Exposure to Air Pollution from Road Traffic and Incidence of Respiratory Diseases in the City of Meknes, Morocco
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objectives and Research Hypothesis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Presentation of the Study Area
2.2. Study of the Concentrations of the Pollutant Surveyed
2.2.1. Choice of the Pollutant Studied: Nitrogen Dioxide
2.2.2. Measurement Periods
2.2.3. Sensors Used for Monitoring Nitrogen Dioxide Levels
2.2.4. Determination of Nitrogen Dioxide
2.2.5. Geolocation of NO2 Sampling Sites
2.2.6. Mapping Representation
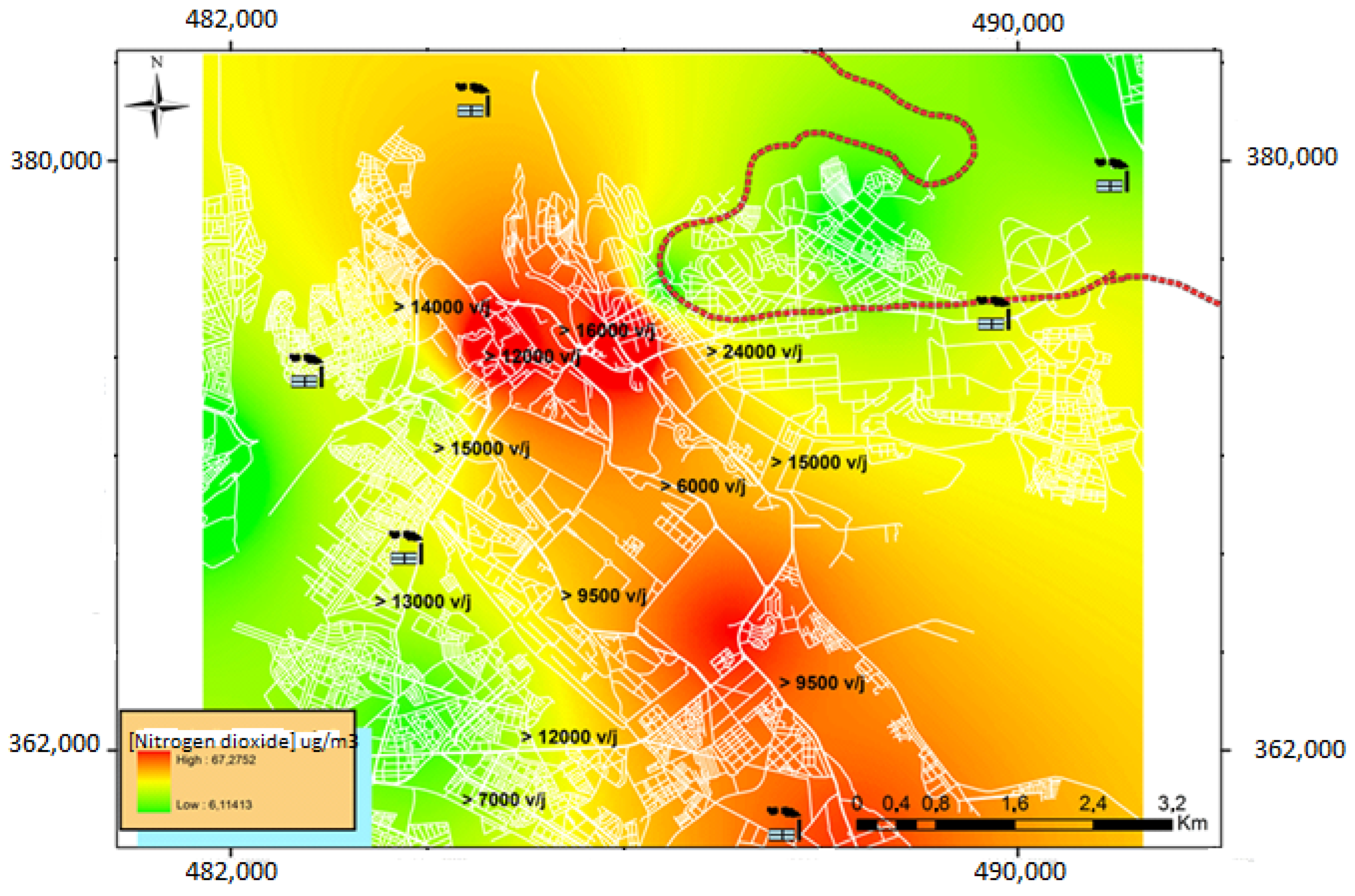
2.3. Comptage du Trafic Routier
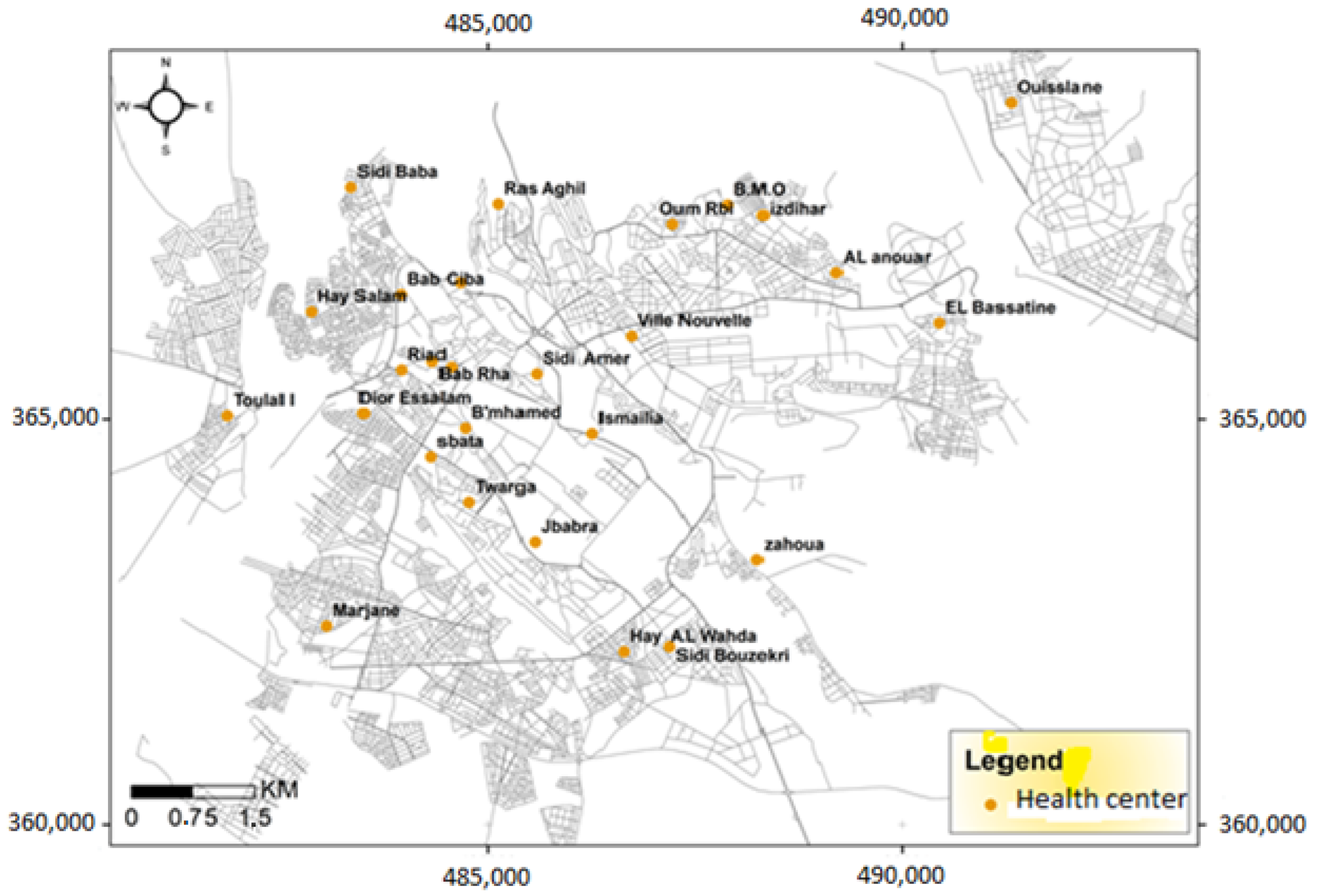
2.4. Study of the Epidemiological Profile of Respiratory Pathologies
3. Results
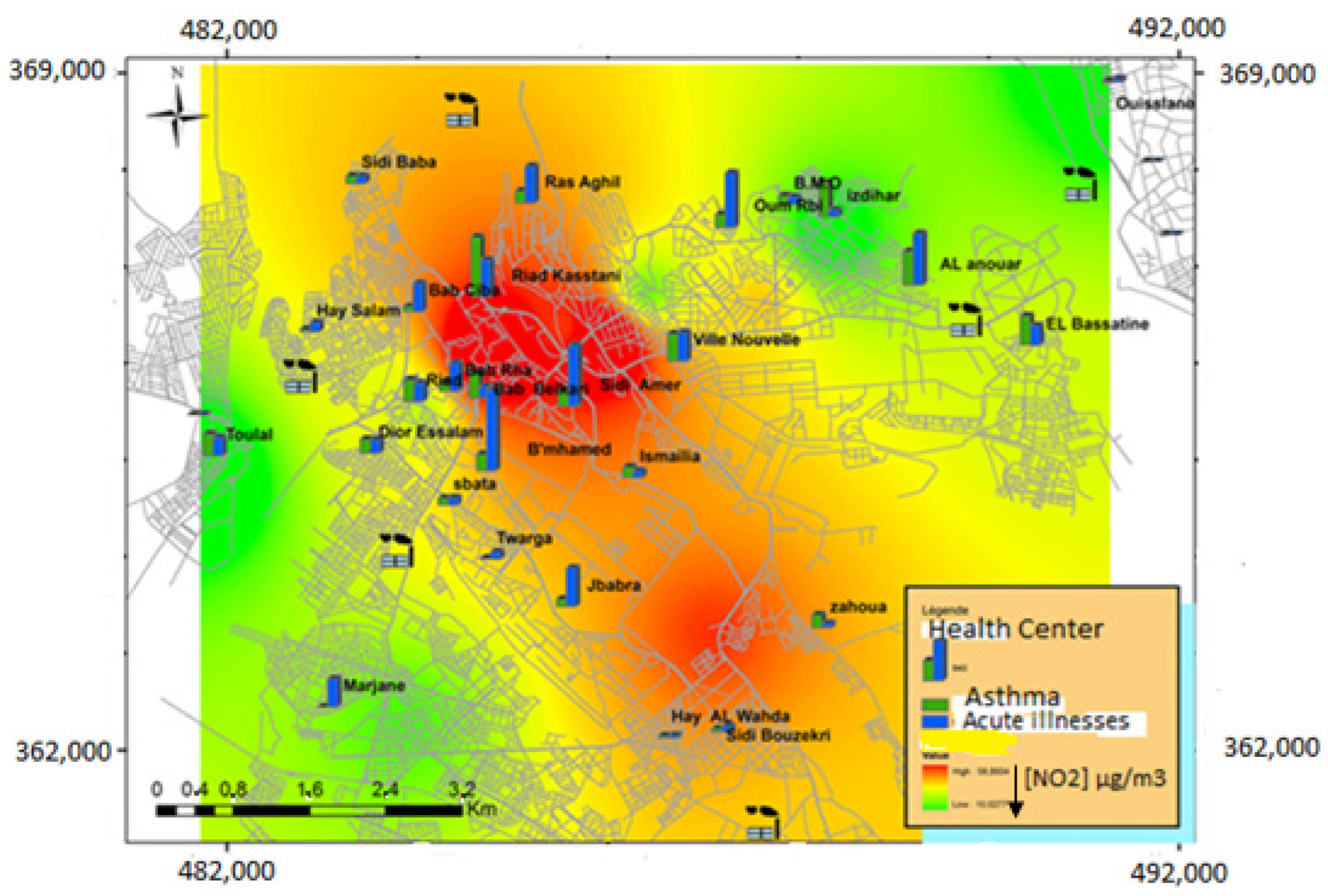
3.1. Study of NO2 Levels
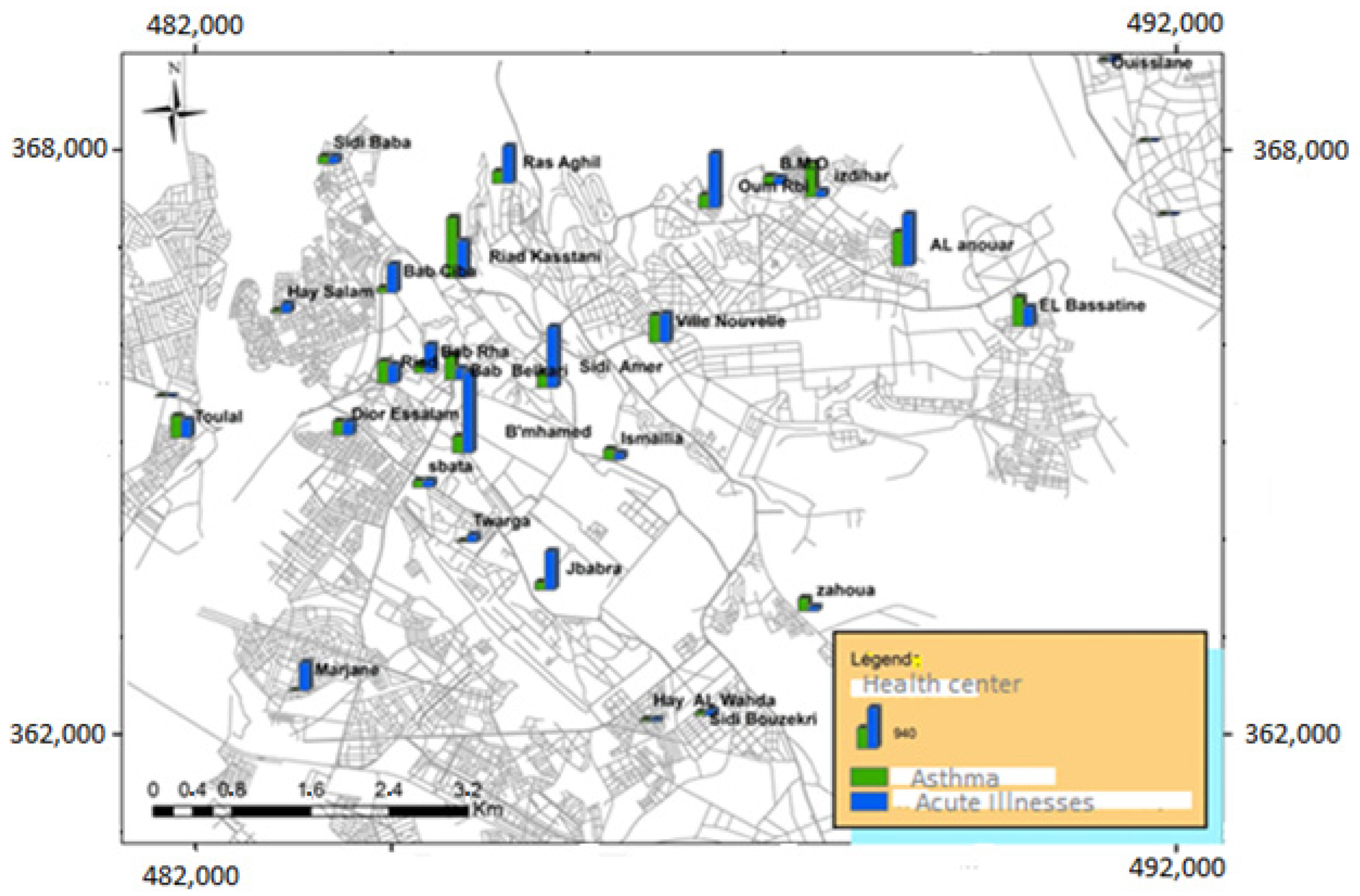
3.2. Study of the Epidemiological Profile of Respiratory Pathologies in Subjects Aged 5 Years and Over
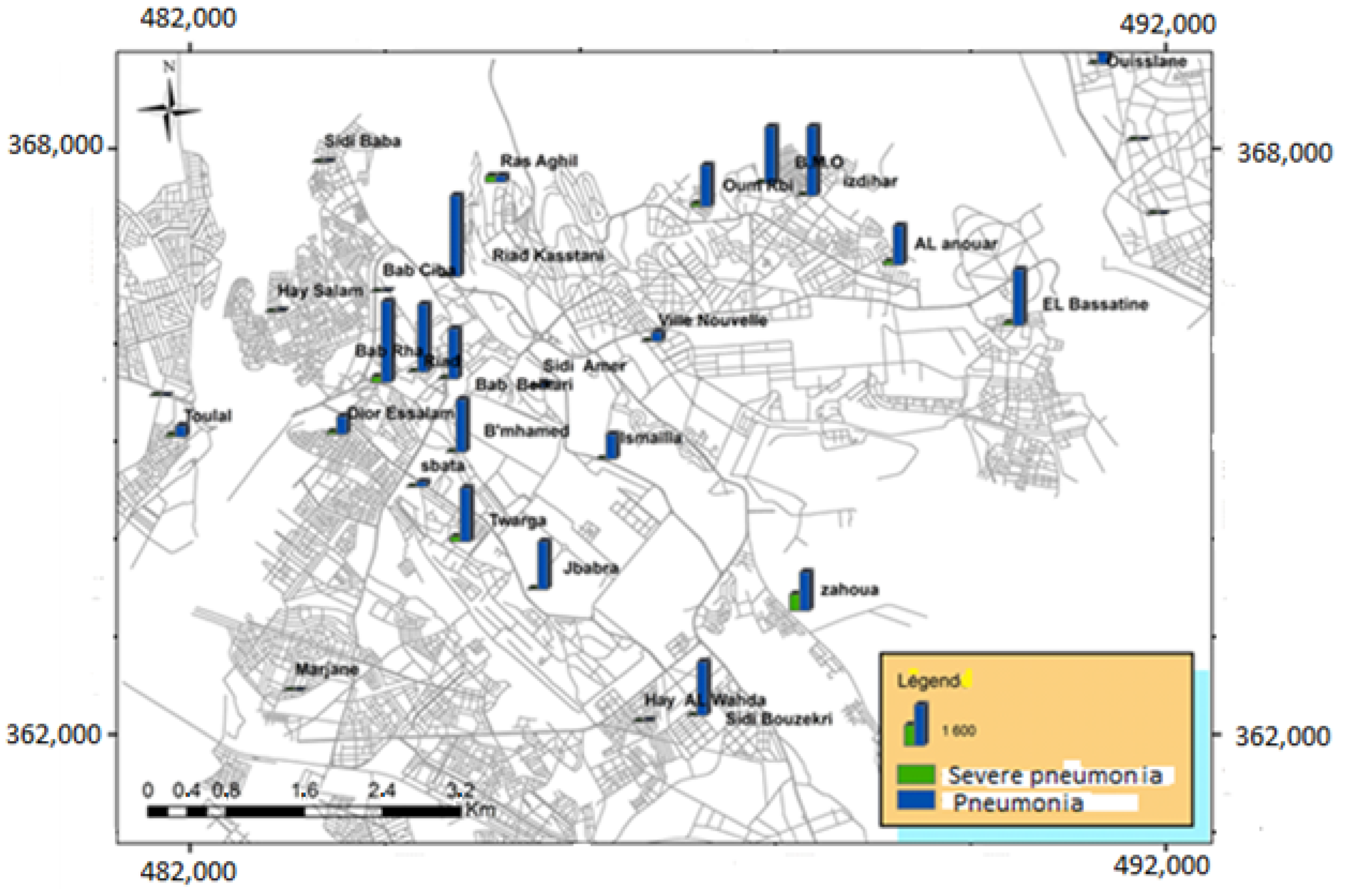
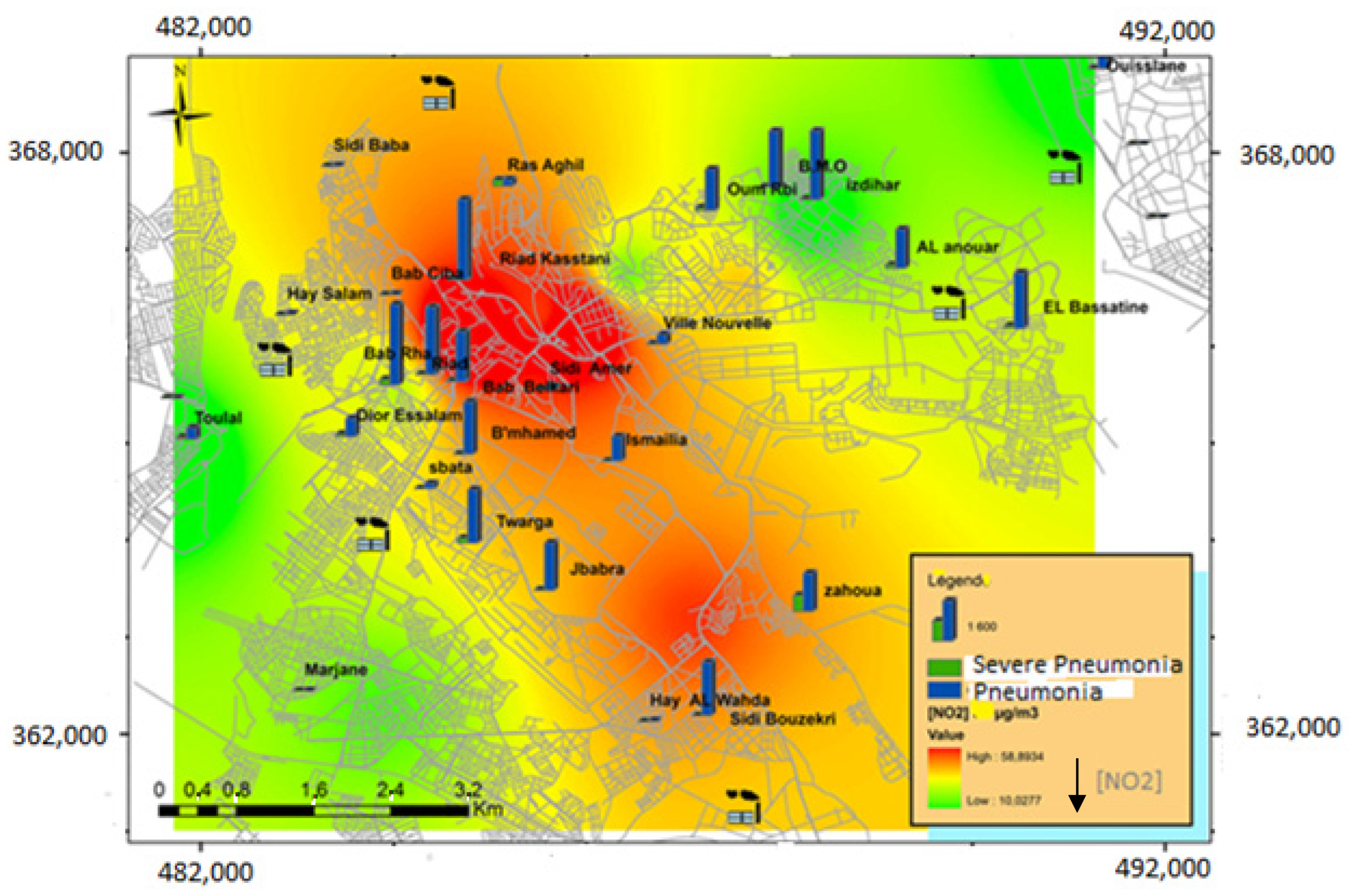
3.3. Study of the Epidemiological Profile of Respiratory Diseases in Children under 5 Years of Age
4. Discussions
| Study Area | [NO2] µg/m3 | Study Period | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kocaeli | 14 | July 2006 | Turkey | [77] |
| Bouni Region | 14.8 * | Average of 7 months of measurement in 2011 | Algeria | [78] |
| Windsor | 23.31 | Average of four 14-day campaigns in February, May, August and October 2004 | Canada | [74] |
| Malaga | 22.8 | September 2001 and from December 2001 to February 2002 | Spain | [64] |
| Pampelune | 23 | From June 2006 to 2007 | Spain | [69] |
| Gothenburg and Mölndal | 23.5 | 7–20 May 2011 | Sweden | [79] |
| Asturies | 23.6 | Average of two 7-day campaigns in June and November 2005 | Spain | [80] |
| Northern Ireland | 24.3 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| Kampala | 24.9 | From 30 June to 13 July, 2014 | Uganda | [82] |
| Kocaeli | 25 | January 2007 | Turkey | [77] |
| Wales | 27.26 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| Scotland | 27.26 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| Bamako | 30.45 | From June 2008 to 2009 | Mali | [53] |
| Meknes | 30.41 | From 14 July to 28 July 2014 and from 25 December 2014 to 12 January 2015 | Morocco | This study |
| Elche | 32 | Average for 2007–2008 | Spain | [83] |
| East Anglia | 34.78 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| South East England | 34.78 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| Edimbourg | 34 | From 2 December 2013 to 13 January 2014 | UK | [73] |
| West Midlands | 35.72 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| Granada | 36.5 | Average of two campaigns: from July to September 1999 and from December 1999 to February 2000 | Spain | [64] |
| Kanpur | 36.9 | February and March 2004 | India | [68] |
| Edimbourg | 37 | From 2 August to 13 September 2013 | UK | [73] |
| East Midlands | 40.42 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| Yourkshire-and-Humber | 42.3 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| London | 42.3 | Annual average for 1997 | UK | [81] |
| Agadir | 44 | From 20 April to 27 April, 2006 | Morocco | [22] |
| Durban | 45.12 | Average of one week in summer 2001 | South Africa | [75] |
| Rawalpindi | 55.74 | Annual average for 2008 | Pakistan | [84] |
| Dakar | 59.9 | From January 2008 to December 2009 | Senegal | [53] |
| Al-ain | 59.3 | From 21 February 2005 to 20 February 2006 | United Arab Emirates | [85] |
| Delhi | 68.6 | February and March 2004 | India | [68] |
| Sfax | Between 37.6 and 112.8 * | Fall 1996, Winter 1997, Spring and Summer 1998 | Tunis | [63] |
| Durban | 110.92 | Average of one week in winter of 2001 | South Africa | [75] |
5. Conclusions
- -
- The replacement of fossil fuel vehicles by electric and hybrid cars;
- -
- The creation of low emission zones;
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OMS. Neuf Personnes sur 10 Respirent un Air Pollué dans le Monde; Communiqué de Presse de l’Organisation Mondiale de la Santé: Geneve, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A., III; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsett, M.J.; Ostro, B.D.; Reynolds, P.; Goldberg, D.; Hertz, A.; Jerrett, M.; Smith, D.F.; Garcia, C.; Chang, E.T.; Bernstein, L. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Cardiorespiratory Disease in the California Teachers Study Cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Langrish, J.P.; Nair, H.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.L.; Donaldson, K.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Global association of air pollution and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G.D.; Burnett, R.T.; Turner, M.C.; Shi, Y.; Krewski, D.; Lall, R.; Ito, K.; Jerrett, M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; et al. Ischemic heart disease mortality and long-term exposure to source-related components of U.S. fine particle air pollution. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Tsai, S.-S.; Chiu, H.-F.; Wu, T.-N.; Chen, C.-C.; Yang, C.-Y. Ambient Exposure to Criteria Air Pollutants and Risk of Death from Bladder Cancer in Taiwan. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.C.; Jerrett, M.; Pope, C.A., III; Krewski, D.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; Beckerman, B.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Su, J.; Crouse, D.L.; et al. Long-term ozone exposure and mortality in a large prospective study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAmoudi, O. Prevalence of respiratory diseases in hospitalized patients in Saudi Arabia: A 5 years study 1996–2000. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2006, 1, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, T.; Afzal, A.; Sultana, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.; Shahid, T.; Jabeen, Z.; Turab, N.; Ahmed, Z.; Mahboob, S. Epidemiological estimates of respiratory diseases in the hospital population, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2017, 60, e17160358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Observatoire National de l’Environnement et du Développement Durable du Maroc (ONEED). 3 éme Rapport sur l’état de L’environnement du Maroc. Rapport: Ministère Délégué Auprès du Ministère de l’énergie des Mines, de l’eau et de L’environnement du Royaume du Maroc. 2015. Available online: http://www.environnement.gov.ma/fr/etat-de-l-environnement/119-etatenv/3438-rapport-sur-l-etat-de-l-environnement-au-maroc-reem (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Croitoru, L.; Sarraf, M. Le Coût de la Dégradation de l’Environnement au Maroc; 105633-MA; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation Mondiale de la Santé (OMS). Pneumonie; Aide-mémoire n 331, l’Organisation Mondiale de la Santé: Geneve, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ouarzazi, J.; Terhzaz, M.; Abdellaoui, A.; Bouhafid, A.; Nollet, V.; Dechaux, J.C. Etude descriptive de la mesure de polluants atmosphériques dans l’agglomération de Marrakech. Rev. Pollut. Atmos. 2003, 177, 2268–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoukhi, T.; Cherkaoui, R.; Gaudry, A.; Ayrault, S.; Senhou, A.; Chouak, A.; Moutia, Z.; Chakir, E.M. Air pollution biomonitoring survey in Morocco using k0-INAA. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2004, 213, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounakhla, M.; Fatah, A.; Embarch, K.; Majah, M.I.; Azami, R.; Sabir, A.; Nejjar, A.; Cherkaoui, R.; Gaudry, A. Air pollution Assessment of Salé’s city (Morocco). J. De Phys. IV Fr. 2003, 107, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Bouh, H. Application des Techniques d’Analyses Physico-Chimiques aux Questions Environnementales: Évaluation et Suivi de la Qualité de l’Air dans la Ville de Meknès. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculté des Sciences, Université Moulay Ismail, Meknes, Morocco, 2012; 230p. [Google Scholar]
- Monna, F.; Bouchaou, L.; Rambeau, C.; Losno, R.; Bruguier, O.; Dongarrà, G.; Black, S.; Chateau, C. Lichens used as monitors of atmospheric pollution around Agadir (Southwestern Morocco)—A case study predating lead-free gasoline. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahri, M.; Bounakhla, M.; Zghaïd, M.; Noack, Y.; Benyaïch, F.; Benchrif, A. Evaluation of airborne particulate matter pollution in Kenitra City, Morocco. Rev. Ambiente Água Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 8, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami, F.Z.O.; Elabidi, A.; Mouhir, L.; Fekhaoui, M. Utilisation des lichens comme bio-indicateurs de la pollution atmosphérique par le plomb, cadmium et zinc de la région de Rabat-Sale-Zemmour-Zaêr (Maroc). Afr. Sci. 2014, 10, 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- El Rhzaoui, G.; Divakar, P.K.; Crespo, A.; Tahiri, H. Biomonitoring of air pollutants by using lichens (Evernia prunastri) in areas between Kenitra and Mohammedia cities in Morocco. Lazaroa 2015, 36, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouddane, N.; Mouhir, L.; Fekhaoui, M.; Elabidi, A.; Benaakame, R. Monitoring air pollution at Mohammedia (Morocco): Pb, Cd and Zn in the blood of pigeons (Columba livia). Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirmata, A.; Leghrib, R.; Ichou, I.A. Implementation of the Air Quality Monitoring Network at Agadir City in Morocco. J. Environ. Prot. 2017, 8, 540–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Inchaouh, M.; Tahiri, M. Air pollution due to road transportation in Morocco: Evolution and impacts. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Technol. (JMEST) 2017, 4, 7547–7552. [Google Scholar]
- Ministère de l’Aménagement du Territoire; de l’Eau et de l’Environnement/Ministère de la Santé (MATEE/MS). Etude Casa Airpol: Evaluation de l’Impact de la Pollution Atmosphérique sur la Santé des Populations des Populations dans le Grand Casablanca, Résumé des Résultats. 2000. Available online: https://www.environnement.gov.ma/fr/partenariat-cooperation/partenariat/universites/94-preventions-des-risques/impact-sanitaire-de-la-pollution (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Ministère de l’Aménagement du Territoire, de l’Eau et de l’Environnement/Ministère de la Santé (MATEE/MS). Etude Mohammedia Airpol: Evaluation de l’Impact de la Pollution Atmosphérique sur la Santé des Enfants Asthmatiques de Mohammedia, Résumé des Résultats. 2003. Available online: http://www.environnement.gov.ma/fr/partenariat-cooperation/94-preventions-des-risques/impact-sanitaire-de-la-pollution/186-moham-airpol (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Ouhakki, H. Étude de la Pollution de l’Air de la Ville de Meknès par les Poussières: Cas des Poussières de la Cimenterie LAFARGE-Ciment Meknès. Master’s Thesis, Université Moulay Ismail, Meknes, Morocco, 2009; 130p. [Google Scholar]
- Ait Bouh, H.; Benyaich, F.; Bounakhla, M.; Noack, Y.; Tahri, M.; Zahry, F. Variations Saisonnières des particules atmosphériques et ses composants chimiques dans la Ville de Meknès–Maroc. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ait Bouh, H.; Benyaich, F.; Bounakhla, M.; Noack, Y.; Zahry, F.; Tahri, M. Introduction à la pollution atmospherique dans la ville de Meknès: Dioxyde de soufre, ozone et matière particulaire en suspension. Les Technol. Lab. 2014, 8, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Abdouh, M.; El Harouni, A.; Mechkouri, A. Le Secteur de L’habitat dans la Région Meknès-Tafilalet: Performances et limites; avec le concours du ministère de l’Habitat et de l’Urbanisme; Faculté des Lettres et Sciences Humaines de Meknès: Meknes, Morocco, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ministère d’Equipement, de Transport et de la Logistique (METL). Transport Routier en Chiffres (2006–2014). Ministère d’Equipement, de Transport et de la Logistique du Royaume du Maroc. 2015. Available online: http://www.equipement.gov.ma/chiffrescles/Routier/Pages/Transport-routier-en-chiffres.aspx (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Abdouh, M.; El Atrouz, A.; Mechkouri, A. Profil Environnemental de Meknès, Agenda 21 Locaux Pour la Promotion de l’Environnement et du Développement Durable en Milieu Urbain; Ministère de l’Aménagement du Territoire, de l’Eau et de l’Environnement: Rabat, Morocco, 2004; 94p. [Google Scholar]
- El Ghazi, I. L’utilisation du SIG Pour l’Analyse de la Relation Entre la Pollution Atmosphérique et l’Incidence de Certaines Maladies Respiratoires et Cardiovasculaires au Niveau de la Ville de Meknès. Master’s Thesis, Université Moulay Ismail-Meknès, Meknes, Morocco, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Belhassan, M. Les Bioindicateurs Végétaux de la Pollution de l’Air au Niveau de la Ville de Meknès. Master’s Thesis, Université Moulay Ismail-Meknès, Meknes, Morocco, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vallet, J.; Kamel, S.; Bromblet, P.; Meunier, J.; Mahjoubi, R.; Ajakane, R.; Bouabib, R.; Noack, Y.; Borschnek, D. Study of the historical buildings of Meknès (Morocco) and their alterations–Proposal of various tools for their conservation. In Proceedings of the 7th European Commission Conference “SAUVEUR”, Prague, Czech Republic, 31 May–3 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1090–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Ministère de l’Habitat et de la Politique de la Ville (MHPV). Etude du Schéma Régional d’Aménagement du Territoire (SRAT) de la Région Meknès-Tafilalt. Inspection Régionale de l’Habitat, de l’Urbanisme et de la Politique de la Ville, Meknès-Tafilalt. 2012. Available online: http://www.region-fes-meknes.ma/fr/administration-regionale/etudes/schema-regional-damenagement-du-territoire/ (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Ministère de l’Intérieur. Monographie de la Région Fès-Meknès. Direction Générale des Collectivités Locales, Ministère de l’Intérieur du Royaume du Maroc. 2015. Available online: http://www.equipement.gov.ma/Carte-Region/RegionFes/Presentation-de-la-region/Monographie/Pages/Monographie-de-la-region.aspx (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Haut-Commissariat au Plan (HCP). Recensement Général de la Population et de l’Habitat 2014. Direction Régionale de Meknès-Tafilalt. 2015. Available online: www.hcp.ma (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Driouech, F. Distribution des Précipitations Hivernales sur le Maroc dans le Cadre d’un Changement Climatique: Descente d’Échelle et Incertitude. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Toulouse, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Pelizzetti, E.; Harrison, M.A.J.; Olariu, R.-I.; Arsene, C. Photochemical reactions in the tropospheric aqueous phase and on particulate matter. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, Z.S.; Russo, M.R.; Butler, T.M.; Archibald, A.T.; Lawrence, M.G.; Telford, P.J.; Abraham, N.L.; Pyle, J.A. Modelling the impact of megacities on local, regional and global tropospheric ozone and the deposition of nitrogen species. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12215–12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M.; Della Massa, J.-P.; Simon, V.; Grasset, E.; Toress, L. Etude de la Distribution Atmosphérique de Composés Organiques Volatils Aromatiques: Benzène, Toluène, Xylènes (BTX) et du Dioxyde d’Azote sur l’Agglomération Toulousaine. Pollut. Atmos. Clim. St. Société 2000, 168, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akdemir, A. The creation of pollution mapping and measurement of ambient concentration of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide with passive sampler. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation Mondiale de la Santé (OMS). Health Effects of Transport-Related Air Pollution; World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Health Effects Institute (HEI). Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure, and Health Effects; HEI Special Report 17; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Saeger, E.; Gerbolès, M.; Payrissat, M. La surveillance du Dioxyde d’azote à Madrid au Moyen D’échantillonneurs Passifs. Evaluation Critique de la Conception du Réseau; Rapport de la Commission Européenne, Institut de l’Environnement EUR 14175: Brussels, Belgium, 1991; 60p. [Google Scholar]
- Fouque, S.G.; Plaisance, H.; Houdret, J.-L.; Mathé, F.; Galloo, J.-C.; Guillermo, R. Improvements of passive sampling techniques for the measurements of ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide in ambient air. In Proceedings of the Conférence Internationale de Venise Air quality in Europe: Challenges for the 2000s, Venice, Italy, 21 May 1999; 19–21 Mai. Session Monitoring techniques and standardization, Poster Sampling and Analysis 1999b. [Google Scholar]
- Deletraz, G. Géographie des Risques Environnementaux Liés aux Transports Routiers en Montagne: Incidences des Émissions d’Oxydes d’Azote en Vallée d’Aspe et de Biriatou (Pyrénées). Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Pau et des Pays de l’Adour, Pau, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, G.; Keywood, M.; Gillett, R.; Manins, P.; Malfroy, H.; Bardsley, T. Validation of passive diffusion samplers for SO2 and NO2. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 3587–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasius, M.; Carlsen, M.F.; Hansen, T.S.; Lohse, C. Measurements of nitrogen dioxide on Funen using diffusion tubes. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.H. Monitoring the ambient environment with diffusive samplers: Theory and practical considerations. J. Environ. Monit. 2000, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, K.; Safavi, A.; Tahon, R. Air Pollution Assessment in Shiraz by Passive Sampling Techniques. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 2005, 29, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Dhammapala, R.; Lachmann, G.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Pienaar, J. Long-term measurements of sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, ammonia, nitric acid and ozone in southern Africa using passive samplers. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2007, 103, 336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Adon, M.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Yoboué, V.; Delon, C.; Lacaux, J.P.; Castera, P.; Gardrat, E.; Pienaar, J.; Al Ourabi, H.; Laouali, D.; et al. Long term measurements of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, ammonia, nitric acid and ozone in Africa using passive samplers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7467–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmes, E.D.; Gunnison, A.F.; Dimattio, J.; Tomczyk, C. Personal sampler for nitrogen dioxide. Am. Ind. Hyg. Ind. J. 1976, 37, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafkenscheid, T.; Fromage-Mariette, A.; Goelen, E.; Hangartner, M.; Pfeffer, U.; Plaisance, H.; de Santis, F.; Saunders, K.; Swaans, W.; Tang, Y.S.; et al. Review of the Application of Diffusive Samplers in the European Union for the Monitoring of Nitrogen Dioxide in Ambient Air; JRC Scientific and Technical Reports; European Commission: Luxembourg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pienaar, J.; Beukes, J.P.; Van Zyl, P.G.; Lehmann, C.; Aherne, J. Chapter 2-Passive Diffusion Sampling Devices for Monitoring Ambient Air Concentrations. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Forbes, P.B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 70, pp. 13–52. [Google Scholar]
- NBN EN 16339; Ambient air-Method for the Determination of the Concentration of Nitrogen Dioxide by Diffusive Sampling. European standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- Boularab, I. Pollution Atmosphérique Due au Dioxyde d’Azote: Mise au Point d’un Indicateur Composite Pour la Ville de Meknès. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Moulay Ismail, Faculté des Sciences de Meknès, Meknes, Morocco, 2018; 224p. [Google Scholar]
- Puddu, M.; Bayingana, K.; Tafforeau, J. L’Asthme et la Pollution de l’Air: Etat des Connaissances et Données Disponibles Pour le Développement d’une Politique de Santé en Belgique; IPH/EPI Reports Nr. 2003–012, N° de dépôt: D/2003/2505/23; Institut Scientifique de la Santé Publique: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Just, A.; Nikasinovic, L.; Laoudi, Y.; Grimfeld, A. Pollution de l’air et asthme de l’enfant. Rev. Française D’Allergol. D’Immunol. Clin. 2007, 47, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurinavičienė, D.; Dėdelė, A. Measurement of nitrogen dioxide concentration in cold and warm seasons using a passive sampling method. Biologija 2014, 59, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Monographie Régionale de l’Environnement, Région Meknès Tafilalet. 2001; 64p, Available online: https://www.hcp.ma/downloads/Monographies-regionales_t11957.html (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Azri, C.; Tlijani, A.; Abida, H.; Maalej, A.; Medhioub, K. Seasonal evolutions of ozone (O3) and its nitrogen precursors (NO, NO2) in urban Sfax (Tunisia). Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 35, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.; Usero, J.; Vanderlinden, E.; Raez, J.; Contreras, J.; Navarrete, B. Air quality monitoring network design to control nitrogen dioxide and ozone, applied in Malaga, Spain. Microchem. J. 2009, 93, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, T.; Ross, Z.; Kheirbek, I.; Eisl, H.; Johnson, S.; Gorczynski, J.; Kass, D.; Markowitz, S.; Pezeshki, G.; Clougherty, J. Monitoring intraurban spatial patterns of multiple combustion air pollutants in New York City: Design and implementation. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerrett, M.; Arain, A.; Kanaroglou, P.; Beckerman, B.; Potoglou, D.; Sahsuvaroglu, T.; Morrison, J.; Giovis, C. A review and evaluation of intraurban air pollution exposure models. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2004, 15, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, L.; Frey, R.; Benter, T. Simultaneous measurement of nitric oxide (NO) and Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) in simulated automobile exhaust using medium pressure ionization-mass spectrometry. Appl. Spectrosc. 2006, 60, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Mishra, P.; Nayak, P.; Damez-Fontaine, B.; Tahon, R. Passive measurement of NO2 and application of GIS to generate spatially-distributed air monitoring network in urban environment. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, M.; Elustondo, D.; Bermejo, R.; Santamaría, J. Ambient air levels of volatile organic compounds (VOC) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in a medium size city in Northern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Mukerjee, S.; Gonzales, M.; Stallings, C.; Neas, L.; Norris, G.; Özkaynak, H. Use of GIS and ancillary variables to predict volatile organic compound and nitrogen dioxide levels at unmonitored locations. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3773–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defra. Review of Transboundary Air Pollution (RoTAP): Acidification, Eutrophication, Ground Level Ozone and Heavy Metals in the UK; Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Midlothian, UK, 2012.
- Niepsch, D.; Clarke, L.J.; Tzoulas, K.; Cavan, G. Spatiotemporal variability of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) pollution in Manchester (UK) city centre (2017–2018) using a fine spatial scale single-NOx diffusion tube network. Env. Geochem. Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Feng, X.; Heal, M.R. Temporal persistence of intra-urban spatial contrasts in ambient NO2, O3 and Ox in Edinburgh, UK. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.J.; Smith-Doiron, M.; Xu, X.; Gilbert, N.L.; Brook, J.R. Intra-urban variability of air pollution in Windsor, Ontario—Measurement and modeling for human exposure assessment. Environ. Res. 2008, 106, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, K.G.; Singh, S.; Govender, S. Passive monitoring of nitrogen dioxide in urban air: A case study of Durban metropolis, South Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2145–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewné, M.; Cyrys, J.; Meliefste, K.; Hoek, G.; Brauer, M.; Fischer, P.; Gehring, U.; Heinrich, J.; Brunekreef, B.; Bellander, T. Spatial variation in nitrogen dioxide in three European areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 332, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekey, B.; Ozaslan, U. Spatial Distribution of SO2, NO2, and O3 Concentrations in an Industrial City of Turkey Using a Passive Sampling Method. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, D.; Laifa, A.; Djamai, R.; Kholladi, M. Metrological data of some air pollutants in a town in north-eastern Algeria for use in epidemiological studies: Case of respiratory. Phys. Chem. News 2011, 57, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Habermann, M.; Billger, M.; Haeger-Eugensson, M. Land use Regression as Method to Model Air Pollution. Previous Results for Gothenburg/Sweden. Procedia Eng. 2015, 115, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Somoano, A.; Tardon, A. Socioeconomic status and exposure to outdoor NO2 and benzene in the Asturias INMA birth cohort, Spain. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2014, 68, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, K.; Bush, T.; Mooney, D. Five years of nitrogen dioxide measurement with diffusion tube samplers at over 1000 sites in the UK. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirenga, B.J.; Meng, Q.; Van Gemert, F.; Aanyu-Tukamuhebwa, H.; Chavannes, N.; Katamba, A.; Obai, G.; Van Der Molen, T.; Schwander, S.; Mohsenin, V. The State of Ambient Air Quality in Two Ugandan Cities: A Pilot Cross-Sectional Spatial Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8075–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, S.; Esclapez, R.; Galindo, N.; Mantilla, E.; Crespo, J. Use of a passive sampling network for the determination of urban NO2 spatiotemporal variations. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.S.; Biiker, P.; Emberson, L.; Shabbir, R. Monitoring Nitrogen Dioxide Levels in Urban Areas in Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 220, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.A.; Soliman, A.A.; El-Haty, I.A. Determination of nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, ozone, and ammonia in ambient air using the passive sampling method associated with ion chromatographic and potentiometric analyses. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2009, 2, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Nitrogen Dioxide–Health Criteria; Office of Research and Development, United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Declercq, C.; Pascal, M.; Chanel, O.; Corso, M.; Ung, A.; Pascal, L.; Blanchard, M.; Larrieu, S.; Medina, S. Impact Sanitaire de la Pollution Atmosphérique dans Neuf Villes Françaises. Résultats du Projet Aphekom; Institut de veille sanitaire: Saint-Maurice, France, 2012; 33p. [Google Scholar]
- Tétreault, L.-F. Asthme Infantile et Polluants du Trafic Routier. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Montréal, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2016; 268p. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M.S.; Powell, K.E.; Hutwagner, L.; Graham, L.M.; Teague, W.G. Impact of Changes in Transportation and Commuting Behaviors During the 1996 Summer Olympic Games in Atlanta on Air Quality and Childhood Asthma. JAMA 2001, 285, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, A.; Stroh, E.; Montnémery, P.; Nihlén, U.; Jakobsson, K.; Axmon, A. Traffic-related air pollution associated with prevalence of asthma and COPD/chronic bronchitis. A cross-sectional study in Southern Sweden. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2009, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.-Y.; Wilhelm, M.; Rull, R.; English, P.; Ritz, B. Traffic and outdoor air pollution levels near residences and poorly controlled asthma in adults. Ann. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2007, 98, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, J.I.; Lanki, T.; Yli-Tuomi, T.; Kulmala, M.; Tiittanen, P.; Pekkanen, J. Urban air pollution, and asthma and COPD hospital emergency room visits. Thorax 2008, 63, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.H.; Edgerton, E.S.; Wyzga, R.; Tolsma, D. A two-time-period comparison of the effects of ambient air pollution on outpatient visits for acute respiratory illnesses. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grineski, S.; Staniswalis, J.; Bulathsinhala, P.; Peng, Y.; Gill, T. Hospital admissions for asthma and acute bronchitis in El Paso, Texas: Do age, sex, and insurance status modify the effects of dust and low wind events? Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustini, A.; Stafoggia, M.; Colais, P.; Berti, G.; Bisanti, L.; Cadum, E.; Cernigliaro, A.; Mallone, S.; Scarnato, C.; Forastiere, F. Air pollution and multiple acute respiratory outcomes. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burra, T.A.; Moineddin, R.; Agha, M.M.; Glazier, R.H. Social disadvantage, air pollution, and asthma physician visits in Toronto, Canada. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Giner, F.; Kunzli, N.; Jacquemin, B.; Forsberg, B.; de Cid, R.; Sunyer, J.; Jarvis, D.; Briggs, D.; Vienneau, D.; Norback, D.; et al. Traffic-related air pollution, oxidative stress genes, and asthma (ECHRS). Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 117, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, B.; Sunyer, J.; Forsberg, B.; Aguilera, I.; Briggs, D.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Gotschi, T.; Heinrich, J.; Järvholm, B.; Jarvis, D.; et al. Home outdoor NO2 and new onset of self-reported asthma in adults. Epidemiology 2009, 20, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modig, L.; Toren, K.; Janson, C.; Jarvholm, B.; Forsberg, B. Vehicle exhaust outside the home and onset of asthma among adults. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzieva, O.; Bergström, A.; Hulchiy, O.; Kull, I.; Lind, T.; Melén, E.; Moskalenko, V.; Pershagen, G.; Bellander, T. Exposure to Air Pollution from Traffic and Childhood Asthma Until 12 Years of Age. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, T.; Shen, S.; Atenafu, E.; Guan, J.; McLimont, S.; Stocks, B.; Licskai, C. The Air Quality Health Index and Asthma Morbidity: A Population-Based Study. Environ. Healh Perspect. 2013, 121, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation Mondiale de la Santé (OMS). Classification et Traitement des Cas de Pneumonie Chez l’Enfant dans les Établissements de Santé Selon l’OMS; 2014; Available online: https://www.who.int/fr/publications-detail/9789241507813 (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Neupane, B.; Jerrett, M.; Burnett, R.; Marrie, T.; Arain, A.; Loeb, M. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and risk of hospitalization with community-acquired pneumonia in older adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.T. Creature comforts—living with mites and moulds. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, T.; Hering, M.; Bürkner, K.; Hirsch, D.; Leupold, W.; Kerkmann, M.-L.; Kuhlisch, E.; Jatzwauk, L. House-dust-mite allergen concentrations (Der f 1) and mold spores in apartment bedrooms before and after installation of insulated windows and central heating systems. Allergy 2000, 55, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OMS. La Pollution de l’Air à l’Intérieur des Habitations et la Santé. Aide-Mémoire N° 292. 2005. Available online: https://www.who.int/fr/news-room/household-air-pollution-and-health (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Wheeler, B.W.; Ben-Shlomo, Y. Environmental equity, air quality, socioeconomic status, and respiratory health: A linkage analysis of routine data from the Health Survey for England. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2005, 59, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, S.; Dales, R.E.; Judek, S. Respiratory Health Effects of Air Pollution Gases: Modification by Education and Income. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2006, 61, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoorter, S.; Niklaus, D.; Rafenberg, C. Rapport de la Commission des comptes et de l’Économie de l’Environnement Santé et Qualité de l’Air Extérieur. Commissariat Général au Développement Durable. 2012; 102p, Available online: http://temis.documentation.developpement-durable.gouv.fr/document.html?id=Temis-0076467 (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M.; Tasco, C.; Picciotto, S.; Agabiti, N.; Cesaroni, G.; Perucci, C. Socioeconomic status, particulate air pollution, and daily mortality: Differential exposure or differential susceptibility. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2007, 50, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

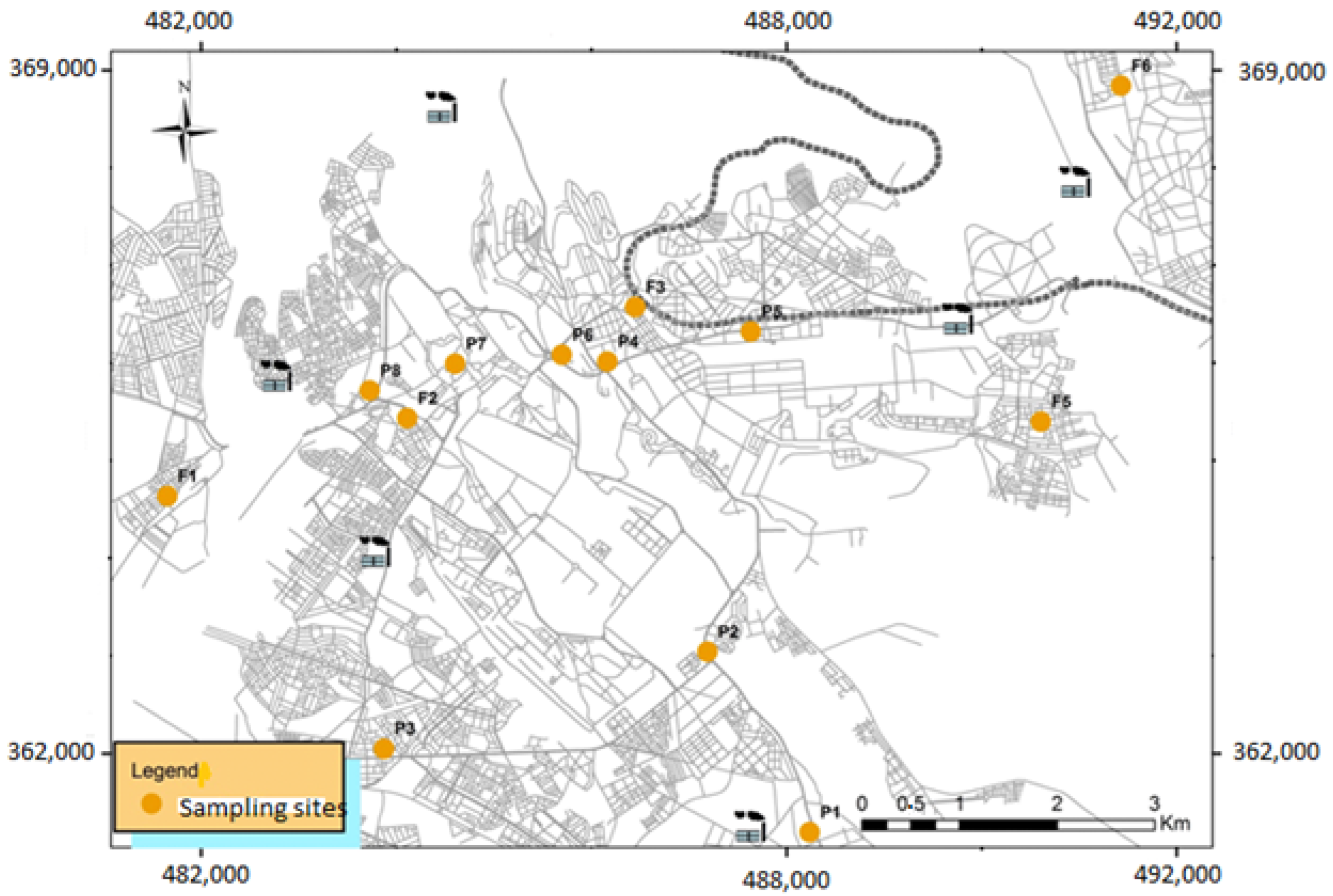


| Points | Location | Typology |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | Point of intersection between the national road n°13 and the national road n°6 | traffic |
| P2 | Point of intersection of Bir Anzarane Avenue and Zitoune Boulevard | traffic |
| P3 | Zitoune Avenue (Marjane district) | traffic |
| P4 | Point of intersection of Bir Anzarane Avenue and the Avenue of the Royal Armed Forces | traffic |
| P5 | Avenue of the Royal Armed Forces (FAR) near the main station | traffic |
| P6 | Point of intersection of Mohammed VI Avenue and the Avenue of the Royal Armed Forces | traffic |
| P7 | Dar Smane Street, the point where the old Medina meets the new city | traffic |
| P8 | The bus station of Meknes city | traffic |
| F1 | Municipality of Toulal | Background |
| F2 | Neighborhood of Riad | Background |
| F3 | New city (station of el Amir Abdelkader) | Background |
| F4 | The neighborhood of the Hacienda | Background |
| F5 | The neighborhood of El Bassatine | Background |
| F6 | Municipality of Ouisslane | Background |
| Consultations Respiratory | Masculin | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Consultations (NC) | Percentage (%) | Number of Consultations | Percentage (%) | |
| Acute illnesses | 56,019 | 4677 | 63,769 | 5323 |
| Asthma attacks | 3996 | 4749 | 4418 | 5251 |
| Respiratory Consultations | [5–14 Years] | [15–49 Years] | >50 Years | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | Percentage (%) | NC | Percentage (%) | NC | Percentage (%) | |
| Acute illnesses | 42,435 | 3542 | 43,780 | 3655 | 33,573 | 2802 |
| Asthma attacks | 870 | 1034 | 3576 | 4250 | 3968 | 4716 |
| Respiratory Consultations | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute illnesses | 29.56% | 24.62% | 21.13% | 24.67% |
| Asthma attacks | 29.44% | 22.98% | 19.95% | 27.62% |
| Respiratory Pathologies | Age Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–11 Months | 12–23 Months | 24–59 Months | |
| Severe pneumonia | 51.15% | 28.12% | 20.72% |
| Pneumonia | 30.75% | 31.57% | 37.67% |
| Respiratory Pathologies | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe pneumonia | 40.61% | 22.29% | 10.82% | 26.27% |
| Pneumonia | 39.93% | 20.45% | 13.11% | 26.49% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Ghazi, I.; Berni, I.; Menouni, A.; Amane, M.; Kestemont, M.-P.; El Jaafari, S. Exposure to Air Pollution from Road Traffic and Incidence of Respiratory Diseases in the City of Meknes, Morocco. Pollutants 2022, 2, 306-327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2030020
El Ghazi I, Berni I, Menouni A, Amane M, Kestemont M-P, El Jaafari S. Exposure to Air Pollution from Road Traffic and Incidence of Respiratory Diseases in the City of Meknes, Morocco. Pollutants. 2022; 2(3):306-327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Ghazi, Ibrahim, Imane Berni, Aziza Menouni, Mohammed Amane, Marie-Paule Kestemont, and Samir El Jaafari. 2022. "Exposure to Air Pollution from Road Traffic and Incidence of Respiratory Diseases in the City of Meknes, Morocco" Pollutants 2, no. 3: 306-327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2030020
APA StyleEl Ghazi, I., Berni, I., Menouni, A., Amane, M., Kestemont, M.-P., & El Jaafari, S. (2022). Exposure to Air Pollution from Road Traffic and Incidence of Respiratory Diseases in the City of Meknes, Morocco. Pollutants, 2(3), 306-327. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants2030020






