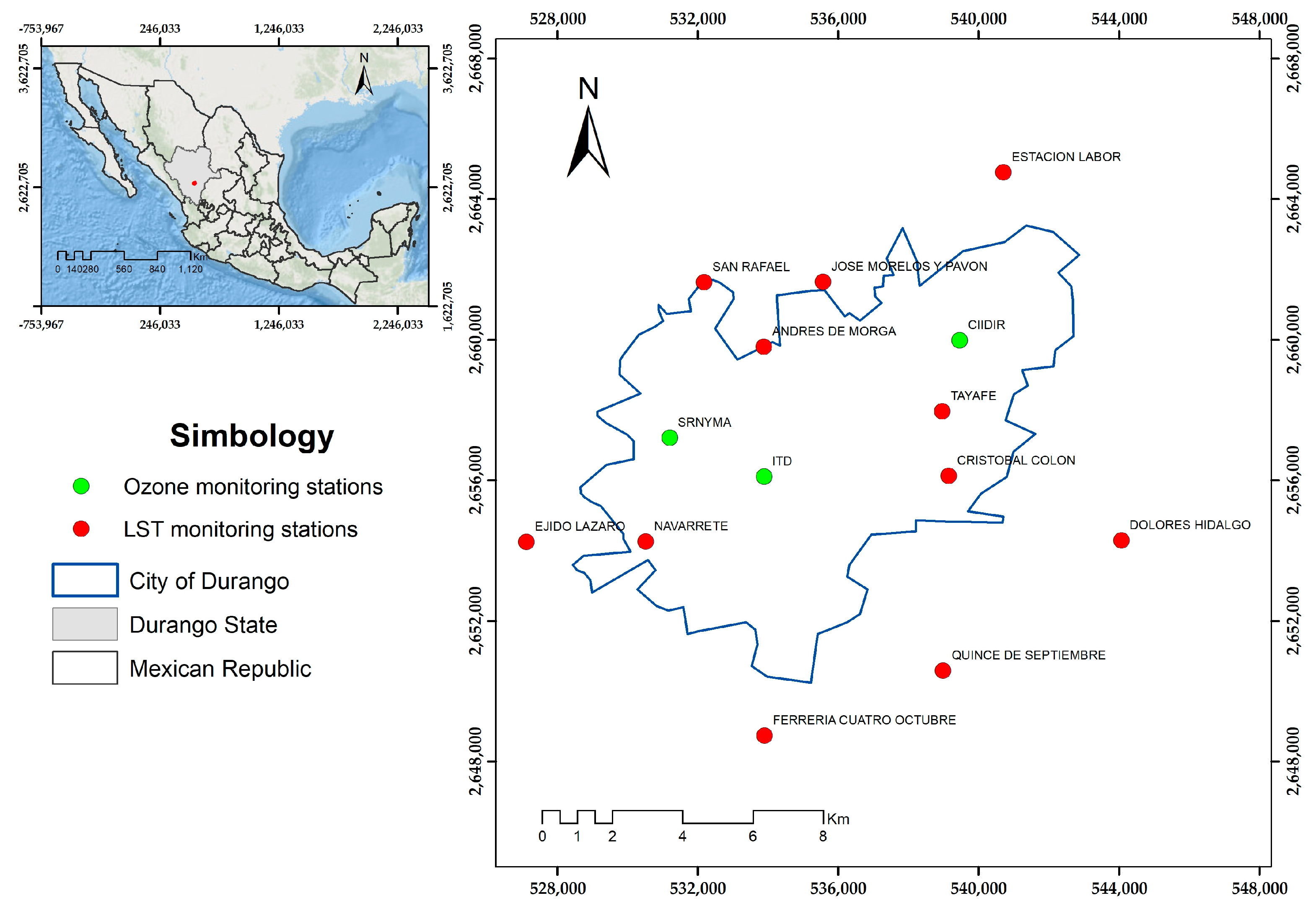
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data on Tropospheric Ozone Concentrations (O3)
2.3. Land Surface Temperature (LST) from Landsat 8 Satellite
2.4. Statistical Analysis
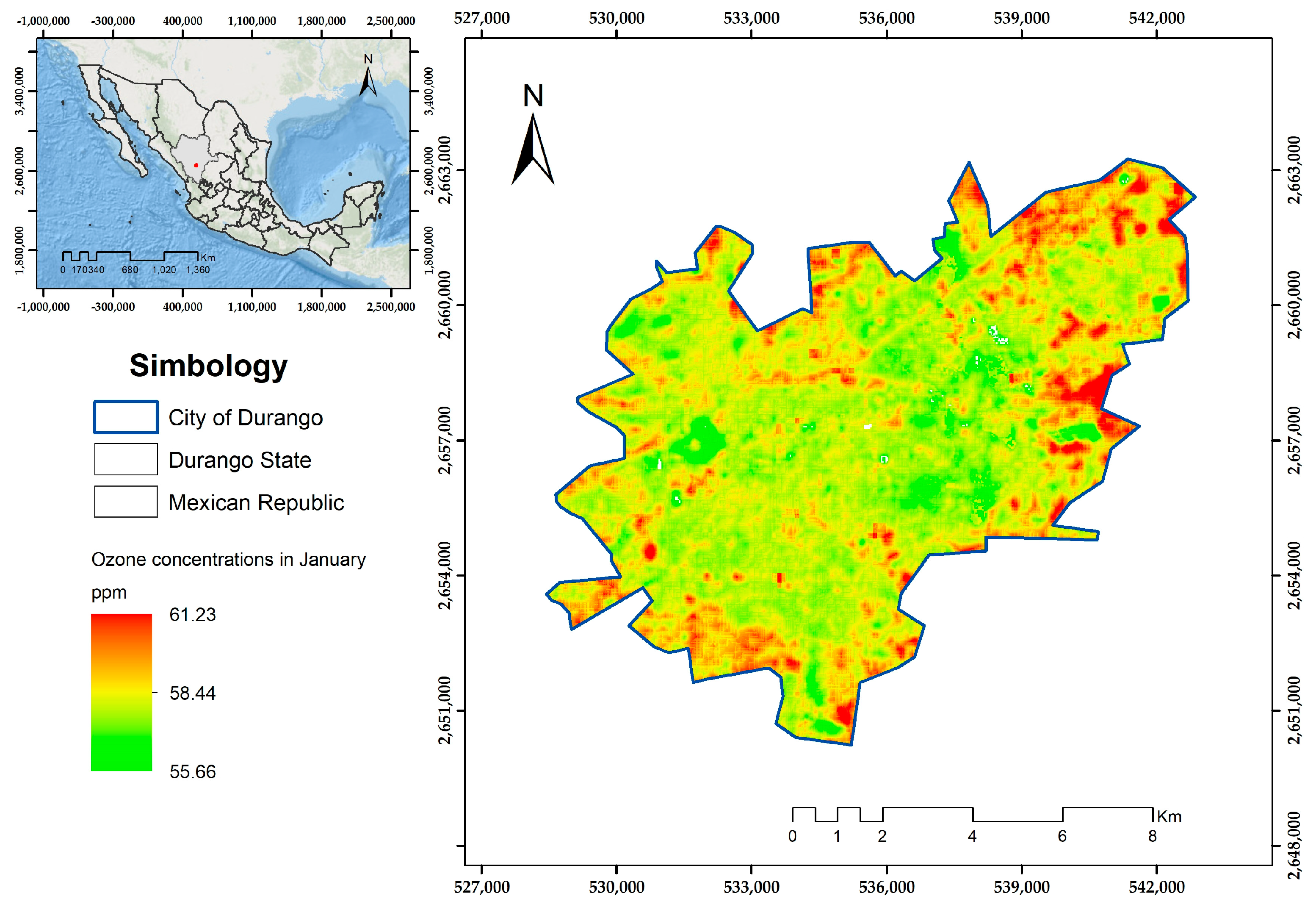
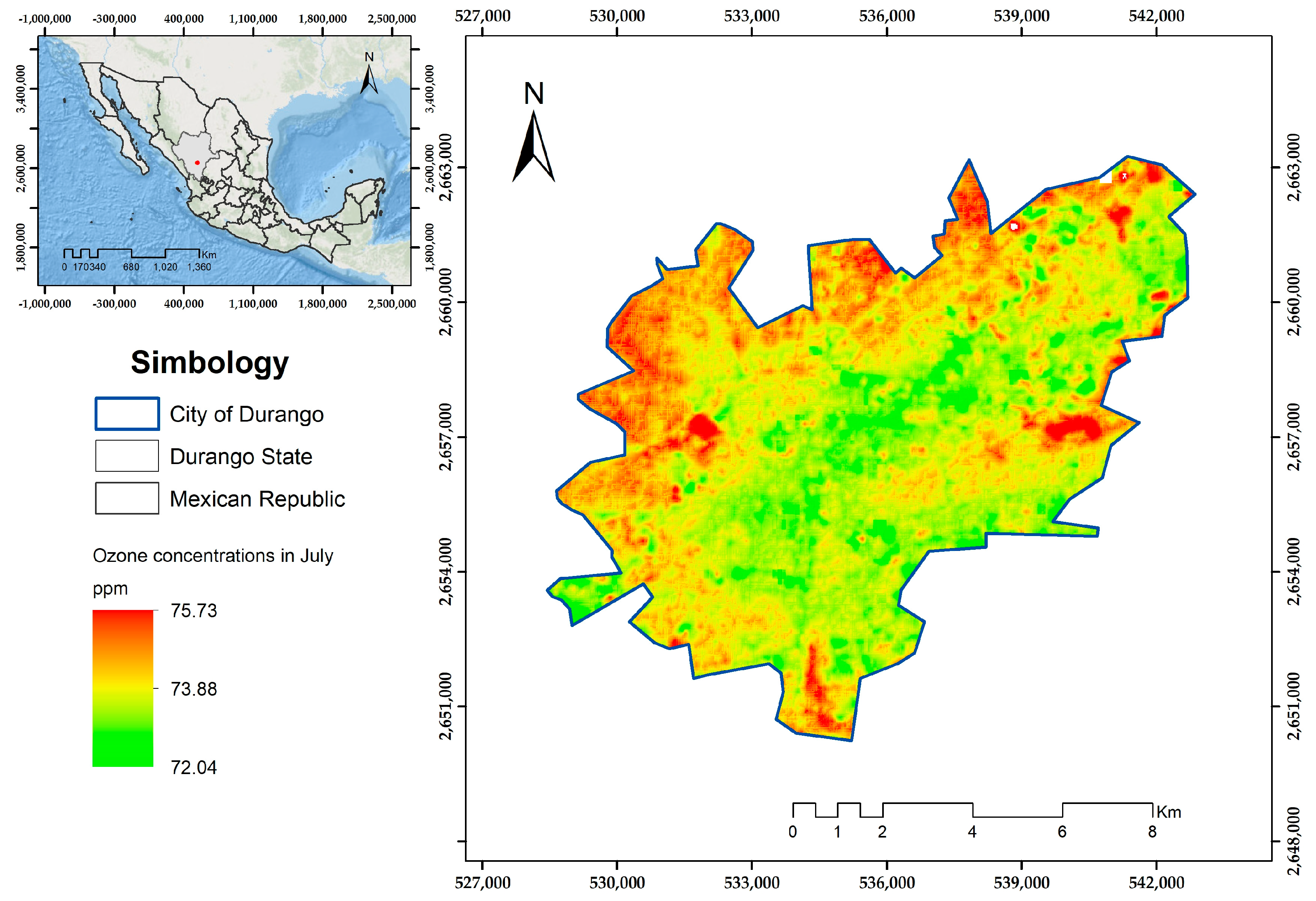
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Ambient Air Quality Database WHO 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/who-ambient-air-quality-database-(update-2023) (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.; Lupascu, A.; Nalam, A. Attribution of ground-level ozone to anthropogenic and natural sources of nitrogen oxides and reactive carbon in a global chemical transport model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10707–10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monks, P.S.; Archibald, A.; Colette, A.; Cooper, O.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.; Fowler, D.; Granier, C.; Law, K.S.; Mills, G. Tropospheric ozone and its precursors from the urban to the global scale from air quality to short-lived climate forcer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8889–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.; Rowland, S.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J. A hybrid model for spatially and temporally resolved ozone exposures in the continental United States. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Greenhouse Gas Inventory Data Explorer. 2023. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ghgdata/inventoryexplorer/#allsectors/allsectors/allgas/gas/current (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Lu, X.; Ye, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, Y.; Weng, H.; Kong, H.; Li, K.; Gao, M.; Zheng, B.; Lin, J. The underappreciated role of agricultural soil nitrogen oxide emissions in ozone pollution regulation in North China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Zhang, M.; Di, B. Spatiotemporal prediction of daily ambient ozone levels across China using random forest for human exposure assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, J.; Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Yuan, H. Local and synoptic meteorological influences on daily variability in summertime surface ozone in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, G.J.; Lelieveld, J.; van Dorland, R. A three-dimensional chemistry/general circulation model simulation of anthropogenically derived ozone in the troposphere and its radiative climate forcing. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 23389–23401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echávez, K.; Pastran, Y.; Polo, Á. Estimación del CO2 emitido y capturado en la sede sabanas y el campus deportivo de la universidad popular del cesar. Rev. Ambient. Agua Aire Y Suelo 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cooper, O.R.; Gaudel, A.; Thompson, A.M.; Nédélec, P.; Ogino, S.-Y.; West, J.J. Tropospheric ozone change from 1980 to 2010 dominated by equatorward redistribution of emissions. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Liao, H. A typical weather pattern for ozone pollution events in North China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13725–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumin, E.; Zaini, N.; Ahmed, A.N.; Abdullah, S.; Ismail, M.; Sherif, M.; Sefelnasr, A.; El-Shafie, A. Machine learning versus linear regression modelling approach for accurate ozone concentrations prediction. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2020, 14, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, N.; Sillmann, J.; Mar, K.A.; Rust, H.W.; Solberg, S.; Andersson, C.; Engardt, M.; Bergström, R.; Bessagnet, B.; Colette, A. A multi-model comparison of meteorological drivers of surface ozone over Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12269–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beristain-Montiel, E.; Gavilán-García, A.; Maldonado-Cabrera, S.C. Were biogenic volatile organic compounds mainly responsible for ozone pollution during the COVID-19 lockdown In Mexico City? J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2023, 67, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, X. Geoestadística; Universidad de Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, J.; Sharif, H.O.; Sunil, T.; Alamgir, H. Application of validation data for assessing spatial interpolation methods for 8-h ozone or other sparsely monitored constituents. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Rao, L.; Wang, Y.; Letu, H.; Shi, C.; Tana, G.; Wang, W.; Zhu, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Remote sensing of tropospheric ozone from space: Progress and challenges. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 4, 0178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettig, M.; Landgraf, J.; Hasekamp, O.P.; Brown, S.S.; Zuraski, K.; Chace, W.; Womack, C.C.; Peischl, J.; Hair, J.; Shingler, T.; et al. The Small Mobile Ozone Lidar (SMOL): Instrument description and first field measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 18, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huo, Y.; Mu, X.; Jiang, P.; Xun, S.; He, B.; Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. A High-Performance Convolutional Neural Network for Ground-Level Ozone Estimation in Eastern China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, X. Evaluation of satellite-based measurements of tropospheric ozone for air quality management: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6693–6705. [Google Scholar]
- Buele, M.; Alexander, E. Utilización de Información Satelital Para Estimar la Calidad del Aire a Nivel de Superficie Evaluación de Datos Satelitales de Ozono Troposférico en Contraste con la Información de Superficie de la Red Metropolitana de Monitoreo de Quito; Escuela Politecnica Nacional: Quito, Ecuador, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ma, P. Advances of ozone satellite remote sensing in 60 years. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.V.; Perilla, J.K. Análisis de la Calidad del Aire en Villa de Leyva-Boyacá a Partir de Mediciones de Dióxido de Azufre Generadas por el Satélite Sentinel 5P; Universidad Distrital Francisco José de Caldas: Bogotá, Colombia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.Y.; Yao, J.; Qiao, D.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhong, C.Y.; Tang, L.J. Three-hourly PM2.5 and O3 concentrations prediction based on time series decomposition and LSTM model with attention mechanism. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, R.; Naderalvojoud, B.; Güllü, G. A Comparative Study of Deep Learning Models on Tropospheric Ozone Forecasting Using Feature Engineering Approach. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Fang, F.; Navon, I.M.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, J.; Pain, C. Assessing uncertainty and heterogeneity in machine learning-based spatiotemporal ozone prediction in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Manna, S. Monthly and annual oscillation of methane and ozone in eastern India using Sentinel-5P TROPOMI: Assessment and validation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipa, S. Análisis de Contaminantes del aire Atmosférico a Través de Imágenes Sentinel 5P de la Región de Apurímac, Perú Periodo 2018–2021 Escuela de Posgrado Newman. 2023. Available online: https://repositorio.epnewman.edu.pe/handle/20.500.12892/716 (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- García Santos, D. Estimación de Calidad del aire en Superficie a Partir de Medidas Satelitales (Projecte Final de Màster Oficial); UPC, Escola Politècnica Superior d’Enginyeria de Manresa, Departament d'Enginyeria Minera, Industrial i TIC: Barcelona, Spain, 2021; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2117/354974 (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Song, H.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Hou, W.; Chen, L.; Ma, P. Ozone Sensitivity Analysis and Ozone Formation Regimes Division in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, D.; Faican, G.; Zalakeviciute, R.; Matovelle, C.; Bonilla, S.; Sobrino, J.A. Spatio-temporal evaluation of air pollution using ground-based and satellite data during COVID-19 in Ecuador. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28152. [Google Scholar]
- David, M.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Idrus, S.M.; Azmi, A.I.; Ngajikin, N.H.; En Marcus, T.C.; Yaacob, M.; Salim, M.R.; Aziz, A.A. Progress in ozone sensors performance: A review. J. Teknol. 2015, 73, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Lagouarde, J.P.; Nerry, F.; Ottlé, C. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Techniques and Applications. Therm. Remote Sensing in Land Surface Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 33–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ermida, S.L.; Soares, P.; Mantas, V.; Göttsche, F.-M.; Trigo, I.F. Google Earth Engine Open-Source Code for Land Surface Temperature Estimation from the Landsat Series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loera-Sánchez, J.M.; Ramírez-Aldaba, H.; Meléndez Soto, A.; García-Montiel, E.; González-Laredo, R. Aplicaciones geoestadísticas para la evaluación de la contaminación por ozono en la ciudad de Durango, México. Nova Sci. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Wang, W.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Leung, A.Y. Prediction of maximum daily ozone level using combined neural network and statistical characteristics. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberger, E.H.; Ganor, E. High ozone concentrations at night in Jerusalem and Tel-Aviv. Atmos. Environ. 1980, 14, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón-Domínguez, P.; Jiménez-Hornero, F.; De Rave, E.G. Proposal for estimating ground level ozone concentrations at urban areas based on multivariate statistical methods. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, C.M.; García, C.O. Impacto de la Meteorología en la Concentración de Ozono Troposférico; Universidad Complutense de Madrid: Madrid, Spain. Available online: https://cmougan.github.io/CV/files/tfg.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Cano Baudino, Y.N.; Morales Mariño, J.A.; Sánchez Castillo, L.J.; Colina Rincón, M.N.; Torres Puente, J.C. Evaluación de los niveles de ozono en la Ciudad de Maracaibo, Estado Zulia, Venezuela. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambiental. 2016, 32, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Malley, C.S.; Henze, D.K.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.; Vallack, H.W.; Davila, Y.; Anenberg, S.C.; Turner, M.C.; Ashmore, M.R. Updated global estimates of respiratory mortality in adults ≥30 years of age attributable to long-term ozone exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 087021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, B.J.; Stehr, J.W.; Piety, C.A.; Salawitch, R.J.; Dickerson, R.R. Observed relationships of ozone air pollution with temperature and emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.L.; Nava, M.M.; Muhlia, A. Relaciones entre la magnitud del valor máximo de ozono, la radiación solar y la temperatura ambiente en la Zona Metropolitana de la Ciudad de México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambiental. 2000, 16, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gorai, A.; Biswal, S.; Mitra, G. Effects of meteorology on ground level ozone (GLO) concentrations and identifying the hot spots having significantly higher GLO concentration in a semi-urban area. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 1461–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunthe, S.; Beig, G.; Sahu, L. Study of relationship between daily maxima in ozone and temperature in an urban site in India. Curr. Sci. 2016, 110, 1994–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avino, P.; Manigrasso, M. Ten-year measurements of gaseous pollutants in urban air by an open-path analyzer. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4138–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasaitis, D.; Vasiliauskienė, V.; Chadyšienė, R.; Pečiulienė, M. Surface ozone concentration and its relationship with UV radiation, meteorological parameters and radon on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, M.; Dida, M.R.; Savastru, R.; Savastru, D.; Dida, A.; Ionescu, O. Ground level ozone (O3) associated with radon (222Rn) and particulate matter (PM) concentrations in Bucharest metropolitan area and adverse health effects. J. Radio Anal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 300, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusede, S.; Gentner, D.; Wooldridge, P.; Browne, E.; Rollins, A.; Min, K.-E.; Russell, A.; Thomas, J.; Zhang, L.; Brune, W. On the temperature dependence of organic reactivity, nitrogen oxides, ozone production, and the impact of emission controls in San Joaquin Valley, California. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3373–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.; Lu, Z.; Xing, J.; Streets, D.G.; Tan, Q.; O’Brien, T.; Kamberos, J. Response of the summertime ground-level ozone trend in the Chicago area to emission controls and temperature changes, 2005–2013. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, W.C.; Heald, C.L. The mechanisms and meteorological drivers of the summertime ozone–temperature relationship. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13367–13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlink, U.; Dorling, S.; Pelikan, E.; Nunnari, G.; Cawley, G.; Junninen, H.; Greig, A.; Foxall, R.; Eben, K.; Chatterton, T. A rigorous inter-comparison of ground-level ozone predictions. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, S1352–S2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, S.; Rivero, M. Análisis de la Radiación Solar en Tres Ciudades de Coahuila y Durango. Rev. Cienc. Ing. Y Desarro. Tec Lerdo 2017, 3, 123–126. [Google Scholar]

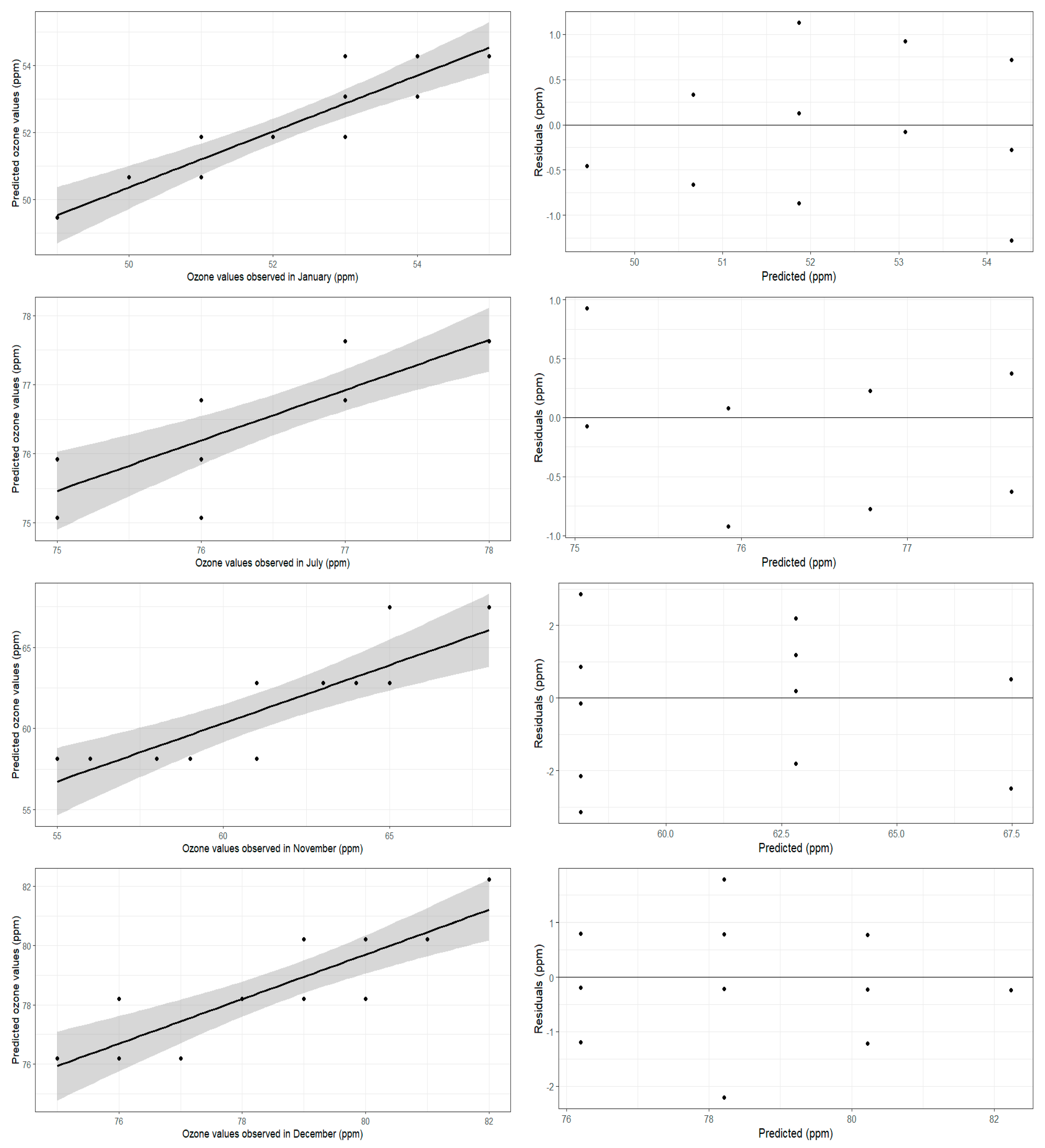
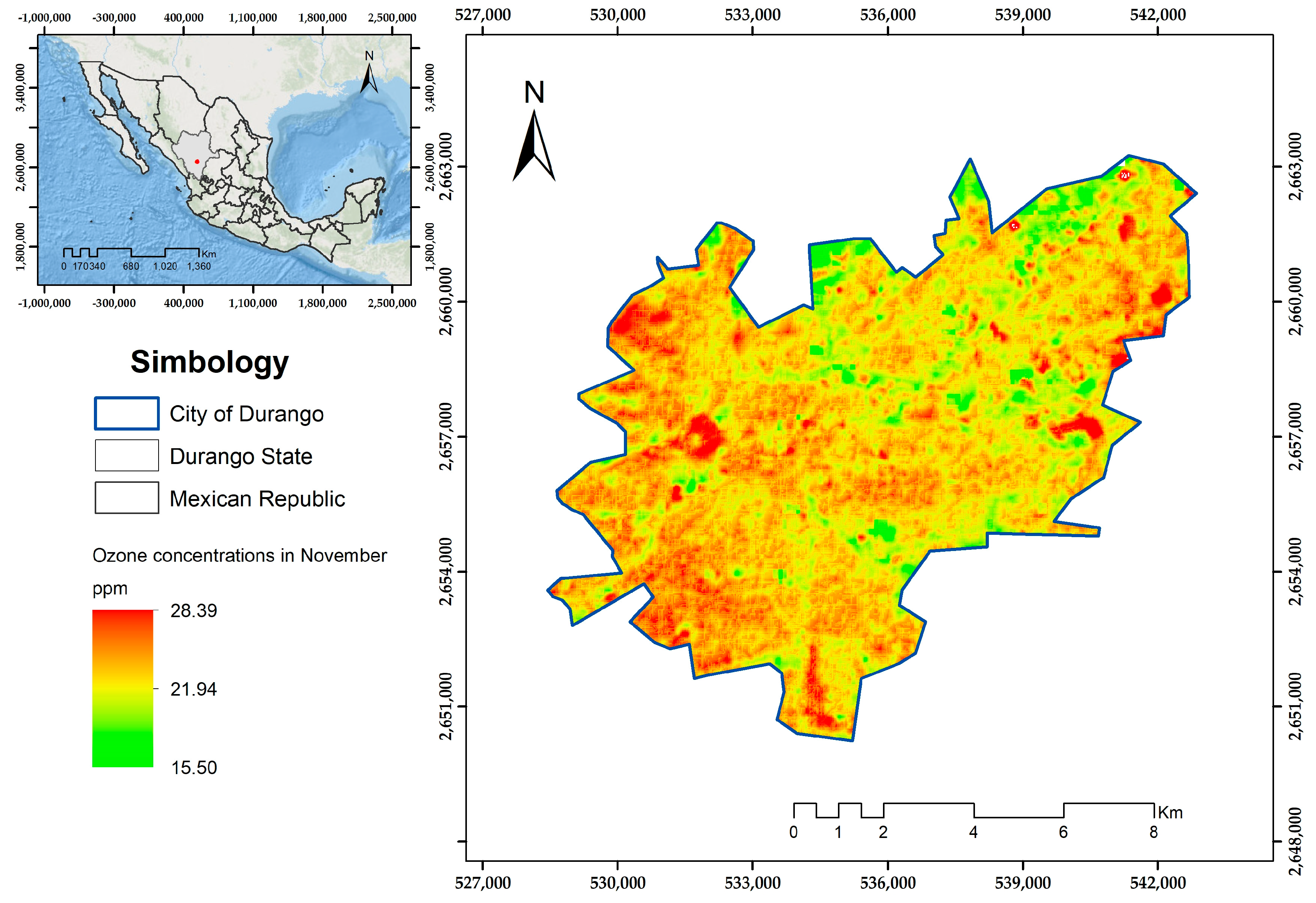
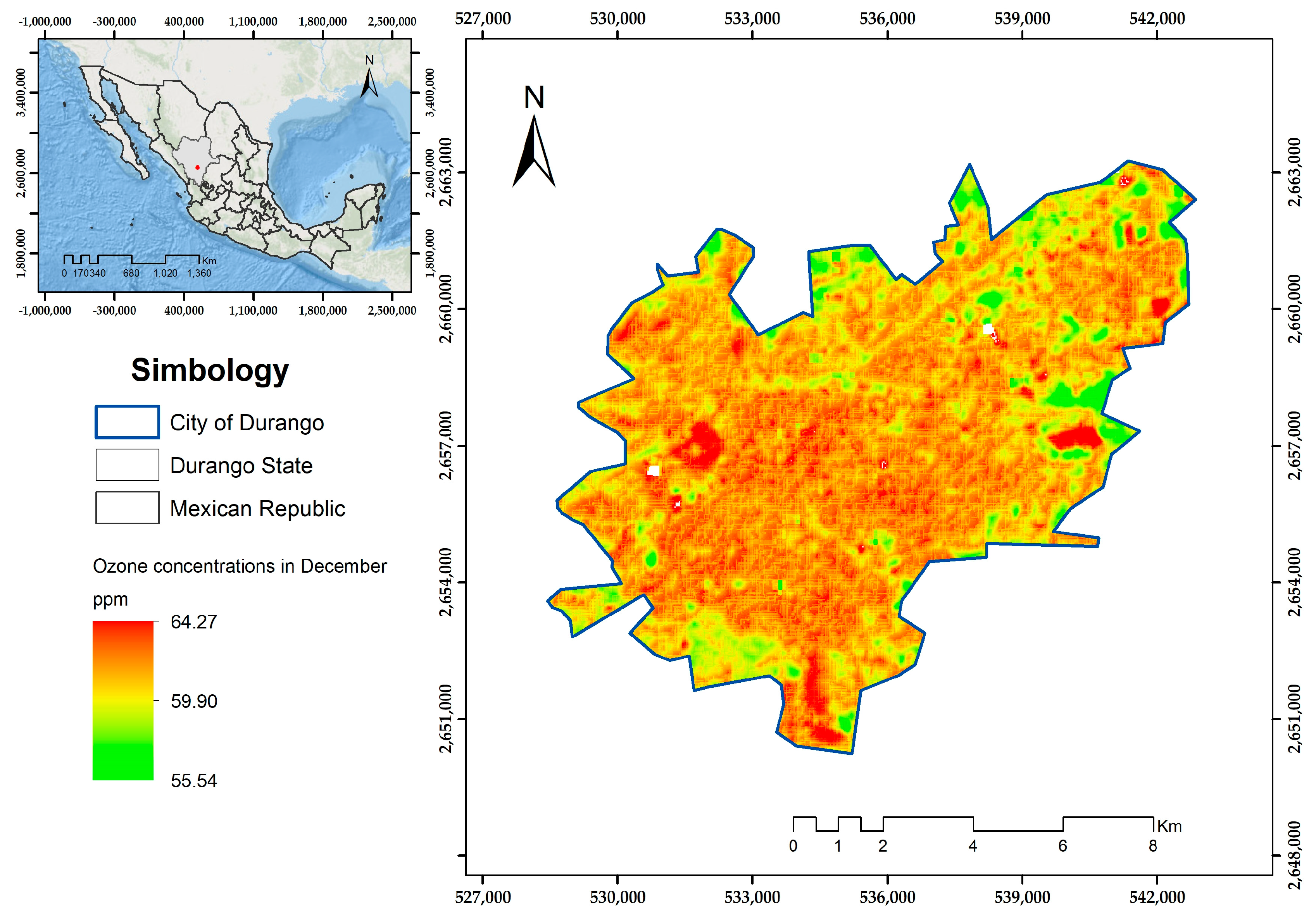
| Month | Model | r | Standard Residual Error | p-Value | R2 | RMSE (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | y = 24.14 + 1.20 (LST) | 0.91 | 0.7099 | 0.0005 | 0.83 | 0.65 |
| February | y = 113.41 − 0.27 (LST) | −0.28 | 0.6111 | 0.3253 | 0.08 | 0.56 |
| March | y = 215.67 − 4.90 (LST) | −0.51 | 7.5021 | 0.0611 | 0.26 | 6.94 |
| April | y = 89.84 + 0.13 (LST) | 0.28 | 0.4681 | 0.3286 | 0.08 | 0.43 |
| May | y = 141.74 − 1.58 (LST) | −0.33 | 3.9141 | 0.2435 | 0.11 | 3.62 |
| June | y = 160.15 − 1.51 (LST) | −0.59 | 1.796 | 0.0246 | 0.35 | 1.66 |
| July | y = 101.47 − 0.85 (LST) | −0.85 | 0.5794 | 0.0001 | 0.73 | 0.53 |
| August | y = 67.10 − 0.13 (LST) | −0.31 | 0.4691 | 0.2754 | 0.09 | 0.43 |
| September | y = 81.05 − 0.18 (LST) | −0.27 | 1.092 | 0.3505 | 0.07 | 1.02 |
| October | y = 61.47 − 0.26 (LST) | −0.36 | 0.5928 | 0.2021 | 0.14 | 0.54 |
| November | y = 160.95 − 4.67 (LST) | −0.85 | 2.276 | 0.0001 | 0.72 | 2.18 |
| December | y = 122.50 − 2.01 (LST) | −0.87 | 1.094 | 0.0005 | 0.75 | 1.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Aldaba, H.; López-Serrano, P.M.; García-Montiel, E.; Morones-Esquivel, M.M.; Bocanegra-Salazar, M.; Borrego-Núñez, C.; Loera-Sánchez, J.M. Prediction of Tropospheric Ozone Levels from Land Surface Temperature in the Urban Area of Durango, Dgo., Mexico. Pollutants 2025, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5010003
Ramírez-Aldaba H, López-Serrano PM, García-Montiel E, Morones-Esquivel MM, Bocanegra-Salazar M, Borrego-Núñez C, Loera-Sánchez JM. Prediction of Tropospheric Ozone Levels from Land Surface Temperature in the Urban Area of Durango, Dgo., Mexico. Pollutants. 2025; 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Aldaba, Hugo, Pablito Marcelo López-Serrano, Emily García-Montiel, Miriam Mirelle Morones-Esquivel, Melissa Bocanegra-Salazar, Carlos Borrego-Núñez, and José Manuel Loera-Sánchez. 2025. "Prediction of Tropospheric Ozone Levels from Land Surface Temperature in the Urban Area of Durango, Dgo., Mexico" Pollutants 5, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5010003
APA StyleRamírez-Aldaba, H., López-Serrano, P. M., García-Montiel, E., Morones-Esquivel, M. M., Bocanegra-Salazar, M., Borrego-Núñez, C., & Loera-Sánchez, J. M. (2025). Prediction of Tropospheric Ozone Levels from Land Surface Temperature in the Urban Area of Durango, Dgo., Mexico. Pollutants, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants5010003








