Extraction of Lead from Hydrometallurgical Processing of Copper Shaft Flue Dust †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2021: Sand and Gravel (Industrial); U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; ISBN 9781411343986.
- Demand, V. Copper Drives Electric Vehicles. Available online: https://www.copper.org/publications/pub_list/pdf/A6191-ElectricVehicles-Factsheet.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Ballinger, B.; Stringer, M.; Schmeda-Lopez, D.R.; Kefford, B.; Parkinson, B.; Greig, C.; Smart, S. The vulnerability of electric vehicle deployment to critical mineral supply. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuiness, P.J.; Ogrin, R. Securing Technology-Critical Metals for Britain: Ensuring the United Kingdom’s Supply of Strategic Elements & Critical Materials for a Clean Future; University of Birmingham: Birmingham, UK, 2021; ISBN 9780704429697. [Google Scholar]
- Top Ten Global Copper Producers 2017–2020. Available online: https://nma.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Top-Ten-Global-Copper-Mine-Producers-by-Equity-Shares-2017-to-2021.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Orac, D.; Laubertova, M.; Piroskova, J.; Klein, D.; Bures, R.; Klimko, J. Characterization of dust from secondary copper production. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2020, 56, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oráč, D.; Klimko, J.; Klein, D.; Pirošková, J.; Liptai, P.; Vindt, T.; Miškufová, A. Hydrometallurgical Recycling of Copper Anode Furnace Dust for a Complete Recovery of Metal Values. Metals 2022, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhan, O. Leaching and cementation of heavy metals from electirc arc furnance dust in alkaline medium. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 78, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halli, P.; Hamuyuni, J.; Leikola, M.; Lundström, M. Developing a sustainable solution for recycling electric arc furnace dust via organic acid leaching. Miner. Eng. 2018, 124, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halli, P.; Agarwal, V.; Partinen, J.; Lundström, M. Recovery of Pb and Zn from a citrate leach liquor of a roasted EAF dust using precipitation and solvent extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirošková, J.; Laubertová, M.; Miškufová, A.; Oráč, D. Hydrometallurgical treatment of copper shaft furnace dust for lead recovery. World Metall. ERZMETALL 2018, 71, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ružičková, M.; Laubertová, M. Charakterizácia Šachtových Úletov zo Sekundárnej Výroby Medi a Teoretický Návrh Ich Spracovania; Technická univerzita v Košiciach: Košice, Slovensko, 2023; pp. 151–158. ISBN 978-80-553-4392-1. [Google Scholar]
- Fedoročková, A.; Raschman, P.; Sučik, G.; Ivánová, D.; Kavuličová, J. Utilization of chrysotile-type tailings for synthesis of high-grade silica by controlled precipitation. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2016, 37, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubertová, M.; Kollová, A.; Trpčevská, J.; Plešingerová, B.; Briančin, J. Hydrometallurgical Treatment of Converter Dust from Secondary Copper Production: A Study of the Lead Cementation from Acetate Solution. Minerals 2021, 11, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
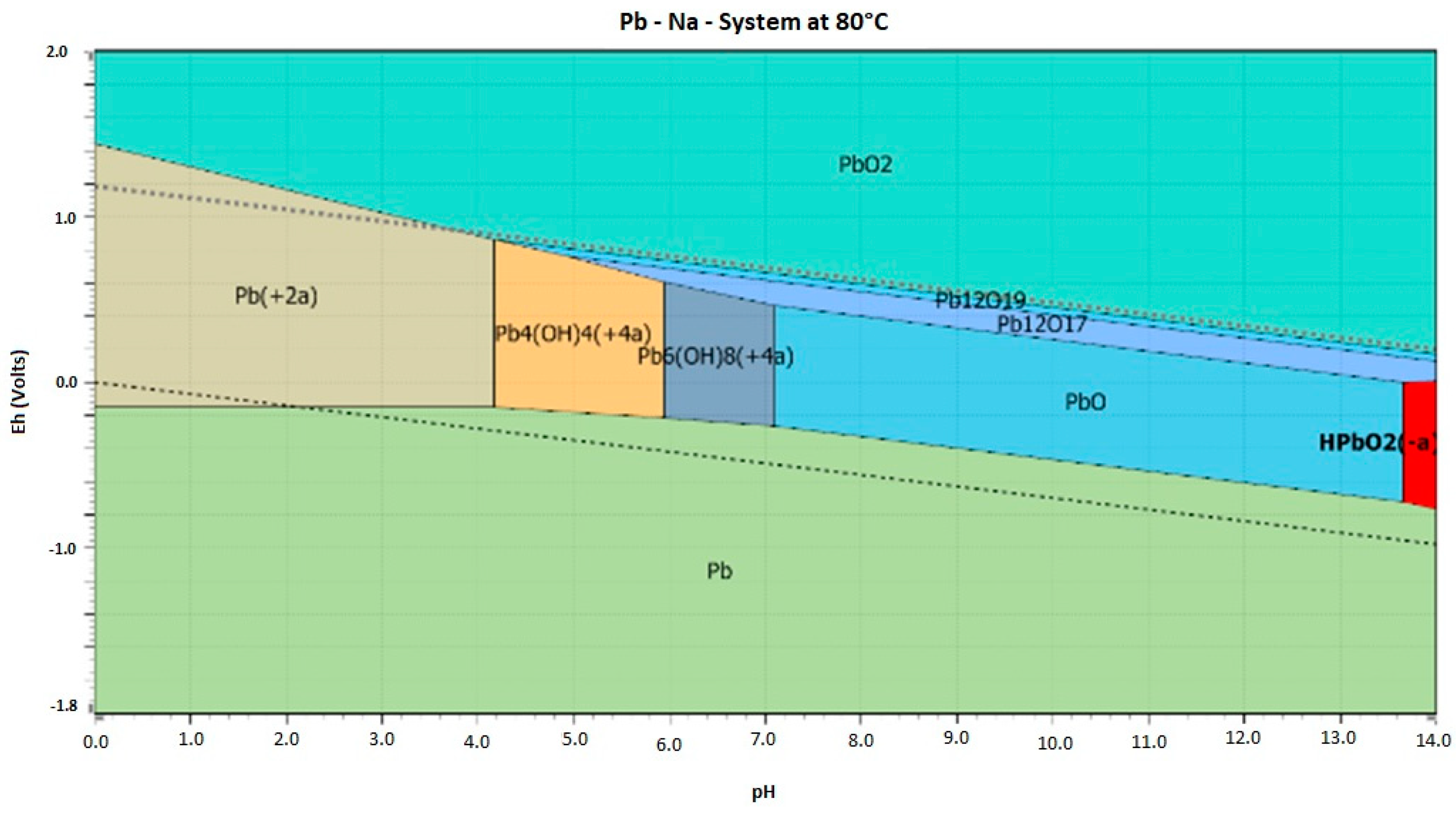
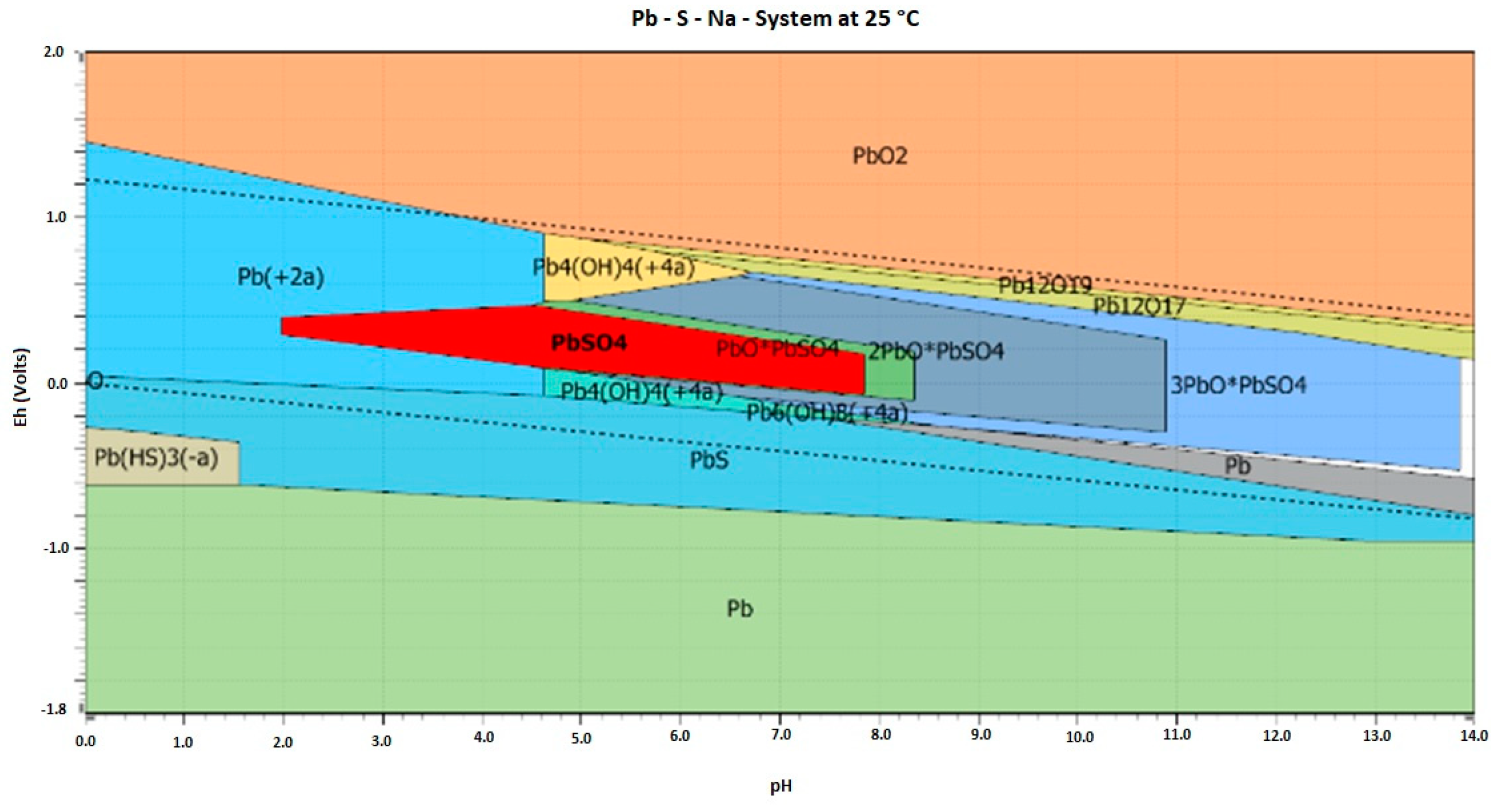
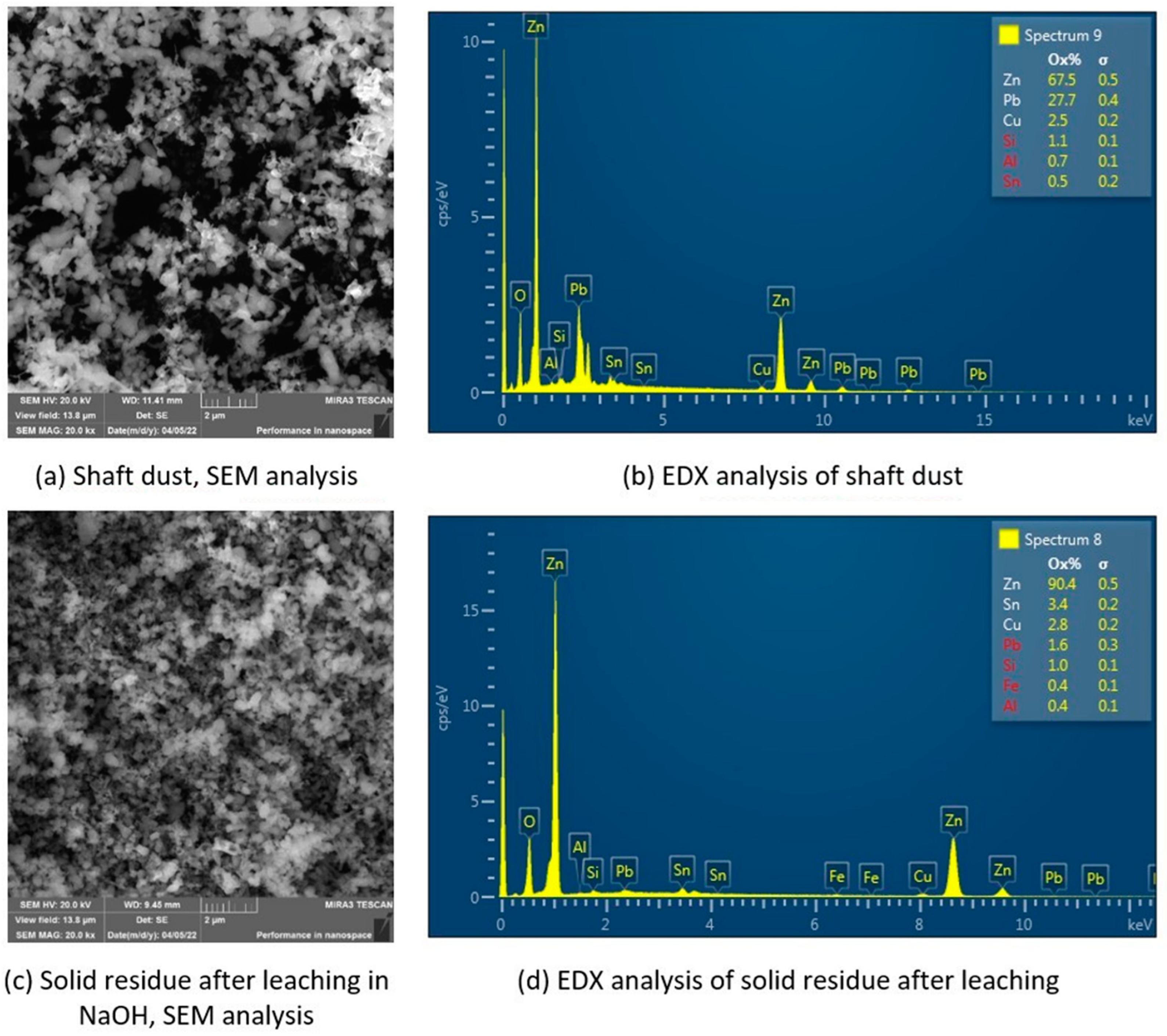
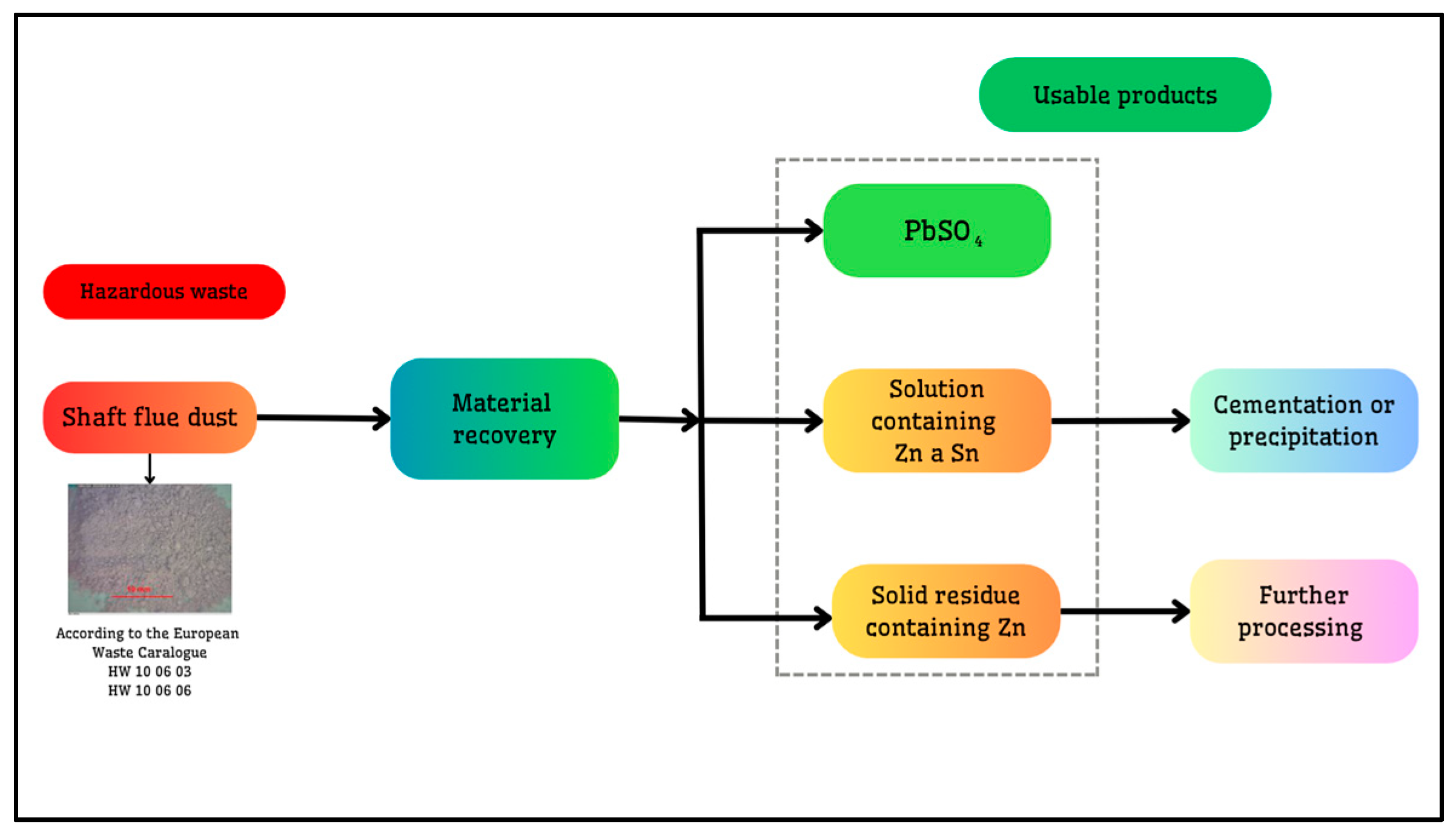
| pH | Pb (μg·mL−1) | Zn (μg·mL−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leachate (solution before precipitation) | 14 | 4968 | 622 |
| Solution after precipitation | 7 | 6.07 | 283 |
| 3 | 1.62 | 589 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruzickova, M.; Laubertova, M.; Trpcevska, J.; Kollova, A.; Takacova, Z.; Vindt, T. Extraction of Lead from Hydrometallurgical Processing of Copper Shaft Flue Dust. Eng. Proc. 2024, 64, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024064001
Ruzickova M, Laubertova M, Trpcevska J, Kollova A, Takacova Z, Vindt T. Extraction of Lead from Hydrometallurgical Processing of Copper Shaft Flue Dust. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 64(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024064001
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuzickova, Michaela, Martina Laubertova, Jarmila Trpcevska, Alexandra Kollova, Zita Takacova, and Tomas Vindt. 2024. "Extraction of Lead from Hydrometallurgical Processing of Copper Shaft Flue Dust" Engineering Proceedings 64, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024064001
APA StyleRuzickova, M., Laubertova, M., Trpcevska, J., Kollova, A., Takacova, Z., & Vindt, T. (2024). Extraction of Lead from Hydrometallurgical Processing of Copper Shaft Flue Dust. Engineering Proceedings, 64(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024064001







