A Comparative Analysis of Immunity-Inspired Cybersecurity Approaches †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Paper Selection Strategy
- Relevance to immunity-inspired cybersecurity
- Clarity in the biological mechanism used
- Originality of the proposed approach
- Impact within the field
2.2. Analysis Framework
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tallam, K. The Cyber Immune System: Harnessing Adversarial Forces for Security Resilience. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.17698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarinde, M.O.; Abiona, A.A.; Ajinaja, M.O. Adaptive and privacy-preserving security for federated learning using biological immune system principles. Asian J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.M.; Sadanandan, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sarwari, A.R.; Reece, R. Building cyber-attack immunity in electric energy systems inspired by infectious disease ecology. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 175338–175356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrom, E.; Kinzig, A.; Forrest, S.; Graham, A.L.; Levin, S.A.; Bergstrom, C.T.; Castillo-Chavez, C.; Collins, J.P.; De Boer, R.J.; Doupé, A.; et al. Challenges in cybersecurity: Lessons from biological defense systems. Math. Biosci. 2023, 362, 109024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, T.; Hu, A. Research on endogenous security methods of embedded systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 11–14 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Forrest, S. Biology and Computers: Drawing Parallels Between Immunology and Cyber-Security. 2017. Available online: https://profsforrest.github.io/homepage/data/publications/2017-sc-article.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Dutt, I.; Borah, S.; Maitra, I. Intrusion detection system using artificial immune system. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 144, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, J.; ElAarag, H. Malware detection inspired by the human immune system and making use of honeytokens. In Proceedings of the Spring Simulation Multiconference, Alexandria, VA, USA, 12–15 April 2015; Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:10679031 (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Stacey, B.C.; Bar-Yam, Y. Principles of security: Human, cyber, and biological. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancaniello, P.; Holness, G.; Darvill, J.; Craven, M.J.; Lardieri, P.J. AIR: A Framework for Adaptive Immune Response for Cyber Defense. 2012. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:14747952 (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Greensmith, J.; Aickelin, U.; Twycross, J. Detecting danger: Applying a novel immunological concept to intrusion detection systems. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1002.0696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, C.; Ultes-Nitsche, U. Immune System-Based Intrusion Detection System. In Proceedings of the Information Security for South Africa, Johannesburg, South Africa, 7–9 July 2008; 2008. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:364566 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Harmer, P.K.; Williams, P.D.; Gunsch, G.H.; Lamont, G.B. An artificial immune system architecture for computer security applications. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 252–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bentley, P.J. The Human Immune System and Network Intrusion Detection. 1999. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:10912100 (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Hofmeyr, S.A.; Forrest, S. Immunity by Design: An Artificial Immune System. 1999. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:6215531 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Forresty, S.; Hofmeyry, S.A.; Somayajiy, A. Infect Recognize Destroy. 1996. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:218464589 (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Forrest, S.; Perelson, A.S.; Allen, L.; Cherukuri, R. Self-nonself discrimination in a computer. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Computer Society Symposium on Research in Security and Privacy, Oakland, CA, USA, 16–18 May 1994; pp. 202–212. [Google Scholar]
| Ref | Title & Year | Main Immunity Concept Used | Cybersecurity Application | Key Findings/Insights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | The Cyber Immune System: Harnessing Adversarial Forces for Security Resilience (2025) | Parasites mechanisms | General Cybersecurity | Explains how adversarial attacks same as parasites expose systemic vulnerabilities |
| [2] | Adaptive and Privacy-Preserving Security for Federated Learning Using Biological Immune System Principles (2024) | Adaptive anomaly detection, self-defense mechanisms | Federated Learning Cybersecurity | The paper proposed an Immunity-based framework for decentralized systems. |
| [3] | Building Cyber-Attack Immunity in Electric Energy System Inspired by Infectious Disease Ecology (2024) | Multi-layered Immune Defense, Adaptive Immunity | Smart Grid Security | Proposes an AIS-based architecture for detecting, classifying, and responding to cyber-attacks in smart grids |
| [4] | Challenges in Cybersecurity: Lessons from Biological Defense Systems (2023) | Immunology, Self/Non-Self-Discrimination | General cybersecurity | Framework comparing cybersecurity and biological immunity aims to inspire new defense mechanisms. |
| [5] | Research on Endogenous Security Methods of Embedded Systems (2020) | Human immune and neural reflex mechanisms | Embedded system security | Introduces bionic immune mechanisms for embedded systems security. |
| [6] | Biology and Computers: Drawing Parallels Between Immunology and Cyber-Security (2017) | General biological analogy | General cybersecurity | Explores high-level analogies between immune systems & cybersecurity. |
| [7] | Intrusion Detection System Using Artificial Immune System (2016) | Adaptive & Multi-layered Immune Defense | Intrusion Detection | Two-layer IDS (innate-like & adaptive) improves threat detection. |
| [8] | Malware Detection Inspired by the Human Immune System (2015) | Danger Theory, Adaptive Response | Malware detection | Multi-stage malware detection algorithm based on immune system concepts. |
| [9] | Principles of Security: Human, Cyber, and Biological (2013) | System-wide immune defenses | General cybersecurity | Security should focus on system-wide protection, not individual devices. Inspired by biological immunity. |
| [10] | AIR: A Framework for Adaptive Immune Response for Cyber Defense (2012) | Adaptive immune response | Anomaly detection | Describes a framework for continual threats modeled on adaptation immune to cyber adaptation. |
| [11] | Detecting Danger: Applying a Novel Immunological Concept to Intrusion Detection Systems (2010) | Danger Theory | Intrusion Detection | Introduces Danger Theory for IDS. IDS should detect threats based on danger signals, not just anomalies. |
| [12] | Immune System-Based Intrusion Detection System (2008) | Self/Non-Self-Discrimination, Adaptive immune response | Intrusion Detection | IDS mimicking immune adaptability can detect unknown attacks. |
| [13] | Artificial Immune System Architecture for Computer Security Applications (2002) | Negative Selection Algorithm memory-based detection | Intrusion Detection, Malware Detection | Developed distributed multi-layer IDS mirroring immune response. |
| [14] | The Human Immune System and Network Intrusion Detection (1999) | Immune System distribution, self-organisation and lightweight | Intrusion Detection | Examines immune mechanisms satisfying IDS design goals for intrusion detection models. |
| [15] | Immunity by Design: An Artificial Immune System (1999) | Self/Non-Self-Discrimination | Network security | Proposed distributed AIS system for anomaly detection, inspired by the immune system. |
| [16] | Infect Recognize Destroy (1996) | Immune memory, evolutionary immunity | General cybersecurity | Immune system properties (memory, diversity) could enhance cyber defenses. |
| [17] | Self–Non-self-Discrimination in a Computer (1994) | Self/Non-Self-Discrimination | Anomaly Detection | Formalized Negative Selection Algorithm as a method for cyber anomaly detection. |
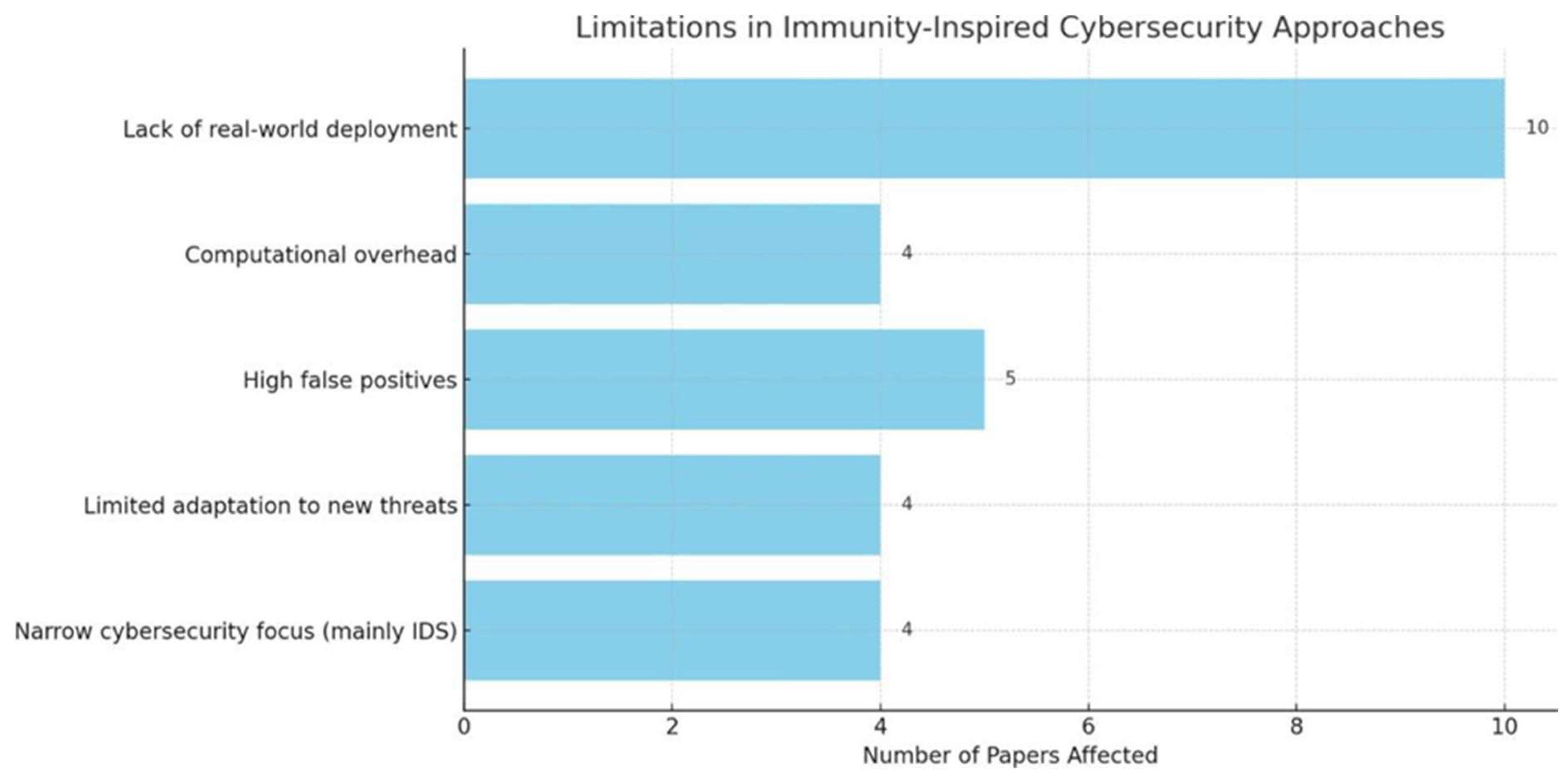
| Limitation | Papers Affected | Why It’s a Problem? | Proposed Future Directions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lack of real-world deployment | [1,2,3,4,5,6,9,10,11,14,16] | Many ideas remain theoretical or simulated | Conduct shadow deployments of adaptive immune-based cybersecurity solutions in real enterprise environments, operating them in parallel with existing security systems to assess effectiveness without disrupting operations. |
| Computational overhead | [7,12,13,17] | Algorithms like negative selection are resource-heavy | Optimize models using parallel computing. |
| High false positives | [4,7,12,15,17] | Incorrectly classifies normal behavior as threats. | Move beyond self/non-self-detection; use context-aware models like Danger Theory. |
| Limited adaptation to new threats | [4,8,9,11,13] | adjustments to zero-day Lacks real-time attacks | Deepen the research in immune memory mechanisms and explore reinforcement learning for proactive defense adjustments |
| Narrow cybersecurity focus (mainly IDS) | [7,11,12,13,14] | It only mimics detection, ignoring key immune functions like response, adaptation, prevention, and memory | Expand immunity principles into response systems and self-healing cybersecurity. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bala, A.; El Bhiri, B.; Bahnasse, A.; Mohy-Eddine, M. A Comparative Analysis of Immunity-Inspired Cybersecurity Approaches. Eng. Proc. 2025, 112, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112073
Bala A, El Bhiri B, Bahnasse A, Mohy-Eddine M. A Comparative Analysis of Immunity-Inspired Cybersecurity Approaches. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 112(1):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112073
Chicago/Turabian StyleBala, Abir, Brahim El Bhiri, Ayoub Bahnasse, and Mouaad Mohy-Eddine. 2025. "A Comparative Analysis of Immunity-Inspired Cybersecurity Approaches" Engineering Proceedings 112, no. 1: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112073
APA StyleBala, A., El Bhiri, B., Bahnasse, A., & Mohy-Eddine, M. (2025). A Comparative Analysis of Immunity-Inspired Cybersecurity Approaches. Engineering Proceedings, 112(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025112073





