Abstract
This study investigated whether moderate soil contamination by Cd and Pb may negatively affect seed germination, photosynthesis and foliar accumulation in the medicinal plant Hypericum perforatum. Seeds were incubated with Cd and Pb solutions of 10 and 100 µM, and two-month-old plants were watered weekly for three weeks with the same solutions. Control samples were treated with deionized water. The percentage of seed germination and seedling length, as well as chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence and foliar reflectance, were measured, along with the foliar Cd and Pb concentrations. The results indicated that seed germination is not affected, while seedling length is decreased by approximately 81% by high Cd levels. Cadmium was subjected to foliar translocation from the soil depending on the supplied concentration, thus causing reductions in the chlorophyll content (−24%). It is of interest that foliar Cd levels in Cd-treated plants were close to or above the limit for the European Pharmacopoeia. Negative effects of Pb were not detected, but accumulation and blockage of this metal at the root level, although not approached experimentally, cannot be ruled out.
1. Introduction
Environmental pollution by heavy metals is of great concern worldwide, especially in developing countries. In Europe, during recent decades, metal deposition has been considerably reduced thanks to policies regulating their emission [1], such as the Aarhus Protocol [2], which targeted three toxic metals: cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg).
Cd and Pb are among the commonest heavy metals in polluted environments, being very often released by the same source, e.g., power-generating plants, metal and steel production, incinerators and cement works [3]. Pb pollution experienced a huge decrease after the phasing out of leaded gasoline [4]. In non-contaminated soils, total concentrations of Cd and Pb are ca. 0.1 µg·g−1 and 17 µg·g−1, respectively [5]. However, following the effects of pollution, their levels may be strongly increased, reaching concentrations even several orders of magnitude higher [6,7].
High concentrations of toxic metals in the soil may affect the physiology of plants and limit seed germination, thus hampering the ability of plants to thrive and survive in polluted environments. Cd and Pb are known to inhibit seed germination and seedling development but with a species-specific effect. For example, albizia plants (Albizia lebbeck) showed negative effects in both seed germination and seedling development after exposure to very low concentrations (10 µM) of these metals [8], while mustard (Sinapis alba) clearly indicated a higher toxicity for Cd than for Pb [9]. Similarly, seeds and seedlings of white leadtree (Leucaena leucocephala) showed a lower tolerance for Cd compared to Pb following exposure to concentrations as high as 50 µg·g−1 [10]. Exposure to Cd and Pb also caused toxic effects in adult plants, affecting their metabolism, photosynthesis, water balance and respiration [11]. Cd seems to be more toxic to plants than Pb, causing a greater reduction in the yield of barley (Hordeum vulgare) [12] and in the leaf area and dry biomass of beech (Fagus sylvatica) [13], besides inhibiting the root length and stem height of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) [14].
Hypericum perforatum L., Saint John’s wort, is a herbaceous plant with a long history in folk medicine, being used for remedies of physical and non-physical disorders [15], and to fight mild to moderately severe depressive disorders [16]. Presently, therapeutic plants hold a large share of the pharmacological market and there is thus an increasing concern for their trace metal content [17] in order to protect consumers from their potential toxic effects [18], as well as to understand the relationships between trace metals and the expression of their active compounds [19,20].
Several studies investigated the accumulation of toxic heavy metals in H. perforatum [21,22,23,24,25,26] and some recommended caution for its harvesting on polluted soils [27] since this plant seems to show good features as a Cd accumulator [28]. Conversely, studies on the toxicity of heavy metals on their seed development are lacking, and information on their effects on the physiology of adult plants is largely unexplored [21]. For this purpose, this study aimed to investigate if ecologically relevant soil contamination by Cd and Pb may negatively affect seed germination, photosynthesis and foliar accumulation in the medicinal plant H. perforatum.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seed Experiment
2.1.1. Seed Collection
Spontaneous plants of H. perforatum were collected in the Botanical Garden of the University of Siena (Italy) during July 2019. In the laboratory, seeds were removed by rubbing flowers by hand pressure. The seeds were then put inside a paper bag and stored at room temperature until their use.
2.1.2. Seed Pre-Treatment and Exposure
Five batches of 25 seeds, counted under a stereomicroscope, were randomly collected inside 2 mL tubes and then stored at 4 °C for two weeks for cold stratification [29], the process that breaks seed dormancy and induces germination. After the stratification, seeds were surface sterilized by dipping in 3% sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) for two minutes and then washed thoroughly with sterile deionized water. Later, each batch of 25 seeds was randomly divided and put into five Petri dishes (Ø = 145 mm) with two filter papers (Ø = 125 mm). Each Petri dish was then treated with 5 mL of single solutions containing sterile deionized water (control), Cd 10 µM, Cd 100 µM, Pb10 µM and Pb100 µM, prepared by diluting a stock solution (1 mM) of each water-soluble metal salt, namely cadmium chloride (CdCl2) and lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) in sterile deionized water. After the treatment, all Petri dishes were incubated in total darkness at 22 °C using a growth chamber. To avoid seed drying and ensure the adequate exposure of the seeds to the two metals, an additional volume of 1.5 mL of solutions was added every three days to each respective Petri dish. The experiment lasted 10 days because no further germinations were observed (this parameter was, however, checked additionally for another five days). After 10 days, the number of germinated seeds and the length of the seedlings were quantified under a stereomicroscope. The experiment was replicated independently three times.
Before the beginning of the experiment, all the materials used (Petri dishes, filter papers, pipette tips, tweezers and deionized water) were UV sterilized for one hour to avoid the growth of pathogens (e.g., fungi and bacteria) inside the Petri dishes. The selected Cd and Pb exposure concentrations were within the range of concentrations detected in the exchangeable fraction and hence potentially phytoavailable [30] in geochemically altered (ultramafic serpentine) soils [24].
2.2. Plant Experiment
2.2.1. Plant Growth
Plants of H. perforatum were obtained from seedlings germinated in deionized water (as indicated for control samples in Section 2.1.2). After their separation from the seed coat, 25 seedlings were transplanted inside pots (Ø = 200 mm) filled with soil (pH = 7.2) from the Botanical Garden of the University of Siena. Five pots (statistical replicates) were prepared for each treatment. After the transplantation, seedlings were allowed to grow inside a climatic chamber (volume = 1.5 m3) at 22 ± 2 °C, RH = 80 ± 5%, photoperiod of 16 h at a photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) of 600 μmol m−2 s−1, corresponding to a daily light integral (DLI) of 35 mol m−2 d−1 for 60 days, a period necessary to obtain approximately 10–15 plants with an average height of ca. 15 cm for each pot. To enhance plant growth, soils were fertilized with 50 mL of a commercial liquid fertilizer; this procedure was carried out only once, 30 days after the transplantation. All pots were regularly watered with 100 mL of mineral water every two days. The volume of 100 mL was accurately selected to provide the complete hydration of each pot without generating water leaks from their bottom. All pots were randomly rotated every two days to avoid the possible influence of microclimatic conditions.
2.2.2. Plant Exposure
After 60 days, each pot was contaminated with 100 mL of a freshly prepared solution containing deionized water (control), Cd 10 µM, Cd 100 µM, Pb10 µM and Pb100 µM prepared as described in Section 2.1.2. Metal contamination was carried out at the beginning of every week and the experiment lasted three weeks.
2.2.3. Physiological Parameters
Photosynthetic parameters (namely, total chlorophyll content, chlorophyll a fluorescence and foliar reflectance as NDVI, see below), used as indicators of plant vitality and health, were investigated immediately before the first contamination and one week after the last treatment. Ten measurements were taken for each pot, randomly selecting the leaves to measure.
The total chlorophyll content index (CCI), expressed as chlorophyll content per square meter of biological material (mg·m−2), was evaluated using a chlorophyll content meter (CCM-300, Opti-Science, Hudson, USA).
Chlorophyll a fluorescence was assessed using the widely used indicator of photosynthetic efficiency FV/FM, which indicates the maximum quantum efficiency of Photosystem II (PS II) photochemistry, and the performance index (PI), an overall indicator of Photosystem I (PS I) and PS II functionality. Prior to the analysis, leaves were dark-adapted for 15 min. The analysis was carried out by flashing samples with a saturating (3000 μmol m−2 s−1) red light (650 nm) pulse for one second, using a plant efficiency analyzer (Handy PEA, Hansatech Ltd., Norfolk, UK).
Measurements of the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), a general indicator of plant health, were carried out using a handy NDVI device (PlantPen NDVI 310, Photon System Instruments, Brno, Czech Republic).
2.2.4. Accumulation of Cd and Pb
The aerial parts of the plants were harvested and dried at 65 °C for six hours. Then, the leaves were crushed by hand pressure and powdered using a ceramic mortar and pestle. Dry samples (200 mg) were mineralized for 20 min with a mixture of 3 mL of 70% nitric acid (HNO3) and 0.5 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in a microwave system (Milestone Ethos 900). The content of Cd and Pb was quantified by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Perkin Elmer–Sciex, Elan 6100). The certified standard reference material NCS DC73350 “Leaves of Poplar” was used to evaluate the analytical quality, which indicated recoveries in the range 98–102%. The precision was estimated by the coefficient of variation of four replicates and was within 5% for both elements. Results are expressed on a dry weight basis (μg·g−1 dw).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Differences in the percentage of germinated seeds, seedling length and foliar accumulation of Cd and Pb were checked using a pairwise permutation t-test for independent samples, applying a correction for multiple testing according to [31]. Prior to the analysis, percent data were arcsin transformed. In order to account for the temporal dimension and for some variability in pre-exposure values in photosynthetic parameters, the results of all investigated physiological variables were expressed as ratios between post- (after three weeks) and pre-exposure values. A generalized linear mixed model (GLMM) was run to check for statistically significant differences between treated and control samples as well as between treatments, with treatment as a fixed effect and pot as a random effect. The significance of the GLMM model was checked with the analysis of deviance (type II Wald chi-square). Post hoc pairwise comparisons were run with the Tukey test. All calculations were run using the free software R [32].
3. Results
Exposure to Cd and Pb did not inhibit the germination of H. perforatum seeds, while seedling length was significantly impaired at the highest (100 µM) Cd concentration (Table 1).

Table 1.
Results (mean ± SE) of germination (%) and seedling length (mm) of H. perforatum after 10 days of exposure to solutions containing either water (Control), Cd or Pb (10 and 100 µM).
Compared to controls, plants grown in soils contaminated with 100 µM Cd showed a reduction of the chlorophyll content (−24%), while NDVI, photosynthetic efficiency and performance index showed only modest and statistically insignificant reductions (Table 2). Plants grown in soils contaminated with 10 µM Cd showed only a reduction of the chlorophyll content (Table 2). Plants grown soils contaminated by 10 µM and 100 µM Pb did not show negative alterations in any of the investigated photosynthetic parameters, even though the NDVI and the performance index showed a slight but not statistically significant increase (Table 2).

Table 2.
Expressions (mean ± SE) of the investigated physiological parameters in H. perforatum after three weeks of exposure to solutions containing either water (Control), Cd or Pb (10 and 100 µM).
Cd and Pb concentrations in control samples were consistent with background levels reported for several spontaneous plants [33]. Cadmium was significantly translocated in leaves of H. perforatum depending on the concentration supplied to the soil: leaves of plants grown in soils contaminated with 10 µM Cd showed concentrations four times higher than those measured in control values, while in plants treated with 100 µM Cd, values were 11 times higher (Figure 1). Plants grown in soils contaminated with 10 µM and 100 µM showed Pb enrichment in their leaf content, but these values were not statistically significantly different from those in the control (Table 2).
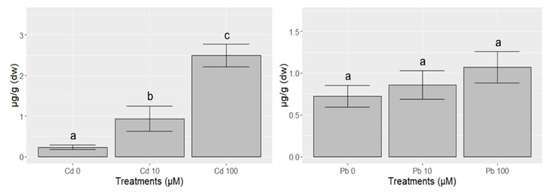
Figure 1.
Concentrations (µg·g−1 ± SE) of Cd and Pb in leaves of H. perforatum after 3 weeks of the exposure to solutions containing either water (Cd 0 and Pb 0), Cd or Pb (10 and 100 µM). Different letters indicate statistically significant (p < 0.05) differences between treatments.
4. Discussion
The exposure of H. perforatum seeds to the investigated Cd and Pb concentrations (10 and 100 µM) did not generate alterations in the seed germination, while seedling length was impaired only at the highest Cd concentration. The coat of the seeds is the first barrier to Cd and Pb penetration [11], thus explaining why inhibition of seed germination occurs only at high exposure levels [9]. Consistent with our observations, Ahmad et al. [34] reported a higher ability of Cd to inhibit seedling development than seed germination. Negative effects on seedling development following Cd exposure may occur as a consequence of its toxic action on respiration and sugar metabolism [35]. Cd may affect all seed respiration phases [35] as well as the activity of the enzymes responsible for the hydrolysis of starch (i.e., α- and β-amylase) [35,36,37], leading to reductions in the energy available for seed development. Additionally, Cd is also known to impair the mechanism of sugar translocation from the seeds to the newly forming seedlings, leaving the process of seedling development without energy [37], as observed in rice (Oryza sativa) seeds following exposures to Cd 10 and 100 µM [38]. We did not experimentally assess the sugar content of our H. perforatum seeds, but we can suggest that a similar mechanism may have occurred. The lack of negative effects on seedling development following Pb exposure may be related to a mechanism of resistance to Pb accumulation at the intracellular level. Pb is largely blocked extracellularly in the cell wall [39], and this may occur as a consequence of its complexation to crystals or amorphous deposits on the cell wall [40], as observed in corn (Zea mays) plants following exposure to Pb solutions provided as soluble lead chloride (PbCl2) and Pb(NO3)2 salts [41].
Plants exposed to Cd showed leaf Cd enrichment, with levels increasing with soil concentrations, while those exposed to Pb did not show appreciable accumulations compared to control plants treated only with water. These results suggest a great soil–plant translocation for Cd in H. perforatum, as reported for native H. perforatum plants grown in geochemically polluted soils [24]. Cd is characterized by a high mobility in plants [42], owing to its chemical similarity to Zn [43], and it is distributed around the whole plant through its release in the xylem [44] following the common dilution process: roots > shoot > leaves [45]. A limited soil–plant (at least soil–leaf) translocation was evident for Pb, which, contrary to Cd, is also characterized by a limited mobility in adult plants since its accumulation mainly occurs at the root level [46]. Higher Pb accumulation in roots compared to shoots has been reported in ca. 75% and 92% of the plants investigated by Rotkittikhun et al. [47] and Yoon et al. [48], respectively. Plants of H. perforatum grown in Pb-enriched soils at concentrations ranging from 360–7250 µM showed a clear trend of Pb accumulation for roots, while the dynamic of shoot accumulation was not clear [19]. The limited Pb translocation to the epigeal parts is determined by the blocking of this toxic metal at the root level, as a consequence of the passive action of several defense barriers: carboxyl groups of mucilage uronic acids, the ion exchange sites of the cell wall and the root endodermis [39]. Among these, the latter seems to be the most involved mechanism [49,50]. Lead values measured in our study are in line with the concentrations reported for commercial H. perforatum plants [51]. Cadmium concentrations found in our control leaves are in line with those measured in the shoots of spontaneous Hypericum plants growing in non-contaminated soils [22], while those grown on Cd-enriched soils are 3–10 times lower than those detected in shoots of H. perforatum plants from mining sites [23]. It is noteworthy that leaves of H. perforatum grown in soils contaminated with the highest Cd concentration (100 µM) showed an average Cd concentration 2.5 times higher than the limit of 1 mg·kg−1 proposed for St. John’s wort herb, but slightly lower than the limit for the European Pharmacopoeia (4 mg·kg−1) [52]. It should be noted that the most common Hypericum preparations derive mainly from hydroalcoholic extraction of their aerial parts [53], including flowers, stems and leaves, which are obviously not free from metals such as Cd and Pb [54], but characterized by concentrations generally below the limit proposed for dried plant materials, based on acceptable daily intake values [55].
The accumulation of Cd determines several toxic effects on plants, such as impairment of the water balance, stomatal opening, oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and damage to the photosynthetic system [45,56,57]. Data on the effects of Cd accumulation on the photosynthesis of H. perforatum are not available, but the toxicity of this metal on several physiological processes of this plant is well documented [58]. A decrease in chlorophyll content following Cd accumulation has been observed for several plant species following exposure to Cd concentrations comparable to those tested in this study [59,60,61]. Additionally, and similarly to our results, reductions of the chlorophyll content of maize (Zea mays) leaves were observed as a consequence of an accumulation of 1.7 µg·g−1 of this metal [62]. Harmful effects of Cd on chlorophyll are related to the replacement of Mg in PSII [63], including its action on chlorophyll biosynthesis steps, such as protochlorophyllide reductase, or its action on PSII-related electron transport [64]. The latter may explain the additional effect on NDVI expression. Consistently with our observations, Cd caused a modest decrease in the NDVI value of barley (Hordeum vulgare) following exposure to very high (1 and 10 mM) Cd concentrations [65]. On the contrary, NDVI was not influenced in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants after Cd exposure of up to 10 mM [66].
Although Pb has been reported to have several negative effects on a number of plant species, e.g., to inhibit photosynthesis, impair mineral nutrition and water balance, change the hormonal balance and affect membrane structure and permeability [67], H. perforatum seems to be a tolerant species. This resistance, as highlighted above, is probably determined by the capacity of this species to block Pb extracellularly, preventing entrance into the cytosol and consequent toxicity. Nevertheless, plants exposed to Pb, as well as Cd, are known to synthesize phytochelatins, cysteine-rich low molecular weight polypeptides, which bind to Pb ions sequestering them, thus acting as an important detoxification mechanism in plants [68]. Additionally, although no Pb accumulation was found in H. perforatum leaves, treatments with Pb generated a modest, yet not statistically significant, increase in reflectance (+21%) and photosynthetic performance (+20%). These outcomes may be related to the fact that Pb was supplied as nitrate (Pb(NO2)3), which may have acted as a source of nitrogen, although modest (i.e., 12.4 mg·kg−1), but still able to increase these parameters, as commonly observed in plants fertilized with nitrogen [69,70,71,72].
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the ability of H. perforatum to thrive in soils moderately polluted by Cd and Pb, and the results indicated that seed germination is not affected, while seedling length is decreased by high Cd levels. Cd was subjected to foliar translocation from the soil depending on the supplied concentration, thus generating reductions in the chlorophyll content. It is of interest that foliar Cd levels in Cd-treated plants were close to or above the limit for the European Pharmacopoeia. Effects of Pb were not detected, but accumulation and blockage of this metal at the root level, although not assessed experimentally, cannot be ruled out.
Author Contributions
S.L. and A.V. conceived and designed the experiments; M.J. and A.V. performed the experiments; A.V. analyzed the data; M.J. and A.V. wrote the paper; S.L. and F.M. supervised the text. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to Paolo Castagnini and Andrea Donati for kindly providing the seeds of Hypericum perforatum.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- European Environmental Agency. 2020. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/eea32-heavy-metal-hm-emissions-1/assessment-10 (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Aarhus Protocol on Heavy Metals. 1998. Available online: http://www.unece.org/env/lrtap/hm_h1.html (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M.; Fudala, J.; Strzelecka-Jastrzab, E.; Hlawiczka, S.; Panasiuk, D.; Nitter, S.; Pregger, T.; Pfeiffer, H.; Friedrich, R. Current and future emissions of selected heavy metals to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8557–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Boyle, E.A. Lead in the western North Atlantic Ocean: Completed response to leaded gasoline phaseout. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 3279–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J.; Steinnes, E. Anthropogenic Additions of Cadmium to Soils. In Cadmium in Soils and Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Markus, J.; McBratney, A.B. A review of the contamination of soil with lead II. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of soil lead. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, Z.R.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Kabir, M.; Shafiq, M. Toxic effects of lead and cadmium on germination and seedling growth of Albizia lebbeck (L.) Benth. Pak. J. Bot. 2009, 41, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Fargašová, A. Effect of Pb, Cd, Hg, As, and Cr on germination and root growth of Sinapis alba seeds. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 52, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, M.; Iqbal, M.; Mohammad, A. Effect of lead and cadmium on germination and seedling growth of Leucaena leucocephala. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seregin, I.V.; Ivanov, V.B. Physiological Aspects of Cadmium and Lead Toxic Effects on Higher Plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 48, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aery, N.C.; Jagetiya, B.L. Relative toxicity of cadmium, lead, and zinc on barley. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1997, 28, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breckle, S.-W.; Kahle, H. Effects of toxic heavy metals (Cd, Pb) on growth and mineral nutrition of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Vegetatio 1992, 101, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Ahmad, P.; Gadgil, K.; Sharma, S. Cadmium and lead-induced changes in lipid peroxidation, antioxidative enzymes and metal accumulation in Brassica juncea L. at three different growth stages. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2009, 55, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemow, K.M.; Bartlow, A.; Crawford, J.; Kocher, N.; Shah, J.; Ritsick, M. 11 Medical Attributes of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum). In Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, J.; Anderson, L.A.; Phillipson, J.D. St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.): A review of its chemistry, pharmacology and clinical properties. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, R.A. Heavy metals in medicinal plant products—An African perspective. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 82, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M. Biological effects of heavy metals: An overview. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Zarinkamar, F.; Ghelich, S.; Soleimanpour, S. Toxic Effects of Pb on Anatomy and Hypericin Content in Hypericum perforatum L. Bioremediat. J. 2013, 17, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajayer, B.A.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Nikabadi, S. Heavy metals in contaminated environment: Destiny of secondary metabolite biosynthesis, oxidative status and phytoextraction in medicinal plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murch, S.J.; Haq, K.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Saxena, P.K. Nickel contamination affects growth and secondary metabolite composition of St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2003, 49, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizzola, R.; Lukas, B. Variability of the Cadmium Content in Hypericum Species Collected in Eastern Austria. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 170, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Peñalosa, J.M.; Manzano, R.; Carpena-Ruiz, R.O.; Gamarra, R.; Esteban, E. Heavy metals distribution in soils surrounding an abandoned mine in NW Madrid (Spain) and their transference to wild flora. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 162, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, D.; Karadjova, I. Toxic Element Profiles in Selected Medicinal Plants Growing on Serpentines in Bulgaria. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 156, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaljev, Z.; Zivkov-Balos, M.; Cupić, Z.; Jaksić, S. Levels of some microelements and essential heavy metals in herbal teas in Serbia. Acta Poloniae Pharm. 2014, 71, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonari, G.; Monaci, F.; Nannoni, F.; Angiolini, C.; Protano, G. Trace Element Uptake and Accumulation in the Medicinal Herb Hypericum perforatum L. Across Different Geolithological Settings. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obratov-Petković, D.; Bjedov, I.; Belanović, S. The content of heavy metals in the leaves of Hypericum perforatum L. on serpentinite soils in Serbia. Glas. Šumarskog Fak. 2008, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Marquard, D.R. Investigations on the uptake of cadmium in Hypercum perforatum. L. (St. John’s wort). Int. Symp. Med. Ar. Plant 1995, 426, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, S. Ottimizzazione Delle Strategie di Conservazione del Germoplasma di Hypericum spp. della Flora Spontanea Siciliana. Ph.D. Thesis, Università degli Studi di Palermo, Palermo, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich, S.M.; Ramsey, M.H.; Helios-Rybicka, E. Total and exchangeable concentrations of heavy metals in soils near Bytom, an area of Pb/Zn mining and smelting in Upper Silesia, Poland. J. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Bargagli, R. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Plants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; p. 171. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Akhtar, M.J.; Zahir, Z.A.; Jamil, A. Effect of cadmium on seed germination and seedling growth of four wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Chugh, L.K.; Sawhney, S.K. Effect of cadmium on germination, amylases and rate of respiration of germinating pea seeds. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 92, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, N.R.; Sheoran, I.S.; Singh, R. Effect of cadmium and nickel on mobilisation of food reserves and activities of hydrolytic enzymes in germinating pigeon pea seeds. Biol. Plant. 1993, 35, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, S.V.; Prasad, M.N.V. Cadmium stress affects seed germination and seedling growth in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench by changing the activities of hydrolyzing enzymes. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 54, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, J.L.; Ros, R.; Picazo, I. Influence of cadmium and nickel on growth, net photosynthesis and carbohydrate distribution in rice plants. Photosynth. Res. 1993, 36, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallavi, S.; Rama, S.D. Lead toxicity in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppe, D.E. The uptake, distribution, and effect of cadmium and lead in plants. Sci. Total Environ. 1977, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, C.; Koeppe, D.E.; Miller, R.J. Localization of Lead Accumulated by Corn Plants. Plant Physiol. 1974, 53, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzyński, M.; Kłobus, G. Changes of photosynthetic parameters in cucumber leaves under Cu, Cd, and Pb stress. Photosynthetica 2004, 42, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Påhlsson, A.M. Toxicity of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb) to vascular plants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1989, 47, 287–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.G.M.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant science: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, M.P.; Gallego, S.M.; Tomaro, M.L. Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecka, A.; Piechalak, A.; Morkunas, I.; Tomaszewska, B. Accumulation of lead in root cells of Pisum sativum. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2008, 30, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotkittikhun, P.; Kruatrachue, M.; Chaiyarat, R.; Ngernsansaruay, C.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Paijitprapaporn, A.; Baker, A.J.M. Uptake and accumulation of lead by plants from the Bo Ngam lead mine area in Thailand. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, L.Q. Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, G.; Temple, P.J. Uptake and localization of lead in corn (Zea mays L.) seedlings, a study by histochemical and electron microscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 188, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seregin, I.V.; Shpigun, L.K.; Ivanov, V.B. Distribution and Toxic Effects of Cadmium and Lead on Maize Roots. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 51, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokalıoğlu, Ş. Determination of trace elements in commonly consumed medicinal herbs by ICP-MS and multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 2504–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, U.; Klier, B.; Kühn, A.V.; Steinhoff, B. Current Findings on the Heavy Metal Content in Herbal Drugs. Pharmeuropa 2009, 1, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Galeotti, N. Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) beyond depression: A therapeutic perspective for pain conditions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 200, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismat, N.; Hifsa, M.; Zeb, S. Characterization of heavy metals in extracts of Hypericum medicinal plant by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Asian J. Chem. 2010, 22, 4387–4392. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Quality Control Methods for Medicinal Plant Materials. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/41986 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Di Toppi, L.S.; Gabbrielli, R. Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1999, 41, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Mota, A.; Devarennes, A.; Pinto, F. Influence of organic matter on the uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron by sorghum plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 326, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babula, P.; Klejdus, B.; Kovacik, J.; Hedbavny, J.; Hlavna, M. Lanthanum rather than cadmium induces oxidative stress and metabolite changes in Hypericum perforatum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, D.; Puranik, R.M.; Srivastava, H.S. Inhibition of Chlorophyll Biosynthesis by Cadmium in Greening Maize Leaf Segments. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1990, 186, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewais, E.A. Effects of cadmium, nickel and lead on growth, chlorophyll content and proteins of weeds. Biol. Plant. 1997, 39, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Ali, S.; Noman, A.; Ali, Q.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Irshad, M.K. Phosphorus amendment decreased cadmium (Cd) uptake and ameliorates chlorophyll contents, gas exchange attributes, antioxidants, and mineral nutrients in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under Cd stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagriffoul, A.; Mocquot, B.; Mench, M.; Vangronsveld, J. Cadmium toxicity effects on growth, mineral and chlorophyll contents, and activities of stress related enzymes in young maize plants (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 1998, 200, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpper, H.; Küpper, F.; Spiller, M. In Situ detection of heavy metal substituted chlorophylls in water plants. Photosynth. Res. 1998, 58, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, F.; Clijsters, H. Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 1990, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, B.B.M.; Han, F.X.; Diehl, S.V.; Monts, D.L.; Su, Y. Spectral reflectance and leaf internal structure changes of barley plants due to phytoextraction of zinc and cadmium. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1041–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, D.P.; Serrano, H.C.; Da Silva, A.B.; Branquinho, C.; Magalhães, S. Effect of Cadmium Accumulation on the Performance of Plants and of Herbivores that Cope Differently with Organic Defenses. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, F.; Aziz, T. A mini review on lead (Pb) toxicity in plants. J. Biol. Life Sci. 2015, 6, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbett, C.S. Phytochelatin biosynthesis and function in heavy-metal detoxification. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 2000, 3, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Gamon, J.A.; Fredeen, A.L.; Merino, J.; Field, C.B. Physiological Changes in Nitrogen-and. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.; Vidal, D.; Simon, E.; SOLl3-SUGRANES, L. Radiometric characteristics of Triticum aestivum cv, Astral under water and nitrogen stress. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živčák, M.; Olšovská, K.; Slamka, P.; Galambošová, J.; Rataj, V.; Shao, H.B.; Brestič, M. Application of chlorophyll fluorescence performance indices to assess the wheat photosynthetic functions influenced by nitrogen deficiency. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 60, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swoczyna, T.; Lata, B.; Stasiak, A.; Stefaniak, J.; Latocha, P. JIP-test in assessing sensitivity to nitrogen deficiency in two cultivars of Actinidia arguta (Siebold et Zucc.) Planch. ex Miq. Photosynthectica 2019, 57, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).