Pansharpening Remote Sensing Images Using Generative Adversarial Networks †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. The Ground Truth from Pansharpening
2.2. The Ground Truth from Adobe Photoshop
2.3. The Network Architecture
2.4. The Loss Function
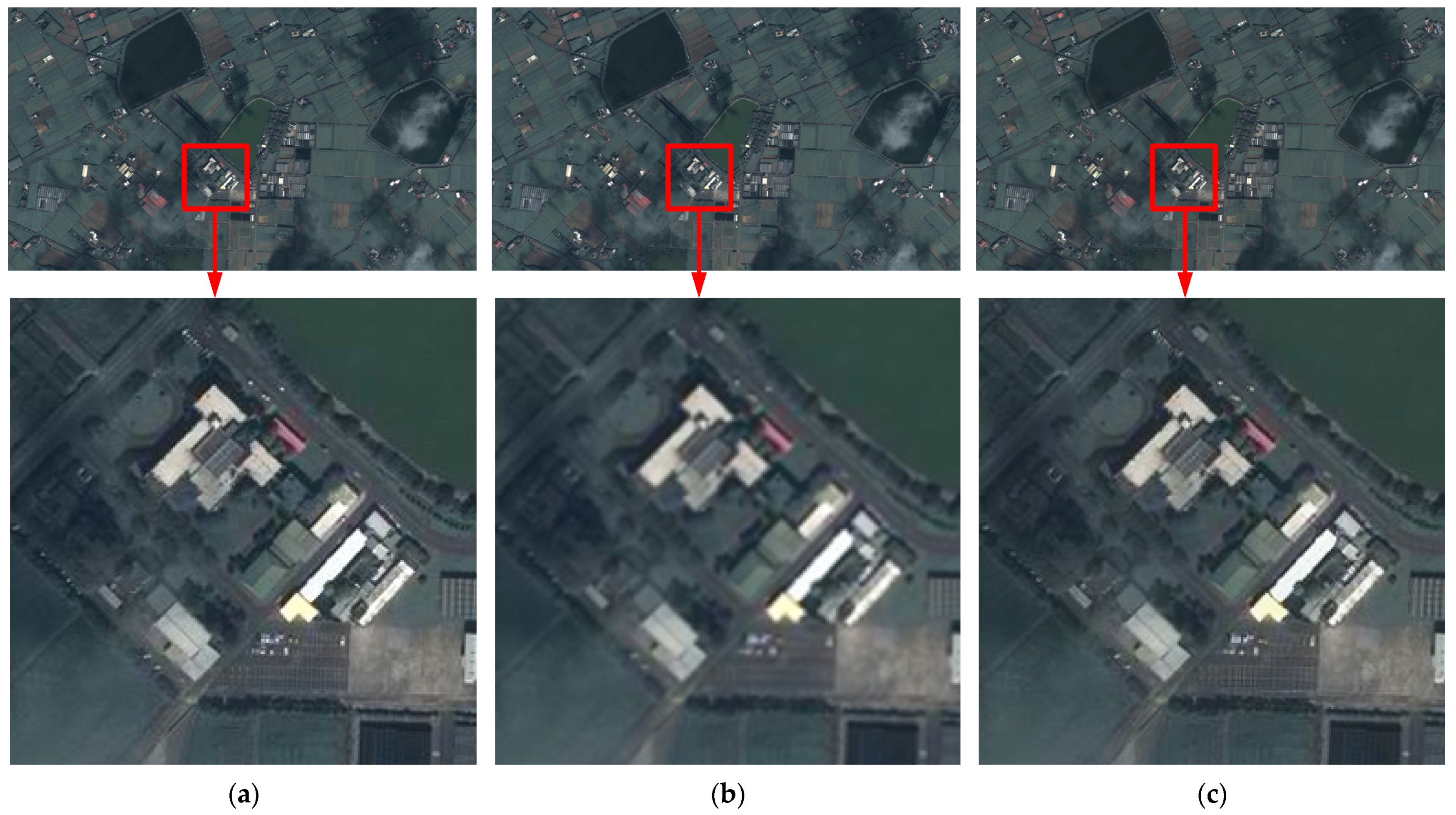
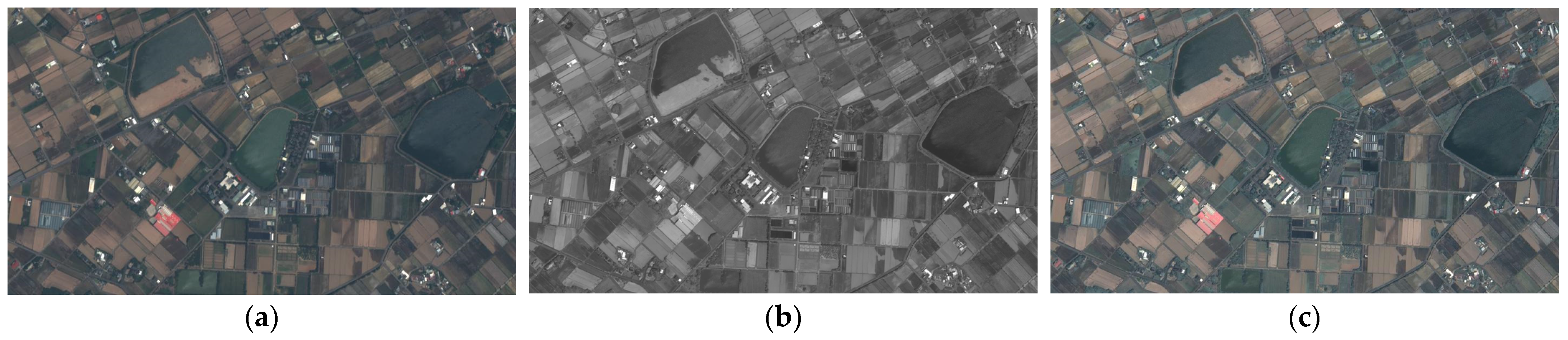
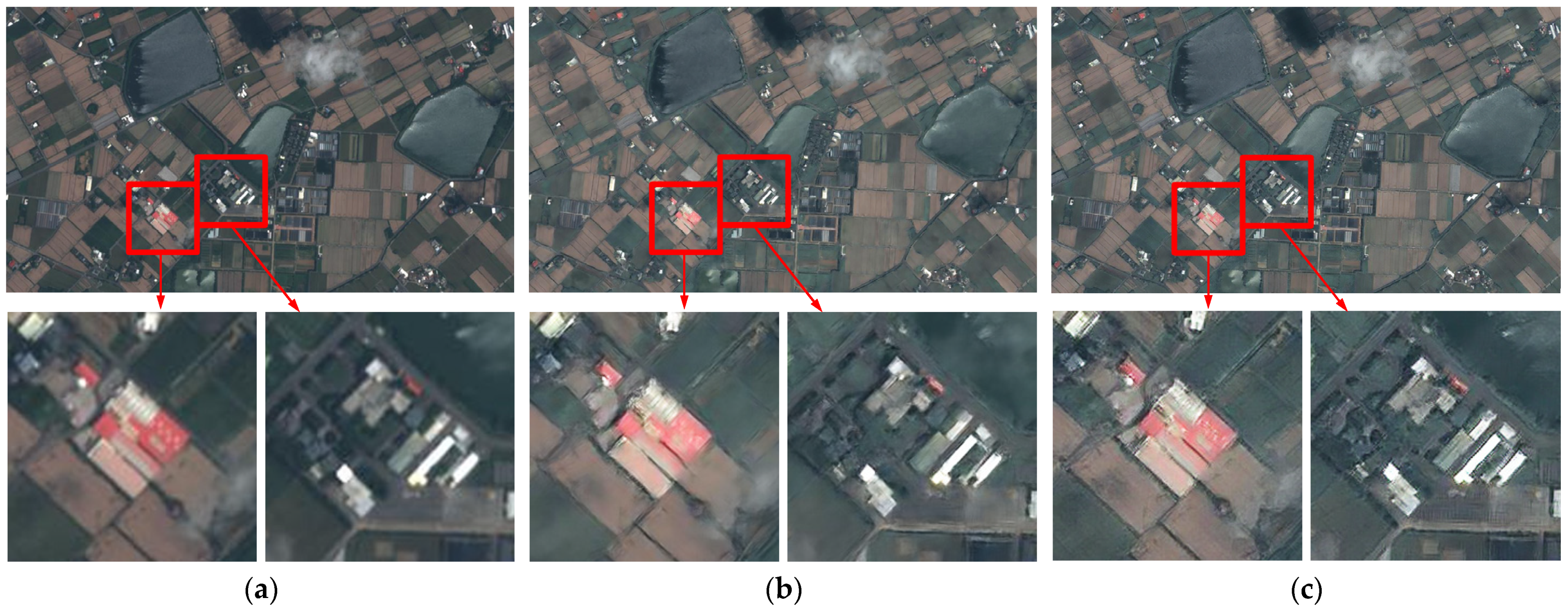
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Dataset
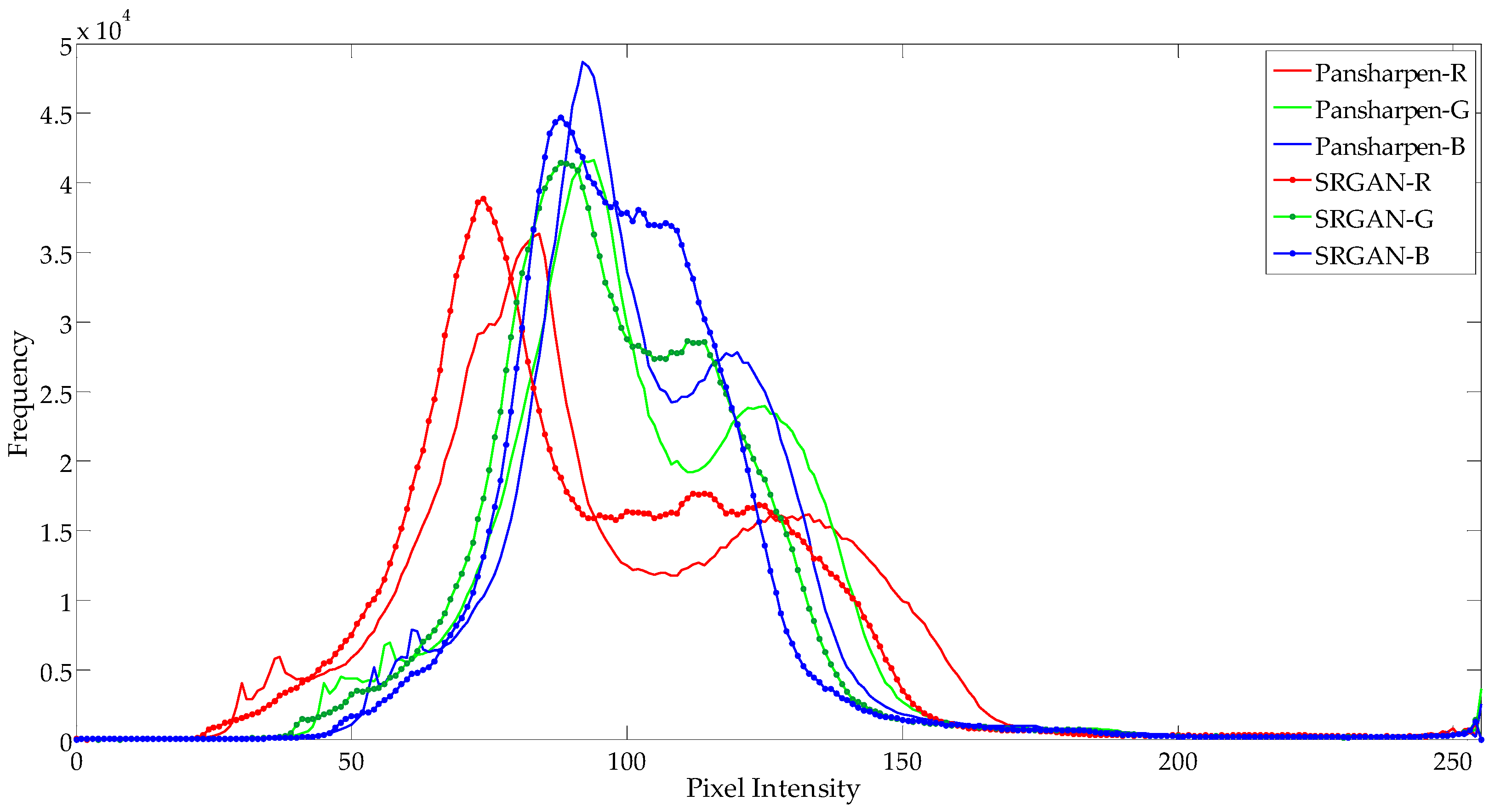
3.2. The Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Shih, M.-J. Interpretation of transplanted positions based on image super-resolution approaches for rice paddies. In Proceedings of the 2023 Sixth International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control (IS3C), Taichung, Taiwan, 30 June–3 July 2023; pp. 358–361. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, M.-J.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-C. Detection and interpretation of transplanted positions using drone’s eye-view images for rice paddies. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 3rd Eurasia Conference on IOT, Communication and Engineering (ECICE), Yunlin, Taiwan, 29–31 October 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gastineau, A.; Aujol, J.-F.; Berthoumieu, Y.; Germain, C. Generative adversarial network for pansharpening with spectral and spatial discriminators. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4401611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. PSGAN: A generative adversarial network for remote sensing Image Pan-Sharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 10227–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; He, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, F. Super-resolution reconstruction, recognition, and evaluation of laser confocal images of hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum endocytosis vesicles based on deep learning: Comparative study of SRGAN and SRResNet. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1146485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Husz, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Li, F.F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08155. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.08155 (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Bruna, J.; Sprechmann, P.; LeCun, Y. Super-resolution with deep convolutional sufficient statistics. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1511.05666. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05666 (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadiey, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozairz, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2014, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wright, J.; Huang, T.S.; Ma, Y. Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Space and Remote Sensing Research, National Central University. Available online: https://www.csrsr.ncu.edu.tw/ (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Lakhwani, K.; Murarka, P.D.; Chauhan, N.S. Color space transformation for visual enhancement of noisy color image. Int. J. ICT Manag. 2015, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, G.; Yamuna, G.; Nandhini, S. Real time implementation of RGB to HSV/HSI/HSL and its reverse color space models. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 6–8 April 2016; pp. 462–466. [Google Scholar]




| Neural Network | SRResNet | SRGAN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Truth | |||
| Pansharpened | 28.44 dB | 25.87 dB | |
| Adobe Photoshop | 17.10 dB | 16.97 dB | |
| Neural Network | SRResNet | SRGAN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | |||
| Execution Time | 7.97 s | 8.02 s | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, B.-H.; Jung, J.-H.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Shih, M.-J.; Tsai, F. Pansharpening Remote Sensing Images Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Eng. Proc. 2025, 92, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025092032
Chung B-H, Jung J-H, Chiou Y-S, Shih M-J, Tsai F. Pansharpening Remote Sensing Images Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 92(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025092032
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Bo-Hsien, Jui-Hsiang Jung, Yih-Shyh Chiou, Mu-Jan Shih, and Fuan Tsai. 2025. "Pansharpening Remote Sensing Images Using Generative Adversarial Networks" Engineering Proceedings 92, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025092032
APA StyleChung, B.-H., Jung, J.-H., Chiou, Y.-S., Shih, M.-J., & Tsai, F. (2025). Pansharpening Remote Sensing Images Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Engineering Proceedings, 92(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025092032








