Assessing Viscoelastic Parameters of Polymer Pipes via Transient Signals and Artificial Neural Networks †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transient Flow Governing Equations for Polymer Pipes
2.2. Multilayer Perceptron
2.3. CFP and PWS Estimation Based on Transient-Pressure-Based ANN Model
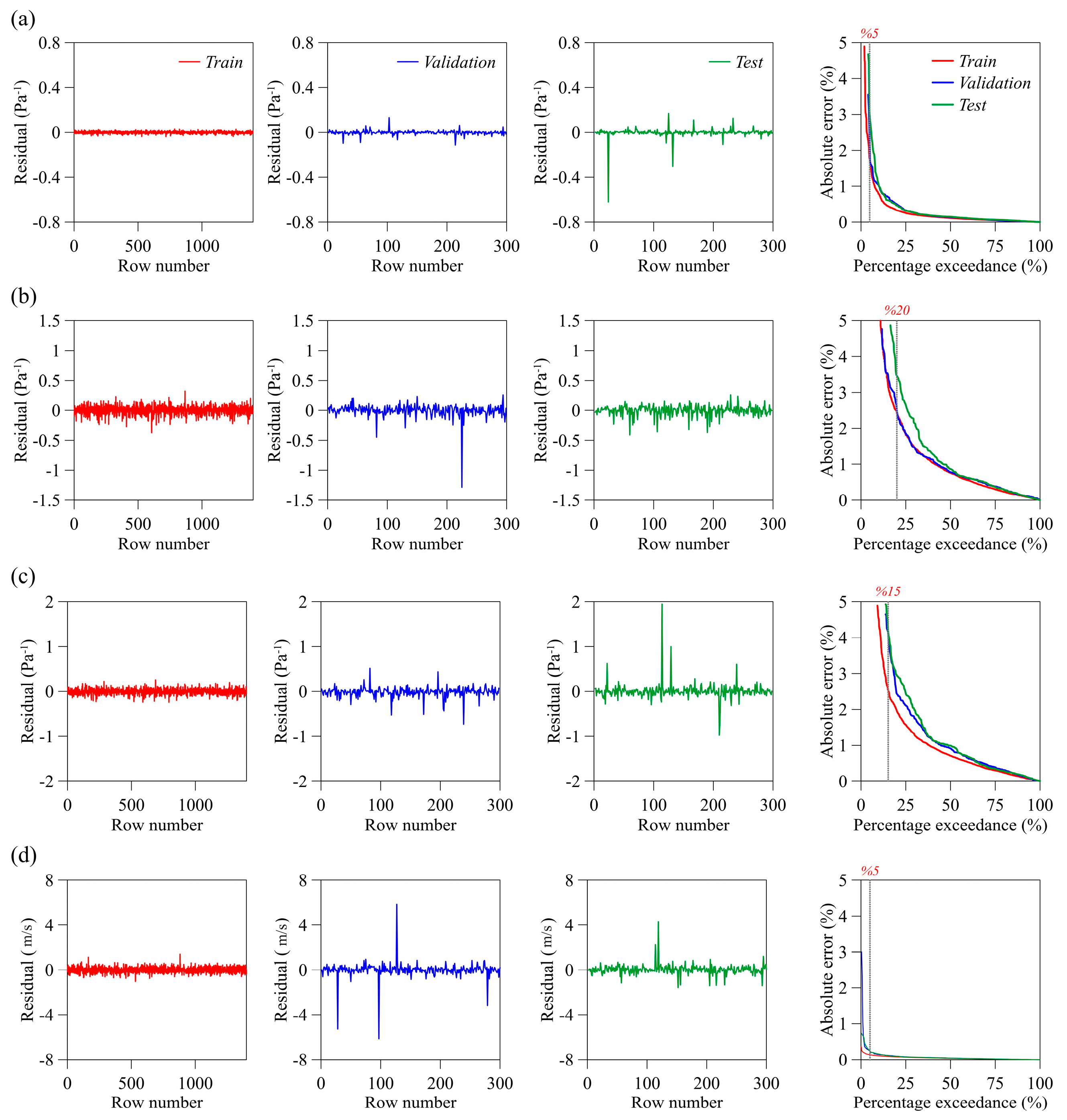
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddique, M.F.; Ahmad, Z.; Kim, J.M. Pipeline Leak Diagnosis Based on Leak-Augmented Scalograms and Deep Learning. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2023, 17, 2225577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Nguyen, T.K.; Kim, J.M. Leak Detection and Size Identification in Fluid Pipelines Using a Novel Vulnerability Index and 1-D Convolutional Neural Network. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2023, 17, 2165159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zecchin, A.C.; Lambert, M.F.; Simpson, A.R. Determination of the Creep Function of Viscoelastic Pipelines Using System Resonant Frequencies with Hydraulic Transient Analysis. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Duan, H.F.; Meniconi, S.; Urbanowicz, K.; Che, T.C.; Brunone, B. Multistage Frequency-Domain Transient-Based Method for the Analysis of Viscoelastic Parameters of Plastic Pipes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 146, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, J.; Ghidaoui, M.S.; Meniconi, S.; Brunone, B. Estimating Viscoelasticity of Pipes with Unknown Leaks. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 143, 106821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramat, A.; Fathi-Moghadam, M.; Zanganeh, R.; Rahmanshahi, M.; Tijsseling, A.S.; Jabbari, E. Experimental Investigation of Transients-Induced Fluid–structure Interaction in a Pipeline with Multiple-Axial Supports. J. Fluids Struct. 2020, 93, 102848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahmanshahi, M.; Duan, H.-F.; Keramat, A.; Rad, N.V.; Nadian, H.A. Assessing Viscoelastic Parameters of Polymer Pipes via Transient Signals and Artificial Neural Networks. Eng. Proc. 2024, 69, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069074
Rahmanshahi M, Duan H-F, Keramat A, Rad NV, Nadian HA. Assessing Viscoelastic Parameters of Polymer Pipes via Transient Signals and Artificial Neural Networks. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 69(1):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069074
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahmanshahi, Mostafa, Huan-Feng Duan, Alireza Keramat, Nasim Vafaei Rad, and Hossein Azizi Nadian. 2024. "Assessing Viscoelastic Parameters of Polymer Pipes via Transient Signals and Artificial Neural Networks" Engineering Proceedings 69, no. 1: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069074
APA StyleRahmanshahi, M., Duan, H.-F., Keramat, A., Rad, N. V., & Nadian, H. A. (2024). Assessing Viscoelastic Parameters of Polymer Pipes via Transient Signals and Artificial Neural Networks. Engineering Proceedings, 69(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069074





