Utilization of Stone Wool Kiln Ash in Cement-Based Materials †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Selection and Characterization
2.2. Compressive Strength
2.3. Vicat Needle Test
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of Cement Pastes
3. Results and Discussion
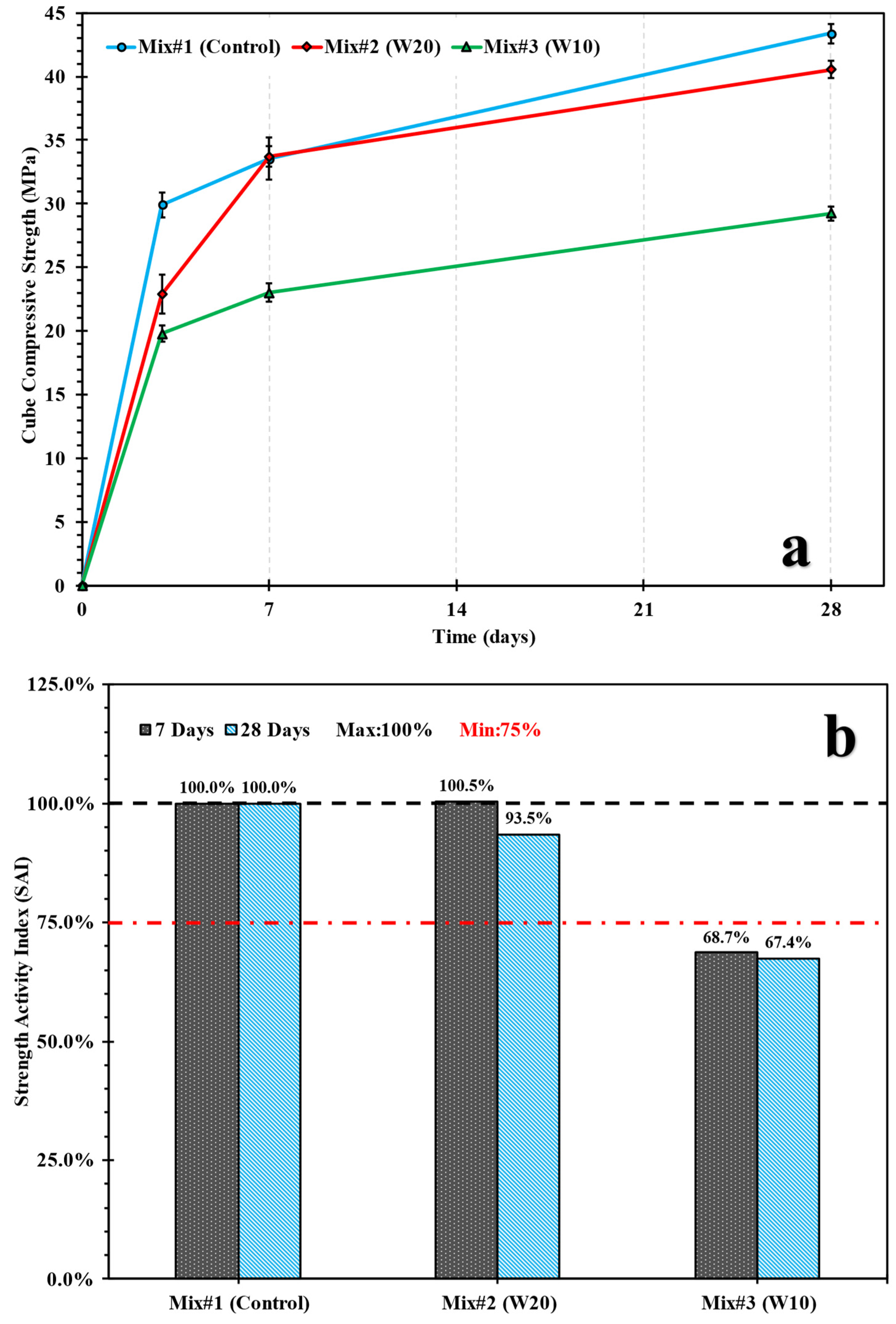
3.1. Pozzolanicity of Stone Wool Kiln Ash and Its Impact on the Compressive Strength
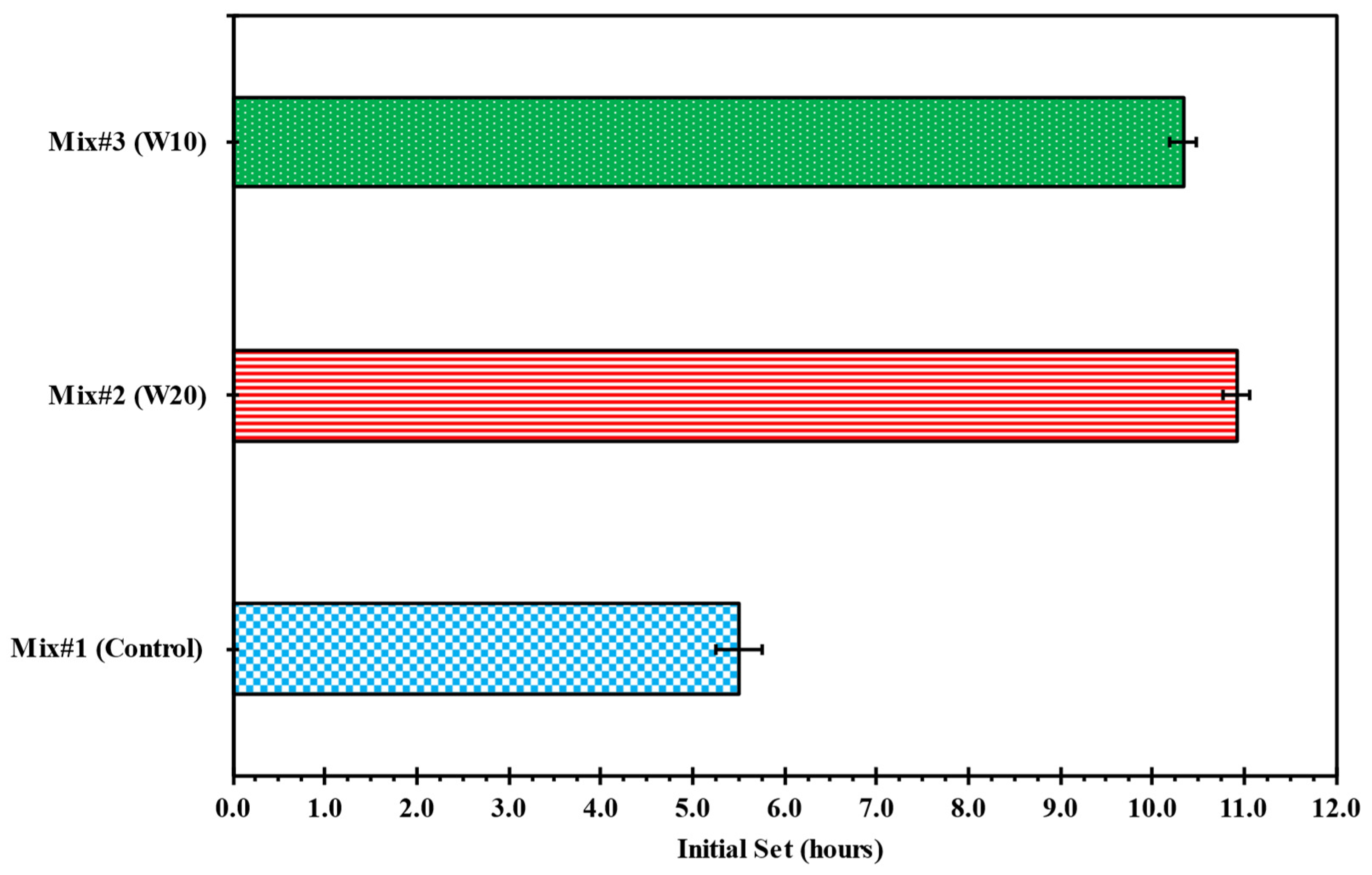
3.2. Impact on Fresh State Properties: Initial Setting Time
3.3. Impact on Composition: Calcium Carbonate and Calcium Hydroxide Content
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicoara, A.I.; Stoica, A.E.; Vrabec, M.; Rogan, N.Š.; Sturm, S.; Ow-Yang, C.; Gulgun, M.A.; Bundur, Z.B.; Ciuca, I.; Vasile, B.S. End-of-life materials used as supplementary cementitious materials in the concrete industry. Materials 2020, 13, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasile, B.S.; Nicoara, A.I.; Surdu, V.A.; Ene, V.L.; Neacsu, I.A.; Stoica, A.E.; Oprea, O.; Boierasu, I.; Trusca, R.; Vrabec, M.; et al. Fly-Ash Evaluation as Potential EOL Material Replacement of Cement in Pastes: Morpho-Structural and Physico-Chemical Properties Assessment. Materials 2022, 15, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications, 3rd ed.; Institut Géopolymère: Saint-Quentin, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Siddique, R. Recent advances in understanding the role of supplementary cementitious materials in concrete. Cem Concr Res. 2015, 78, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Winnefeld, F.; Provis, J.L.; Ideker, J.H. Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cem Concr Res. 2011, 41, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Snellings, R.; Bernal, S.A. Supplementary cementitious materials: New sources, characterization, performance insights. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C305-14; Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes andMortars of Plastic Consistency. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C 311; Standard Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Fly Ash or Natural Pozzolans for Use in Portland-Cement Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C109/C 109M-13; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ASTM C191-13; Standard Test Methods for Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Alarcon-ruiz, L.; Platret, G.; Massieu, E.; Ehrlacher, A. The use of thermal analysis in assessing the effect of temperature on a cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C 618; Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete1. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023. [CrossRef]
| Binder | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | CaCO3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 10.70 | 2.65 | 69.90 | 5.00 | 2.35 | 0.71 | 3.37 | 0.70 |
| W10 | 23.60 | 6.86 | - | 48.00 | 4.13 | 4.00 | 5.15 | 2.65 |
| W20 | 46.40 | 1.96 | - | 8.54 | 2.82 | 7.53 | 4.26 | 13.60 |
| Cement (g) | W10 (g) | W20 (g) | Water (g) | Standard Sand (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mix#1 | 600 | - | - | 300 | 1800 |
| Mix#2 | 480 | - | 120 | 300 | 1800 |
| Mix#3 | 180 | 120 | - | 300 | 1800 |
| 7-Days | 28-Days | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portlandite (%) | CaCO3(%) | Portlandite (%) | CaCO3(%) | |
| Mix#1 | 6.5 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 2.7 |
| Mix#2 | 5.3 | 3.2 | 5.0 | 2.7 |
| Mix#3 | 6.1 | 4.1 | 5.3 | 4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydın, T.; Bundur, Z.B.; Aksoy, K.; Karabıyık, B.; Perin, E.; İnce, T.; Sarı, M. Utilization of Stone Wool Kiln Ash in Cement-Based Materials. Mater. Proc. 2023, 15, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015089
Aydın T, Bundur ZB, Aksoy K, Karabıyık B, Perin E, İnce T, Sarı M. Utilization of Stone Wool Kiln Ash in Cement-Based Materials. Materials Proceedings. 2023; 15(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015089
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydın, Tolga, Zeynep Başaran Bundur, Kaan Aksoy, Barış Karabıyık, Ezgi Perin, Türker İnce, and Mihriban Sarı. 2023. "Utilization of Stone Wool Kiln Ash in Cement-Based Materials" Materials Proceedings 15, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015089
APA StyleAydın, T., Bundur, Z. B., Aksoy, K., Karabıyık, B., Perin, E., İnce, T., & Sarı, M. (2023). Utilization of Stone Wool Kiln Ash in Cement-Based Materials. Materials Proceedings, 15(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2023015089





