Abstract
Bulk cobalt- and nickel-based metallic materials exhibit superior resistance to cavitation erosion and sliding wear. Thus, thermally deposited High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) coatings seem promising for increasing the wear resistance of the bulk metal substrate. However, the effect of chemical composition on the cavitation erosion and sliding wear resistance of M(Co,Ni)CrAlY and NiCrMo coatings has not yet been exhaustively studied. In this study, High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) coatings such as CoNiCrAlY, NiCoCrAlY, and NiCrMoFeCo were deposited on AISI 310 (X15CrNi25-20) steel coupons. The microstructure, hardness, phase composition and surface morphology of the as-sprayed coatings were examined. Cavitation erosion tests were conducted using the vibratory method in accordance with the ASTM G32 standard. Sliding wear was examined with the use of a ball-on-disc tribometer, and friction coefficients were measured. The mechanism of wear was identified with the scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) method. In comparison to the NiCrMoFeCo coating, the CoNiCrAlY and NiCoCrAlY coatings have a lower sliding and cavitation wear resistance.
1. Introduction
Bulk cobalt- and nickel-based metal alloys have superior resistance to both cavitation erosion and sliding [1,2,3,4,5]. Moreover, Co-, Ni- or even Fe-based overlay deposits are considered highly resistant to abrasion and erosion [1,2,6]. Thus, High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) thermal spraying seems to be the next step in increasing the wear resistance of bulk metal substrates. Various cermet coating systems have been investigated in relation to sliding, abrasive or erosion wear [7,8,9,10,11,12]. It is known that thermally sprayed coatings increase the wear resistance of machine and equipment components and make it possible to prevent or reduce various damage processes. Abrasive damage, erosion by solid particles and corrosion are the most frequently described damage processes in literature [13,14,15,16]. Despite the fact that the HVOF method is widely used for metallic or cermet coating deposition [7,9,15,17,18,19,20], the anti-wear properties of HVOF coatings are still being investigated. New studies on the abrasive wear of thermally deposited coatings are published, and even though these issues seem to be quite well-known there are relatively few scientific reports combining both sliding and cavitation testing of HVOF metallic coatings. The effect of alloying composition on the cavitation erosion and sliding wear resistance of Ni-based coatings deposited by the HVOF method has not been exhaustively investigated. In comparison to other thermal spraying processes, e.g., plasma spraying or flame spraying, HVOF-deposited coatings exhibit low porosity and homogeneous structure. This is mainly due to the low process temperature and the high speed of the particles being sprayed [14,21,22]. It is well known that the homogeneous structure of the material has a positive effect on its resistance to cavitation erosion [23,24]. Furthermore, the investigation into wear resistance is an up-to-date problem from the point of view of both scientific and engineering practice [8,9,20,25,26]. In this paper, the sliding and cavitation erosion wear resistance of NiCrMoFeCo, CoNiCrAlY and NiCoCrAlY coatings is investigated.
2. Experimental
The nominal chemical compositions of powders used for the deposition of HVOF coatings are given in Table 1. The substrate was AISI 310 (X15CrNi25-20) with the thickness ranging from 180 to 200 µm and the initial roughness of deposited coatings, Ra, ranging between 4 and 6 µm. The coatings were examined on their top surfaces using an SEM microscope (Phenom ProX Desktop SEM, Phenom World (Waltham, MA, USA)). Phase composition was estimated by the X-ray diffraction (XRD) method. Hardness was measured on the metallographic cross-sections with a nano-hardness tester (Anton Paar CSM Instruments, Ostfildern, Germany) having a load of 500 mN.

Table 1.
Nominal chemical composition of feedstock powders.
Sliding wear tests were performed by the ball-on-disc method with a tribotester from CSM Instruments, Switzerland, in compliance with the procedure described in [27,28]. The counter-ball was made of 100Cr6 steel; the applied load was 15 [N] and the sliding distance was set equal to 200 [m]. The mass loss of the samples was estimated with an accuracy of 0.01 mg. Wear traces were first examined with the Dektak 150 contact profilometer (Veeco Instruments, Plainview, NY, USA) for calculating volume loss. After that, they were also examined with the use of a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Cavitation erosion tests were conducted using a vibratory rig operating under the conditions given in the ASTM G32 standard [29] and described in previous papers [8,30]. The stationary specimen test method and distilled water were used. The samples were weighed in specified time intervals with an accuracy of 0.01 mg. The worn areas were analyzed with the SEM microscope.
3. Results
3.1. Coating Characterization
The surface morphology of the coatings is presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The top-view of the coatings indicates their lamellar microstructure and the presence of unmelted powder particles, porosity and oxides that are typical of thermally sprayed coatings [14,31,32]. According to the XRD analysis results, the coatings A and B form a γ solid solution with the structure of fcc and phases β-(Co,Ni)Al and Cr3Ni. This is in agreement with the data reported in the literature [14,19]. The hardness ranges from 4.7 to 5.8 GPa, which is comparable with the literature data [19,33].
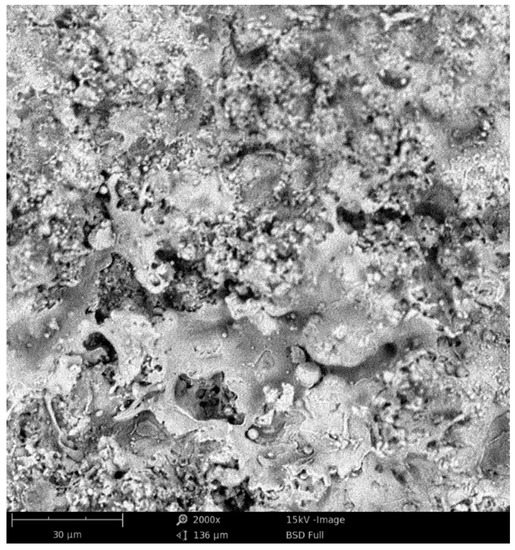
Figure 1.
Surface morphology of coating A (SEM).
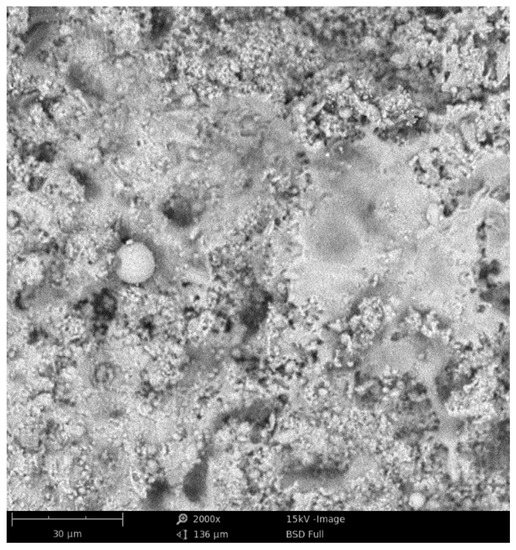
Figure 2.
Surface morphology of coating C (SEM).
3.2. Sliding Wear Results
Sliding wear results are given in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 and in Table 2. The results clearly demonstrate that coating A has undergone the highest wear, while coating C is the most resistant to wear. The friction coefficients are in agreement with the mass loss data, as shown in Figure 3. At the initial stage of the wear process, the top surface peaks of the coatings are cut out or smashed, and, subsequently, a great amount of debris occurs in the wear trace. The wear results are complementary with the surface roughness measurements of the coatings. Moreover, it can be observed that the wear of the C (nickel-based) coating is much lower.
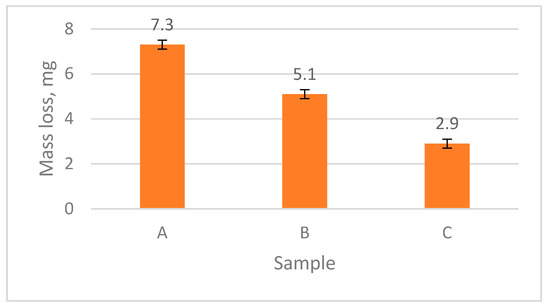
Figure 3.
Sliding wear results.
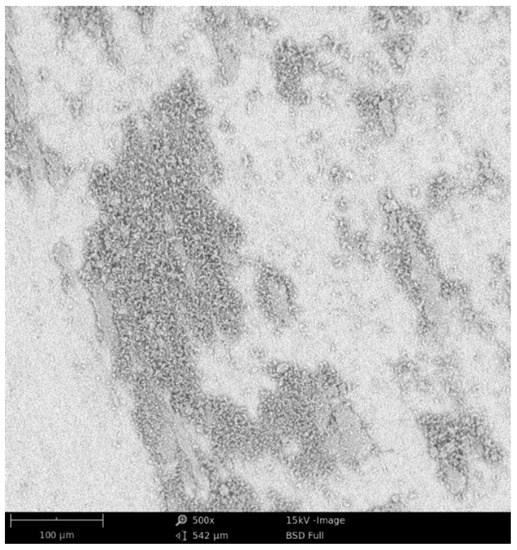
Figure 4.
Wear trace of coating A (SEM).
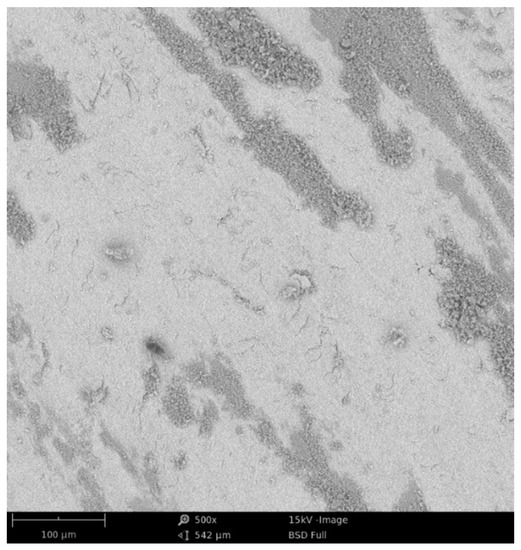
Figure 5.
Wear trace of coating C (SEM).

Table 2.
Friction coefficients of the tested coatings.
Figure 4 shows the wear traces of M(Ni,Co)CrAlY coatings and Figure 5 shows the wear trace of the Ni-based coating. All wear traces show the presence of oxides (primary oxides or material oxides due to wear). Moreover, it can be observed that the wear mechanism relies on smearing the coating material and, especially in the case of coating C, on low-cyclic fatigue resulting in the delamination of the coating material. The material removal is a result of the cyclic compression and smearing of the HVOF-deposited material. Moreover, the observed delamination is in agreement with the splat dimensions indicating splat-induced detachment. Wear debris also plays an important role due to its smearing through the wear trace and cyclic deformation leading to a fatigue detachment of the coating material.
3.3. Cavitation Erosion
Cavitation erosion curves of the HVOF coatings are given in Figure 6. It can be observed that, in comparison to M(Ni,Co)CrAlY, the C (nickel-based) coating exhibits a higher resistance to cavitation. The material loss of the coatings A and B is comparable, and it is twice higher than that of coating C. The wear mechanism in the M(Ni,Co)CrAlY-type coatings is similar and it consist in the detachment of loose splats and cracking induced by non-uniformities (unmelted particles, oxides and lamellae borders). Material erosion is followed by the plastic deformation of the coating material. Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the cavitation-eroded surfaces of the coatings B and C. A comparison of the SEM images reveals the presence of plastic strains. Moreover, it can be observed that, in the case of coating B, the material is removed in massive chunks, while the C coating exhibits a much more compact morphology and lower surface roughness, which increases its wear resistance. In contrast to coating C, the coatings A and B have a Ni-Co-based matrix. It seems that the deformability of nickel leads to an increased wear resistance of coating C.
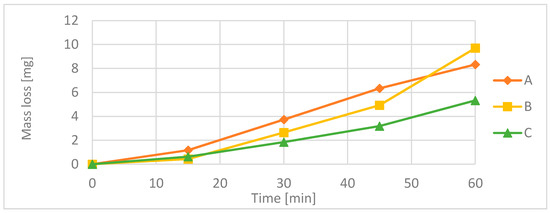
Figure 6.
Cavitation erosion curves of High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) coatings.
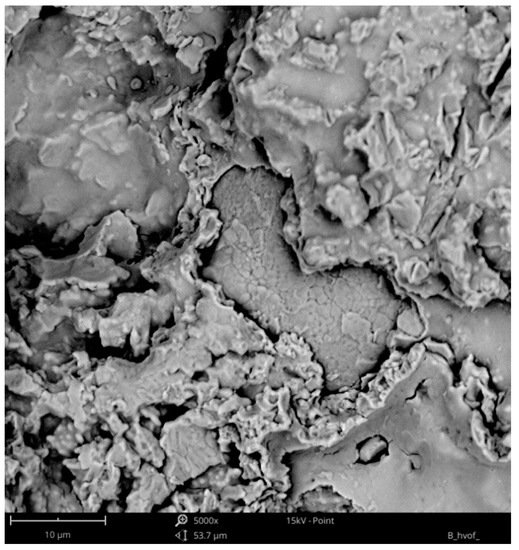
Figure 7.
Cavitation-eroded surface of coating B (SEM).
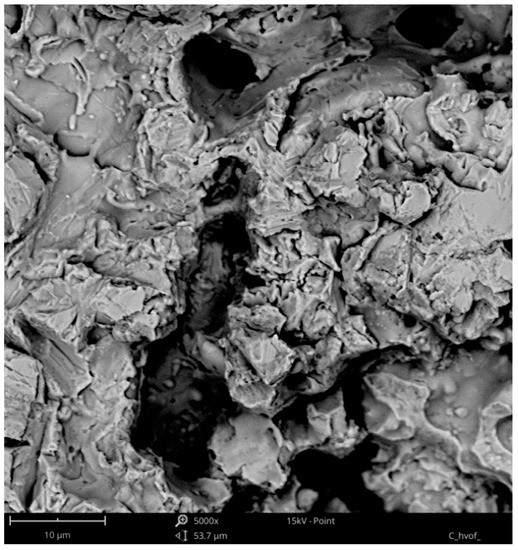

Figure 8.
Cavitation-eroded surface of coating C (SEM).
4. Conclusions
The results of the study lead to the following conclusions:
- The sliding wear resistance increases with increasing the nickel content as follows: CoNiCrAlY < NiCoCrAlY < NiCrMoFeCo;
- the friction coefficient increases with increasing the Co content as follows: NiCrMoFeCo < NiCoCrAlY < CoNiCrAlY;
- the resistance to cavitation erosion of the M(Co,Ni)CrAlY coatings is almost two times lower than that of the NiCrMoFeCo deposit;
- a combination of adhesive, oxidation and low-cyclic fatigue is the dominant sliding wear mechanism;
- cavitation erosion damage is induced by plastic deformation of the coating material; it is initiated at the non-uniform areas (unmelted particles, oxides and lamellae borders) and results in the removal of the HVOF deposited material.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.; methodology, M.S., M.W., L.Ł. and K.G.; validation, M.S., M.W. and L.Ł.; formal analysis, M.S., M.W. and L.Ł.; investigation, M.S., M.W., L.Ł. and K.G.; resources, M.S., M.W., L.Ł. and K.G.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, M.S. and L.Ł.; visualization, M.S.; supervision, M.S.; project administration, M.S.; funding acquisition, M.S. and M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The project/research was financed in the framework of the project Lublin University of Technology—Regional Excellence Initiative, funded by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education (contract no. 030/RID/2018/19).
References
- Hattori, S.; Mikami, N. Cavitation erosion resistance of stellite alloy weld overlays. Wear 2009, 267, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejwowski, T.; Marczewska-Boczkowska, K.; Kobayashi, A. A comparative study of electrochemical properties of metallic glasses and weld overlay coatings. Vacuum 2013, 88, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Hejwowski, T.; Lenart, I. Cavitation erosion resistance of Ni-Co based coatings. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2014, 8, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hejwowski, T. Sliding wear resistance of Fe-, Ni- and Co-based alloys for plasma deposition. Vacuum 2006, 80, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, M.; Budzyński, P.; Szala, M.; Turek, M. Tribological properties of the Stellite 6 cobalt alloy implanted with manganese ions. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 421, 032012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D.M. High Power Diode Laser Cladding of Wear Resistant Metal Matrix Composite Coatings. Available online: https://www.scientific.net/ssp.199.587 (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Zhang, P.; Jiang, J.H.; Ma, A.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, Y.P.; Lin, P.H. Cavitation Erosion Resistance of WC-Cr-Co and Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings Prepared by HVOF. Available online: https://www.scientific.net/AMR.15-17.199 (accessed on 22 August 2018).
- Szala, M.; Hejwowski, T. Cavitation Erosion Resistance and Wear Mechanism Model of Flame-Sprayed Al2O3-40%TiO2/NiMoAl Cermet Coatings. Coatings 2018, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillon, G.; Pougoum, F.; Lavigne, S.; Ton-That, L.; Schulz, R.; Bousser, E.; Savoie, S.; Martinu, L.; Klemberg-Sapieha, J.-E. Cavitation erosion mechanisms in stainless steels and in composite metal–ceramic HVOF coatings. Wear 2016, 364, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; An, Y.; Hou, G.; Li, S.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. Effect of substrate preheating treatment on the microstructure and ultrasonic cavitation erosion behavior of plasma-sprayed YSZ coatings. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Dudek, A.; Maruszczyk, A.; Walczak, M.; Chmiel, J.; Kowal, M. Effect of atmospheric plasma sprayed TiO2-10% NiAl cermet coating thickness on cavitation erosion, sliding and abrasive wear resistance. Acta Phys. Pol. A. 2019, 136, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Nakahama, S.; Hattori, S.; Nakano, K. Slurry wear and cavitation erosion of thermal-sprayed cermets. Wear 2005, 258, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegadeeswaran, N.; Ramesh, M.R.; Bhat, K.U. Combating Corrosion Degradation of Turbine Materials Using HVOF Sprayed 25% (Cr3C2-25(Ni20Cr)). Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijc/2013/824659/ (accessed on 22 August 2018).
- Davis, J.R. Handbook of Thermal Spray Technology; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-87170-795-6. [Google Scholar]
- Szymański, K.; Hernas, A.; Moskal, G.; Myalska, H. Thermally sprayed coatings resistant to erosion and corrosion for power plant boilers—A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 268, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. Microstructure and Sliding Wear Behaviour of In-Situ TiC-Reinforced Composite Surface Layers Fabricated on Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying. Materials 2018, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Lin Peng, R.; Li, X.-H.; Johansson, S.; Zhang, P.; Lin Peng, R.; Li, X.-H.; Johansson, S. Investigation of Element Effect on High-Temperature Oxidation of HVOF NiCoCrAlX Coatings. Coatings 2018, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Deng, C.; Zeng, K. High temperature wear performance of HVOF-sprayed Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo and Cr3C2-NiCr hardmetal coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, S.; Voisey, K.T.; McCartney, D.G. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of VPS and HVOF CoNiCrAlY Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, S.; Pougoum, F.; Savoie, S.; Martinu, L.; Klemberg-Sapieha, J.E.; Schulz, R. Cavitation erosion behavior of HVOF CaviTec coatings. Wear 2017, 386, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ying, G.; Li, G.; Gao, W.; Wang, B.; Guo, W. Microstructure and cavitation–silt erosion behavior of high-velocity oxygen–fuel (HVOF) sprayed Cr3C2–NiCr coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 225, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksa, M.; Turunen, E.; Suhonen, T.; Varis, T.; Hannula, S.-P.; Oksa, M.; Turunen, E.; Suhonen, T.; Varis, T.; Hannula, S.-P. Optimization and Characterization of High Velocity Oxy-fuel Sprayed Coatings: Techniques, Materials, and Applications. Coatings 2011, 1, 17–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Hejwowski, T.J. Zwiększanie odporności kawitacyjnej stopów metali przez napawanie powłok. Przegląd Spaw. Weld. Technol. Rev. 2015, 87, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Steller, J. International Cavitation Erosion Test and quantitative assessment of material resistance to cavitation. Wear 1999, 233, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łatka, L.; Szala, M.; Michalak, M.; Pałka, T. Impact of atmospheric plasma spray parameters on cavitation erosion resistance of Al2O3-13%TiO2 coatings. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2019, 136, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Boy, J.; Zatorski, R.; Stephenson, L.D. Thermal spray and weld repair alloys for the repair of cavitation damage in turbines and pumps: A technical note. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2005, 14, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żebrowski, R.; Walczak, M. Effect of the Shot Peening on Surface Properties and Tribological Performance of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Produced by Means of DMLS Technology. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2019, 64, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Szala, M.; Walczak, M. Cavitation erosion and sliding wear resistance of HVOF coatings. Weld. Technol. Rev. 2018, 90, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G32-10: Standard Test Method for Cavitation Erosion Using Vibratory Apparatus; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Szala, M.; Walczak, M.; Pasierbiewicz, K.; Kamiński, M. Cavitation Erosion and Sliding Wear Mechanisms of AlTiN and TiAlN Films Deposited on Stainless Steel Substrate. Coatings 2019, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, M.; Łatka, L.; Sokołowski, P.; Niemiec, A.; Ambroziak, A. The Microstructure and Selected Mechanical Properties of Al2O3 + 13 wt % TiO2 Plasma Sprayed Coatings. Coatings 2020, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruszczyk, A.; Dudek, A.; Szala, M. Research into Morphology and Properties of TiO2-NiAl Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed Coating. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2017, 11, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Miramontes, J.A.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Estupiñan-Lopez, F.H.; Pedraza-Basulto, G.K.; Poblano-Salas, C.A. Parameter Studies on High-Velocity Oxy-Fuel Spraying of CoNiCrAlY Coatings Used in the Aeronautical Industry. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijc/2014/703806/ (accessed on 22 August 2018).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).