CO2 Absorption Using Potassium Carbonate as Solvent †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rate Based Method
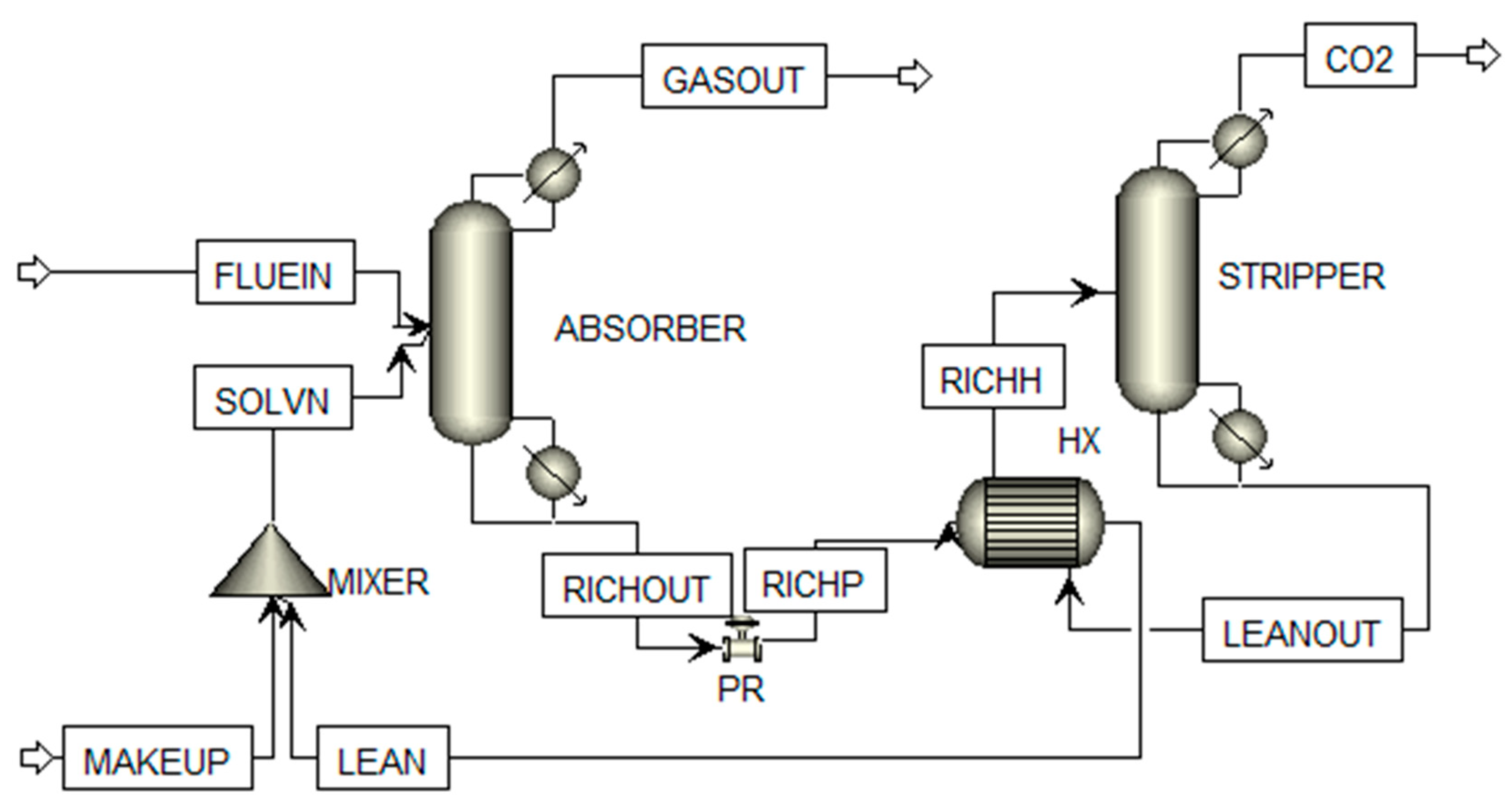
2.2. Simulation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borowski, P.F. Management of Energy Enterprises in Zero-Emission Conditions: Bamboo as an Innovative Biomass for the Production of Green Energy by Power Plants. Energies 2022, 15, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, P.F.; Patuk, I.; Bandala, E.R. Innovative Industrial Use of Bamboo as Key “Green” Material. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; Olabi, A.G.; Sayed, E.T.; Elsaid, K.; Abdelkareem, M. Progress in carbon capture technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.; Knuutila, H.K.; Gu, S. ASPEN PLUS simulation model for CO2 removal with MEA: Validation of desorption model with experimental data. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4693–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, F.; Zabiri, H.; Ng, N.K.; Shariff, A.M. CO2 removal via promoted potassium carbonate: A review on modeling and simulation techniques. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2018, 76, 236–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, T.N.; Azarpour, A.; Akbari, V.; Alwi, S.R.; Manan, Z.A. CO2 capture with potassium carbonate solutions: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 41, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.; Anderson, C.; Hooper, B. Comparative life cycle assessment of potassium carbonate and monoethanolamine solvents for CO2 capture from post combustion flue gases. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 28, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, J.; Idem, R.; Gelowitz, D.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Parrain, G.; Bonneau, A. Corrosion in MEA units for CO2 capture: Pilot plant studies. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuenphan, T.; Yurata, T.; Sema, T.; Chalermsinsuwan, B. Techno-economic sensitivity analysis for optimization of carbon dioxide capture process by potassium carbonate solution. Energy 2022, 254 Pt A, 124290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamborg, E.S.; Kersten, S.R.; Versteeg, G.F. Absorption and desorption mass transfer rates in non-reactive systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-H.; Zhang, N.; Smith, R. Rate-Based Modelling of CO2 Capture Process by Reactive Absorption with MEA. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 39, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chikukwa, A.; Enaasen, N.; Kvamsdal, H.M.; Hillestad, M. Dynamic modeling of post-combustion CO2 capture using amines–A review. Energy Procedia 2012, 23, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.-C. Thermodynamic modeling for CO2 absorption in aqueous MDEA solution with electrolyte NRTL model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, L.; Mahmoud, A.; Sunarso, J. Aspen Plus simulation-based parametric study of Benfield process using hot potassium carbonate promoted by diethanolamine. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 778, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, F.; Zabiri, H.; Harun, N.; Shariff, A.M. CO2 Removal via an Environmental Green Solvent, K2CO3–Glycine (PCGLY): Investigative Analysis of a Dynamic and Control Study. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18213–18228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayittey, F.K.; Saptoro, A.; Kumar, P.; Wong, M.K. Parametric study and optimisation of hot K2CO3-based post-combustion CO2 capture from a coal-fired power plant. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Absorber Temperature (°C) | 35 |
| Absorber Pressure (bar) | 1 |
| Stripper Temperature (°C) | 80, 85, 100 |
| Stripper Pressure (bar) | 0.3, 0.7, 1 |
| Gas flow rate (slpm) | 1 |
| Solvent flow rate (slpm) | 0.1 |
| Concentration of K2CO3 (%v/v) | 15, 20, 25 |
| Concentration of CO2 (%v/v) | 15 |
| Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stripper pressure | 1.6902 | 0.8451 | 101.3366 | 7.9357 × 10−12 |
| Stripper temperature | 0.3185 | 0.1592 | 2.0396 | 1.5562 × 10−5 |
| Error | 0.1835 | 0.0083 |
| Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent concentration | 2.1473 × 10−6 | 1.0736 × 10−6 | 20.0785 | 7.5094 × 10−6 |
| Error | 1.2833 × 10−6 | 5.3472 × 10−8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karali, D.; Peloriadi, K.; Margaritis, N.; Grammelis, P. CO2 Absorption Using Potassium Carbonate as Solvent. Eng. Proc. 2023, 31, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2022-13824
Karali D, Peloriadi K, Margaritis N, Grammelis P. CO2 Absorption Using Potassium Carbonate as Solvent. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 31(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2022-13824
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarali, Dimitra, Konstantina Peloriadi, Nikolaos Margaritis, and Panagiotis Grammelis. 2023. "CO2 Absorption Using Potassium Carbonate as Solvent" Engineering Proceedings 31, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2022-13824
APA StyleKarali, D., Peloriadi, K., Margaritis, N., & Grammelis, P. (2023). CO2 Absorption Using Potassium Carbonate as Solvent. Engineering Proceedings, 31(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2022-13824









