1. Introduction
With the growing prevalence of technology, the heightened interest in electronic technologies such as virtual reality (VR) facilitates varied experiences [
1]. In Buddhism, meditation is the art of cultivating flow. In other words, Buddhist meditation is a way to develop the positive qualities of wisdom and compassion and explore the fundamental characteristics of the purest awareness of human nature. Zen meditation, or Zazen, is rooted in Buddhist psychology [
2]. For centuries, Buddhist meditation has positively developed the human mind. Therefore, we created an innovative religious and cultural experience by integrating VR technology into Buddhist meditation.
Digital media technology, while no longer considered an emerging technology, has become an integral part of modern life as a daily routine. The new trend in digital multimedia is the Metaverse’s VR technology, which has been developed for various applications. The Metaverse’s VR technology was used in this study to develop a new method of studying Buddhism, making full use of VR’s immersive 3D visual capabilities to create a unique approach to learning Buddhism.
The educational development of Buddhist meditation using VR technology is important. Given the profound theoretical and technical requirements of both Buddhist meditation and Metaverse technology, we collaborated with Xiangguang Temple, a local Buddhist institute in Chiayi, to develop the learning system. The system helps students understand the essence of Buddhist meditation and promotes their positive mental growth. Additionally, with digital technology companies, students are provided opportunities for industry–academia cooperation. The objectives of this study include developing metaverse VR Buddhist meditation, establishing digital functional models for meditation practices in VR, and innovating Buddhist education in the metaverse realm.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Metaverse
The term “metaverse” traces back to writer Neal Town Stephenson’s 1992 novel
Snow Crash [
3]. The English term “metaverse” is composed of “meta” and “verse”; “meta” means beyond, and “verse” refers to the universe, thus representing a new space “beyond the universe” [
4]. The metaverse has garnered global attention not only because of the integration of the physical and digital worlds but also its vast commercial potential [
5]. The economic value of the metaverse in the real world is projected to be USD 500 billion by 2030, equivalent to the size of Japan’s economy, indicating its considerable scale [
6]. Metaverse companies have raised USD 10.4 billion through 612 transactions, and over USD 120 billion flowed into the metaverse sector in 2022, demonstrating a significant opportunity [
7]. Thus, the metaverse presents enormous business prospects for the future, and investment in research and development is urgent.
The metaverse is a virtual world composed of simulated environments, functioning not only as an independent virtual space but also as a parallel world interacting with the real world [
8]. The metaverse is built through immersive experiences, forming a virtual social structure that includes digital content and products from various industries. People entering the metaverse assume virtual identities and engage in socializing, entertainment, shopping, and other economic activities [
9].
Currently, there is no clear definition of the metaverse, similar to when the “Internet” first emerged. We clarify and define the concept of the metaverse through various technologies, literature, and data. The metaverse is a parallel space that integrates the virtual and the real, allowing users to live within the virtual world. Therefore, the metaverse technology was used to create a virtual space for Buddhist meditation practice in this study. This innovative concept provides new methods for enhancing human well-being and opens up new fields in Buddhist studies.
2.2. VR
The concept of VR emerged in the 1960s. With the advancement of VR technology, the concept of the metaverse is becoming a reality applied to gaming, education, social interaction, and commerce. It is regarded as an important future trend in the digital industry, holding tremendous commercial potential and profoundly impacting the various aspects of people’s lives, work, and entertainment [
10,
11]. VR transports users into a virtual environment where they can have experiences as if they are in the real world. When using VR technology, users often feel an immersive sensation, which is the most distinctive feature of VR.
VR technology creates virtual environments that offer users a different visual and auditory experience from that of traditional settings. It bridges people and images by expanding media tools into sensory tools to maximize the sensory experience [
12]. VR also offers high real-time responsiveness and interactivity. For example, in interior design, consumers can view their surroundings in real time and engage in in-depth communication with designers [
13], and others have explored the learning outcomes of using VR in interior design education. An innovative curriculum integrating VR can be used in teaching interior design to enhance students’ interest in learning and improve communication skills. By using VR in Buddhist education, the technology’s immersive capabilities are ensured to engage users deeply in the learning process.
3. Research Method
The goal of this research is to develop an educational system that applies VR technology from the metaverse to Buddhism and meditation. We focused on “Buddhist culture”, “interactive design”, and the “metaverse”. The content within these three areas includes exploring the development of “Buddhist culture” in the Chiayi region through the application of digital technology, with the main research subject being the Xiangguang Temple in Chiayi. “Interactive design” involves exploring the content of Buddhist education and meditation culture, further integrating interactive design techniques to develop new realms of digital technology.
The “metaverse” represents a major trend in online media today, creating VR spaces for Buddhist studies that allow users to learn remotely while breaking the constraints of time and space.
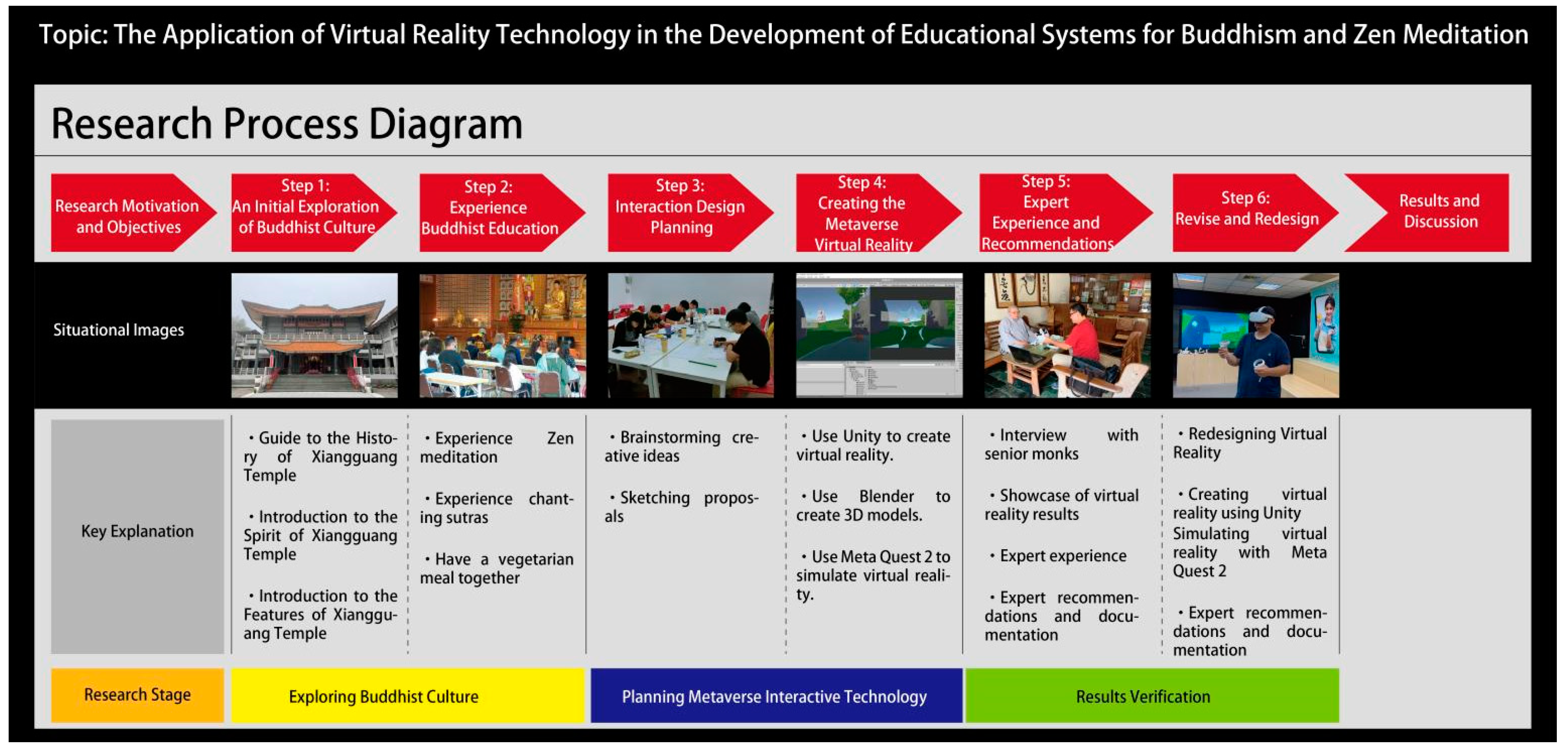
Research Process
From ancient times to the present, Buddhism in Taiwan has a history of over a hundred years and has developed many unique cultural characteristics. In this study, we collaborated with the Chiayi Xiangguang Temple Buddhist Academy and invited the monks from the temple to participate in the research. The research process comprised six steps, as illustrated in
Figure 1.
- 1.
Step 1: Initial Exploration of Buddhist Culture
The first step involved visiting the local Buddhist academy, Xiangguang Temple, and inviting a monk to guide the tour and explain the history and development of Xiangguang Temple. During the visit, the monk explained the nation of the Buddhist spirit and the unique culture of Xiangguang Temple in detail.
- 2.
Step 2: Experiencing Buddhist Education
This step involved a personal experience of a day of Buddhist practice. Every monk at Xiangguang Temple must study Buddhist courses and follow a fixed daily schedule.
- 3.
Step 3: Interactive Design Planning
After the Buddhist experience, brainstorming sessions were offered to generate interactive design concepts for Buddhist practice. This design concept was used for imaginative thinking and ideas for the digital media were proposed.
- 4.
Step 4: Creating a Metaverse VR
We created a metaverse VR space by incorporating interactive features such as meditation and scripture reading modes. The 3D models for the virtual scene were created using Blender 4.0, while Unity software (Version number: 2023.2.18f1) was used for developing the VR experience.
- 5.
Step 5: Expert Experience and Suggestions
Senior monks from Xiangguang Temple were invited to experience the Buddhist VR. The venue for the interview was the guest room at Xiangguang Temple. The equipment prepared includes a laptop, a Meta Quest 2 VR headset (Meta Platforms, Inc. is a tech company based in Menlo Park, California, USA), and a voice recorder.
- 6.
Step 6: Revision and Redesign
After the expert interviews, the collected experiences and suggestions were transcribed. Based on the experts’ recommendations, modifications were made to the functions and interactive effects of the Buddhist VR to achieve the desired design goals.
In the research process, each step was designed to guide the creative thinking to diverge, design to converge, and interdisciplinary integration. A rigorous planning process was essential for developing suitable project outcomes and cross-disciplinary application methods throughout their participation.
4. Results
Buddhist culture has existed in Taiwan for over three hundred years, with a profound and rich heritage. Therefore, integrating Buddhist culture into interdisciplinary digital technology content presents challenges and achievements.
4.1. VR Experiences
After participating in a meditation practice at Xiangguang Temple, we gained information on Buddhist meditation and chanting. Currently, Buddhist meditation and chanting activities are popular. In addition to Buddhist temples offering meditation instruction, there are many meditation and quiet centers, attracting numerous participants. Therefore, creating an interactive design for Buddhist meditation and chanting has become a key concept in designing VR experiences.
In the creative design and brainstorming phase, we used paper, pens, and simple coloring tools to sketch concept designs. In this step, students freely discussed and searched for information online to inspire their imaginative thinking. Finally, the important elements of the concept design were determined, and seven key design principles were selected as follows:
A natural Buddhist field.
An enormous Buddha statue.
The animated imagery of gentle breezes and falling leaves.
The sound effect of a wooden fish being struck.
The sound effect of chanting Buddhist scriptures.
The element of stone tablet inscription.
The sound of ocean waves.
4.2. Metaverse VR
The students established scenes for Buddhist meditation based on the design principles. The entire virtual scene in an outdoor natural environment was created and featured trees, rocks, grass, and fluttering leaves. In the virtual space, a large Buddha statue was created, resembling the solemn scenery of the Xiangguang Temple Buddha. The background music was selected, incorporating the cheerful sound of a wooden fish being struck.
The first function of the VR for Buddhist meditation was sitting meditation. The students created a stone block on the ground with a wooden fish on top, displaying a prompt to start meditating. When users touched the wooden fish, they entered the sitting meditation mode. The interface for beginning the sitting meditation is shown in
Figure 2.
When users touched the wooden fish, they entered the sitting meditation mode. Based on the experiences during meditation, the beginners’ meditation time was set to 15 min. When entering the sitting meditation mode, a countdown timer for 15 min began. Users listened to the sound of ocean waves while meditating. Once the meditation time was over, the ocean sounds stopped, and the background music returned to the sound of the wooden fish being struck. The interface for initiating sitting meditation is shown in
Figure 3.
Another interactive mode was the chanting function. On the giant stone, symbols were displayed. By touching them, the chanting mode started, as shown in
Figure 4. When the users touched the giant stone, the scriptures appeared, and the audio of the chanting played. After the chanting content was finished, it automatically closed and returned to the background music of the wooden fish being struck. The chanting mode interface is shown in
Figure 5.
The VR for Buddhist meditation allows users to learn Buddhist meditation without the limitation of time and space. Additionally, the interactive teaching mode guides users in easily learning the methods of Buddhist meditation.
5. Verification of VR
We invited a senior monk from Xiangguang Temple to experience the VR software (Unity version number: 2023.2.18f1) and provide some feedback. At the beginning of the experience, the expert was instructed on how to operate the software. The expected duration for the expert’s experience was one hour for a careful and in-depth understanding of the software’s content. After the experience, the expert’s thoughts and opinions were gathered through an interview. The interview process was limited to 30 min, during which a recording device was used to document the content. The findings and suggestions from the expert interview are summarized in
Table 1.
6. Conclusions
The metaverse is developing rapidly, and the lifestyles of the new generation are changing due to new media art. Investing in the development of the metaverse across various fields is expected to become a major trend in the future. We applied VR to the development of Buddhist meditation. The process of integrating Buddhist culture with the development of VR technology was developed, providing a learning opportunity that encompasses both knowledge and skills. Taiwanese Buddhism has undergone several centuries of historical evolution, resulting in a unique cultural identity. While the preliminary application of Buddhist culture in VR technology has been recognized by experts, there are still many unexplored areas in Buddhist studies that are worth developing within the metaverse. It is necessary to delve into Buddhist culture in the future and fully develop it within the metaverse, further utilizing digital technology to promote cultural heritage. Reflections and suggestions are presented in this study. The interactive models of VR developed in this study increased the interest of monks and sparked many innovative ideas. Therefore, verifying the interactive functions of VR warrants further research. Additionally, the practices of Buddhism are vast and profound. Therefore, it is recommended to use participatory design methods to invite monks and nuns to co-develop the project. The result of this study prompts further studies for more developments in the metaverse.
Author Contributions
Compilation and analysis of literature, C.-S.L.; field research and analysis, M.-F.W.; introducing VR experience, Y.-C.H.; learning methods in technology and religion, Y.-C.H. introducing creative thinking and design methods, M.-F.W.; analyzing design elements, M.-F.W., design creativity and brainstorming, Y.-C.H.; VR simulation and drawing, C.-S.L.; questionnaire and result analysis, Y.-C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barta, S.; Flavián, C.; Gurrea, R. Managing consumer experience and online flow: Differences in handheld devices vs PCs. Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.W.; Ryan, R.M.; Creswell, J.D. Mindfulness: Theoretical Foundations and Evidence for its Salutary Effects. Psychol. Inq. 2007, 18, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M. The Metaverse: And How it Will Revolutionize Everything; Liveright: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y. Metaverse and BIM’s business model. Master’s Thesis, Feng Chia University, Taichung, Taiwan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, G.P. A Study on the Impact of Metaverse Trends on Consumer Behavior. Master’s Thesis, Lunghwa University of Science and Technology, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mckinsey and Company. Value Creation in the Metaverse. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/business%20functions/marketing%20and%20sales/our%20insights/value%20creation%20in%20the%20metaverse/value-creation-in-the-metaverse.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Chai, H.C. The Influence of Information Load Levels on Brand Recall, Brand Attitude, Purchase Intention in Metaverse Experiences: An Empirical Study. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shiau, W.L.; Huang, L.C. Scale development for analyzing the fit of real and virtual world integration: An example of Pokémon Go. Inf. Technol. People 2022, 36, 500–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q. Opportunities and Challenges of the New Economic Model in the Metaverse. Account. Res. Mon. 2022, 435, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, P.L. Exploring the Business Opportunities and Challenges of Metaverse. Master’s Thesis, National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chou, R.J. Discussion on the Learning Effectiveness of Using VR in Interior Design Teaching. J. Des. 2023, 28, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.C.; Chen, L.Y.; Peng, H.Y. Exploring the factors influencing consumer’s attitude toward using and use intention of VR games. Int. J. Organ. Innov. 2021, 13, 160–175. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y. Metaverse: A Digital Future. Master’s Thesis, National Chengchi University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).