Combined Corrosion Inhibitors and Mechanical Properties of Concrete Embedded Steel (AISI 316L) during Accelerated Saline Corrosion Test †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Salt Fog Test and Mechanical Behavior
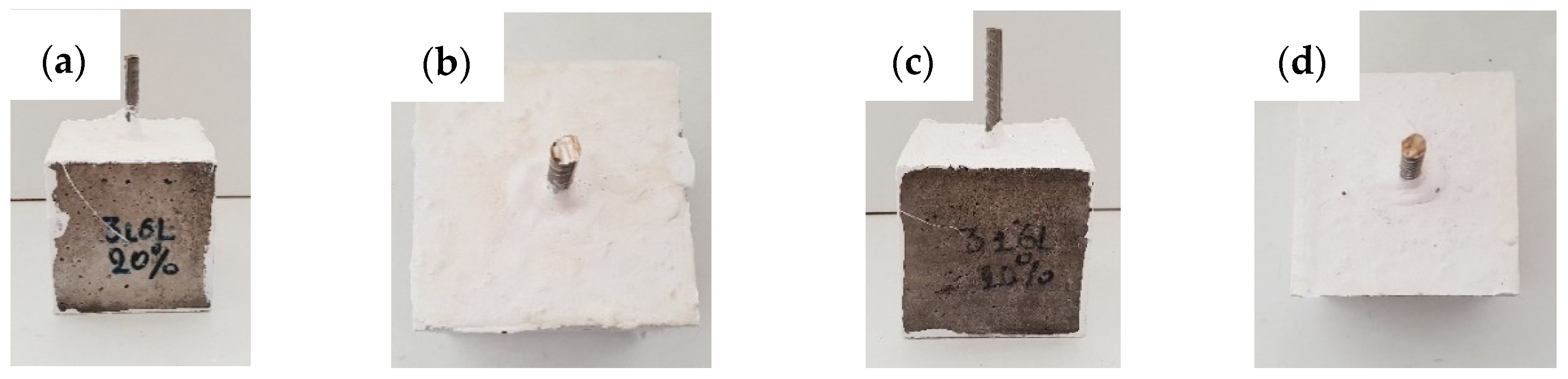
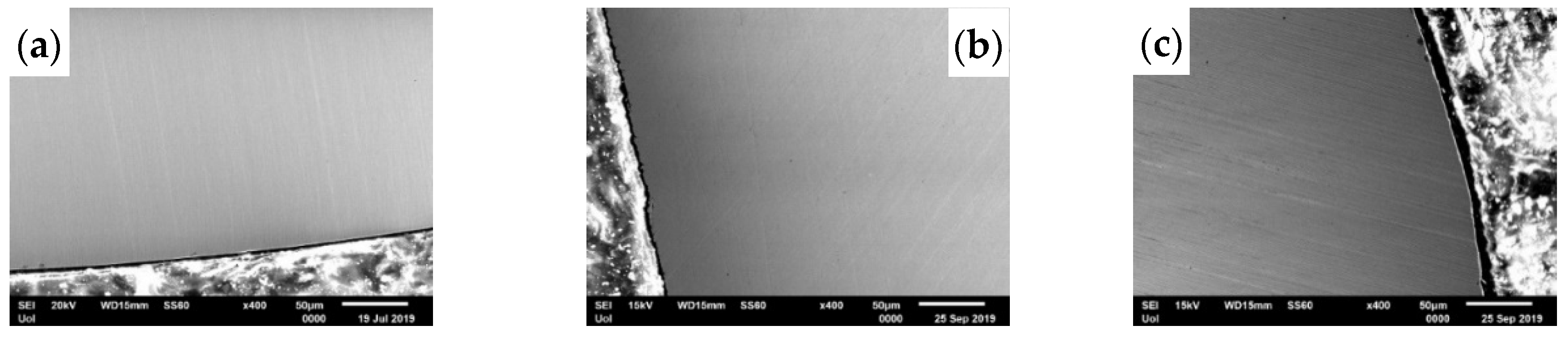
3.2. Microstructure of Corroded 316L Embedded Rebars
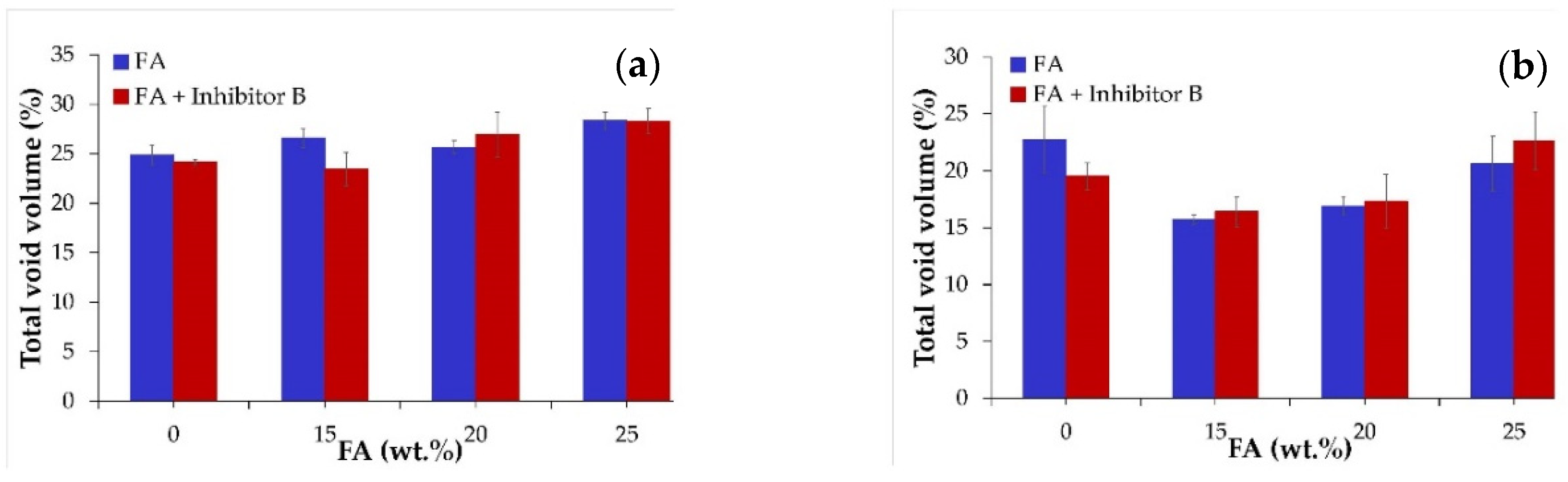
3.3. Porosity of Concrete
4. Conclusions
- Salt fog testing for four months led to small decreases in the mechanical properties of 316L rebars set in concrete cubes containing FA + Inhibitor B with FA increasing. These decreases present statistical significance only in the cases of % elongation and elastic modulus.
- Fly ash addition led to smaller losses of tensile properties compared to concrete cubes free of FA. Cement replacement by 20% FA led to the lowest losses in the tensile properties.
- On visual examination, the concrete cubes reinforced with 316L rebars remained intact of corrosion indications during a salt fog test for a period of four months.
- Microstructural examination of 316L embedded in concrete cubes after 4 m of salt fog testing revealed scarce pitting at the ribs at 25% FA.
- Partial replacement of OPC with FA led to an increase in porosity for both cases (FA-concrete and FA + Inhibitor B-concrete) before salt fog testing.
- After four months of salt fog testing, the addition of FA led to a significant decrease in porosity with 15% and 25% FA presenting the maximum reduction for both cases (FA-concrete and FA + Inhibitor B-concrete).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Reichenbach, S.; Preinstorfer, P.; Hammerl, M.; Kromoser, B. A review on embedded fibre-reinforced polymer reinforcement in structural concrete in Europe. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 124946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Long, X.; Qu, W.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhong, Z. Influence of sulfuric acid corrosion on concrete stress–strain relationship under uniaxial compression. Measurement 2022, 187, 110318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boğa, A.R.; Topçu, İ.B. Influence of fly ash on corrosion resistance and chloride ion permeability of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Sun, W.; Jiang, J.; Song, D.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Passivation characteristics of alloy corrosion-resistant steel Cr10Mo1 in simulating concrete pore solutions: Combination effects of pH and chloride. Materials 2016, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, A.; Angst, U.; Adey, B.; Elsener, B. Modeling of corrosion-induced concrete cover cracking: A critical analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalciner, H.; Eren, O.; Sensoy, S. An experimental study on the bond strength between reinforcement bars and concrete as a function of concrete cover, strength and corrosion level. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.K.; Brooks, R.P.; Ehrensberger, M.T. Effects of simulated inflammation on the corrosion of 316L stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loable, C.; Viçosa, I.N.; Mesquita, T.J.; Mantel, M.; Nogueira, R.P.; Berthomé, G.; Chauveau, E.; Roche, V. Synergy between molybdenum and nitrogen on the pitting corrosion and passive film resistance of austenitic stainless steels as a pH-dependent effect. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 186, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xie, N.; Fortune, K.; Gong, J. Durability of steel reinforced concrete in chloride environments: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Ye, G. The pore structure of cement paste blended with fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 45, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, K.; Fen-chong, T.; Dangla, P. Determination of cement hydration and pozzolanic reaction extents for fly-as cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouli, S.; Lekatou, A.G.; Siozos, E.; Kleftakis, S. Accelerated corrosion performance of AISI 316L stainless steel concrete reinforcement used in restoration works of ancient monuments. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 03003, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsouli, S.; Lekatou, A.G.; Kleftakis, S. The effect of fly ash on the corrosion performance of AISI 316L stainless steel reinforced concrete for application to restoration works of ancient monuments. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on the Conservation of Monuments in the Mediterranean Basin, Athens, Greece, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouli, S.; Lekatou, A.G.; Nikolaidis, C.; Kleftakis, S. Corrosion and tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel concrete reinforcement in harsh environments containing a corrosion inhibitor. Procedia Struct. Int. 2019, 17, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouli, S.; Lekatou, A.G.; Kleftakis, S.; Matikas, T.E.; Dalla, P.T. Corrosion behavior of 304L stainless steel concrete reinforcement in acid rain using fly ash as corrosion inhibitor. Procedia Struct. Int. 2018, 10, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekatou, A.G.; Tsouli, S.; Nikolaidis, C.; Kleftakis, S.; Tragazikis, I.K.; Matikas, T.E. Effect of fly ash on the corrosion performance and structural integrity of stainless steel concrete rebars in acid rain and saline environments. Frat. Integrita Strutt. 2019, 13, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikas, T.E.; Karpur, P.; Shamasundar, S. Measurement of the dynamic elastic moduli of porous titanium aluminide compacts. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsiri, T.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C. Influence of fly ash fineness and shape on the porosity and permeability of blended cement pastes. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2010, 17, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, J.; Yan, P. The microstructure of 4-year-old hardened cement-fly ash paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, V.G. Effect of fly ash on Portland cement systems: Part II. High-calcium fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fly Ash, wt.% | Duration, m | Elastic Modulus, GPa | 0.2% Yield Strength, MPa | Tensile Strength, MPa | Fracture Strength, MPa | % EL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 202 ± 1 | 553 ± 19 | 720 ± 19 | 688 ± 24 | 41 ± 2 |
| 4 | 192 ± 1 | 539 ± 51 | 686 ± 59 | 657 ± 56 | 36 ± 2 | |
| 15 | 0 | 199 ± 1 | 550 ± 20 | 708 ± 22 | 675 ± 27 | 39 ± 1 |
| 4 | 196 ± 1 | 544 ± 23 | 684 ± 31 | 639 ± 22 | 35 ± 2 | |
| 20 | 0 | 199 ± 1 | 541 ± 17 | 701 ± 23 | 652 ± 27 | 40 ± 1 |
| 4 | 193 ± 1 | 540 ± 27 | 689 ± 27 | 645 ± 27 | 39 ± 2 | |
| 25 | 0 | 200 ± 1 | 535 ± 40 | 686 ± 39 | 641 ± 42 | 39 ± 1 |
| 4 | 191 ± 1 | 507 ± 34 | 661 ± 31 | 615 ± 35 | 38 ± 2 |
| Fly Ash, wt.% | Elastic Modulus, % | 0.2% Yield Strength, % | Tensile Strength, % | Fracture Strength, % | % Elongation, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.95 | 2.53 | 4.72 | 4.51 | 12.20 |
| 15 | 1.51 | 1.09 | 3.39 | 5.33 | 10.26 |
| 20 | 3.02 | 0.18 | 1.71 | 1.07 | 2.50 |
| 25 | 4.50 | 5.23 | 3.64 | 4.06 | 2.56 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsouli, S.; Lekatou, A.G.; Kleftakis, S.; Gkoutzos, P.; Tragazikis, I.K.; Matikas, T.E. Combined Corrosion Inhibitors and Mechanical Properties of Concrete Embedded Steel (AISI 316L) during Accelerated Saline Corrosion Test. Mater. Proc. 2021, 5, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005072
Tsouli S, Lekatou AG, Kleftakis S, Gkoutzos P, Tragazikis IK, Matikas TE. Combined Corrosion Inhibitors and Mechanical Properties of Concrete Embedded Steel (AISI 316L) during Accelerated Saline Corrosion Test. Materials Proceedings. 2021; 5(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005072
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsouli, Sofia, Angeliki G. Lekatou, Spyridon Kleftakis, Pantelis Gkoutzos, Ilias K. Tragazikis, and Theodore E. Matikas. 2021. "Combined Corrosion Inhibitors and Mechanical Properties of Concrete Embedded Steel (AISI 316L) during Accelerated Saline Corrosion Test" Materials Proceedings 5, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005072
APA StyleTsouli, S., Lekatou, A. G., Kleftakis, S., Gkoutzos, P., Tragazikis, I. K., & Matikas, T. E. (2021). Combined Corrosion Inhibitors and Mechanical Properties of Concrete Embedded Steel (AISI 316L) during Accelerated Saline Corrosion Test. Materials Proceedings, 5(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005072








