Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Physicochemical Properties of Polycaprolactone, Chitosan, and Sericin Membranes †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Material
2.2.1. Extraction of Sericin (SS)
2.2.2. Preparation of Work Solutions
2.2.3. Preparation of Composite Membranes
2.3. Characterization of the Material
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
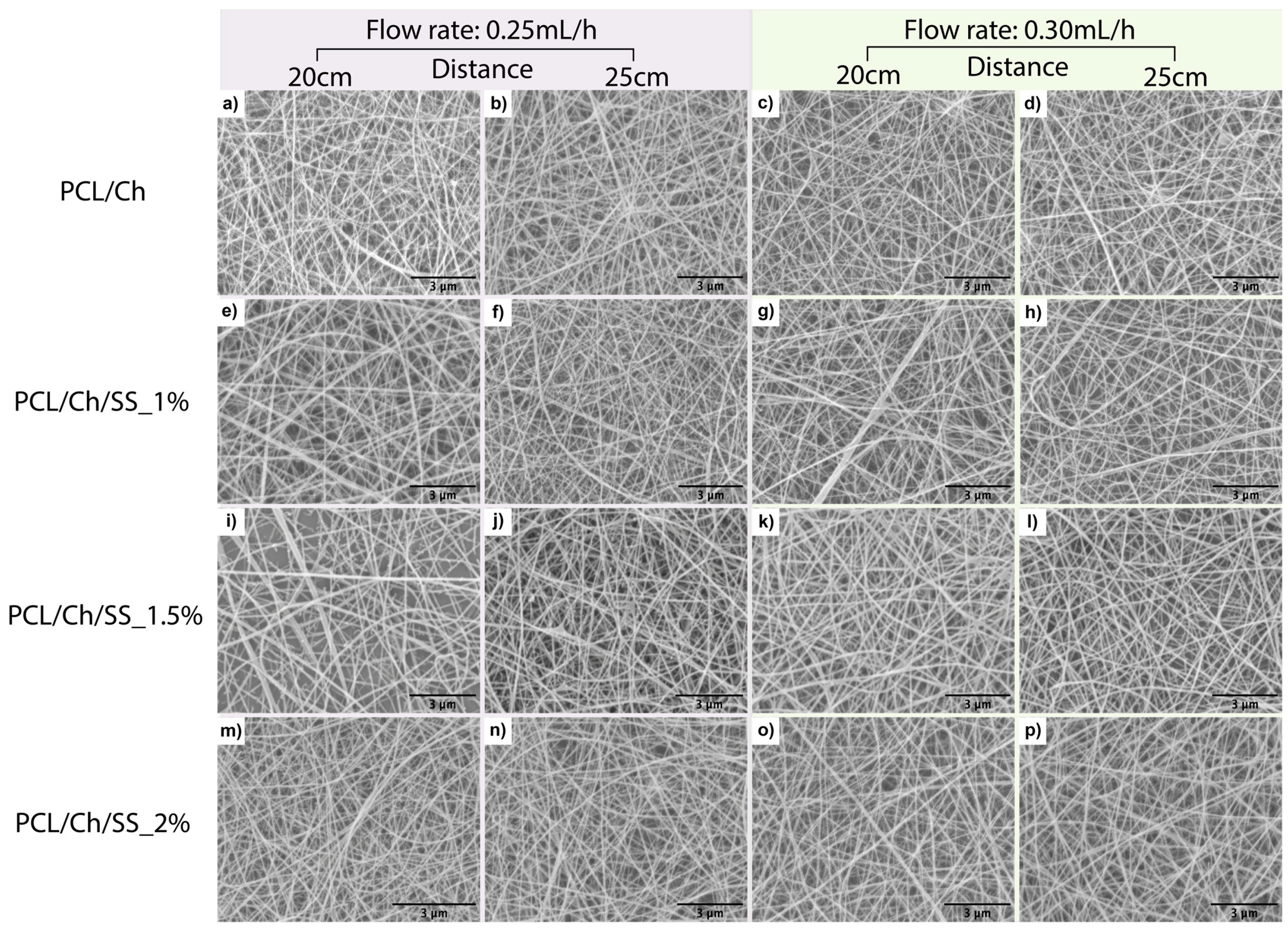
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.2. Fourier Transform Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mochane, M.J.; Motsoeneng, T.S.; Sadiku, E.R.; Mokhena, T.C.; Sefadi, J.S. Morphology and Properties of Electrospun PCL and Its Composites for Medical Applications: A Mini Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaee, A.; Bagheri-Khoulenjani, S.; Amir Afshar, H.; Bogheiri, H. Biomimetic Nanocomposite Scaffolds Based on Surface Modified PCL-Nanofibers Containing Curcumin Embedded in Chitosan/Gelatin for Skin Regeneration. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 177, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, A.E.; Edmondson, D.; Chang, F.C.; Wood, D.; Gong, A.; Levengood, S.L.; Zhang, M. High-throughput and high-yield fabrication of uniaxially-aligned chitosan-based nanofibers by centrifugal electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagam Hanumantharao, S.; Rao, S. Multi-Functional Electrospun Nanofibers from Polymer Blends for Scaffold Tissue Engineering. Fibers 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineis, C.; Cruz Maya, I.; Mowafi, S.; Varesano, A.; Sánchez Ramírez, D.O.; Abou Taleb, M.; Tonetti, C.; Guarino, V.; El-Sayed, H. Synergistic Effect of Sericin and Keratin in Gelatin Based Nanofibers for in Vitro Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qian, Y.; Lin, C.; Li, H.; Jiang, C.; Lv, Y.; Liu, W.; Cai, K.; Germershaus, O.; Yang, L. The Effect of Silk Gland Sericin Protein Incorporation into Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on in Vitro and in Vivo Characteristics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, B.R.; Roberto, S.B.; Bonafé, E.G.; Camargo, S.E.A.; Camargo, C.H.R.; Popat, K.C.; Kipper, M.J.; Martins, A.F. Chitosan Imparts Better Biological Properties for Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Electrospun Membranes than Dexamethasone. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chameettachal, S.; Murab, S.; Vaid, R.; Midha, S.; Ghosh, S. Effect of Visco-Elastic Silk–Chitosan Microcomposite Scaffolds on Matrix Deposition and Biomechanical Functionality for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 1212–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, K.N.; Salameh, J.W.; Wereley, S.T.; Kinzer-Ursem, T.L. Physical Characterization of Nanoparticle Size and Surface Modification Using Particle Scattering Diffusometry. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 054107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, A.; Adhikari, J.; Ghosh, A.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Thomas, S.; Datta, P.; Saha, P. Electrospun Chitosan/Polycaprolactone-Hyaluronic Acid Bilayered Scaffold for Potential Wound Healing Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Tong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C. Nitrofurazone-Loaded Electrospun PLLA/Sericin-Based Dual-Layer Fiber Mats for Wound Dressing Applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 16940–16949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Electrospun Chitosan/Sericin Composite Nanofibers with Antibacterial Property as Potential Wound Dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadipour-Goudarzi, E.; Montazer, M.; Latifi, M.; Aghaji, A.A.G. Electrospinning of Chitosan/Sericin/PVA Nanofibers Incorporated with in Situ Synthesis of Nano Silver. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowmya, B.; Panda, P.K. Electrospinning of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) (PCL) and Poly Ethylene Glycol (PEG) Composite Nanofiber Membranes Using Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK) and N N’-Dimethyl Acetamide (DMAc) Solvent Mixture for Anti-Adhesion Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahaliloglu, Z.; Kilicay, E.; Denkbas, E.B. Antibacterial Chitosan/Silk Sericin 3D Porous Scaffolds as a Wound Dressing Material. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, J.; Kanoujia, J.; Parashar, P.; Tripathi, C.B.; Saraf, S.A. Wound Healing Applications of Sericin/Chitosan-Capped Silver Nanoparticles Incorporated Hydrogel. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, K.; Pandey, J.P.; Kumari, R.; Sinha, A.K.; Gupta, V.P.; Singh, G.P. Free Radical Scavenging Potential of Sericin Obtained from Various Ecoraces of Tasar Cocoons and Its Cosmeceuticals Implication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.N.; Um, I.C. Effects of Solvent on the Solution Properties, Structural Characteristics and Properties of Silk Sericin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekasurya, W.; Sebastian, J.; Puspitasari, D.; Asri, P.P.P.; Asri, L.A.T.W. Synthesis and Degradation Properties of Sericin/PVA Hydrogels. Gels 2023, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Kao, W.A.; Loría-Bastarrachea, M.I.; Pérez-Padilla, Y.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V.; Vázquez-Torres, H.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M. Thermal Degradation of Poly(Caprolactone), Poly(Lactic Acid), and Poly(Hydroxybutyrate) Studied by TGA/FTIR and Other Analytical Techniques. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 4191–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Xi, Y.; Li, Z. One-Step Electrospinning PCL/Ph-LPSQ Nanofibrous Membrane with Excellent Self-Cleaning and Oil-Water Separation Performance. Polymer 2022, 249, 124858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillón Martínez, D.C.; Zuluaga, C.L.; Restrepo-Osorio, A.; Álvarez-López, C. Characterization of Sericin Obtained from Cocoons and Silk Yarns. Procedia Eng. 2017, 200, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SS Concentration (% w/w) | Volumetric Ratio (w/w) | Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (kV) | Flow (mL/h) | Needle-Collector Distance (cm) | ||
| 0% | PCL: Ch (6:4) | 22 | 0.25 | 20 |
| 25 | ||||
| 0.30 | 20 | |||
| 25 | ||||
| 1% | PCL/Ch: SS (8:2) | 22 | 0.25 | 20 |
| 25 | ||||
| 0.30 | 20 | |||
| 25 | ||||
| 1.5% | PCL/Ch: SS (8:2) | 22 | 0.25 | 20 |
| 25 | ||||
| 0.30 | 20 | |||
| 25 | ||||
| 2% | PCL/Ch: SS (8:2) | 22 | 0.25 | 20 |
| 25 | ||||
| 0.30 | 20 | |||
| 25 | ||||
| Type of Material | Electrospinning Parameters | Fiber Diameter | PdI |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL/Ch | 0.25 mL/h; 20 cm | 66 ± 8 | 0.014 |
| 0.25 mL/h; 25 cm | 73 ± 13 | 0.034 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 20 cm | 77 ± 2 | 0.001 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 25 cm | 75 ± 2 | 0.001 | |
| PCL/Ch/SS_1% | 0.25 mL/h; 20 cm | 88 ± 13 | 0.021 |
| 0.25 mL/h; 25 cm | 78 ± 9 | 0.014 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 20 cm | 59 ± 12 | 0.042 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 25 cm | 82 ± 7 | 0.007 | |
| PCL/Ch/SS_1.5% | 0.25 mL/h; 20 cm | 97 ± 30 | 0.094 |
| 0.25 mL/h; 25 cm | 82 ± 8 | 0.011 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 20 cm | 91 ± 8 | 0.009 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 25 cm | 87 ± 8 | 0.010 | |
| PCL/Ch/SS_2% | 0.25 mL/h; 20 cm | 77 ± 2 | 0.001 |
| 0.25 mL/h; 25 cm | 82 ± 1 | 0.000 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 20 cm | 91 ± 1 | 0.000 | |
| 0.30 mL/h; 25 cm | 79 ± 7 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oviedo, M.; Montoya, Y.; Alvarez, C.; Bustamante, J. Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Physicochemical Properties of Polycaprolactone, Chitosan, and Sericin Membranes. Mater. Proc. 2022, 11, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022011005
Oviedo M, Montoya Y, Alvarez C, Bustamante J. Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Physicochemical Properties of Polycaprolactone, Chitosan, and Sericin Membranes. Materials Proceedings. 2022; 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022011005
Chicago/Turabian StyleOviedo, María, Yuliet Montoya, Catalina Alvarez, and John Bustamante. 2022. "Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Physicochemical Properties of Polycaprolactone, Chitosan, and Sericin Membranes" Materials Proceedings 11, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022011005
APA StyleOviedo, M., Montoya, Y., Alvarez, C., & Bustamante, J. (2022). Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Physicochemical Properties of Polycaprolactone, Chitosan, and Sericin Membranes. Materials Proceedings, 11(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2022011005






