Abstract
This study, based on a 25-year dataset (2000–2025) collected from the Scopus database, provides a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of the intellectual structure of research on emotion recognition, prediction, and skills. Using bibliographic coupling as the primary method, the analysis examines the titles, abstracts, keywords, frameworks, and review literature, presenting the most significant articles in this area, along with the headings of 202 relevant papers. The study investigates the temporal distribution of research outputs, focusing particularly on trends from the last decade. To visualize the scientific landscape, the study uses VOSviewer to map co-authorship, keyword co-occurrence, and citation networks. The analysis highlights the most prolific journals, influential authors, dominant subject areas, and frequently used keywords. Additionally, it identifies the algorithms used for emotion recognition in predicting soft skills, along with the objectives of the studies, as well as the data and results involved. The study also identifies the leading countries and educational institutions contributing to this research domain. The findings offer a detailed overview of the field’s development and intellectual trends, providing insights and recommendations for future research directions. This research also helps to understand how emotion recognition can contribute to human development across various domains, as discussed in this article.
1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of technology and the changing landscape of the professional world, soft skills have become increasingly essential for communication, collaboration, and career success. While technology has replaced human involvement in many domains, soft skills such as stress management, communication, leadership, and critical thinking remain uniquely human and indispensable for professional development [1]. Developing these skills is particularly crucial for students, as evidenced by a study conducted in Europe, where 1372 engineers with bachelor’s, master’s, or diploma degrees rated engineering competencies for graduate performance. The findings revealed significant gaps in communication, leadership, and social skills (Bodmer et al., 2002) [2]. These gaps highlight the importance of soft skills in students’ lives, particularly in bridging the difference between the competencies required for employment and those possessed by graduates (Male, Bush & Chapman, 2010) [3]. Furthermore, Masoka and Selesho (2014) [4] pointed out that limited efforts have been made in South Africa to develop employability skills, despite their crucial role in today’s dynamic job market. As Kruss (2007) [5] noted, contemporary jobs are not as narrowly defined as in the past but rather emphasize service-oriented tasks that require strong social and information-handling skills. Employers now seek graduates with a broader range of competencies, including both job-specific and organizational/social skills (Miller, Biggart & Newton, 2013) [6]. Consistently, researchers argue that employers increasingly demand behavioral and cognitive competencies alongside subject-specific knowledge [6]. To address this issue, this study explores how emotion recognition can contribute to the development of soft skills. Emotions play a significant role in learning processes, affecting memory and decision-making (Pekrun, 1992) [7]. The impact of emotions on learning has long been recognized in traditional classroom settings (Bower, 1981) [8] and has recently gained attention in intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) (Sarrafzadeh, Alexander, Dadgostar, Fan, & Bigdeli, 2008) [9]. Emotion recognition, an emerging field in human–computer interaction, offers promising advancements in enhancing online interactions and communication [10].
In order to address these aims, the review is divided into two major parts: systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. The bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review answer the following major research questions:
- What is the distribution of studies addressing emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction from 2000 to 2025?
- What are the most relevant journals and authors contributing to research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?
- Which are the most-cited articles in research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?
- Which countries have been the most productive in publishing research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?
- What are the significant educational institutions leading research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?
- What are the primary research keywords in the field of emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction from 2000 to 2025?
- What are the trends and collaborative networks in research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?
- What are the most important subject areas involving emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?
By addressing these questions, this study aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of emotion recognition in predicting soft skills, thereby contributing to both academic research and practical applications in educational and professional settings.
2. Method
2.1. Research Design
Bibliometric analysis was conducted to map research trends, leading countries, academic institutions, key publications, and influential authors contributing to this domain. Additionally, the study identified common research themes and systematically examined the most widely. For the bibliometric analysis, VOSviewer, version 1.6.19 (Van Eck & Waltman, 2010) was extensively used for data visualization and network analysis, enabling the creation and management of bibliometric networks. Co-authorship, citations, and bibliographic coupling were analyzed to reveal research collaborations and influential works. Articles for this review were sourced from databases such as Scopus, following predefined inclusion criteria focusing on studies that leverage emotion recognition in the prediction of soft skills. By leveraging VOSviewer for bibliometric mapping, this study offers a comprehensive understanding of global research advancements in this field. The use of this tool enabled the identification of the most influential research contributions, geographic trends, and strategic publishing patterns.
2.2. Identification
2.2.1. Database Selection
This review was conducted on 14 January 2025. The Scopus [11] database was selected as the primary database for this review, as it is considered one of the best sources for assessing scientific publications.
2.2.2. Search Strings
To retrieve references from the Scopus database, we identified keywords related to our study topic. The main search query was constructed as follows: (“emotion recognition” OR “emotion detection” OR “affective computing” OR “emotion analysis” OR “sentiment analysis” OR “emotional intelligence” OR “emotion-based analysis” OR “emotion classification” OR “facial emotion recognition” OR “emotion understanding” OR “emotion perception” OR “affective state recognition” OR “emotion modeling” OR “emotion sensing” OR “emotion-aware systems” OR “emotion recognition systems” OR “emotion detection algorithms”) AND (“soft skills” OR “interpersonal skills” OR “employability skills” OR “non-cognitive skills” OR “behavioral competencies” OR “21st-century skills” OR “collaborative skills” OR “communication skills” OR “leadership skills” OR “critical thinking skills” OR “problem-solving skills” OR “creativity” OR “teamwork skills” OR “adaptability” OR “emotional intelligence skills” OR “professional development skills” OR “social-emotional learning” OR “transferable skills”) AND (“prediction” OR “predictive model” OR “assessment” OR “forecasting” OR “evaluation” OR “data-driven prediction” OR “competency mapping” OR “skills analysis” OR “skills forecasting” OR “behavioral prediction” OR “predictive analytics” OR “psychometric evaluation” OR “performance modeling” OR “machine learning models” OR “statistical modeling” OR “AI-driven prediction” OR “data mining” OR “behavioral forecasting” OR “learning analytics” OR “computational prediction” OR “modeling emotional intelligence” OR “predictive performance analysis” OR “soft skills assessment” OR “workforce prediction”), combined using the Boolean operator “AND”, ”OR” in the “Article title, abstract, keyword” search field. This query was combined using the Boolean operators “AND” and “OR” and applied to the “Article title, abstract, keyword” search field in Scopus. The choice of these keywords was guided by our objective to focus on the relationship between emotion recognition and soft skills, as well as the role of emotion recognition in predicting soft skills. This comprehensive selection of keywords ensures the inclusion of the most relevant references within our domain of interest.
2.2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
This study focuses exclusively on English-language publications, as the majority of relevant literature in the field is published in this language. The selected time frame spans from 2000 to 2025, providing comprehensive insights into emotion recognition, soft skills, and methods utilizing emotion recognition for predicting soft skills, along with their applications across various domains and disciplines. To ensure a broad and inclusive review of the literature, all types of sources were included, enabling the capture of diverse perspectives and the most recent contributions. Publications from all subject areas were considered to support a multidisciplinary understanding of the topic. Additionally, open-access sources were prioritized to maximize accessibility and inclusivity, ensuring that findings are representative of the global research landscape.
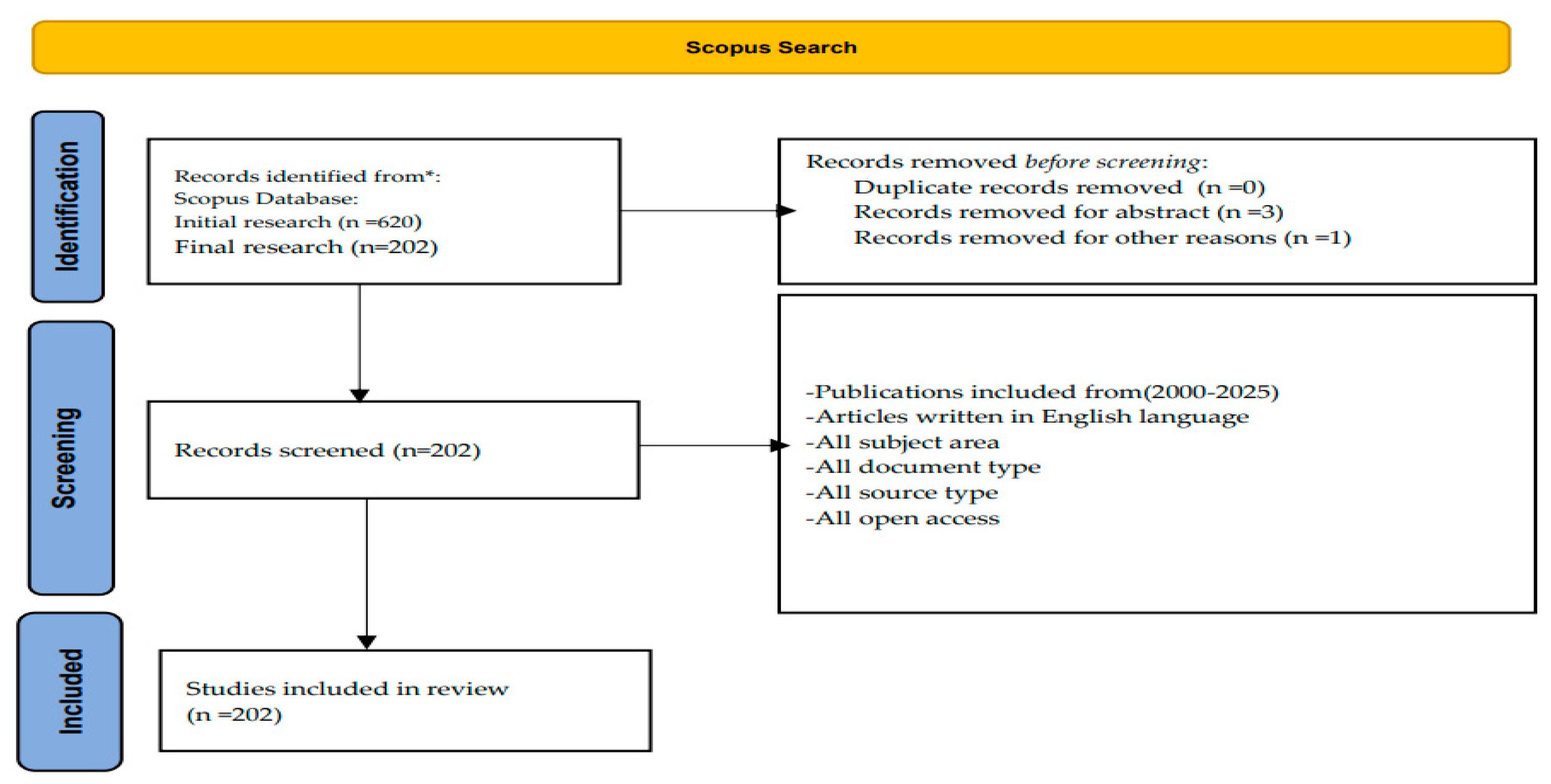
The initial search, using the main keywords, returned 620 documents. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria outlined in Table 1, the number of publications was reduced to 202 in the final selection, with 418 documents being excluded.

Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
- Inclusion and Reporting
The PRISMA framework [12] serves as the basis for reporting the results of this bibliometric investigation (see Figure 1). As a result, the research question will be addressed in the next section.
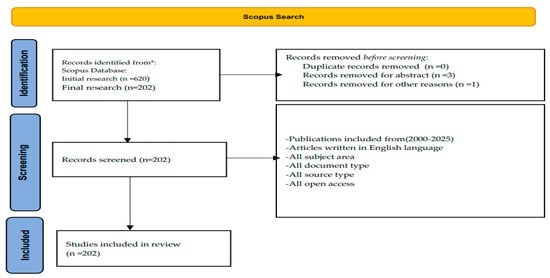
Figure 1.
PRISMA framework for this review. (* Only publications written in English were considered).
3. Result
To identify trends and patterns that give a wider context to the discussion of specific findings, we use bibliometric. This not only contributes to the logical consistency of our findings but also leads to a comprehensive insight into the topic. The bibliometric analysis identifies overarching developments and recurring trends in the field. In this context, we emphasize bibliometric analysis as a powerful methodological tool for defining emotion recognition in the prediction of soft skills. Through the examination of relevant literature, we can establish a comprehensive database that researchers can use in the rapidly evolving field of soft skills prediction.
3.1. The Distribution by Years
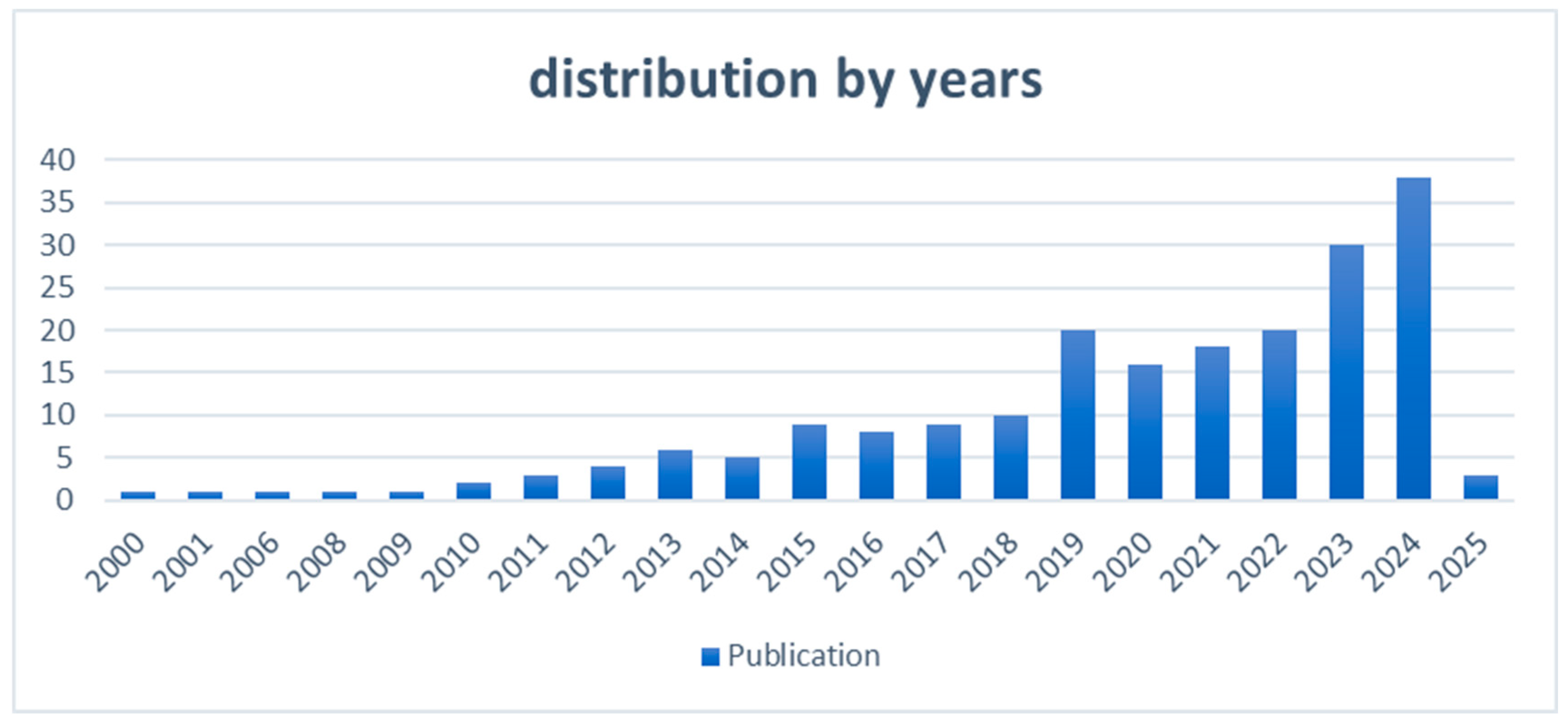
“What is the distribution of studies addressing emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction from 2000 to 2025?” is the research topic that is addressed in this section. Notable patterns in publications during the 25-year period are revealed by the data analysis. After 2012, there was a noticeable rise in the quantity of publications, suggesting that interest in these subjects was increasing.
The distribution of publications across time is depicted in Figure 2, with 2024 having the most publications (38 papers), indicating a peak in scholarly interest. With just three publications, 2025, on the other hand, indicates a little drop, most likely as a result of insufficient data gathering for the year. There was only one publication in the dataset’s first year, 2000, underscoring the impressive rise in scholarly interest over time. All things considered, the pattern shows a consistent increase in research effort concerning soft skills and emotion perception, highlighting their increasing significance in interdisciplinary studies.
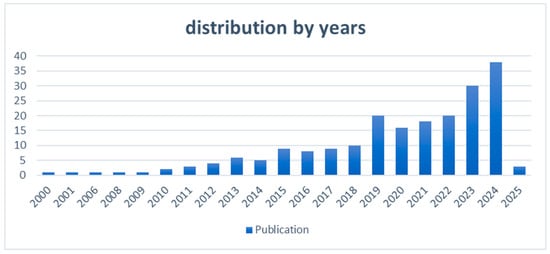
Figure 2.
Distribution of publications by years (2000–2025).
3.2. The Most Relevant Journals and Authors
This section addresses the second research question: “What are the most relevant journals and authors contributing to research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?” Ranking the top 9 journals in this subject by the quantity of papers published between 2000 and 2025 is shown in Table 2. These journals have made significant contributions to advancing knowledge in the domains of emotion recognition, soft skills, and predictive methods.

Table 2.
Top 9 Journals in Research on Emotion Recognition and Soft Skills.
Table 2 demonstrates that “IEEE Access“ exhibits the highest productivity among journals addressing tools for “emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction methods,” with a citation rate of 9.8. It is followed by the “Journal of Nursing Management”, which has a citation rate of 9.4. In terms of total publications (TP), “PLOS ONE” leads with 62,463 articles in the subject area, while the “Journal of Nursing Management” records the lowest number of publications, with 1009. Regarding total citations (TC), “IEEE Access” ranks first with 484,743 citations, whereas the “Journal of Nursing Management” has the fewest, with 9478 citations. Journals with a high number of citations, substantial publication outputs, and notable contributions have played a significant role in advancing research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction methods. These findings highlight the impact of prominent journals in shaping this interdisciplinary field.
- The most Prolific Authors
The information in Table 3 indicates some authors who have made substantial contributions to this area of study.

Table 3.
The top 10 authors in the field.
Table 3 provides a comprehensive compilation of distinguished authors who have written about emotion, skills, and prediction. This paper examines the top 10 prominent authors who have made significant contributions to the study of emotion and skills. Among them, Linares, J.J.G. stands out as a notable figure. His publication record is impressive, with 89 papers, an outstanding H-index of 21, and a total of 1637 citations. He is affiliated with Universidad Autónoma de Chile. Table 3 serves as a comprehensive compilation of the most productive authors who have extensively contributed to the field of emotion, skills, and prediction. These renowned authors are accompanied by numerous significant collaborators from various nations and organizations, whose research and expertise continue to shape the field.
3.3. The Most-Cited Articles
To address the third question of the study, “Which are the most-cited articles in research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction, and what are their main contributions?”, Table 4 below presents the 10 most-cited articles from eight different publishers. These articles were selected based on their scientific impact, measured by the number of citations.

Table 4.
Top 10 most cited research papers by publication period.
With 151 citations overall, the 2017 article is the most cited. “Emotional intelligence: A vital prerequisite for recruitment in nursing” is the second most cited article with 145 citations, followed by that with 124 citations. With 113 citations, the 2000 paper “Measuring emotional intelligence of medical school applicants [24]” comes in at number four. The article names, journals of publication, number of citations, year of publication, and major authors are all listed in the table. These books highlight the key ideas that have influenced this field of study and are among the most significant contributions.
3.4. The Most Significant Countries
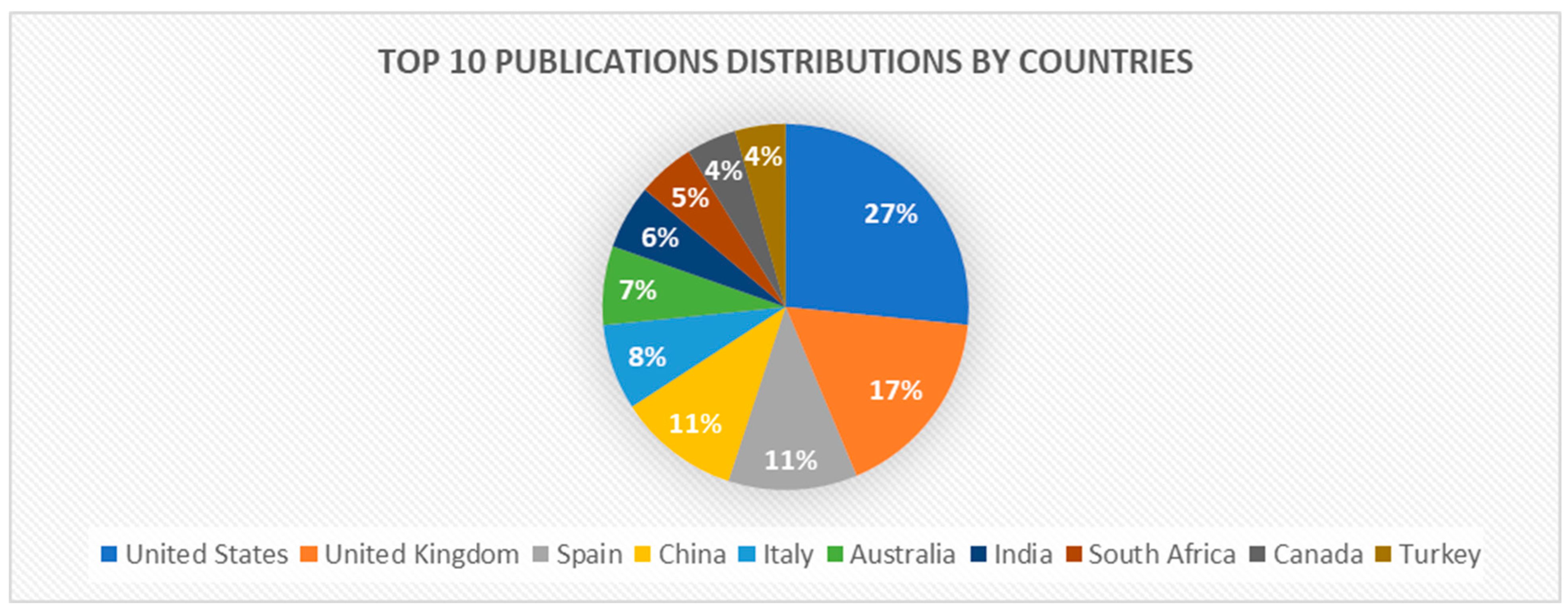
To look into the study’s fourth question: “Which countries have been the most productive in publishing research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?” A review of the data indicates a wide range of worldwide effect, as Figure 3 illustrates.
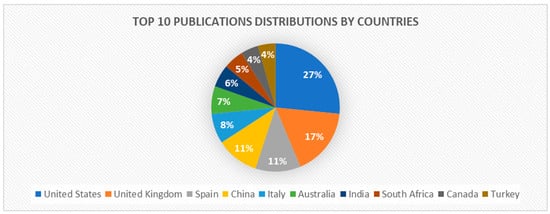
Figure 3.
Top 10 Publications distributions by countries.
The United States leads the top ten countries by number of publications, with 42 articles, or 27% of all publications in this area of research. This is the most significant distribution of publications. The United Kingdom is second, with 27 articles, or 17% of all publications. The below is the publication breakdown that was released in this field of study: Spain represented 11% (18), China represented 11% (17), Italy represented 8% (12), Australia represented 7% (11) and India represented 6% (9) and South Africa represented 5% (8).Turkey, at 4% (7), and Canada, at 4% (7), are the lowest. Together, these nations contribute significantly to the literature on emotion recognition and soft skills around the world. This demonstrates the widespread diversi3ty of interest outside the continent. The variety in contributions shows the significance of the research area globally.
3.5. The Most Significant Educational Institutions
As shown in Table 5, the data provided in response to the fourth research question, “What are the significant educational institutions leading research on emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction? ”, highlights several educational institutions.

Table 5.
The most significant educational institutions in this research.
Table 5 lists the top ten academic institutions that have contributed to the field of “emotion recognition and soft skills”. Spain leads in this research area, with one of the top four institutions being Universidad de Almería, which has contributed a total of 6 publications. Chile ranks second, with 5 publications overall. The United States comes in third, represented by Duke University School of Medicine, with 4 publications. In fourth place is the University of Johannesburg (South Africa), with 3 publications.
3.6. The Primary Research Keywords
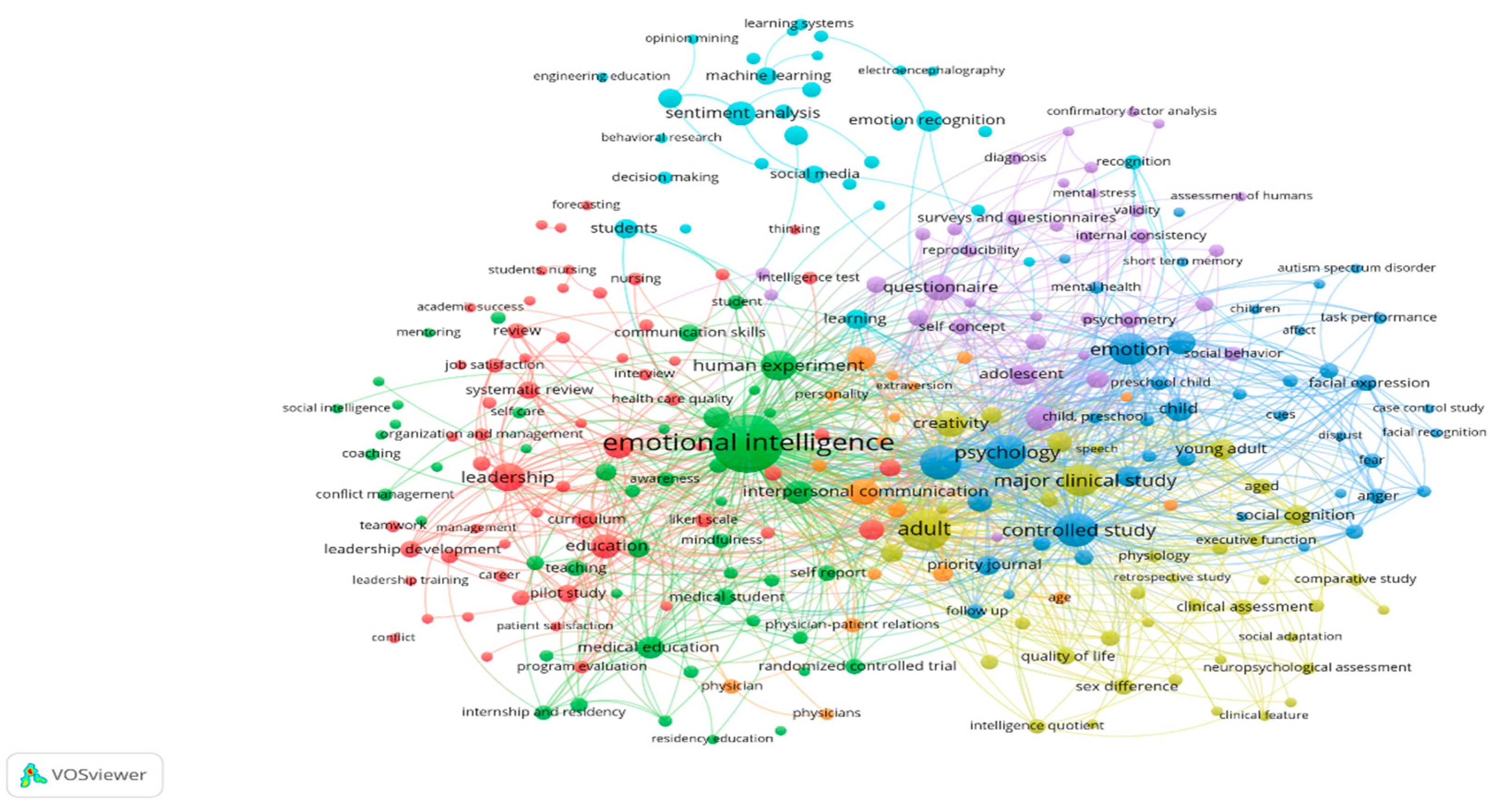
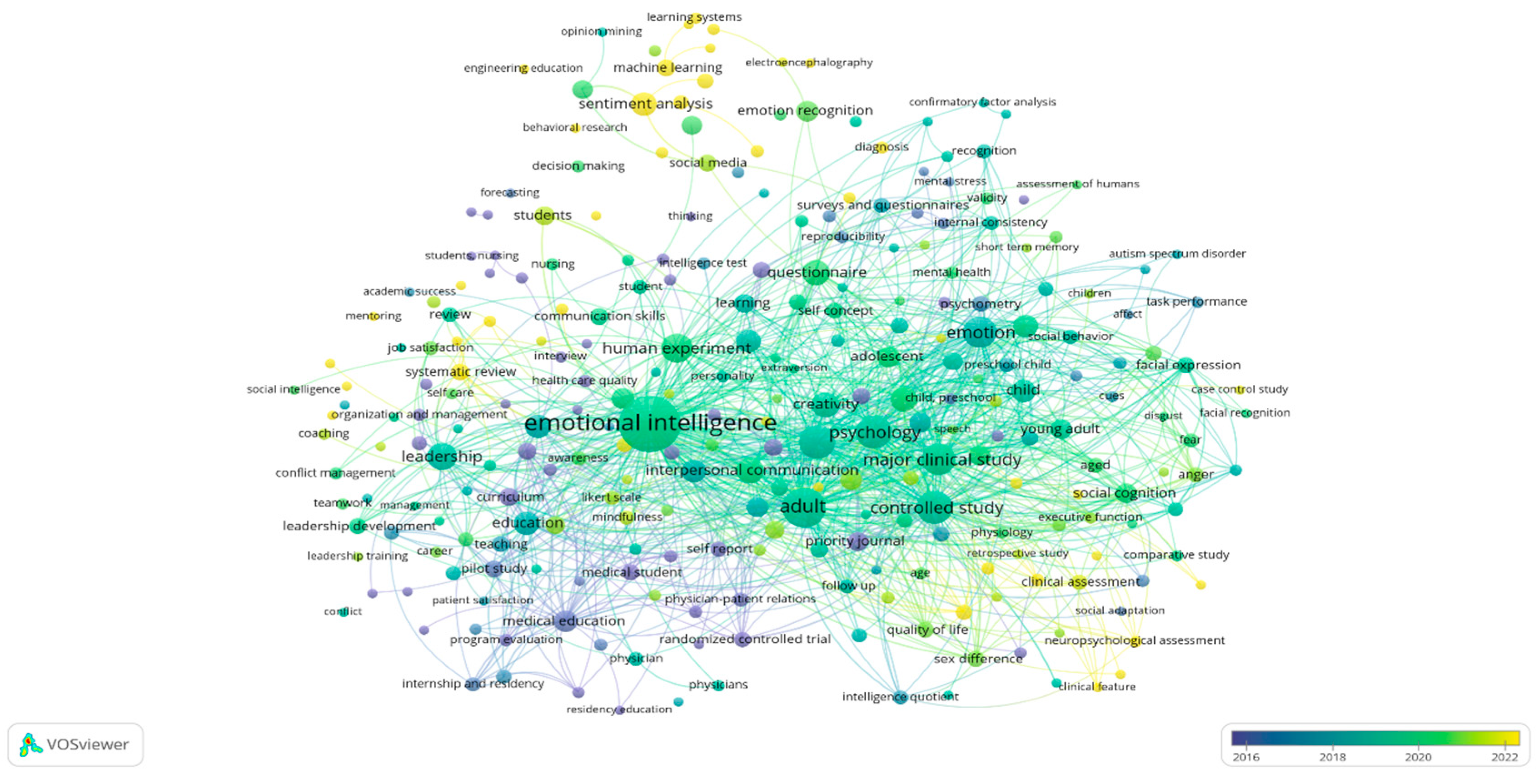
Answer to the fifth question: “What are the primary research keywords over the last decade in the field of personality, emotions, and skills?” may display the most significant research phrases together with how frequently they appear in Figure 4.
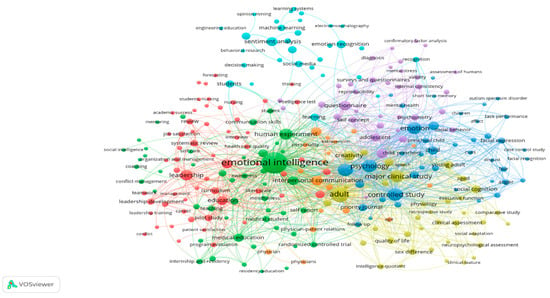
Figure 4.
The primary research keywords and their occurrences.
The graph presents widely used terms in the field of emotion recognition and soft skills research. It provides a close-up visualization of the main topics and their interrelations, and it identifies the most dominant concepts within this field. Among the terms, the most conspicuous is “emotional intelligence,” confirming its important role in the soft skills and emotion recognition literature. The term appears 110 times with a total link strength of 310, indicating its strong interconnectivity with the other key words. Other words that stand out include “students,” “communication skills,” and “recognition,” indicating a strong association of emotional intelligence with education. That “emotion recognition” is among the main keywords also shows its applicability to emotional intelligence, as evidenced in the network. Besides these main terms, other keywords are what drive research directions, explaining the interconnectedness of different concepts shown in the diagram. The clustering here signifies distinct thematic areas, such as psychology, leadership, medical education, and sentiment analysis, each of which contributes to the overall body of knowledge on emotional recognition and its applications. This Table 6 presents the clusters shown in Figure 4, summarized in tabular form.

Table 6.
Authors keyword co-occurrence network.
3.7. The Major Research Trends
The layout shown in the Figure 5 is an overlay visualization map. This map includes a timeline scale displayed below it, representing years through the colors of the clusters. The network’s colors indicate the temporal progression of research: purple represents the period 2016–2018, light green represents 2018–2020, and yellow represents 2020–2022.
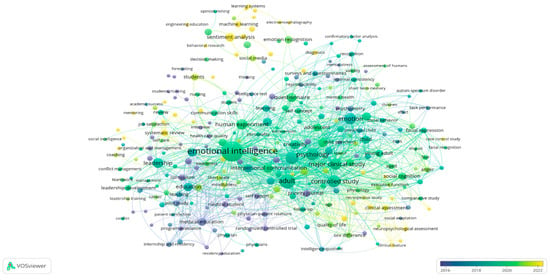
Figure 5.
Keyword co-occurrence visualization by year.
The yellow regions in the map (Figure 5) highlight recent research trends, underlining major tendencies in the fields of emotion recognition and skills. These trends include “sentiment analysis,” “machine learning,” “learning systems,” and “behavioral research.” This overlay visualization demonstrates a shift in research focus over time, transitioning from foundational and theoretical studies to applied and practical investigations. The yellow clusters notably reflect the increasing attention given to contemporary issues, such as the impact of machine learning on the prediction of soft skills. This progression highlights the growing relevance of integrating emotions into diverse fields, including education, engineering, and interviews.
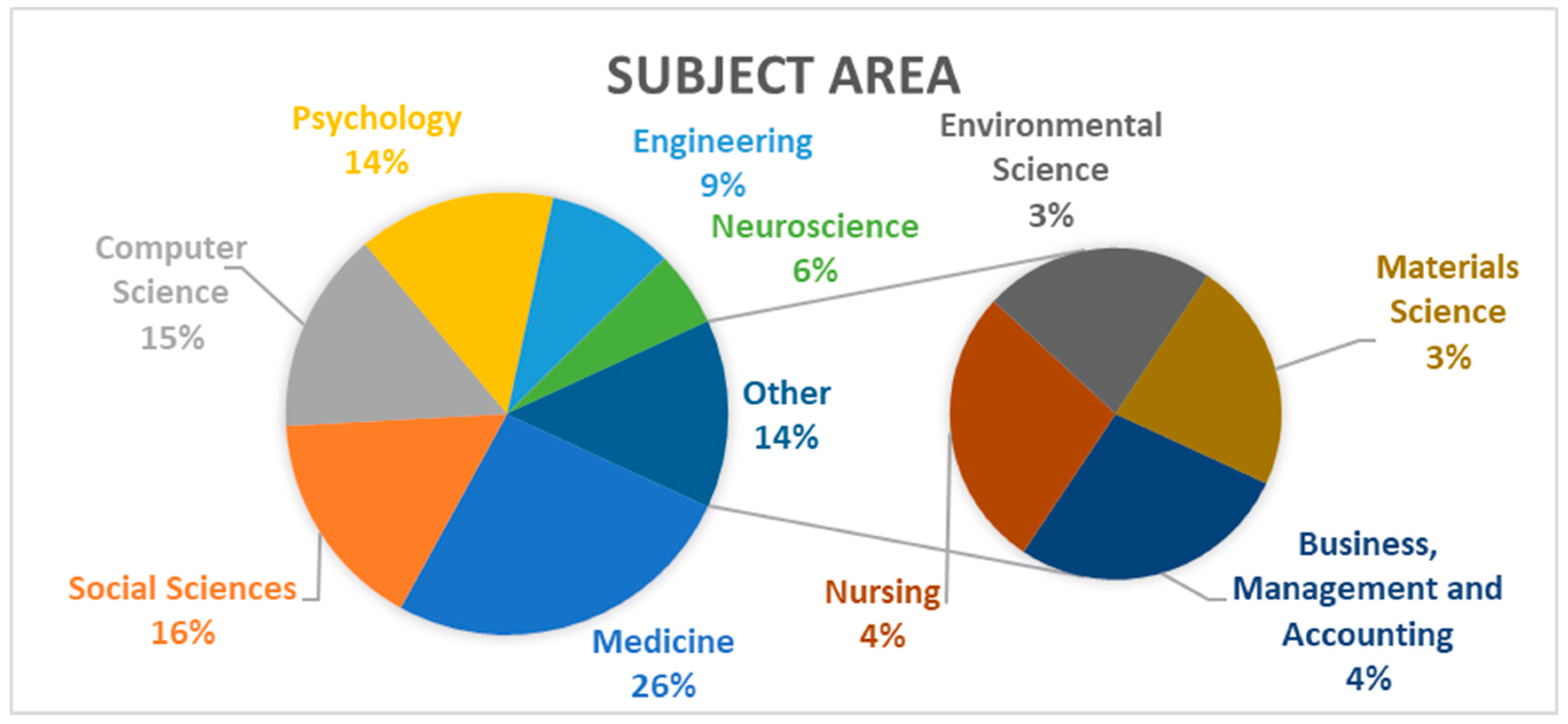
3.8. The Most Important Subject Area
To answer the eighth question of this study: “What are the most important subject areas and subfields involving emotion recognition, soft skills, and prediction?”, the data provided shows that the most important subject area is Medicine, accounting for 26% of the publications, with a total of 76 articles, as illustrated in Figure 6.
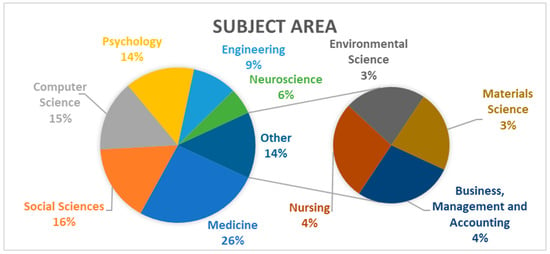
Figure 6.
The most important subject area.
Social Sciences follow as the second most significant field, representing 16% of the articles, with 47 publications. Computer Science is another key area, contributing 15% of the total, with 43 articles, focusing on soft skills prediction. Psychology also plays a crucial role, making up 14% of the research, with 42 contributions. Engineering significantly contributes to advancing research on soft skills, representing 9% (27 articles), while Neuroscience accounts for 6% (16 articles). Additionally, Nursing and Business, Management and Accounting each account for 4% (11 publications each), while Environmental Science and Materials Science represent 3% of the total, with 9 publications each.
4. Discussion
The portion of this paper is the bibliometric analysis section. A summary table that highlights the most crucial details for researchers in this topic is used to convey the literature review. Leading scientific publications, significant research organizations, and the most prominent writers on this subject are identified by the bibliometric study.
5. Conclusions
Within this study, we have conducted a bibliometric analysis on a sample of 202 research papers involving emotion recognition and soft skill prediction. With these analyses, we produced network visualizations using the VOSviewer software, which provided deeper insights into trends and relationships in this research field. No study to our knowledge has integrated bibliometric analysis in this specific field yet. The publications were accessed from the SCOPUS database to ensure complete scientific coverage. Our methodology was staged using bibliometric analysis. The results were examined with bibliometric statistics and network visualizations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.F. and A.M.; methodology, A.R.; software, B.A.; validation, N.F., A.M., B.A. and A.R.; formal analysis, N.F. and A.R.; investigation, N.F.; resources, N.F. and A.M.; data curation, N.F.; writing—original draft preparation, N.F.; writing—review and editing, N.F., A.M., B.A. and A.R.; visualization, N.F.; supervision, A.M.; project administration, N.F. and A.M.; funding acquisition, N.F., A.M., B.A. and A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique et Technique (CNRST, Morocco) under the Doctoral Scholarship “PhD-Associate Scholarship—PASS” program. The authors gratefully acknowledge this financial support, which contributed significantly to the progress of this work.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and derived from publicly accessible sources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vasanthakumari, S. Soft skills and its application in work place. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2019, 3, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Male, S.A. Generic engineering competencies: A review and modelling approach. Educ. Res. Perspect. 2010, 37, 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Male, S.A.; Bush, M.B.; Chapman, E.S. Perceptions of Competency Deficiencies in Engineering Graduates. Australas. J. Eng. Educ. 2010, 16, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoka, J.; Selesho, J. Employability Skills Required amongst Unemployed Youth: A Case at Beverly Hills in the Sedibeng District, Southern Gauteng. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruss, G. 6—Credentials and Mobility: An Analysis of the Profile of Students Studying at Registered Private Higher Education Institutions in South Africa. J. High. Educ. Afr. 2007, 5, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Biggart, A.; Newton, B. Basic and employability skills. Int. J. Train. Dev. 2013, 17, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekrun, R. The impact of emotions on learning and achievement: Towards a theory of cognitive/motivational media-tors. Appl. Psychol. 1992, 41, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, G.H. How might emotions affect learning. In The Handbook of Emotion and Memory; Psychology Press: East Sussex, UK, 2014; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrafzadeh, A.; Alexander, S.; Dadgostar, F.; Fan, C.; Bigdeli, A. “How do you know that I don’t understand?” A look at the future of intelligent tutoring systems. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2008, 24, 1342–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; El Emary, I.M. Speech emotion recognition approaches in human computer interaction. Telecommun. Syst. 2013, 52, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopus Scopus Database. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, M.; Hassan, M.A.; Jaleel, A.; Khalid, H.; Bano, G. A computation model for learning programming and emotional intelligence. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 149616–149629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Collinson, A.; Laidlaw, A.; Humphris, G. How Do medical students respond to emotional cues and concerns expressed by simulated patients during OSCE consultations?—A multilevel Study. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e79166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Pang, W. Are emotionally intelligent people more creative. A meta-analysis of the emotional intelligence–creativity link. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, D.M.; Bernard, K.; Fraser, T.N.; Bohnen, J.; Zeidman, J.; Stone, V.E. Implementing a pilot leadership course for internal medicine residents: Design considerations, participant impressions, and lessons learned. BMC Med. Educ. 2014, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Gardner, D.; Weston, J.; Bolwell, C.; Benschop, J.; Parkinson, T. Fostering the Development of Professionalism in Veterinary Students: Challenges and Implications for Veterinary Professionalism Curricula. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollatos, O.; Georgiou, E.; Kobel, S.; Schreiber, A.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Steinacker, J.M. Trait-Based Emotional Intelligence, Body Image Dissatisfaction, and HRQoL in Children. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez, I.; Jorquera, A.B.; Ruiz-Esteban, C.; Martínez-Ramón, J.P.; Fernández-Sogorb, A. Emotional Intelligence, Bullying, and Cyberbullying in Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadman, C.; Brewer, J. Emotional intelligence: A vital prerequisite for recruitment in nursing. J. Nurs. Manag. 2001, 9, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Peng, L.; Yang, J.; Cong, G. Analysis of User Needs on Downloading Behavior of English Vocabulary APPs Based on Data Mining for Online Comments. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackett, P.R.; Lievens, F.; Van Iddekinge, C.H.; Kuncel, N.R. Individual differences and their measurement: A review of 100 years of research. J. Appl. Psychol. 2017, 102, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, R.; Biotti, F.; Catmur, C.; Press, C.; Happé, F.; Cook, R.; Bird, G. Can Neurotypical Individuals Read Autistic Facial Expressions? Atypical Production of Emotional Facial Expressions in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism Res. 2015, 9, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrothers, R.M.; Gregory, S.W., Jr.; Gallagher, T.J. Measuring emotional intelligence of medical school applicants. Acad. Med. 2000, 75, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbey, A.K.; Colom, R.; Grafman, J. Architecture of cognitive flexibility revealed by lesion mapping. NeuroImage 2013, 82, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dries, N.; Pepermans, R. How to identify leadership potential: Development and testing of a consensus model. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2012, 51, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, I.; Leadbetter, P.; Curran, A.; O’Sullivan, H. A pilot study assessing emotional intelligence training and communication skills with 3rd year medical students. Patient Educ. Couns. 2009, 76, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R. Emotional intelligence as a crucial component to medical education. Int. J. Med Educ. 2015, 6, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero Jurado, M.D.M.; Pérez-Fuentes, M.D.C.; Oropesa Ruiz, N.F.; Simón Márquez, M.D.M.; Gázquez Linares, J.J. Self-Efficacy and Emotional Intelligence as Predictors of Perceived Stress in Nursing Professionals. Medicina 2019, 55, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, M.J.; Parker, J.D.A.; Wiener, J.; Watters, C.; Wood, L.M.; Oke, A. Academic success in adolescence: Relationships among verbal IQ, social support and emotional intelligence. Aust. J. Psychol. 2010, 62, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).